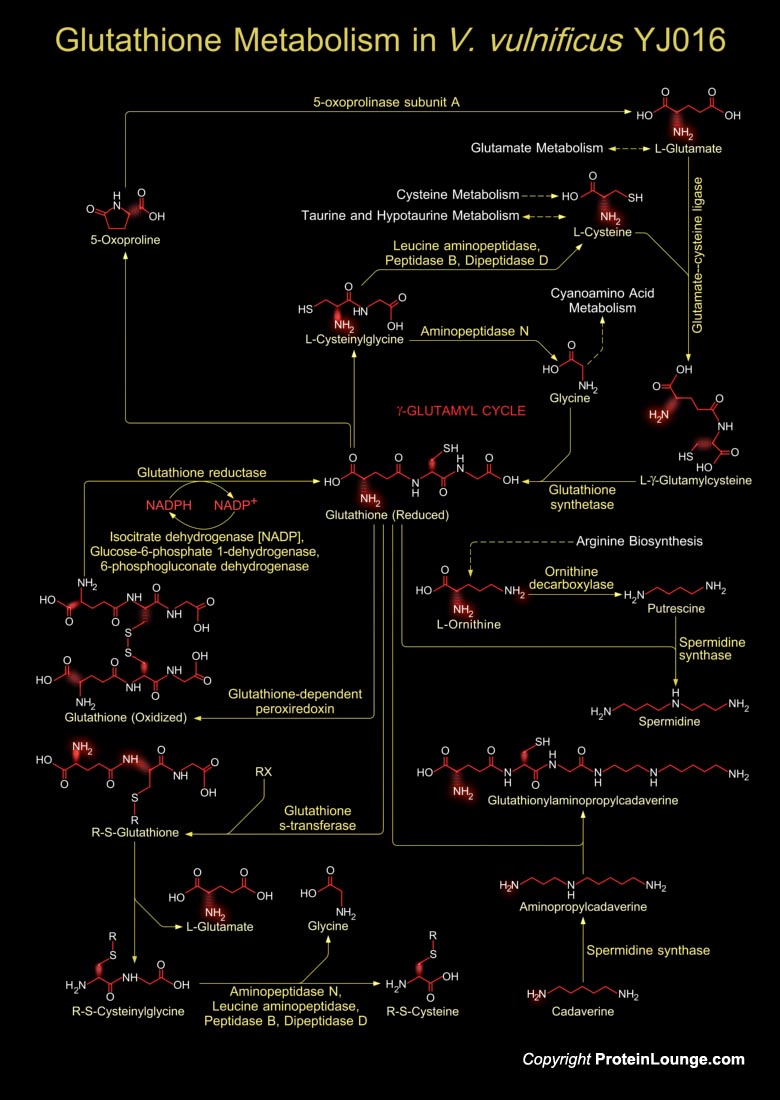
Vibrio vulnificus is an etiologic agent for severe human infection acquired through wounds or contaminated seafood. This is a lactose-fermenting, halophilic, Gram-negative, opportunistic pathogen, is found in estuarine environments and is associated with various marine species such as plankton, shellfish (Oysters, Clams, and Crabs), and finfish (Ref.1). V. vulnificus belong to the Gamma-group of Proteobacteria, and it shares morphological and biochemical characteristics with other human Vibrio pathogens, including Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. It is divided into three biotypes according to its different biochemical and biological properties. The genome of Biotype-1 strain, V. vulnificus YJ016, contains two chromosomes (Ref.2).Glutathione is a tripeptide,[..]
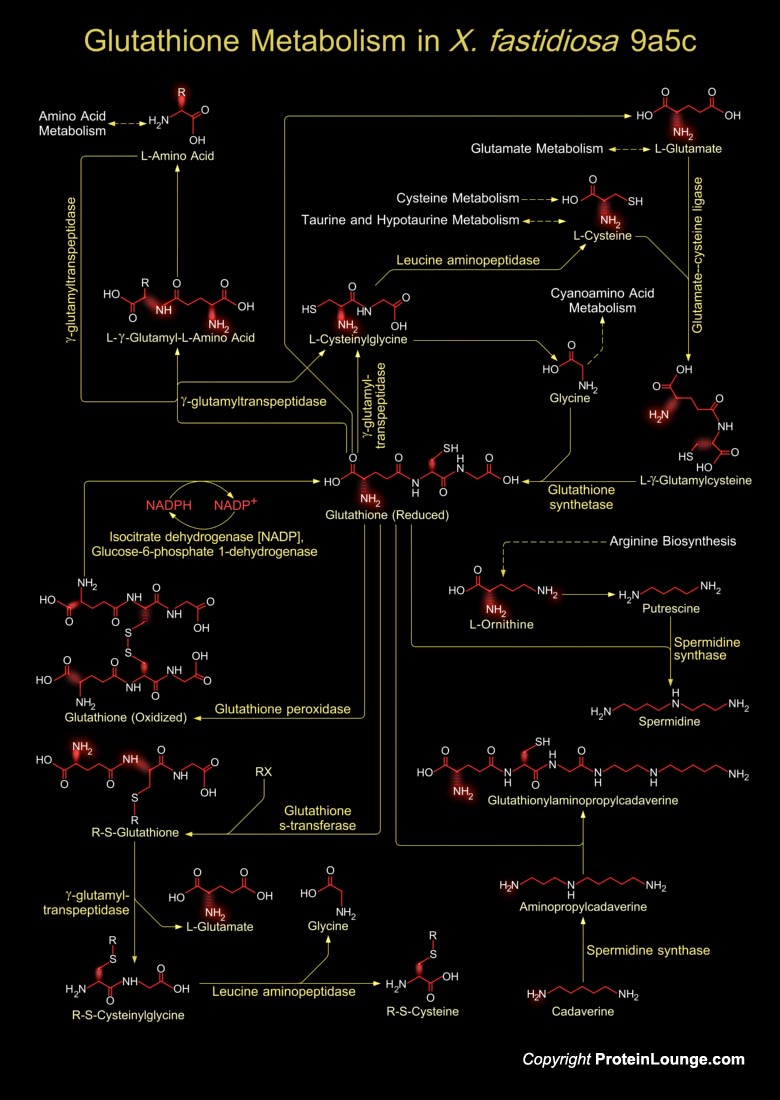
Xylella fastidiosa is a Gram-negative, fastidious, xylem-limited bacterium that causes a range of economically important plant diseases. It causes citrus variegated chlorosis-a serious disease of orange trees. It