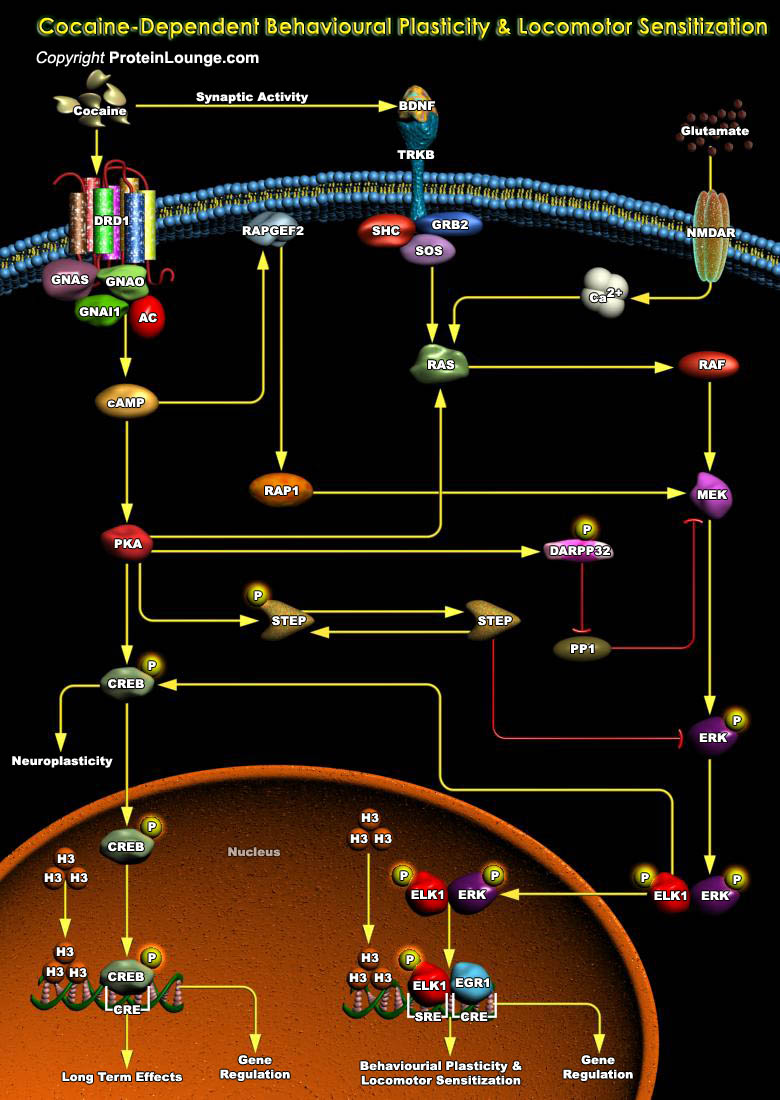
Drug addiction is considered as a chronic and relapsing psychiatric disorder induced by repeated pharmacological manipulation of the so-called mesolimbic reward circuitry by drugs of abuse. It can be viewed as maladaptive neural plasticity that occurs in vulnerable individuals in response to repeated exposure to drugs. Thus, addictive drugs change brain properties that normally permit us to adapt to environmental stimuli. Behavioral plasticity, including locomotors sensitization and development of drug, is associated with psychomotor stimulant-induced neuroadaptations in brain reward circuits linked to addiction. By changing motivational circuitry, addictive drugs progressively orient behavior toward drug-seeking and drug-taking strategies that are life-long behavioral[..]

Drug addiction is considered as a chronic and relapsing psychiatric disorder induced by repeated pharmacological manipulation of mesolimbic reward circuitry during drugs of abuse. It is observe as maladaptive neural plasticity that occurs in vulnerable individuals in response to repeated exposure to drugs. Thus, addictive drugs change brain properties that normally permit us to adapt to environmental stimuli. Cocaine affects the cognitive functions of the NAc (Nucleus Accumbens), particularly in relation to actin cycling in structural and behavioural plasticity of drug addiction. Cytoskeletal changes initiated following cocaine abuse are regulated by the Rho family of GTPases with significant downstream activity in key actin binding proteins. Moreover, signalling via[..]
