Diabetes
Description
Type II Diabetes is a disorder that is characterized by high blood glucose in the context of insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. It is the most common form of diabetes, in which either the body does not produce enough insulin or the cells ignore the insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas, which is needed to convert sugar and other food into energy. When we eat food, the body breaks down all of the sugars and starches into glucose, which is the basic fuel for the cells in the body. Insulin takes the sugar from the blood into the cells.
When one has diabetes, the body either doesnít make enough insulin or canít use its own insulin properly. This causes sugars to build up too high in the blood. Thus, cells may be starved for energy. Over time, high blood glucose levels may hurt eyes, kidneys, nerves or heart. This animation shows a detailed comparison between a normal person and a person with Type II Diabetic condition.
Browse Other Animations
 CRISPR/Cas9...Revolution in Gene Editing
CRISPR/Cas9...Revolution in Gene Editing
 Immunity Against SARS-CoV-2
Immunity Against SARS-CoV-2
 Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer
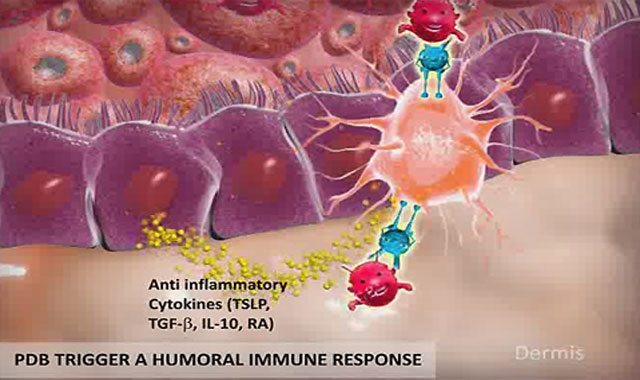 Probiotic Skin Renewal Technology
Probiotic Skin Renewal Technology