is responsible for pathogenicity and virulence involving toxins, antibiotics and ion sequestration systems. Glutathione is a tripeptide present in Xylella sp., which is composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine, and has numerous important functions within cells. The tripeptide is the thiol compound; present in the highest concentration in all types of cells (Ref.1 & 2).Glutathione metabolism in X. fastidiosa involves both the synthesis of Glutathione and its catabolism. Glutathione biosynthesis starts from an L-Amino acid, which in presence of the enzyme[..]
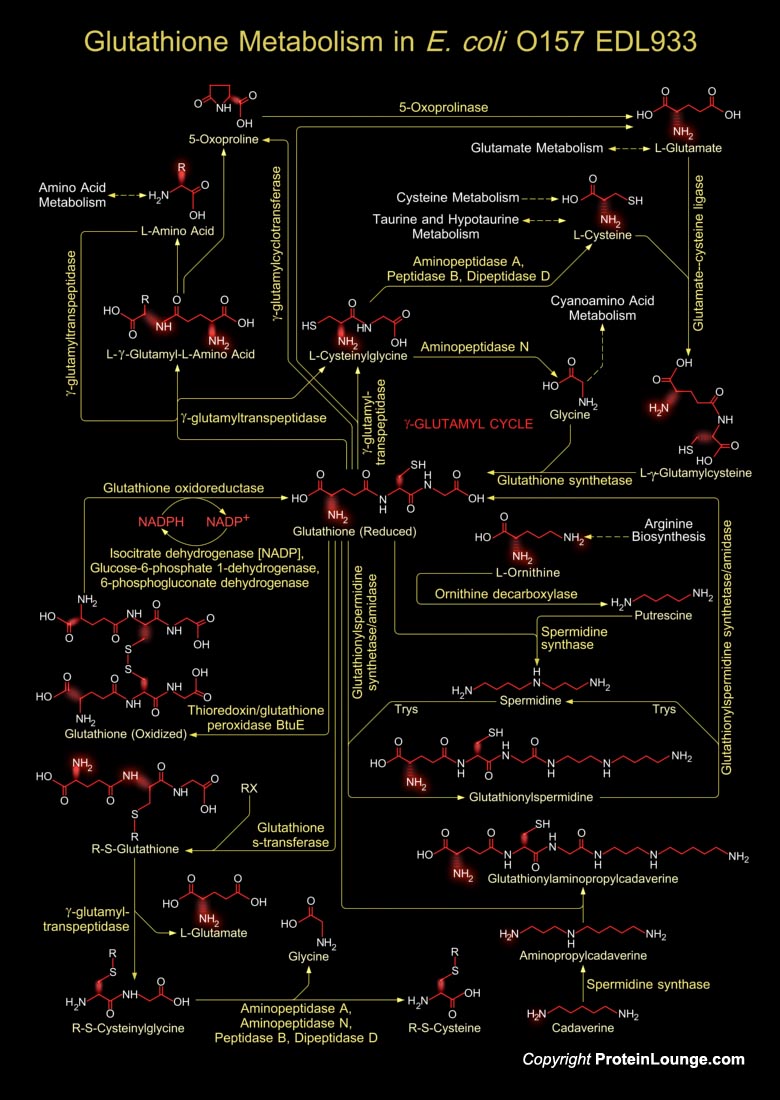
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. It is homeostatically controlled, both inside the cell and outside and often attains millimolar levels inside cells, which makes it one of the most highly concentrated intracellular antioxidants. Glutathione exists in two forms. The antioxidant "reduced Glutathione" tripeptide is conventionally called Glutathione and abbreviated Gsh; the oxidized form is a sulfur-sulfur linked compound, known as[..]
