Pathways
DSB Repair by Non-Homologous End Joining
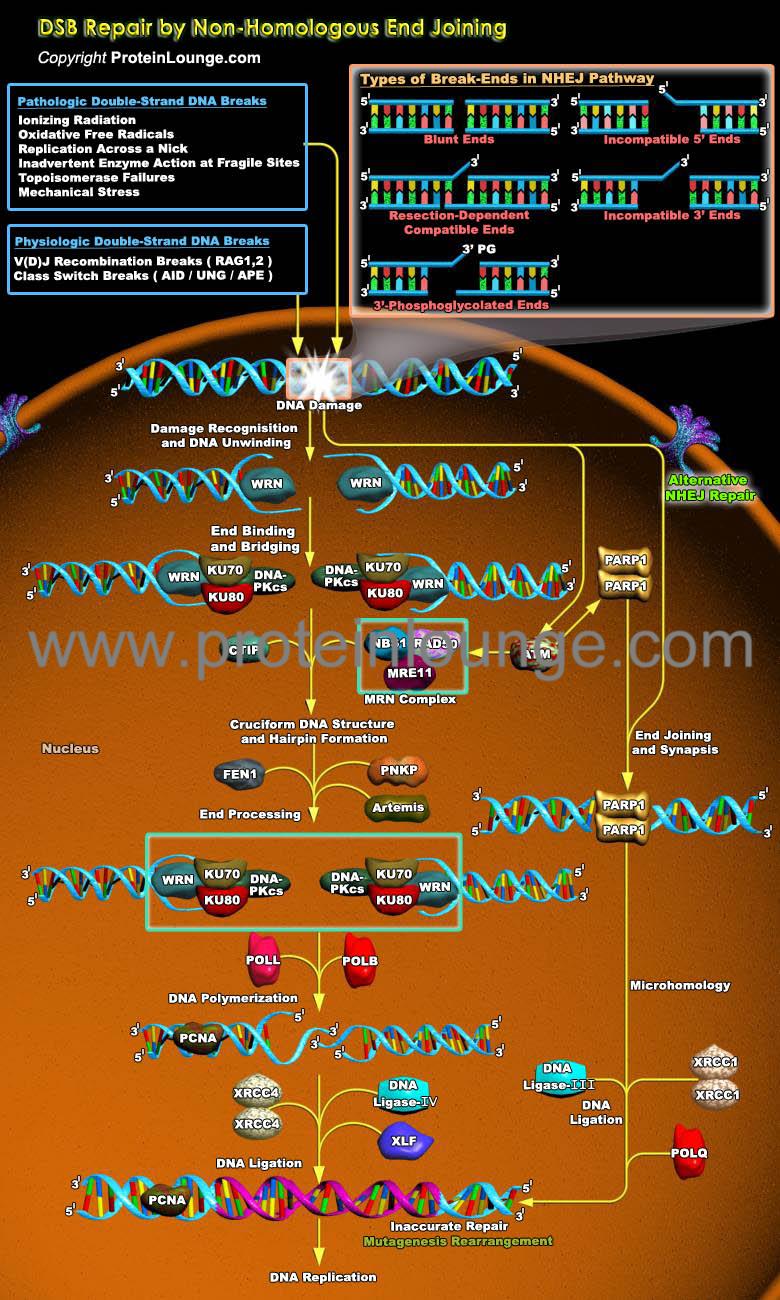
Description:
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are serious lesions that threaten a loss of chromosomal content. Repair of DSBs is particularly challenging because, unlike all other lesions, the DNA substrate is inherently bimolecular. Bringing two DNA molecules together is also dangerous because local mutations and chromosome rearrangements can arise if ends are inappropriately coupled. The cell has two general strategies for repairing DSBs i.e. HR (Homologous recombination) and NHEJ (Non-homologous end joining). HR is a mechanism in which ...
References:
-
Repair of double-strand breaks by end joining.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 May 1;5(5):a012757. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012757. Review. -
Is non-homologous end-joining really an inherently error-prone process?
PLoS Genet. 2014 Jan;10(1):e1004086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004086. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Review. -
The mechanism of double-strand DNA break repair by the nonhomologous DNA end-joining pathway.
Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:181-211. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.052308.093131. -
Repair of double-strand breaks by end joining.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 May 1;5(5):a012757. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012757.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

