Pathways
Nuclear Receptor Activation by Vitamin-A
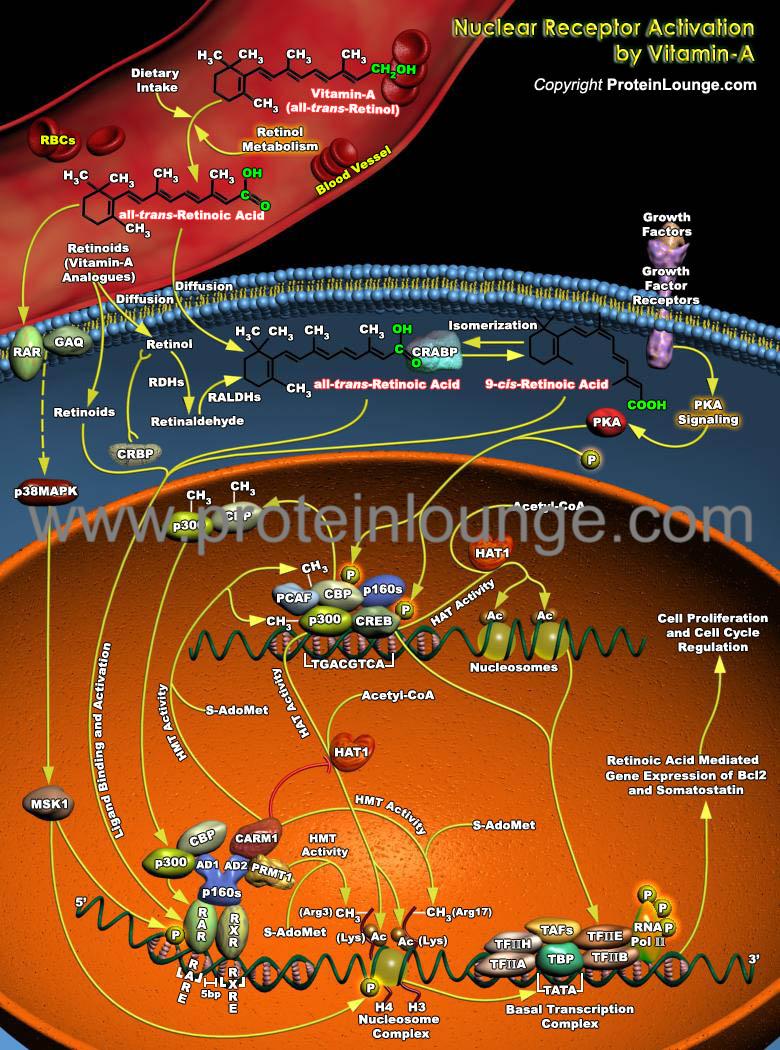
Description:
Vitamin A and its analogs, collectively termed retinoids, have a profound effect on cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and morphogenesis. Retinol, the lipid-soluble vitamin A, is an absolute requirement for normal growth, vision and differentiation of epithelial tissues in mammals. Retinol must be obtained directly through dietary intake, but may also be derived in its provitamin A forms obtained through dietary carotenoids (Ref.1 and 2). Retinoids bind to six distinct nuclear receptors in mammals and regulate the expressi...
References:
-
Retinoic Acid-mediated Nuclear Receptor Activation and Hepatocyte Proliferation.
J Exp Clin Med. 2009 Dec;1(1):23-30. -
Retinoic acid actions through mammalian nuclear receptors.
Chem Rev. 2014 Jan 8;114(1):233-54. doi: 10.1021/cr400161b. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Review. No abstract available. -
Retinoid receptors and therapeutic applications of RAR/RXR modulators.
Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(6):505-27. Review. -
Retinoid pathway and cancer therapeutics.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Oct 30;62(13):1285-98. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2010.07.003. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Review.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