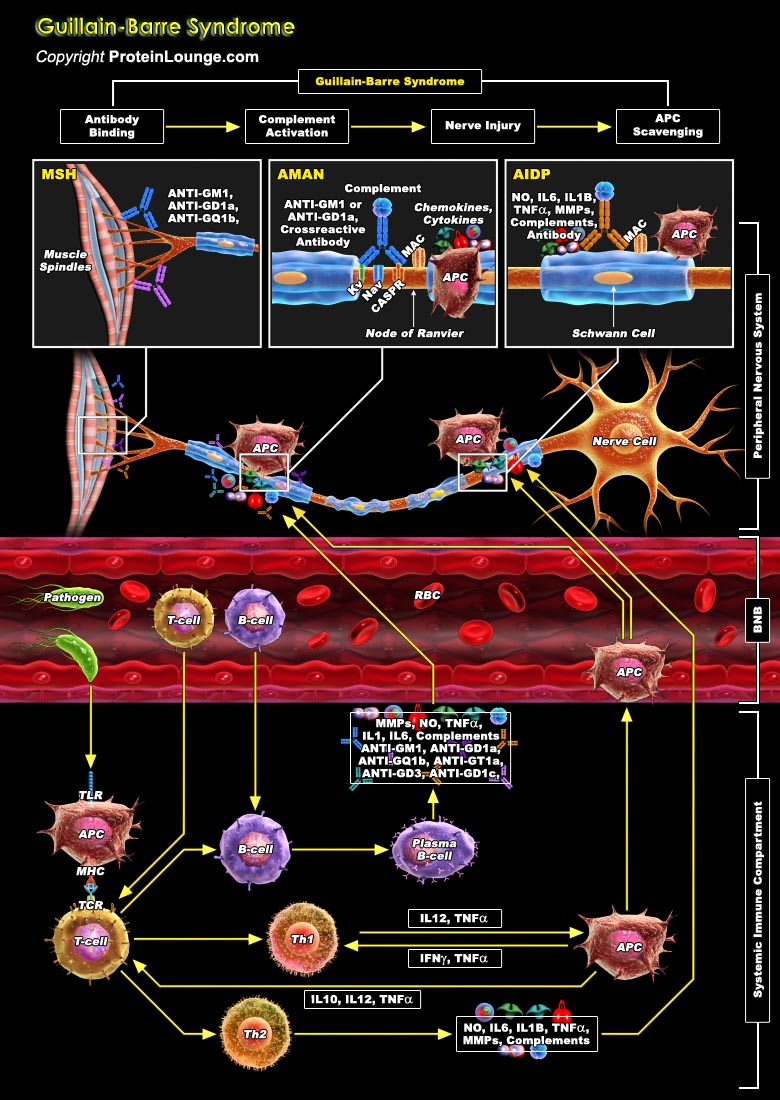
GBS (Guillain-Barré Syndrome) is often known as post infectious, immune-mediated nerve injury. This syndrome results in inflammatory demyelination, characterized by acute weakness of the extremities and areflexia. The pathological features of GBS include inflammation, demyelination, and axonal damage in the PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) (Ref.1 & 2). AIDP (Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy) and AMAN (Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy) are the common subtypes of GBS. Common form of disease, AIDP, presents as progressive motor weakness, usually begin in the legs and advances proximally. More over patients experience severe pain, and have symptoms, such as cardiac arrhythmias, blood pressure instability, or urinary retention. Advancing symptoms[..]
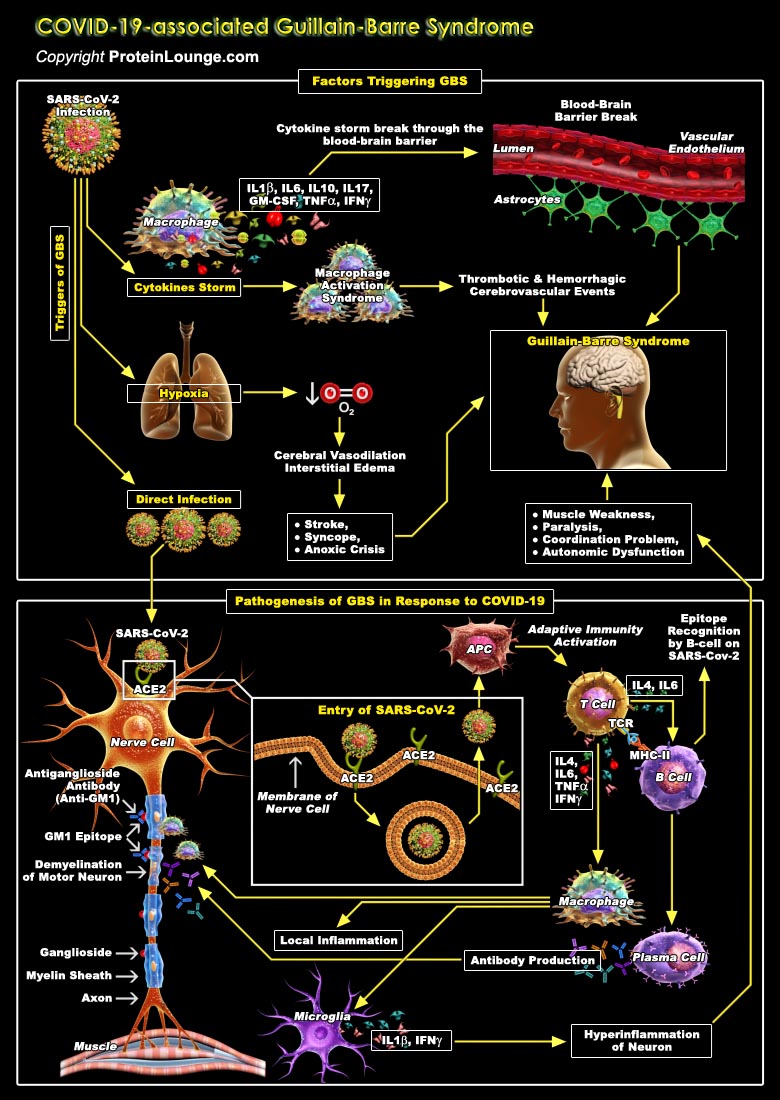
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the disease caused by the beta coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 was believed to be restricted to the respiratory system since its outbreak in January 2020. Later it was found that it also involves multiple other organs including the central and peripheral nervous system. Neurological problems like ischemic, hemorrhagic strokes, venous sinus thrombosis, encephalopathy, cerebral hemorrhage, encephalitis, and neurodegenerative diseases like Guillain–Barre syndrome (GBS) has been found to be associated with COVID-19 (Ref.1 and 2). SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurological damage directly by damaging specific receptors or by causing cytokine-related injury, also through secondary hypoxia and retrograde travel along nerve fibers (Ref.3).GBS is a rare[..]
