Pathways
Repair of Thymine Dimers
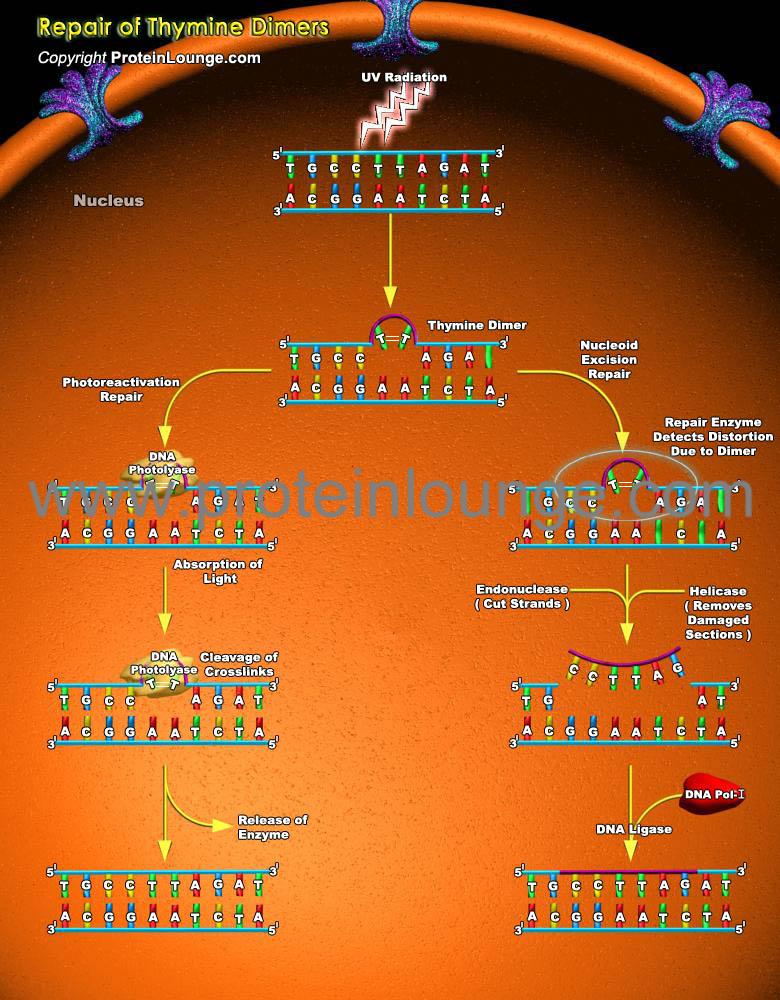
Description:
Irradiation of DNA by UV (Ultraviolet light) causes lesions, such as Cyclobutane-Pyrimidine Dimers or 6-4PPs (6-4 Pyrimidine Pyrimidone). The most common covalently linked adjoining pyrimidines are T-T (Thymine dimers), T-C (Thymine-Cytosine dimers) and C-C (Cytosine-Cytosine dimers). T-T dimers cause kinks in the DNA strand that prevent both replication and transcription of that part of the DNA. Because they block DNA replication (and therefore prevent cells from reproducing), T-T dimers and other forms of UV damage cannot b...
References:
-
Molecular mechanisms of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage and repair.
J Nucleic Acids. 2010 Dec 16;2010:592980. doi: 10.4061/2010/592980. -
Photolyase: Dynamics and electron-transfer mechanisms of DNA repair.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Oct 15;632:158-174. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.08.007. Epub 2017 Aug 9. -
Nucleotide excision repair in human cells: fate of the excised oligonucleotide carrying DNA damage in vivo.
J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 19;288(29):20918-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.482257. Epub 2013 Jun 8. -
The role of altered nucleotide excision repair and UVB-induced DNA damage in melanomagenesis.
Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jan 9;14(1):1132-51. doi: 10.3390/ijms14011132.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

