Pathways
C. pneumoniae Infection in Atherosclerosis
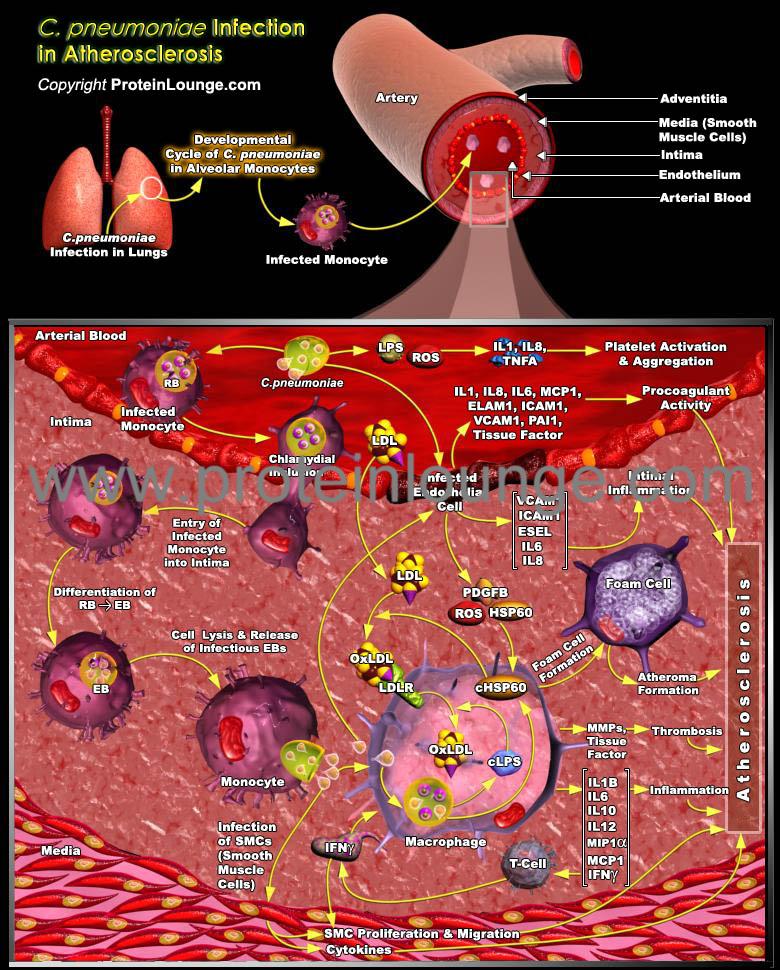
Description:
Atherosclerosis, the pathological basis of CAD (Coronary Artery Disease) and Ischemic Stroke, is the commonest cause of death and disability in the western world. Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial, highly complex disease with numerous aetiologies simultaneously and sequentially collaborating in subtle ways to affect lesion development, progression and maturation to an advanced, disease-provoking entity (Ref.1). The lesion, or Atheroma, is an inflammatory site composed of a necrotic lipid-rich core, modified vascular endotheliu...
References:
-
Chlamydia pneumoniae infection in atherosclerotic lesion development through oxidative stress: a brief overview.
Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 19;14(7):15105-20. doi: 10.3390/ijms140715105. Review. -
Infectious and coronary artery disease.
ARYA Atheroscler. 2016 Jan;12(1):41-9. Review. -
Atherosclerosis Induced by Chlamydophila pneumoniae: A Controversial Theory.
Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2013;2013:941392. doi: 10.1155/2013/941392. Epub 2013 Jul 17. -
Hyperhomocysteinemia, Suppressed Immunity, and Altered Oxidative Metabolism Caused by Pathogenic Microbes in Atherosclerosis and Dementia.
Front Aging Neurosci. 2017 Oct 6;9:324. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00324. eCollection 2017. Review.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