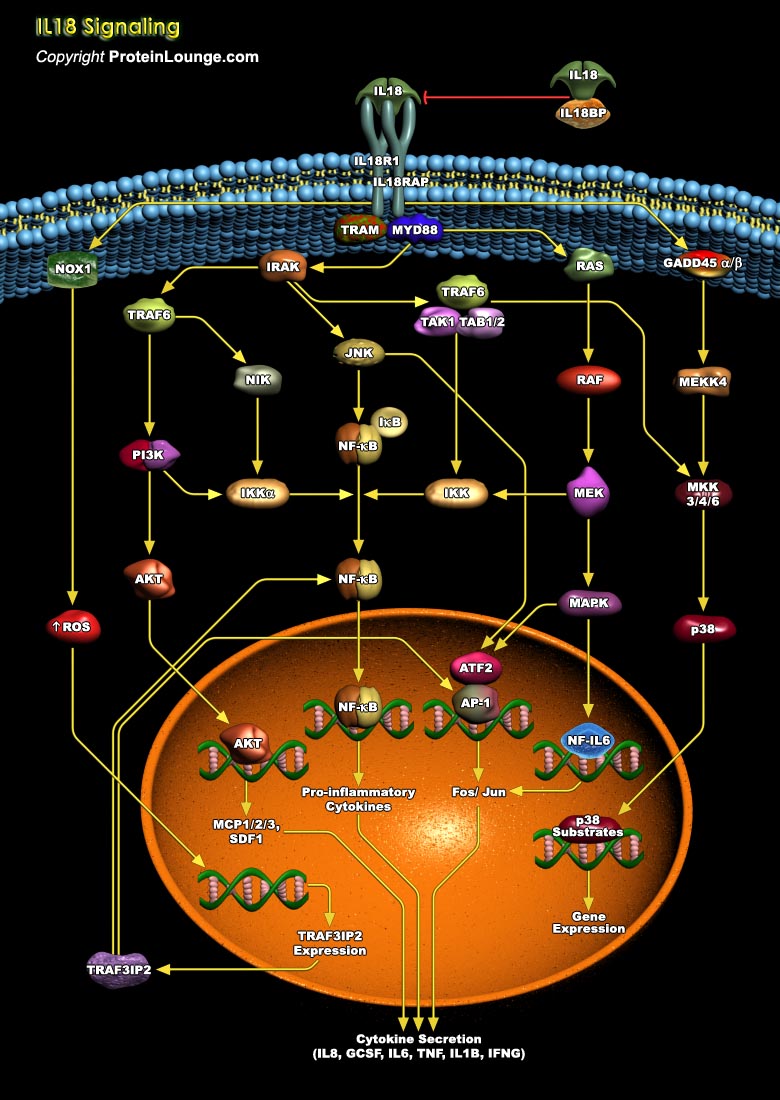
Interleukin18 (IL18) is a pro-inflammatory IL-1 family cytokine that activates hematopoietic cell types involved in Th1 and Th2 responses. IL18 plays an essential role in the host defense against various infectious microorganisms. It also enhances the induction of IFN-gamma, nitric oxide (NO), and ROS in phagocytes. Expressed by both immune and non-immune cells like macrophages, keratinocytes, osteoblasts, kupffer cells, T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, astrocytes, microglia and endothelial cells as inactive precursor pro-IL18, it is cleaved by Caspase-1 enzyme to form the mature and active IL18 molecule (Ref.1 and 2). Once activated, IL18 is released and is free to bind the receptor, IL18 receptor alpha chain (IL18R1), and the co-receptor, IL18R accessory[..]