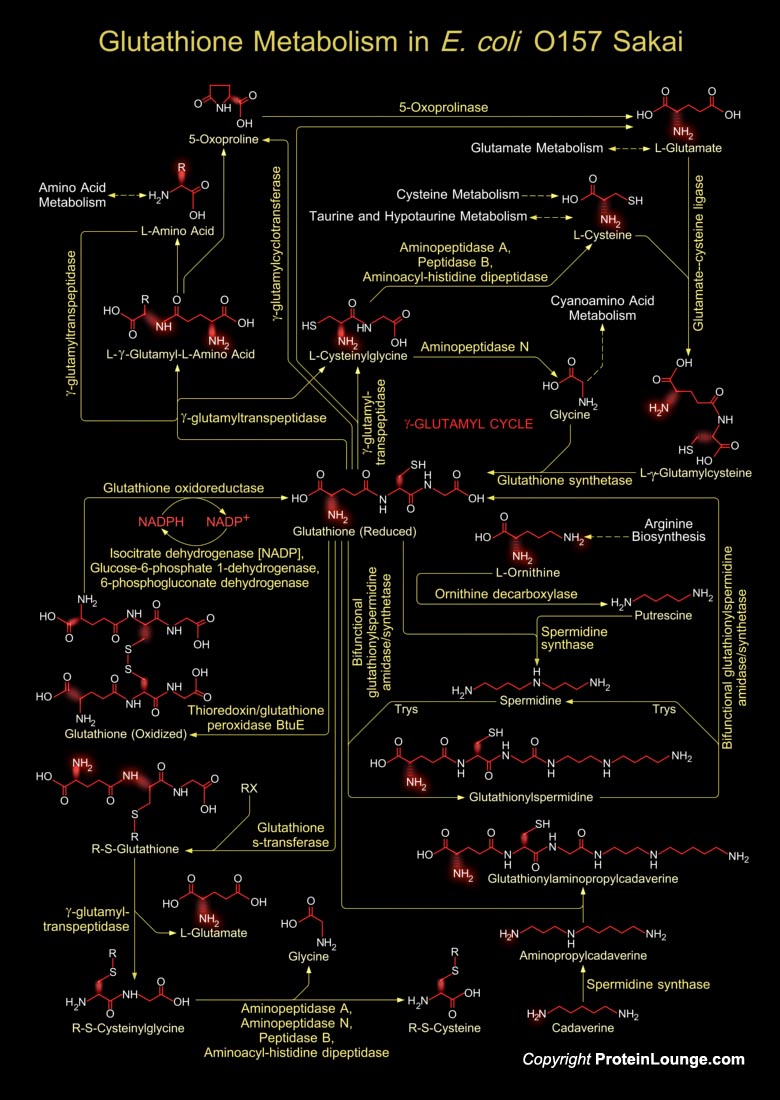
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. It is homeostatically controlled, both inside the cell and outside and often attains millimolar levels inside cells, which makes it one of the most highly concentrated intracellular antioxidants. Glutathione exists in two forms. The antioxidant "reduced Glutathione" tripeptide is conventionally called Glutathione and abbreviated Gsh; the oxidized form is a sulfur-sulfur linked compound, known as[..]
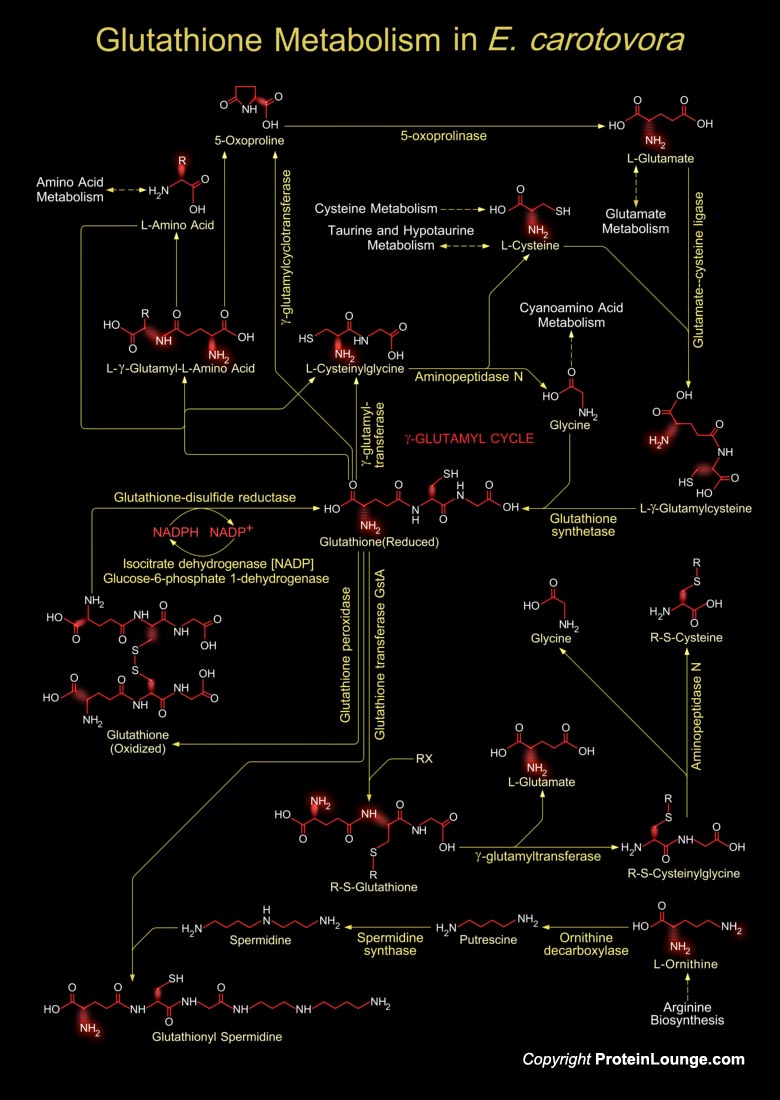
Pectobacterium carotovorum is a bacterium of the family Pectobacteriaceae. It used to be a member of the genus Erwinia. The bacterium is also known as Erwinia carotovora It is a ubiquitous plant pathogen with a wide host range and is able to cause disease in almost any plant tissue it invades. P. carotovorum is a very economically important pathogen in terms of post-harvest losses, and a common cause of decay in stored fruits and vegetables. Decay caused by P. carotovora is often referred to as "bacterial soft rot" (Ref.1). At present there are four described subspecies of P. carotovorum: P. carotovorum, P. brasiliense, P. odoriferum, and P. actinidiae. The symptoms caused by Pectobacterium infection include soft rot and wilts resulting from vascular[..]
