Pathways
Androgen Signaling
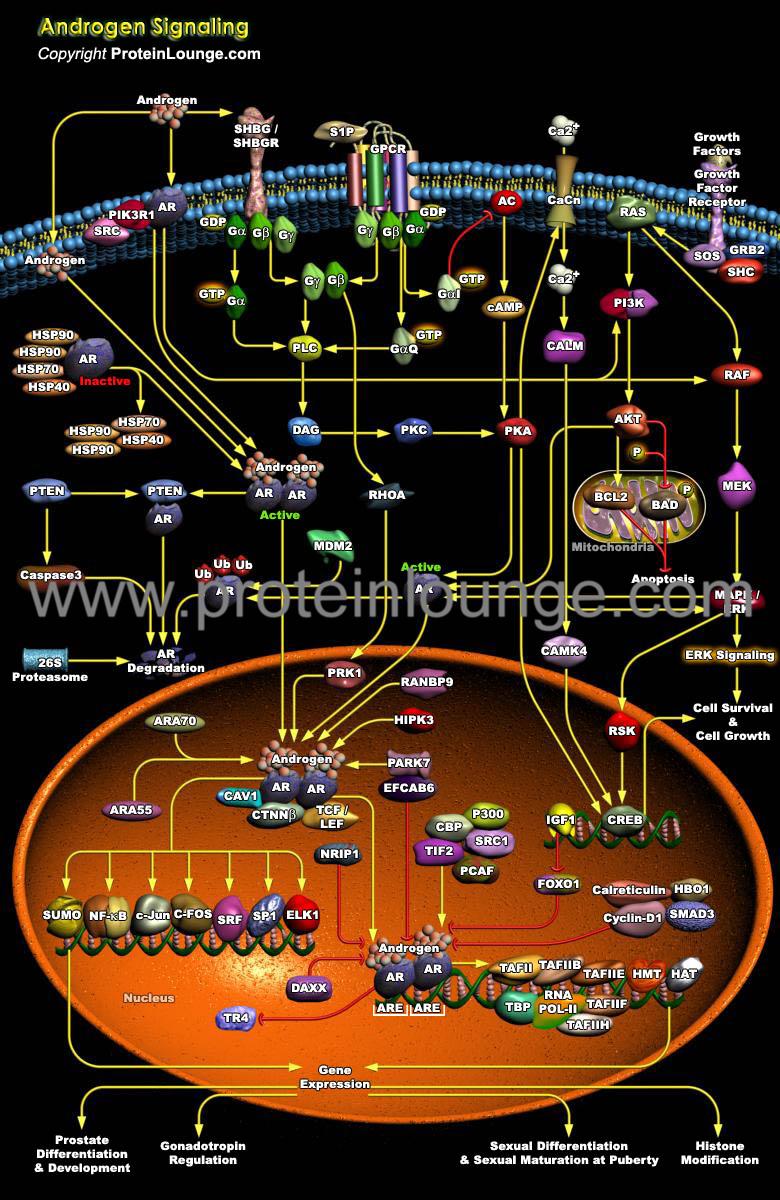
Description:
Androgens are recognized as genotropic inducers of a number of physiological functions mainly associated with the development of sexual characteristics. Androgens promote the growth and differentiation of prostate cells through ligand activation of the AR (Androgen Receptor) (Ref.1&2). The AR, upon activation by Androgens, mediates transcription of target genes that modulate growth and differentiation of prostate epithelial cells. AR signaling is crucial for the development and maintenance of male reproductive organs including t...
References:
-
No reference found.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