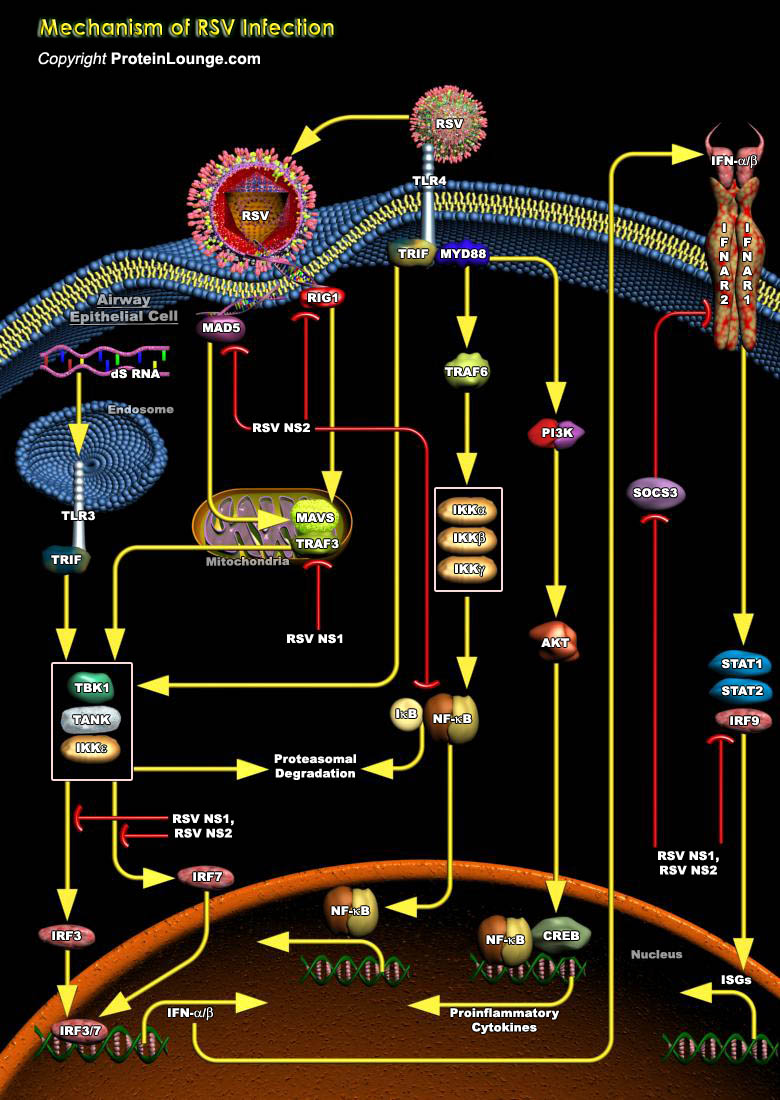
Human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a spherical enveloped virus with a diameter of approximately 150 nm. It is filamentous, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that belongs to the Orthopneumovirus genus of the Pneumoviridae family in the order Mononegavirales. The RNA genome consists of a non-segmented negative-sense single strand RNA along with 10 genes encoding 11 proteins. They are: internal structural proteins (matrix protein [M] and nucleoprotein [N]), proteins required for a functional polymerase complex (phosphoprotein [P] and polymerase [L]), nonstructural proteins involved in evasion of the innate immune response (NS-1 and NS-2), externally exposed transmembrane glycoproteins (small hydrophobic protein [SH], glycoprotein [G], and fusion protein[..]
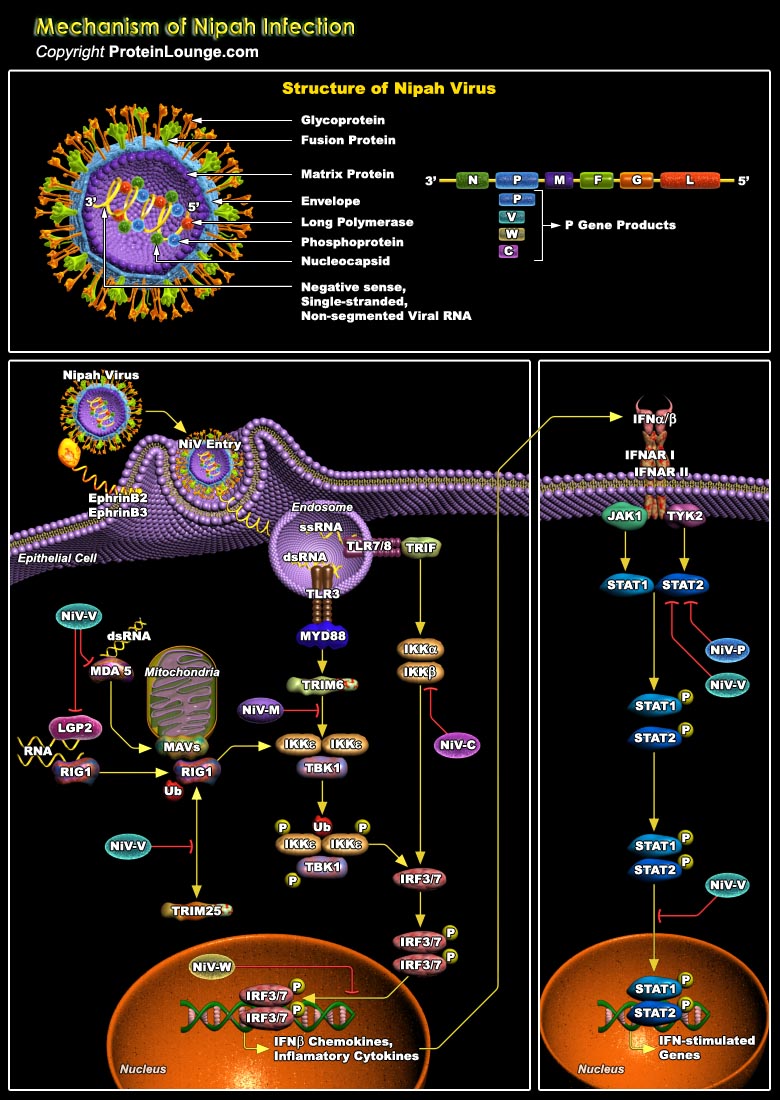
Nipah virus (NiV), is a highly lethal zoonotic paramyxovirus that emerged at the end of last century as a human pathogen capable of causing severe acute respiratory infection and encephalitis. NiV blocks the elicitation of innate and adaptive immune response by inhibiting synthesis of cytokines, interferon type I (IFN α/β) (Ref.1). The effects on humans