Featured Pathways
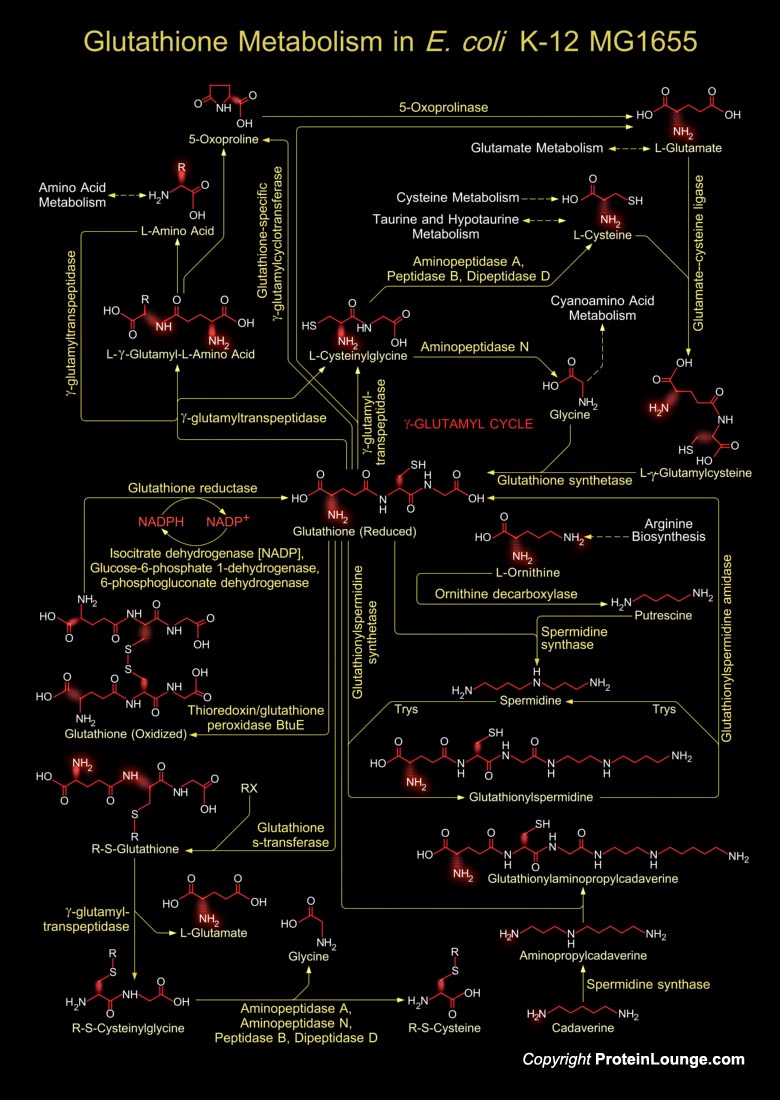
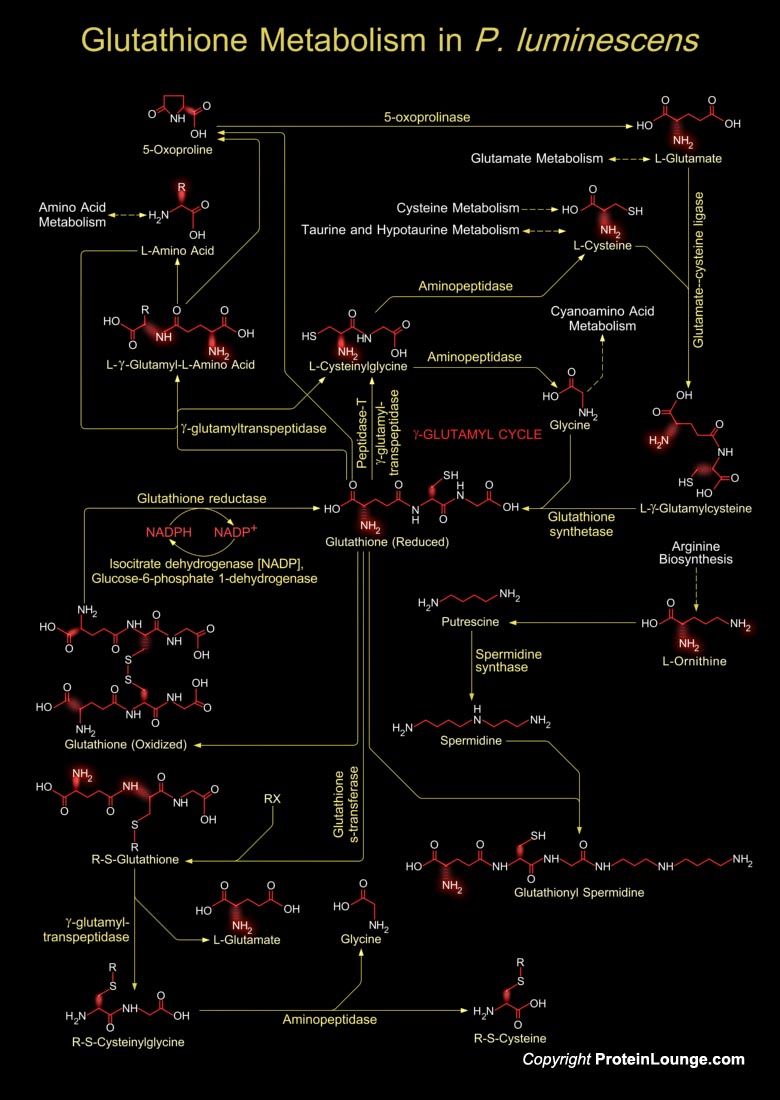
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. It