Pathways
Pathways Regulating Alcoholism
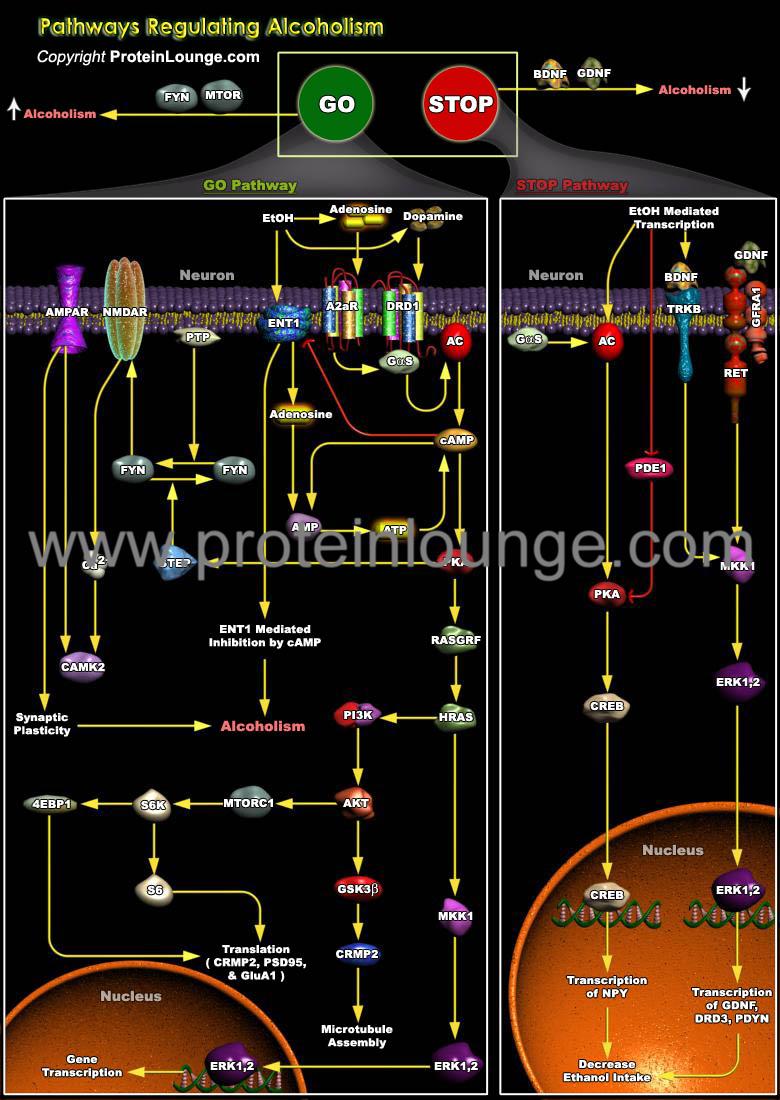
Description:
Ethanol is a psychoactive substance with rewarding and sedative-hypnotic properties that stem largely from its acute effects on specific signaling proteins that lead to changes in localization and post-translational modifications, gene expression and neuronal excitability. Neurons adapt to repeated ethanol exposure through homeostatic changes in cellular signaling pathways that serve to maintain nervous system function in the presence of ethanol. The STOP and GO intracellular signaling pathways control alcohol drinking behavi...
References:
-
Signaling pathways mediating alcohol effects.
Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2013;13:87-126. doi: 10.1007/7854_2011_161. Review. -
Targeting the intracellular signaling "STOP"and "GO" pathways for the treatment of alcohol use disorders.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Jun;235(6):1727-1743. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4882-z. Epub 2018 Apr 14. Review. -
Molecular mechanisms underlying alcohol-drinking behaviours.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Sep;17(9):576-91. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.85. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Review. -
Role of BDNF and GDNF in drug reward and relapse: a review.
Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010 Nov;35(2):157-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Review.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