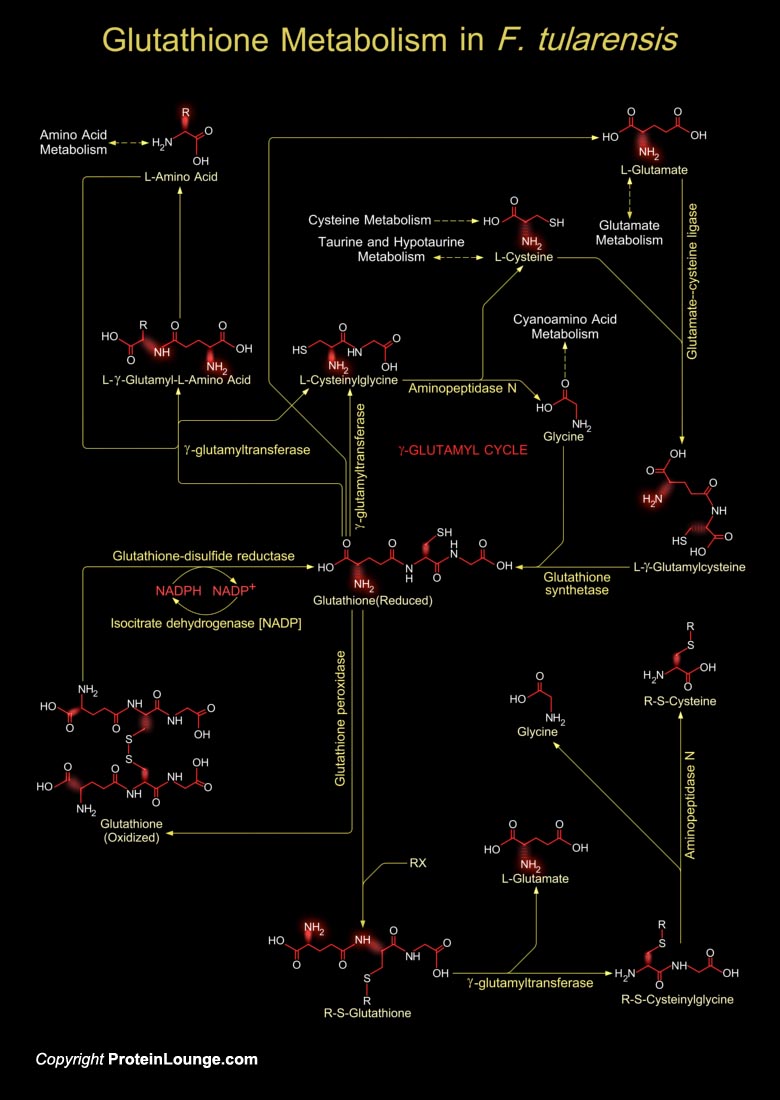
Francisella is a genus of pathogenic bacteria. The type species, F. tularensis is a rod-shaped Gram-negative bacterium and is the causative agent of tularemia or rabbit fever. The bacterium is an aerobic pleiomorphic coccobacillus, which requires oxygen for growth, is variable in shape, with basic shape between a rod and a sphere, do not move by their own power, and do not form spores. Glutathione metabolism in F. tularensis occurs within cells in two closely linked, enzymatically controlled reactions that utilize ATP and draw on nonessential amino acids as substrates (Ref.1). Glutathione is a tripeptide, composed of glutamate, cysteine and glycine, and has numerous important functions within the bacterial cell. This tripeptide is specifically a thiol compound, present[..]