is homeostatically[..]
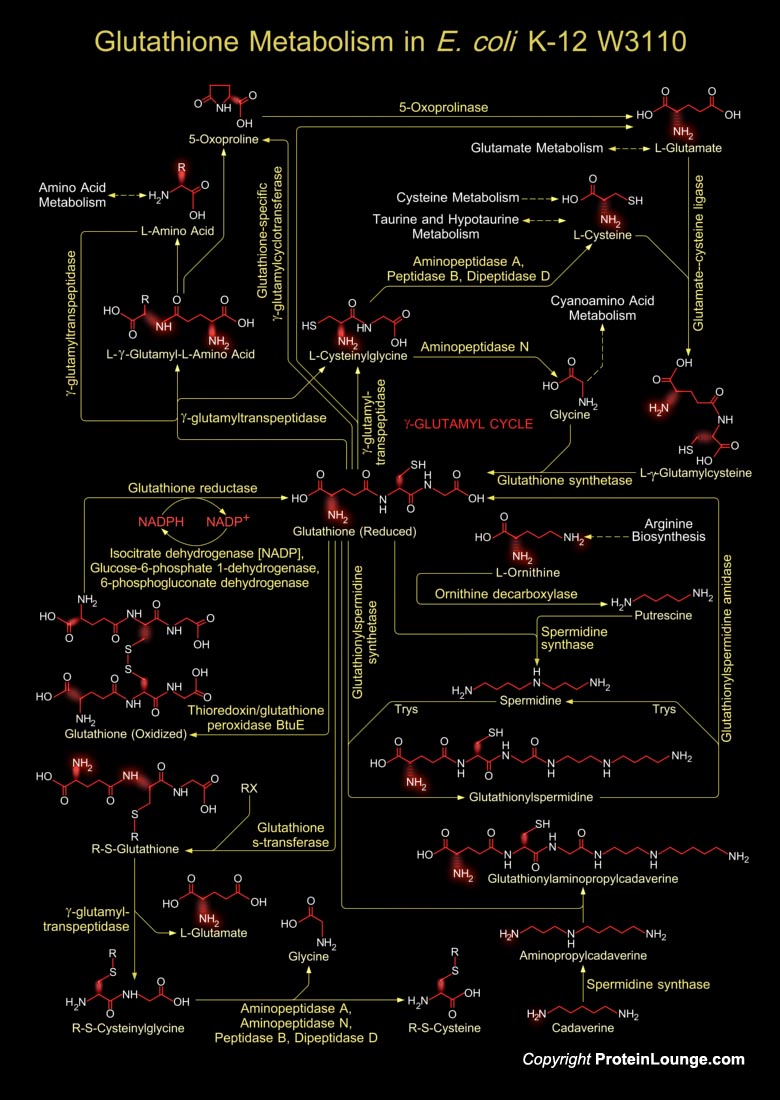
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. It is homeostatically[..]
