Pathways
PD-1 PD-L1 Pathway in Cancer
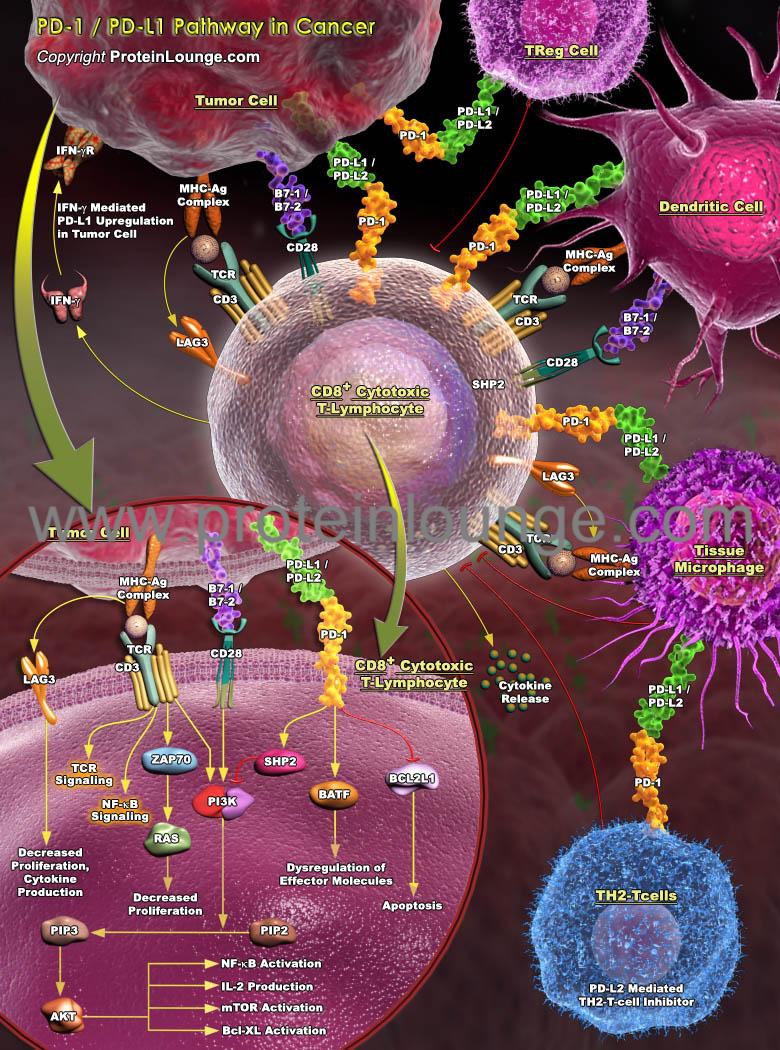
Description:
Immune checkpoints refer to a plethora of inhibitory pathways hardwired into the immune system that are crucial for maintaining self-tolerance and limiting collateral tissue damage during anti-microbial immune responses. Checkpoint molecules include Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Antigen-4 (CTLA-4), Programmed Death-1 (PD-1), Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3 (LAG-3), and T-cell immunoglobulin and Mucin protein-3 (TIM-3) as well as several others (Ref.1). PD-1, an immunoinhibitory receptor of the CD28 family, is a type 1 trans-membrane prote...
References:
-
The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Mar 22;12(4):252-64. doi: 10.1038/nrc3239. Review. -
Development of PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Treatment for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 17;5:13110. doi: 10.1038/srep13110. Review. -
Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 interactions for cancer immunotherapy.
Oncoimmunology. 2012 Nov 1;1(8):1223-1225. -
Role of the PD-1 Pathway in the Immune Response
Am J Transplant. 2012 Oct;12(10):2575-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04224.x. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Review.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

