Pathways
Glycine, Serine and Threonine Metabolism in M. loti
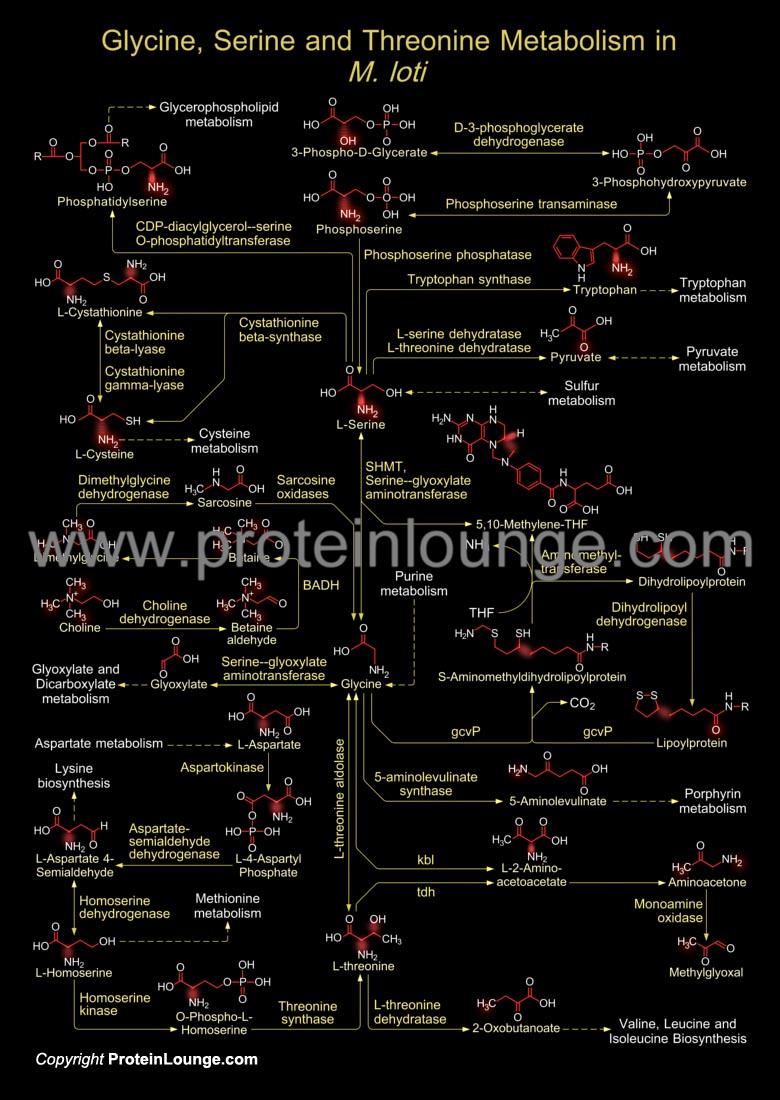
Description:
Rhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Sinorhizobium, and Azorhizobium-collectively known as rhizobia, are Gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing bacteria of agronomic importance because they perform nitrogen-fixing symbioses with leguminous plants (soybean, alfalfa, beans, peas, etc). The metabolism of amino acids like Glycine is indispensable for functioning of one-carbon metabolism and for the establishment of a fully effective, nitrogen-fixing root nodule symbiosis in M. loti
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:References:
Complete genome structure of the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Mesorhizobium loti.
DNA Res. 2000 Dec 31;7(6):331-8.
Complete genome structure of the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Mesorhizobium loti (supplement).
DNA Res. 2000 Dec 31;7(6):381-406.
Comparative sequence analysis of the symbiosis island of Mesorhizobium loti strain R7A.
J. Bacteriol. 2002 Jun;184(11):3086-95.
Production of amino acids by Rhizobium, Mesorhizobium and Sinorhizobium strains in chemically defined media.
Amino Acids. 2004 Oct;27(2):169-74.
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