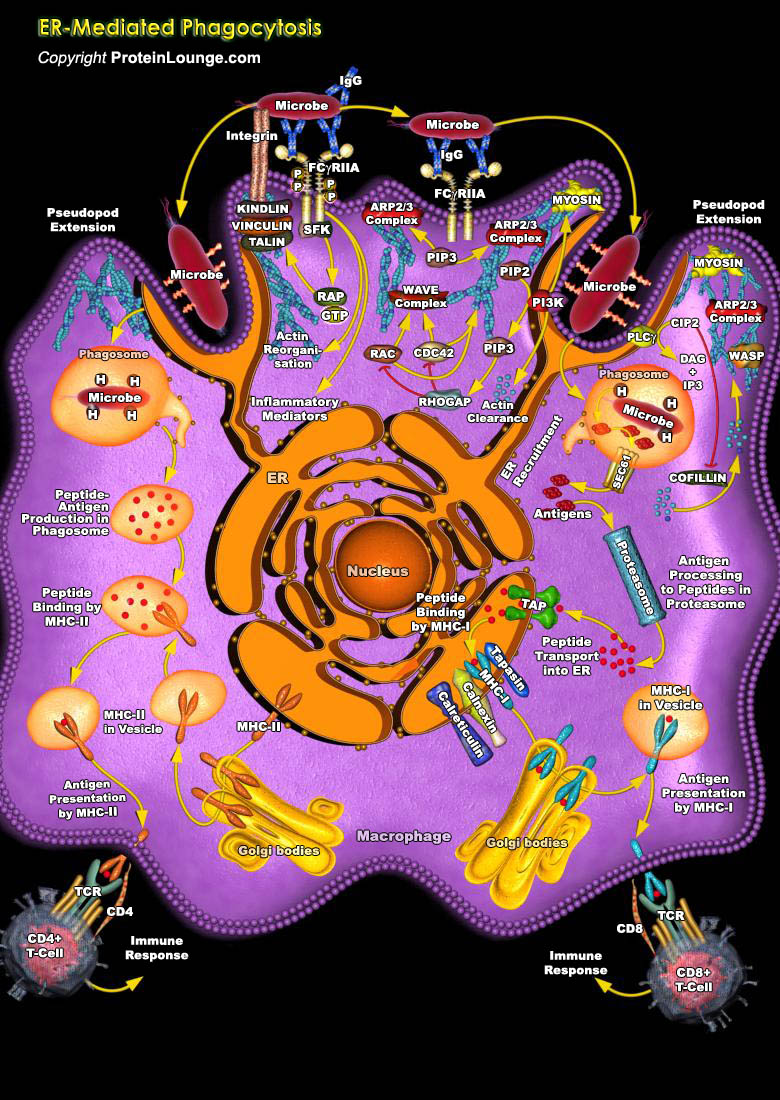
Phagocytosis, defined as the cellular uptake of particulates (>0.5 m) within a plasma-membrane envelope, is closely related to and partly overlaps the endocytosis of soluble ligands by fluid-phase macropinocytic and receptor pathways. The uptake of exogenous particles (heterophagy) has features in common with autophagy, an endogenous process of sequestration and lysosomal disposal of damaged[..]
