Pathways
Actin-Based Motility by Rho Family GTPases
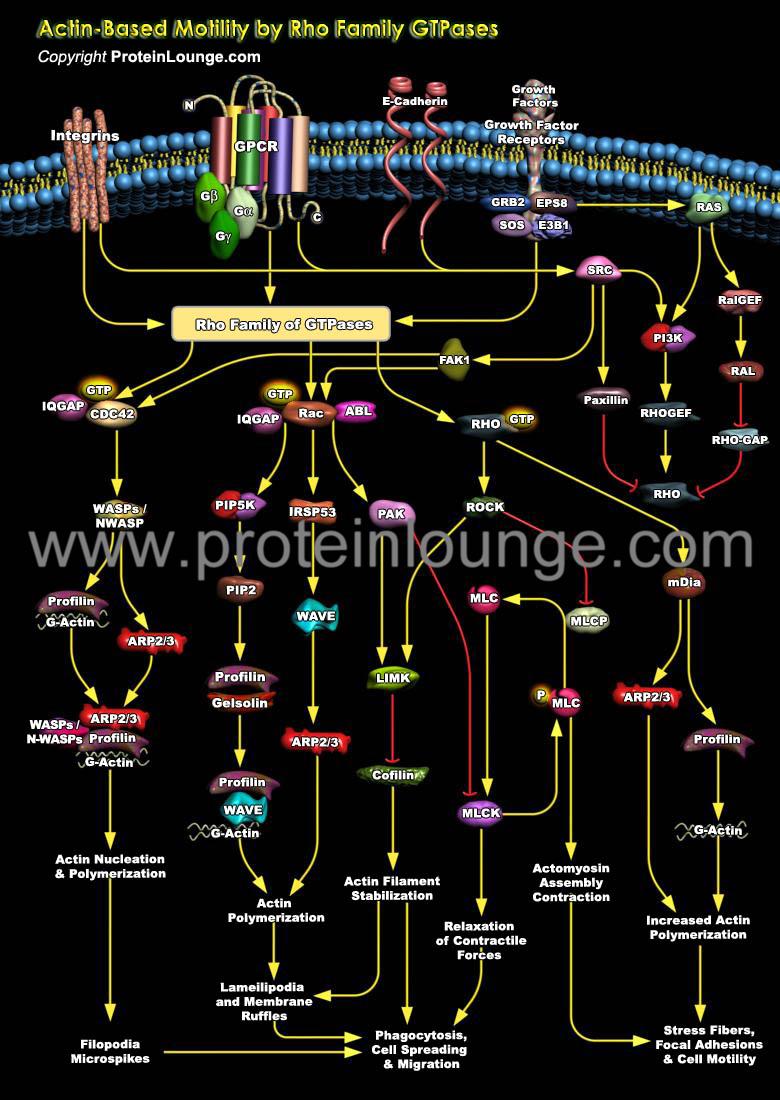
Description:
In response to a variety of extracellular stimuli, actin filament assembly at the leading edge of motile cells causes protrusion during cell crawling and chemotaxis, nerve growth and cell spreading. The actin filament network immediately under the plasma membrane in regions of rapid cellular protrusion consists of short, branched filaments while those deeper in the cortex, as well as at focal adhesions, stress fibers and in microvilli, are much longer and rarely branched (Ref.1). The dynamic organization of the actin cytos...
References:
-
Isotropic actomyosin dynamics promote organization of the apical cell cortex in epithelial cells.
J Cell Biol. 2014 Oct 13;207(1):107-21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201402037. -
Rho GTPases at the crossroad of signaling networks in mammals.
Small GTPases. 2015;6(2):43-8. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2015.1044811. Epub 2015 Jun 25. No abstract available. -
Rho GTPases as therapeutic targets in cancer (Review).
Int J Oncol. 2017 Aug 9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4093. [Epub ahead of print] -
Signaling networks of Rho GTPases in cell motility.
Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):1955-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 May 11. Review.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