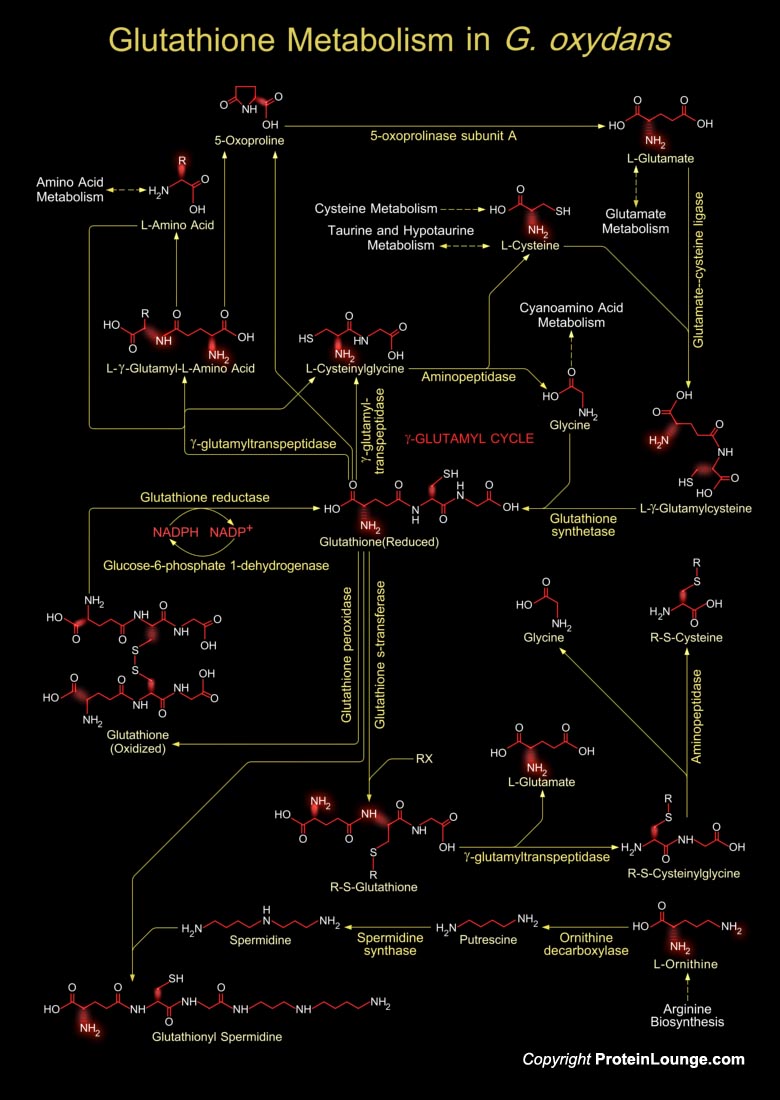
Gluconobacter oxydans is a Gram-negative bacterium belonging to the family Acetobacteraceae. It is a rod-shaped and obligately aerobic bacterium having a respiratory type of metabolism using oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor. It can grow in highly concentrated sugar solutions and at low pH values. It contains many membrane-bound dehydrogenases that are critical for the incomplete oxidation of biotechnologically important substrates (Ref.1). Glutathione (GSH), a tripeptide, is ubiquitous in eukaryotic system, found widely in Gram negative bacteria. Glutathione (GSH) is made-up of three amino acids viz. glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine Glutathione has diverse roles in biological systems for its antioxidative, immune boosting and cellular detoxifying activities.[..]
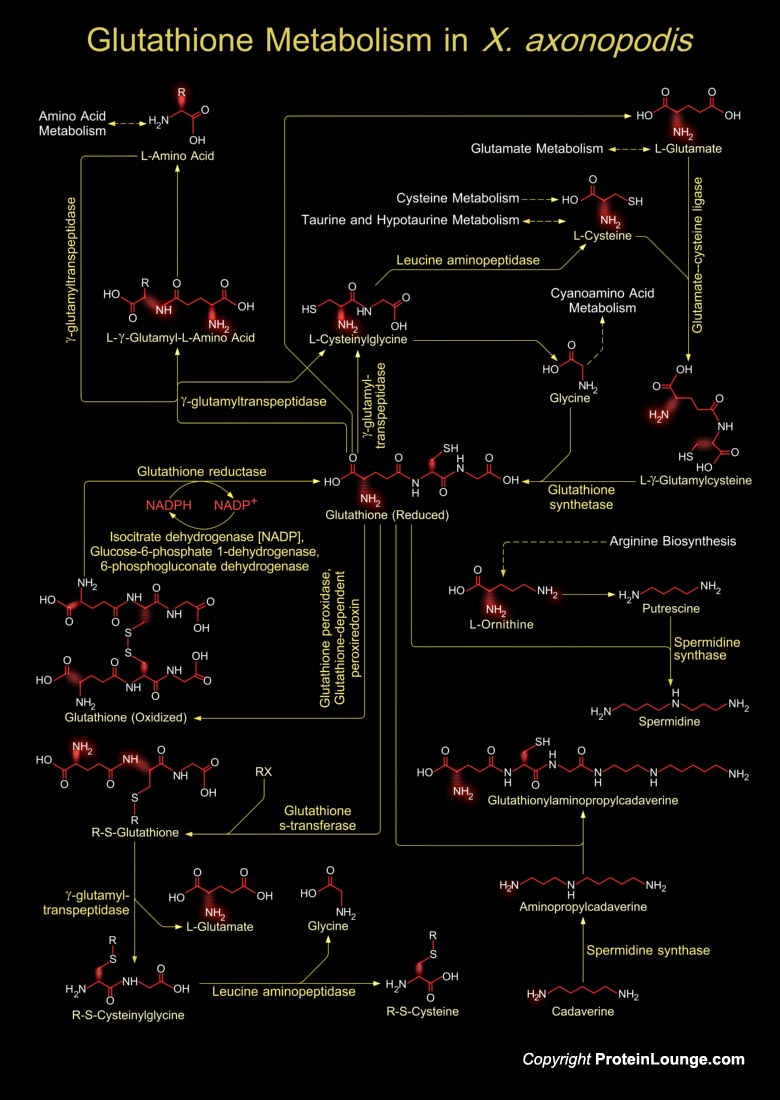
Xanthomonas is a Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium known for being a common plant pathogen. This bacterium is grown commercially to produce the exopolysaccharide xanthan gum, which is used to control viscosity and as a stabilizing agent in many industries. Xanthomonas affects many types of hosts, including citrus, beans, grapes, cotton, and rice. X. axonopodis causes citrus cankers and black rot, which affects many commercial plants. Typical symptoms of the disease include lesions on the leaves, fruit, and stems as well as twig dieback. X. axonopodis is motile by a single polar flagellum and produces slow growing, non-mucoid colonies in culture. It is the causal agent of Asiatic Citrus Canker on most Citrus sp. and close relatives of Citrus in the family Rutaceae[..]