of infection by Nipah virus can range from an asymptomatic infection to fatal encephalitis. The incubation period can vary from four to 45 days. The first stage of the infection is the development of fever, headache, sore throat, myalgia, and vomiting, similar to common flu. The infection can then evolve to dizziness, altered consciousness, drowsiness, and some neurological signs indicating acute[..]
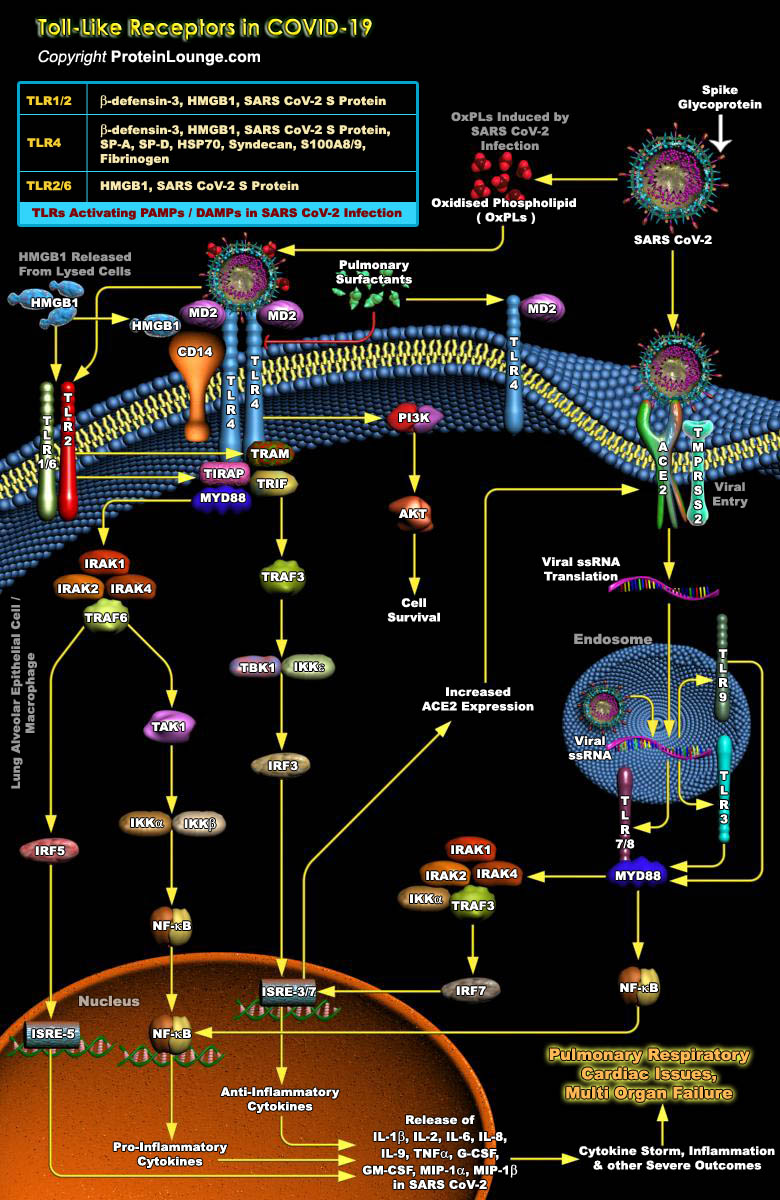
COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by a new coronavirus called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that has infected millions of people throughout the world leading to a global health crisis. COVID-19 declared as pandemic by World Health Organization, generally causes lung inflammation and pneumonia. In extreme cases, it can also cause injury to multiple organs including the lungs, cardiovascular system, liver, kidneys, muscles and brain. Serious patients generally exhibit a “cytokine storm” or hyper-inflammation formed due to excessive production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that not only leads to ARDS in many cases but can also cause extensive tissue damage, organ failure, and death (Ref.1 and 2).The SARS-CoV2 virus belongs[..]
