Pathways
TLR-TRIF Pathway
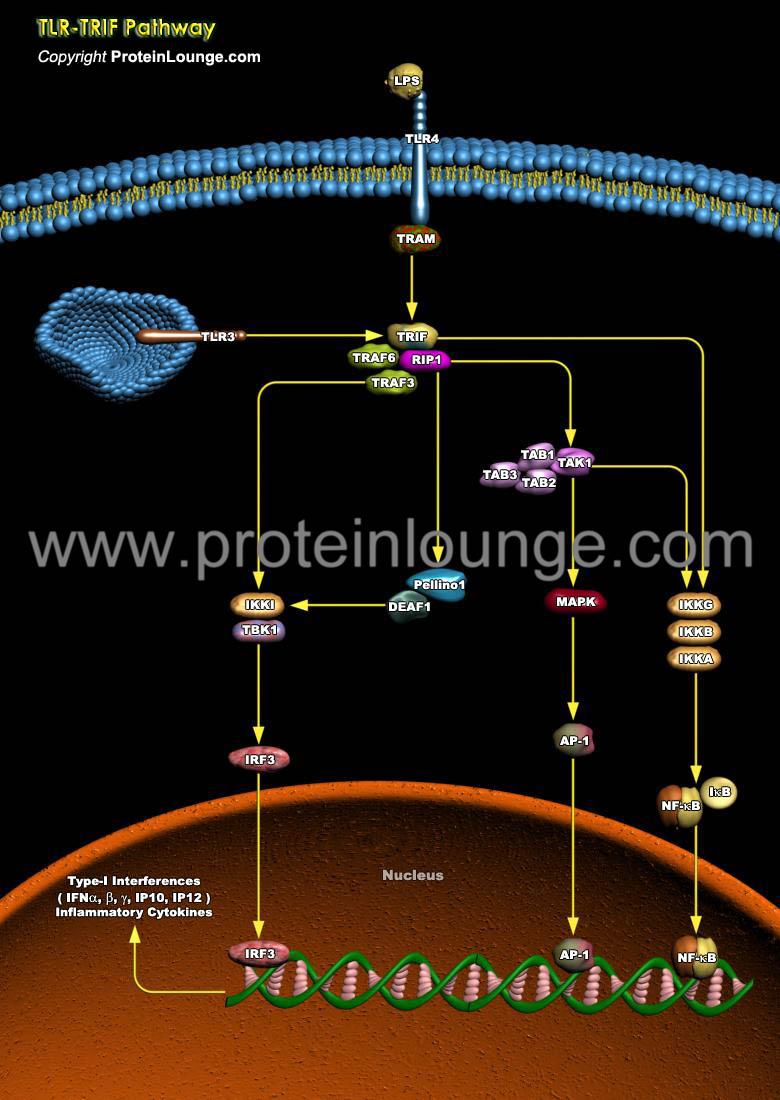
Description:
The Toll-like receptors (TLRs), 13 types known to-date, are a group of pattern-recognition receptors that play a crucial role in danger recognition and induction of the innate immune response against bacterial and viral infections. The major adaptors that bind to the intracellular domain of TLR to activate the proinflammatory response are the myeloid differentiation primary response MYD88 and TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-beta (TRIF). TRIF-dependent signaling is required for TLR-mediated production of type-I ...
References:
-
Beyond MyD88 and TRIF Pathways in Toll-Like Receptor Signaling.
Front Immunol. 2014 Feb 24;5:70. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00070. eCollection 2014. Review. No abstract available. -
TRIF-dependent TLR signaling, its functions in host defense and inflammation, and its potential as a therapeutic target.
J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jul;100(1):27-45. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2RI1115-531R. Epub 2016 May 9. Review. -
TRIF-mediated TLR3 and TLR4 signaling is negatively regulated by ADAM15.
J Immunol. 2013 Mar 1;190(5):2217-28. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201630. Epub 2013 Jan 30. -
TLR-signaling networks: an integration of adaptor molecules, kinases, and cross-talk.
J Dent Res. 2011 Apr;90(4):417-27. doi: 10.1177/0022034510381264. Epub 2010 Oct 12. Review.
You can view details of this pathway by subscribing:
Copyright © Protein Lounge Inc.
Terms & Conditions