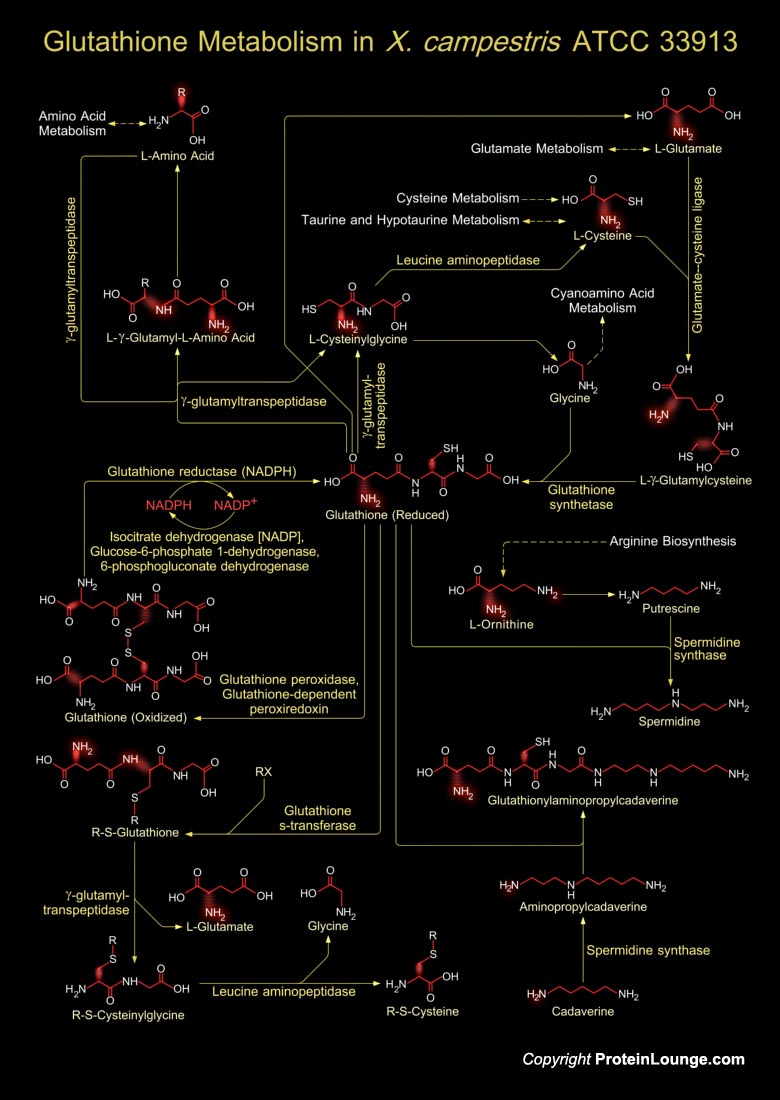
Xanthomonas is a Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium known for being a common plant pathogen. Xanthomonas campestris causes black rot, which affects crucifers such as Brassica and Arabidopsis. Symptoms include marginal leaf chlorosis and darkening of vascular tissue, accompanied by extensive wilting and necrosis. This bacterium is grown commercially to produce the exopolysaccharide xanthan gum, which is used to control viscosity and as a stabilizing agent in many industries. Xanthomonas affects many types of hosts, including citrus, beans, grapes, cotton, and rice. Typical symptoms of the disease include lesions on the leaves, fruit, and stems as well as twig dieback (Ref.1).Glutathione metabolism in Xanthomonas occurs within cells in two closely linked, enzymatically[..]