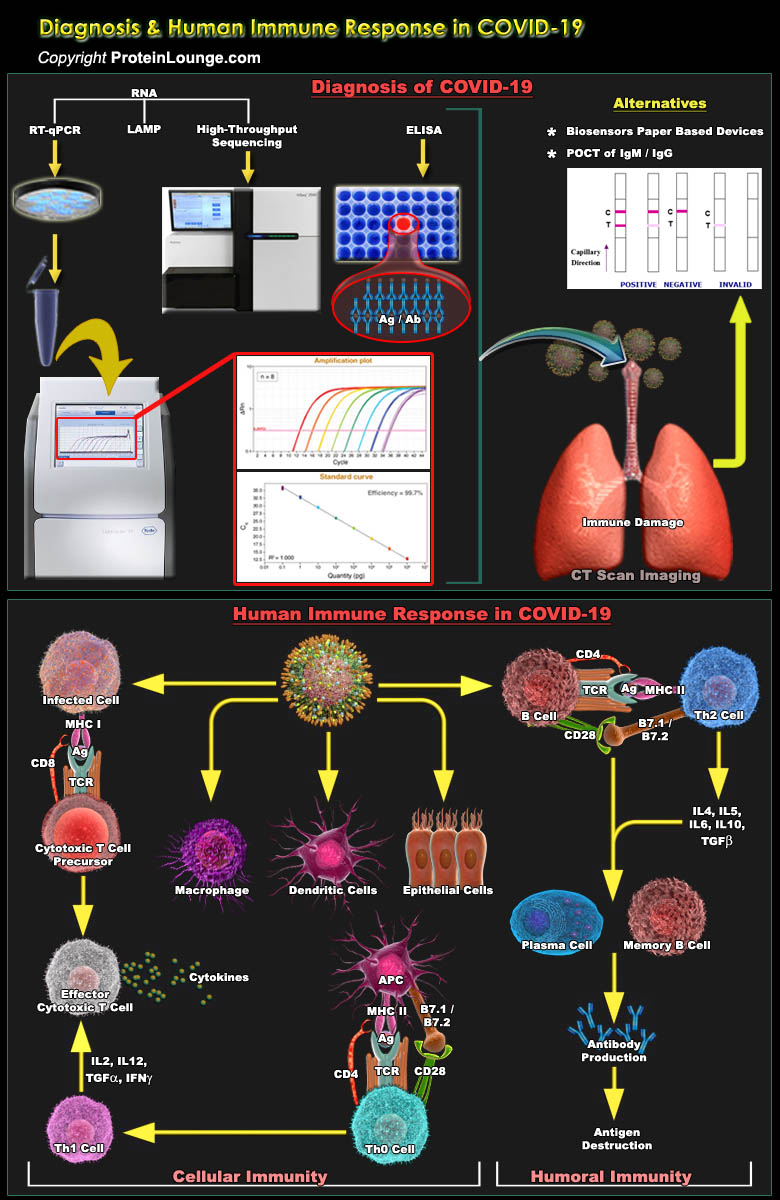
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a pandemic respiratory disease caused by a highly transmissible and pathogenic coronavirus, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which had an unusual outbreak in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. SARS-CoV-2, a novel beta-coronavirus, is characterized by a spherical morphology with spike projections on the surface. It shared high sequence identity with SARS-CoV and bat SARS-like coronavirus (SL-CoV). COVID-19 is an infectious disease which shows symptoms like fever, tiredness, dry cough and shortness of breath. People may be sick with the virus for 1 to 14 days before developing symptoms (Ref.1 and 2). Development of therapeutics and vaccines is underway. Diagnosis and testing of the disease can be the most[..]
