Pathways
Mismatch Repair in Eukaryotes
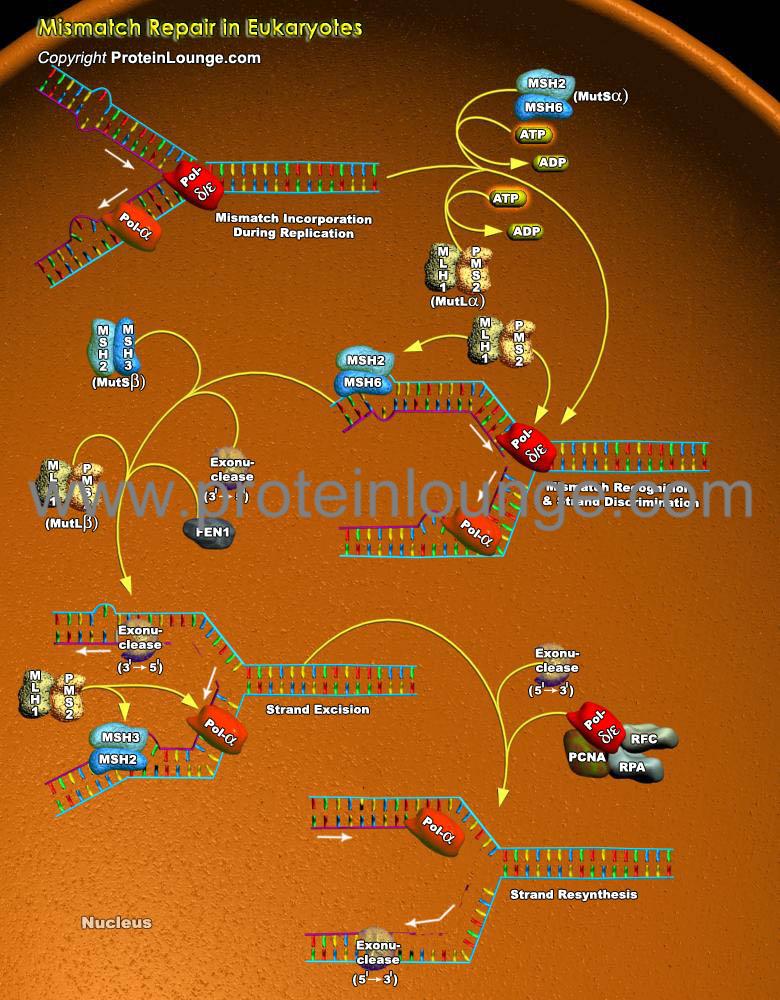
Description:
The major DNA Repair mechanisms take advantage of the facts that DNA is double-stranded and the same information is present in both strands. Consequently, in cases where damage is present in just one strand, the damage can be accurately repaired by cutting it out (excision) and replacing it with new DNA synthesized using the complementary strand as template. All organisms, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, employ at least three excision mechanisms: Mismatch Repair, Base Excision Repair, And Nucleotide Excision Repair. Mismatch repa...
References:
-
The dual nature of mismatch repair as antimutator and mutator: for better or for worse.
Front Genet. 2014 Aug 21;5:287. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00287. eCollection 2014. Review. -
New insights into the mechanism of DNA mismatch repair.
Chromosoma. 2015 Dec;124(4):443-62. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0514-0. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Review. -
Fidelity of DNA replication-a matter of proofreading.
Curr Genet. 2018 Oct;64(5):985-996. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0820-1. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Review. -
Mismatch binding, ADP-ATP exchange and intramolecular signaling during mismatch repair.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jun 14;102(24):8639-43. Epub 2005 Jun 2.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