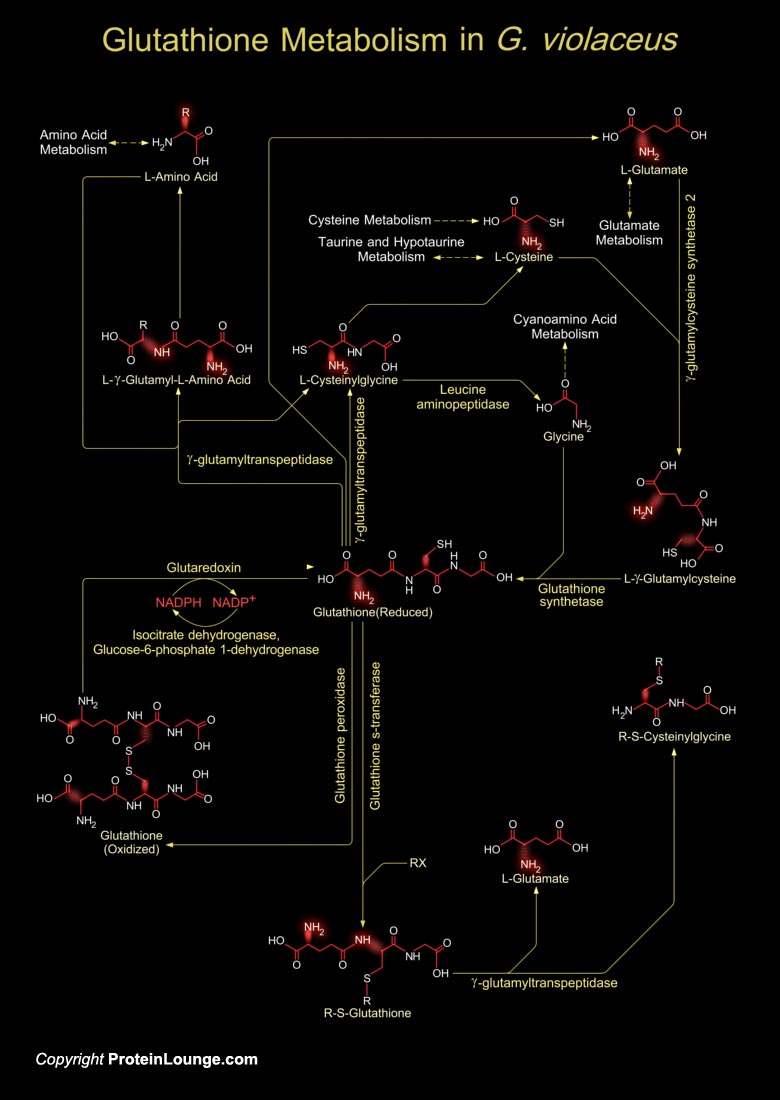
Gloeobacter is a genus of cyanobacteria. Gloeobacter violaceus (G. violaceus) the unicellular cyanobacterium is the only known oxygenic photoautotroph which does not contain thylakoid membranes hence all membrane-bound bioenergetic processes take place in the green plasma membrane of this organism. G. violaceus is a rod-shaped, unicellular cyanobacterium with unusual characteristics. It is an obligate photoautotroph, sensitive to strong light and it has a relatively long generation time (Ref.1). Cyanobacterias are the organisms to be exposed to the toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS): singlet oxygen (1 O2), superoxide anion (O2−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radical (OH) as they have evolved from oxygenic photosynthesis. ROS is generated when[..]
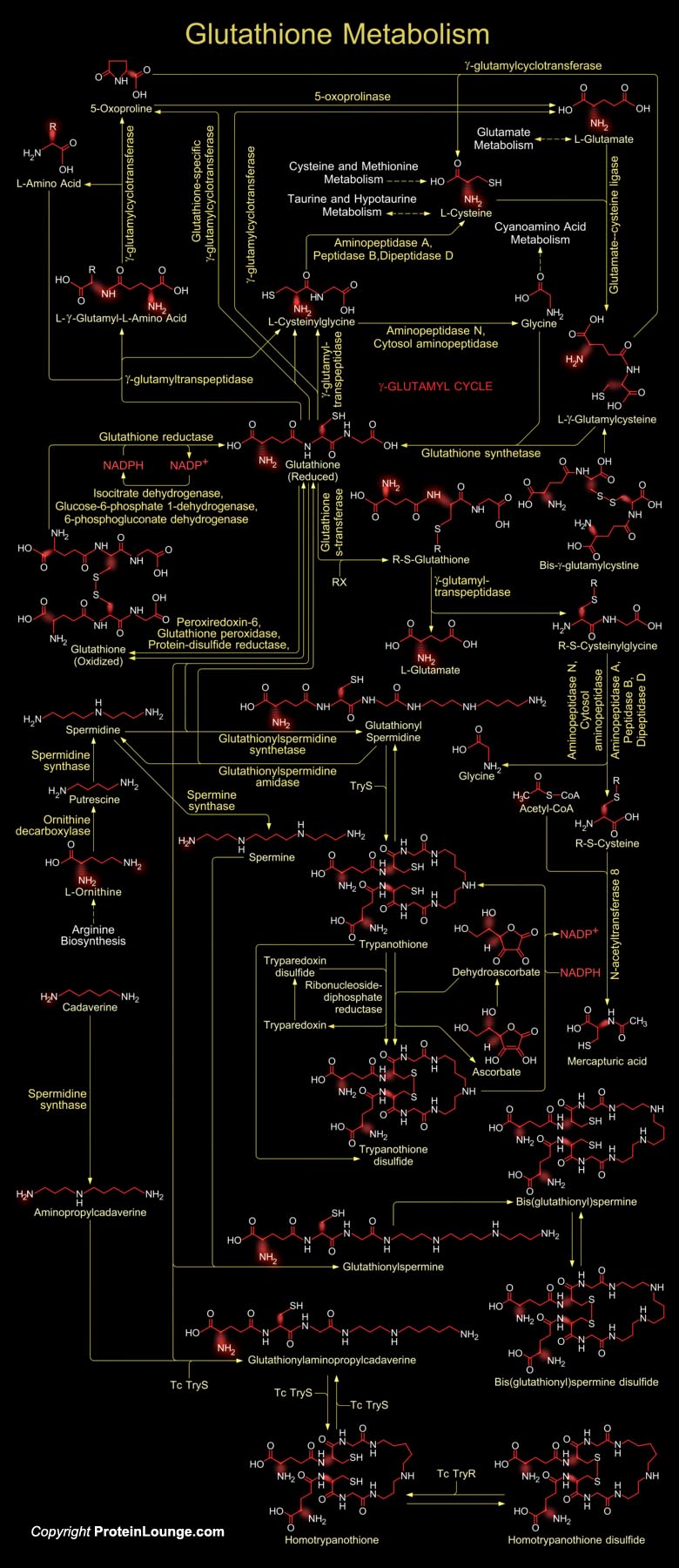