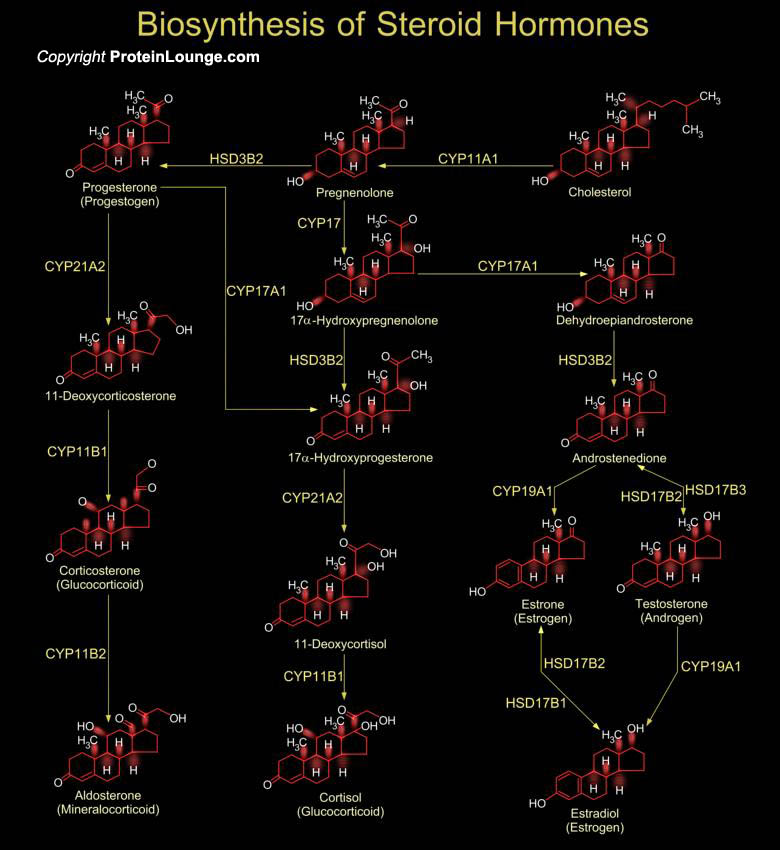
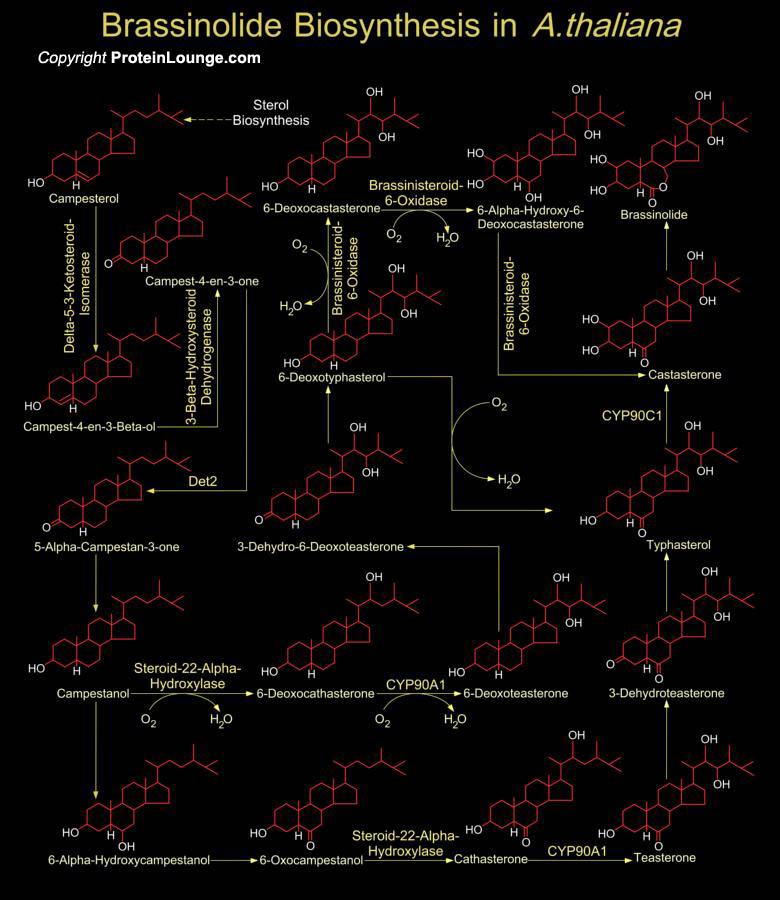
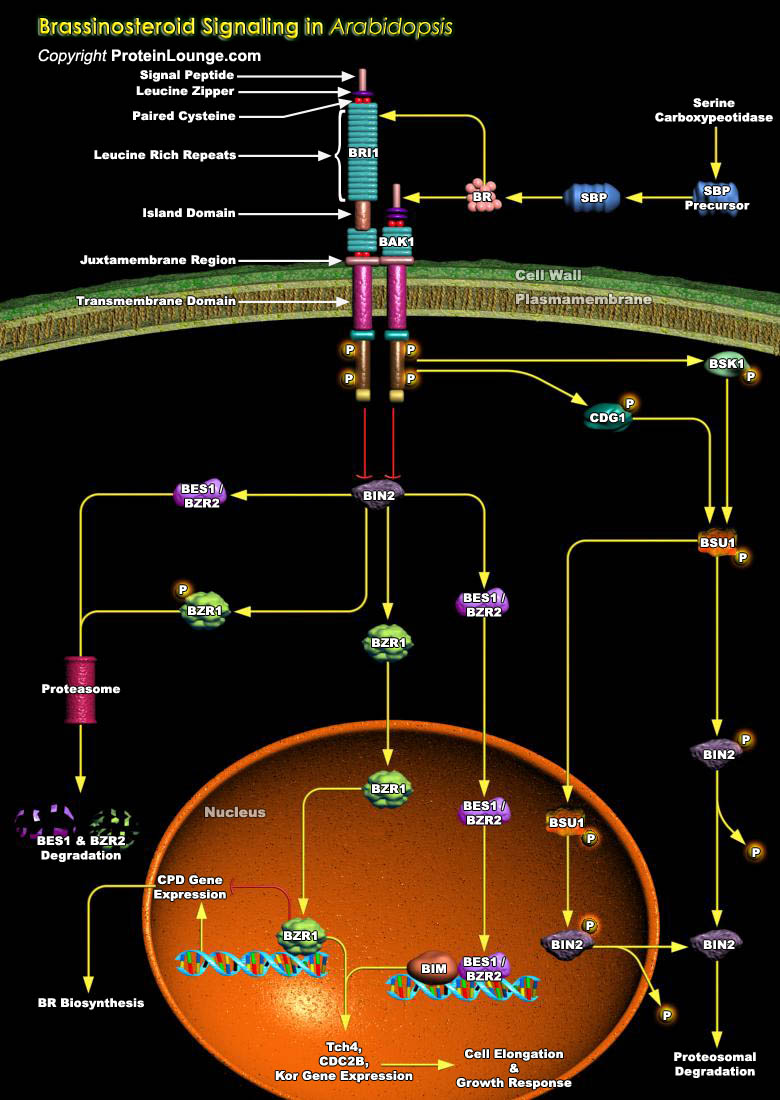
Steroid hormones are crucial substances for the proper functioning of the body. They mediate a wide variety of vital physiological functions ranging from anti-inflammatory agents to regulating events