Pathways
all-trans-Retinoic Acid Mediated Apoptosis
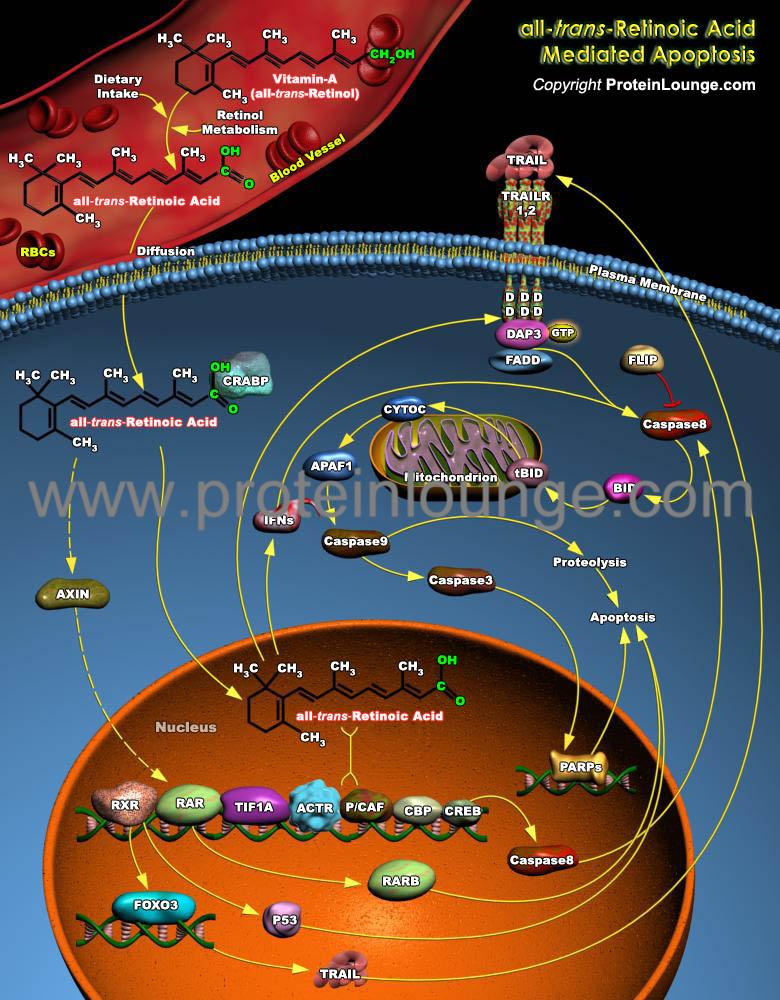
Description:
Retinoic Acid, a lipophilic molecule and a metabolite of Vitamin-A (all-trans-Retinol), affects gene transcription and modulates a wide variety of biological processes like Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, including Apoptosis. Retinoic Acid mediated gene transcription depends on the rate of transport of Retinoic Acid to target cells and the timing of exposure of Retinoic Acid to RARs (Retinoic Acid Receptors) in the target tissues. The all-trans-Retinoic Acid, the Carboxylic Acid form of Vitamin-A is of biological significan...
References:
-
Retinoic acid actions through mammalian nuclear receptors.
Chem Rev. 2014 Jan 8;114(1):233-54. doi: 10.1021/cr400161b. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Review. No abstract available. -
Retinoic acid synthesis and functions in early embryonic development.
Cell Biosci. 2012 Mar 22;2(1):11. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-2-11. -
Retinoic acid enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer cells by upregulating TRAIL receptor 1 expression.
Cancer Res. 2011 Aug 1;71(15):5245-54. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4180. Epub 2011 Jun 17. -
Control of FLIP(L) expression and TRAIL resistance by the extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 pathway in breast epithelial cells.
Cell Death Differ. 2012 Dec;19(12):1908-16. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.78. Epub 2012 Jun 22.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

