Pathways
Threonine Metabolism in H. pylori J99
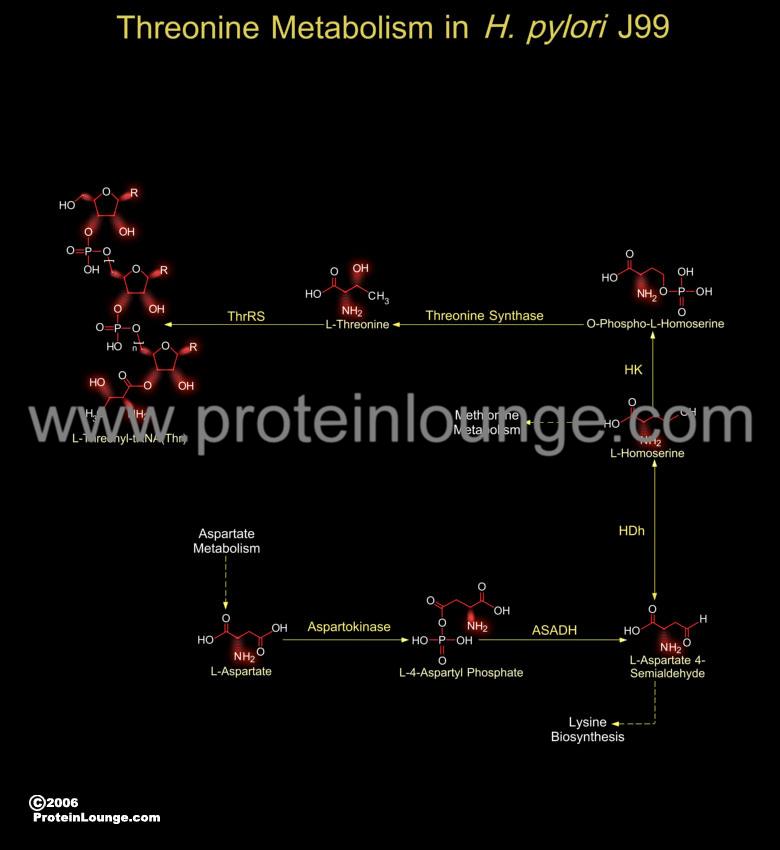
Description:
The H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori) J99 strains are Gram-negative, micro-aerophilic, spiral-shaped and flagellated bacteria, are associated with the pathogenesis of Gastric inflammation and Peptic ulcer disease (Ref.1). Presence of H. pylori J99 in the gastric mucosa is associated with Duodenal ulcers. The H. pylori genome is important for drug discovery and vaccine development and this is exemplified by the genome analysis of not only H. pylori Strain 26695 but also H. pylori J99.
References:
-
Th response to Helicobacter pylori differs between patients with gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer.
Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2005 Jun;40(6):641-7. -
Helicobacter pylori and complex gangliosides.
Infect. Immun. 2004 Mar;72(3):1519-29. -
Alanine-threonine polymorphism of Helicobacter pylori RpoB is correlated with differential induction of interleukin-8 in MKN45 cells.
J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004 Aug;42(8):3518-24. -
Essential domain of receptor tyrosine phosphatase beta (RPTPbeta) for interaction with Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin.
J. Biol. Chem. 2004 Dec 3;279(49):51013-21.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

