Pathways
Apoptotic Pathways in Synovial Fibroblasts
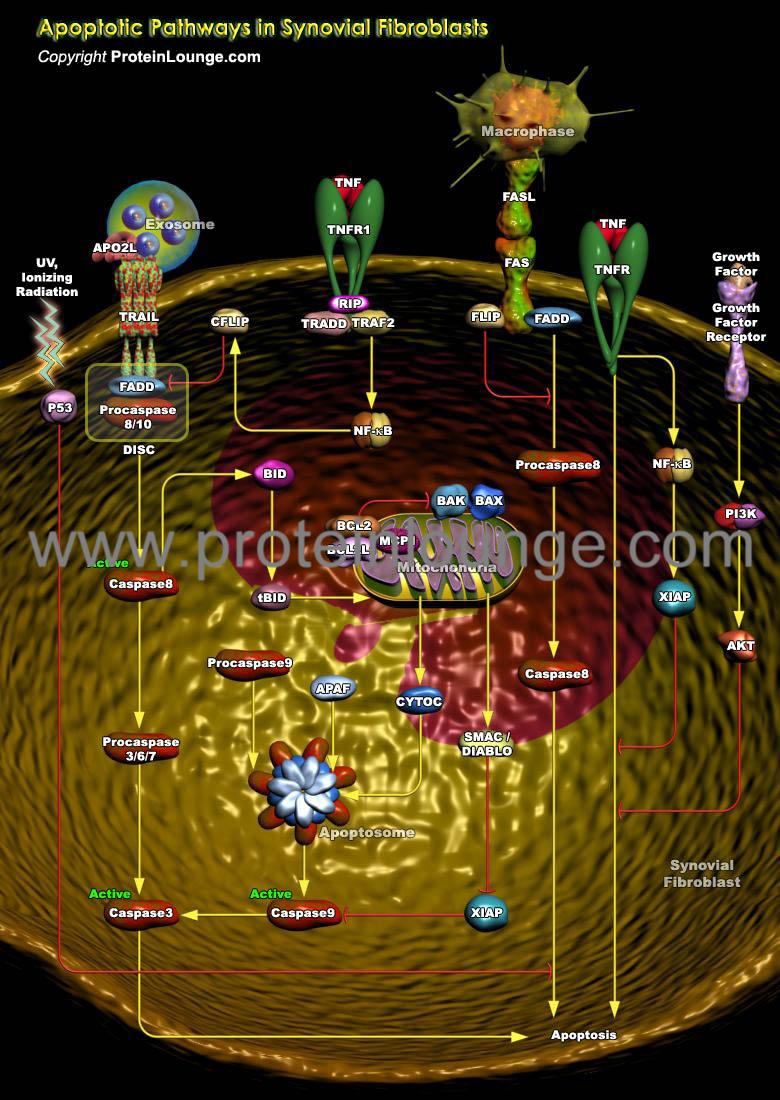
Description:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the lining of the synovial joints and is associated with progressive disability, premature death, and socioeconomic burdens.It is characterized by chronic inflammation and synovial hyperplasia that eventually lead to cartilage and bone destruction. Synovial fibroblasts are mesenchymal cells recognized as a key cell population in RA due to their hyperproliferative and hypersensitive properties in the inflammatory milieu and hyperproduction o...
References:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies.
Bone Res. 2018 Apr 27;6:15. doi: 10.1038/s41413-018-0016-9. eCollection 2018. Review. -
Inflammation and bone destruction in arthritis: synergistic activity of immune and mesenchymal cells in joints.
Front Immunol. 2012 Apr 13;3:77. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00077. eCollection 2012. -
Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages.
Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(6):224. doi: 10.1186/ar2333. -
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in rheumatoid arthritis: what's new?
Clin Exp Med. 2014 May;14(2):115-20. doi: 10.1007/s10238-012-0226-1. Epub 2012 Dec 30. Review.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