during pregnancy. Typically, endocrinologists classify steroid hormones into five major groups, based primarily on the receptor to which they bind, and the[..]
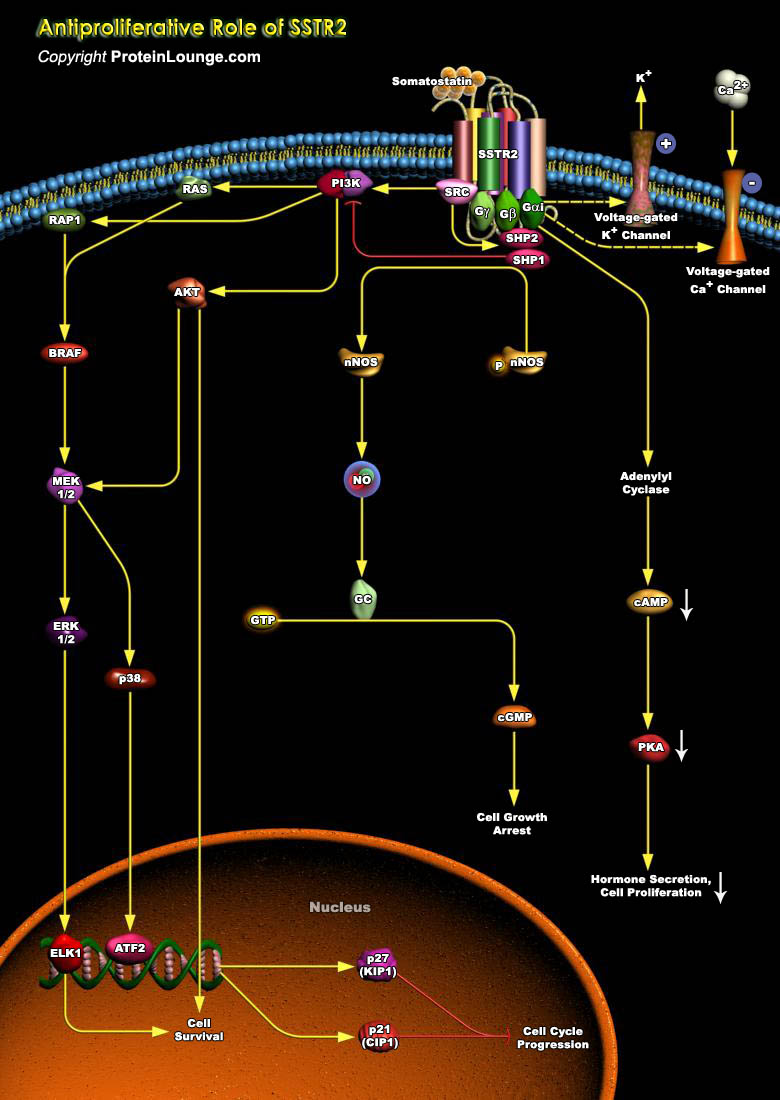
Somatostatin is a widely distributed peptide hormone that plays an important inhibitory role in several biological