Pathways
Biotin Metabolism in M. musculus
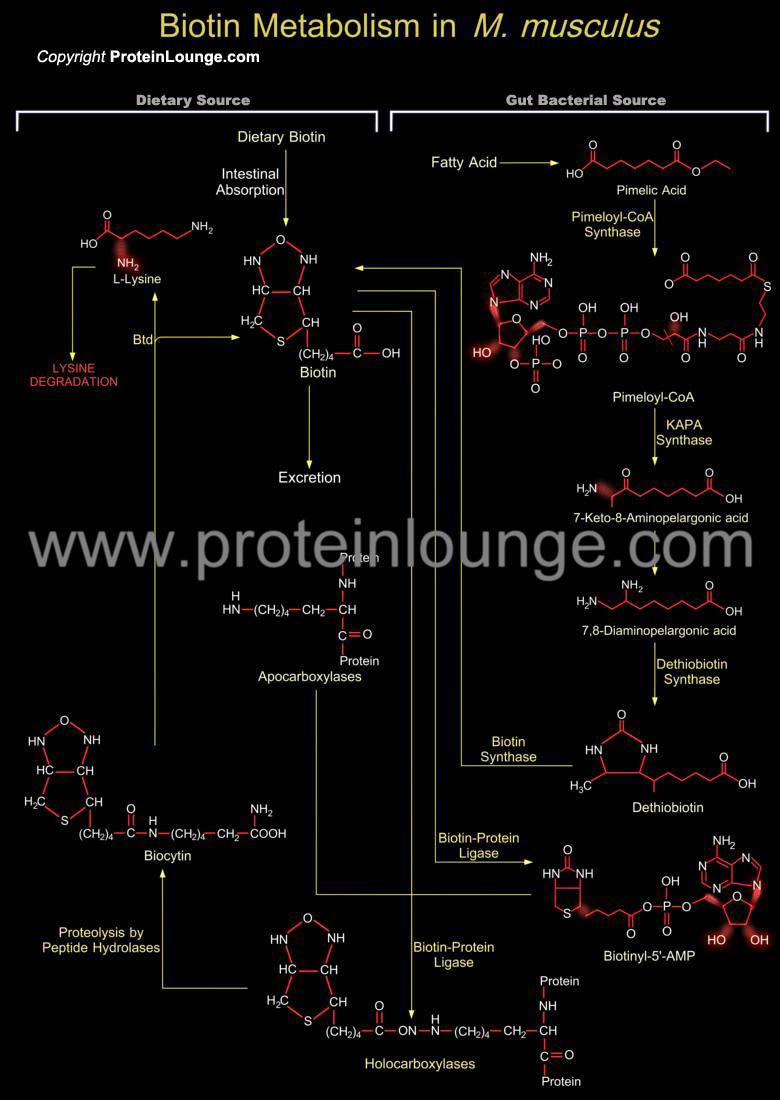
Description:
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin found in all organisms that functions as a cofactor of Biotin-dependent carboxylases. It belongs to the B-Complex group of Vitamins and is an essential micronutrient for all mammals. The role of Biotin (or Vitamin-H) in Carboxylases is to act as vector for carboxyl-group transfer between donor and acceptor molecules during Carboxylation reaction (Ref.1). In M. musculus (Mus musculus), Biotin is a covalently bound as a prosthetic group in Biotin-dependent Carboxylases. It is covalently at...
References:
-
Molecular genetics of biotin metabolism: old vitamin, new science.
J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005 Jul;16(7):428-31. -
Selectivity in post-translational biotin addition to five human carboxylases.
J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 13;287(3):1813-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.275982. Epub 2011 Nov 28. -
Biotin.
Biofactors. 2009 Jan-Feb;35(1):36-46. doi: 10.1002/biof.8. Review. -
Biotinidase: its role in biotinidase deficiency and biotin metabolism.
J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005 Jul;16(7):441-5.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