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. It is composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. Glutathione is homeostatically controlled, both inside the cell and outside. It often attains millimolar levels inside cells, which makes it one of the most highly concentrated intracellular antioxidants. Glutathione exists in two forms. The antioxidant "reduced Glutathione" tripeptide is conventionally called Glutathione and abbreviated Gsh; the oxidized form is a sulfur-sulfur linked compound, known as Glutathione[..]
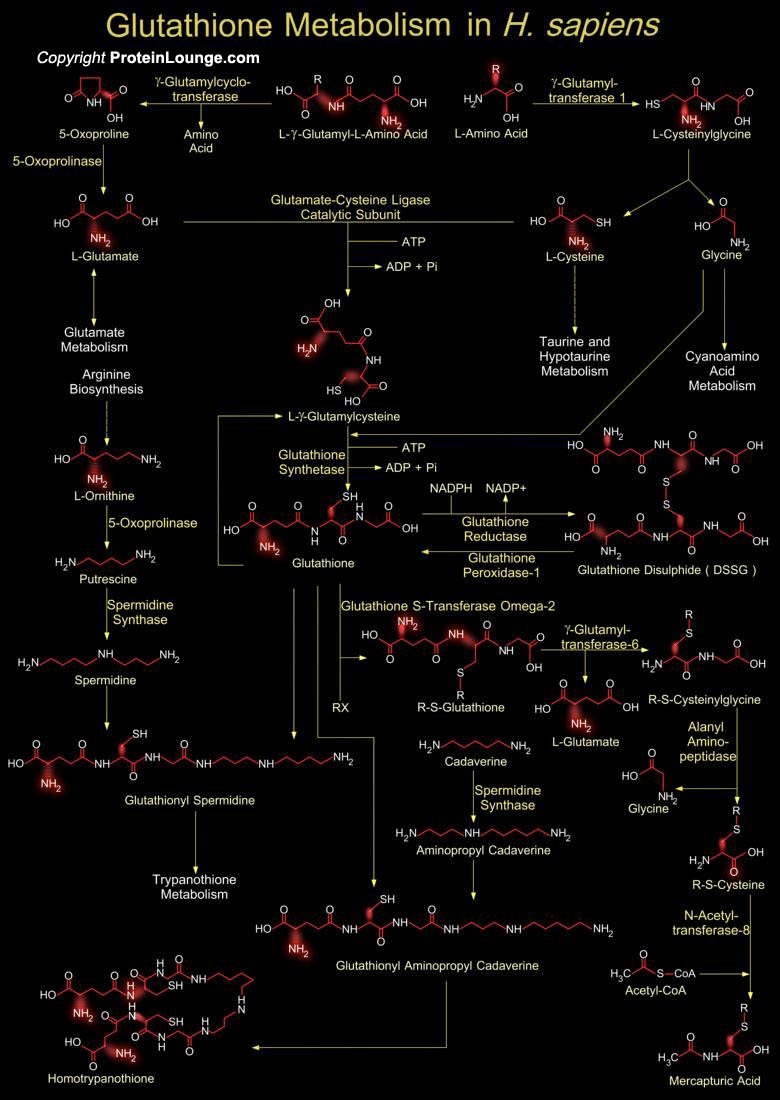
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. Glutathione is homeostatically controlled, both inside the cell and outside. It often attains millimolar levels inside cells, which makes it one of the most highly concentrated intracellular antioxidants. Glutathione exists in two forms. The antioxidant "reduced Glutathione" tripeptide is conventionally called Glutathione. The oxidized form is a sulfur-sulfur linked compound, known as Glutathione[..]

