Pathways
cAMP Signaling in S. pombe
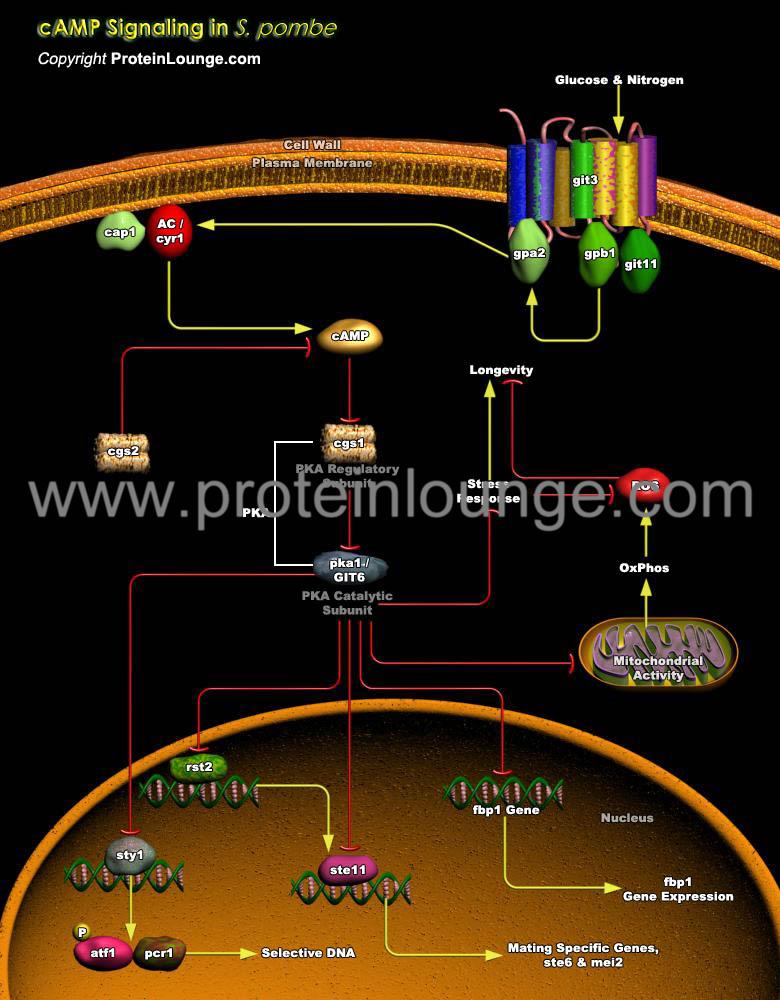
Description:
In most eukaryotic organisms, guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) pathways play a critical role in extracellular environment sensing. The second messenger cyclic 3’-5’ adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is important in G-protein mediated glucose sensing. In the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe (S.pombe), G-proteins produce cAMP via activation of adenylyl cyclase (AC) in response to glucose detection (Ref.1 and 2).
In S.pombe, either Glucose limi...
References:
-
Sck1 negatively regulates Gpa2-mediated glucose signaling in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Feb;13(2):202-8. doi: 10.1128/EC.00277-13. Epub 2013 Dec 2. -
cAMP export by the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
MicroPubl Biol. 2021 Apr 2;2021:10.17912/micropub.biology.000384. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000384. -
Use of PKA-mediated phenotypes for genetic and small-molecule screens in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Dec;41(6):1692-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20130159. -
TOR and PKA pathways synergize at the level of the Ste11 transcription factor to prevent mating and meiosis in fission yeast.
PLoS One. 2010 Jul 9;5(7):e11514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011514.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