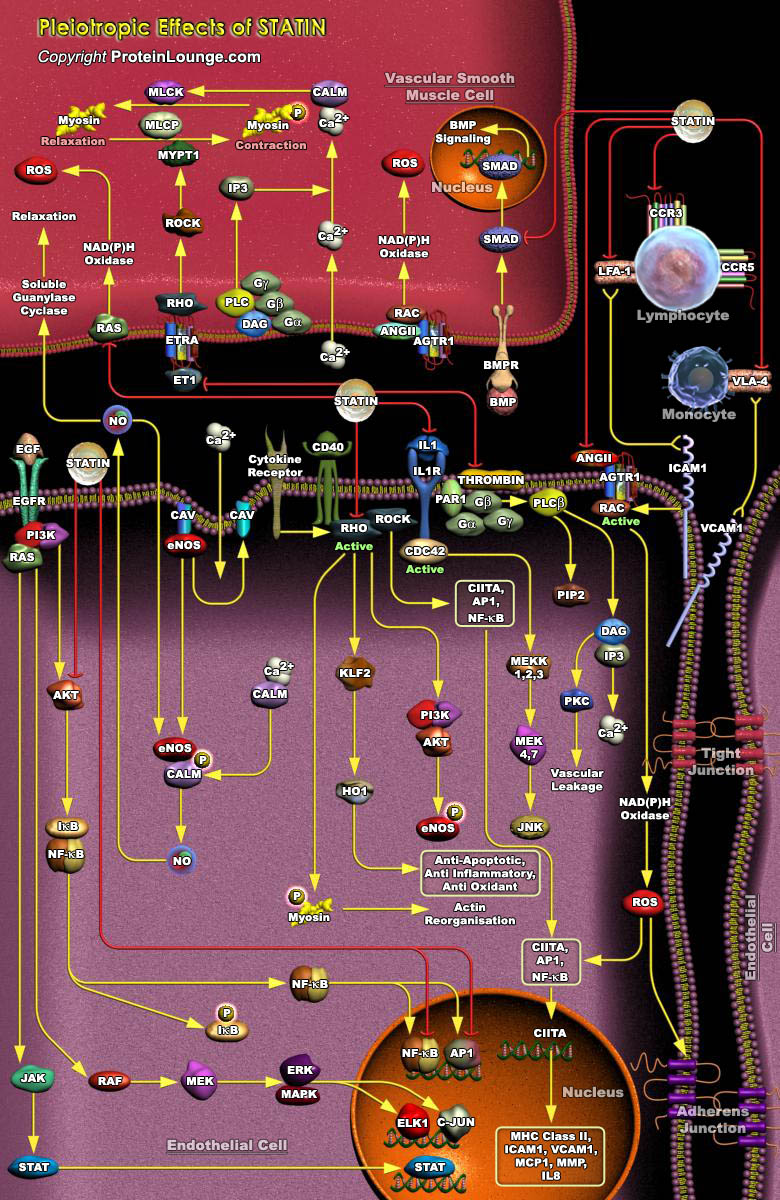
Statins are the most common drug used to treat hyperlipidemia. They also induce several pleiotropic effects like improvement of endothelial dysfunction, increased nitric oxide bioavailability, antioxidant properties, inhibition of inflammatory responses, and stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques. The different pleiotropic effects arise due to marked differences in lipophilicity, solubility and differential localization of statins which is based on the presence or absence of polar moieties on its hydrophobic structures. Lipophilic statins (such as Atorvastatin, simvastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin, cerivastatin and pitavastatin) enter into cells by passive diffusion and appear to be more beneficial as they are taken up by a large number of cells and widely[..]
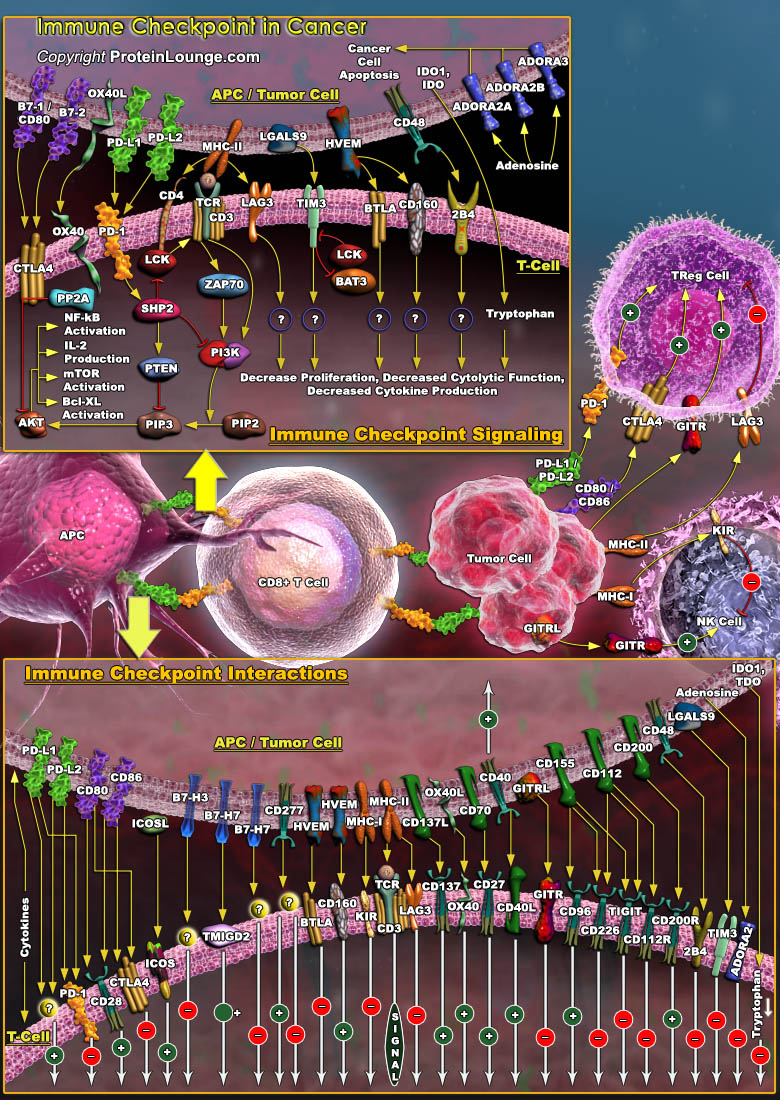
Immune checkpoints are co-stimulatory or inhibitory molecules that serve as regulators of T cells function in the tumor microenvironment. Inhibitory immune checkpoints maintain immune homeostasis, down-regulate anti-tumor responses and prevent autoimmunity (Ref.1). Checkpoint pathways involve costimulatory and inhibitory receptors and their ligands. Costimulatory receptors include CD28 and ICOS (inducible T cell co-stimulator), 4-1BB, OX40, CD27, CD30, CD40, GITR (glucocorticoid inducible TNF receptor-related protein), and HVEM (herpes-virus entry mediator), whereas co-inhibitory receptors include CTLA4, Programmed Death-1 (PD-1), BTLA (B and T lymphocyte attenuator), lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3), TIM3 (T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein[..]
