Pathways
Blood Coagulation Cascade
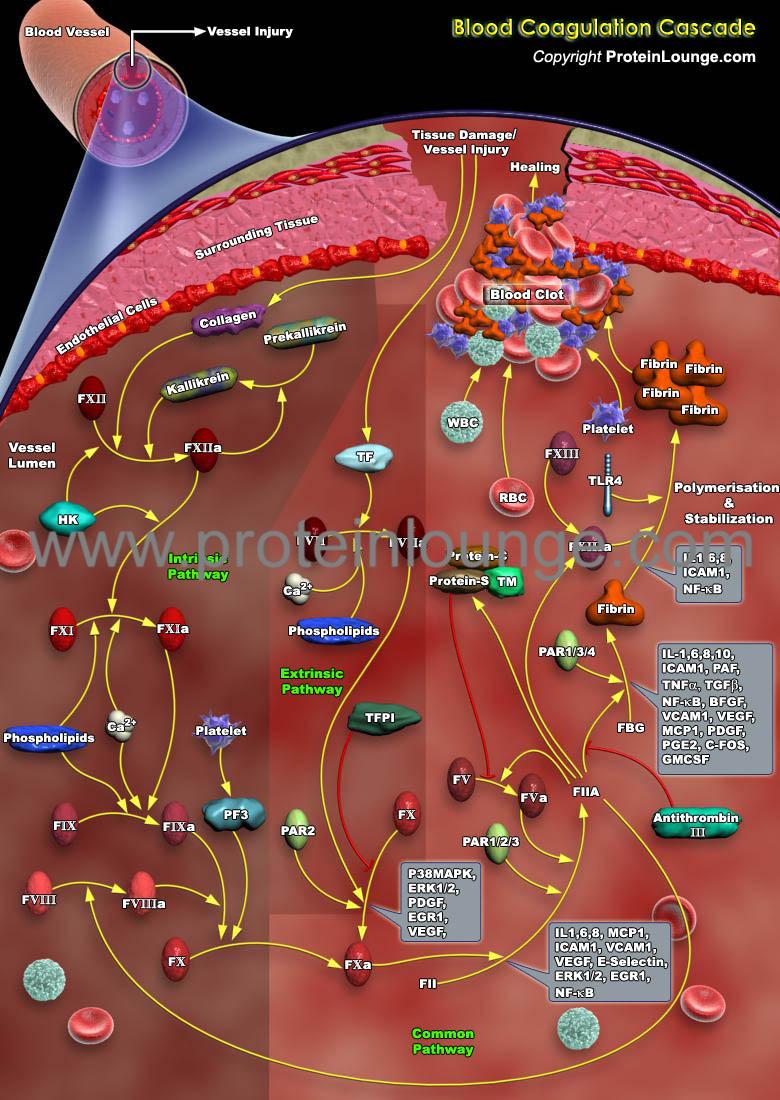
Description:
Coagulation is a dynamic process which involves the regulated sequence of proteolytic activation of a series of zymogens to achieve appropriate and timely haemostasis in an injured vessel, in an environment that overwhelmingly favours an anticoagulant state [Ref.1 & 2]. There are two main mechanisms for triggering the blood clotting, termed as the contact pathway/intrinsic pathway and the tissue factor pathway/extrinsic pathway [Ref.3].
The contact pathway of coagulation is initiated by activation of factor XII (fXII) in ...
The contact pathway of coagulation is initiated by activation of factor XII (fXII) in ...
References:
-
Overview of the coagulation system.
Indian J Anaesth. 2014 Sep; 58(5):515-23. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.144643. Review. -
Review article: Coagulation cascade and therapeutics update: relevance to nephrology. Part 1: Overview of coagulation, thrombophilias and history of anticoagulants.
Nephrology (Carlton). 2009 Aug; 14(5):462-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2009.01128.x. Review. -
How it all starts: Initiation of the clotting cascade.
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015; 50(4):326-36. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2015.1050550. Epub 2015 May 28. Review. -
Tissue factor, blood coagulation, and beyond: an overview.
Int J Inflam. 2011; 2011:367284. doi: 10.4061/2011/367284. Epub 2011 Sep 20.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