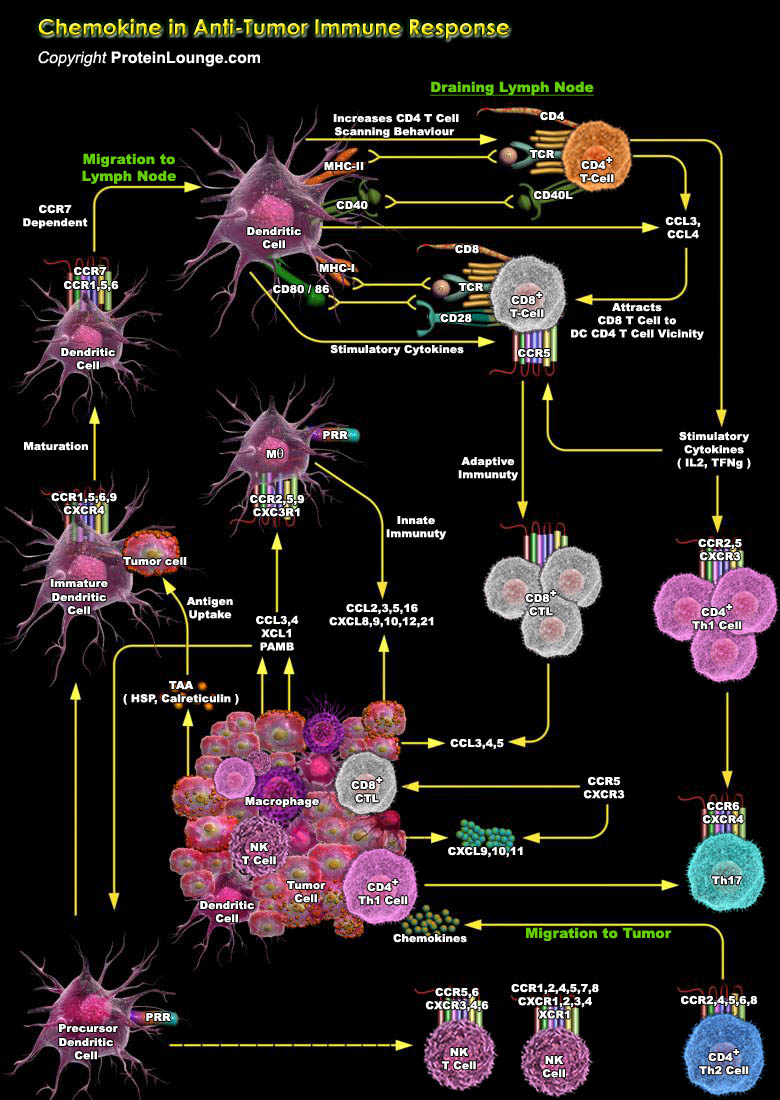
Chemokines are chemotactic cytokines belonging to a large family of small, secreted proteins that stimulate the cells migration and the positioning and interactions of cells within tissue. About 50 endogeneous chemokine ligands and 20 cell surface G protein-coupled heptahelicalchemokine receptors together form the chemokine superfamily. Chemokines regulate leukocyte migration into the tumor microenvironment and thus play important roles in deciding tumor fate, promoting anti-tumor immune responses, or sustaining tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis (Ref.1).Chemokines mediate anti-tumor activities through inhibition of angiogenesis and attraction of immune effector cells to the tumor site. Major immune cells that are recruited to the tumor microenvironment (TME)[..]