processes, including neurotransmission, exocrine and endocrine secretions, and cell proliferation (Ref.1). Somatostatin acts via a family of five GPCRs (G-Protein-Coupled Receptors) SSTR1-SSTR5 (Somatostatin Receptors) that are variably expressed throughout numerous tissues ranging[..]
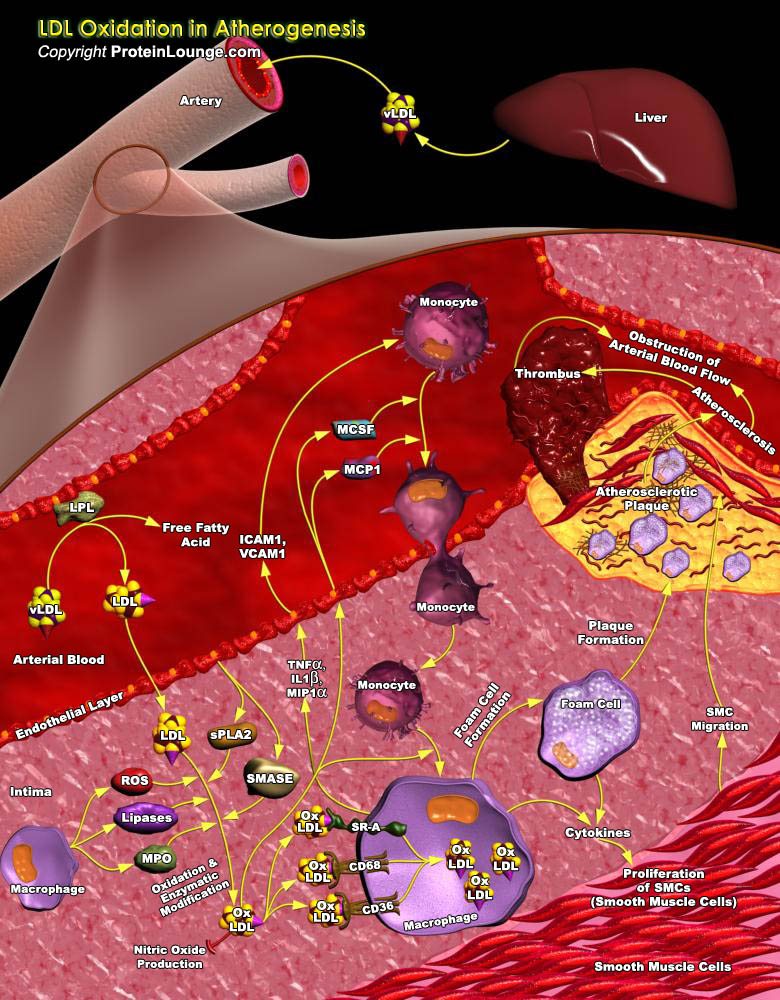
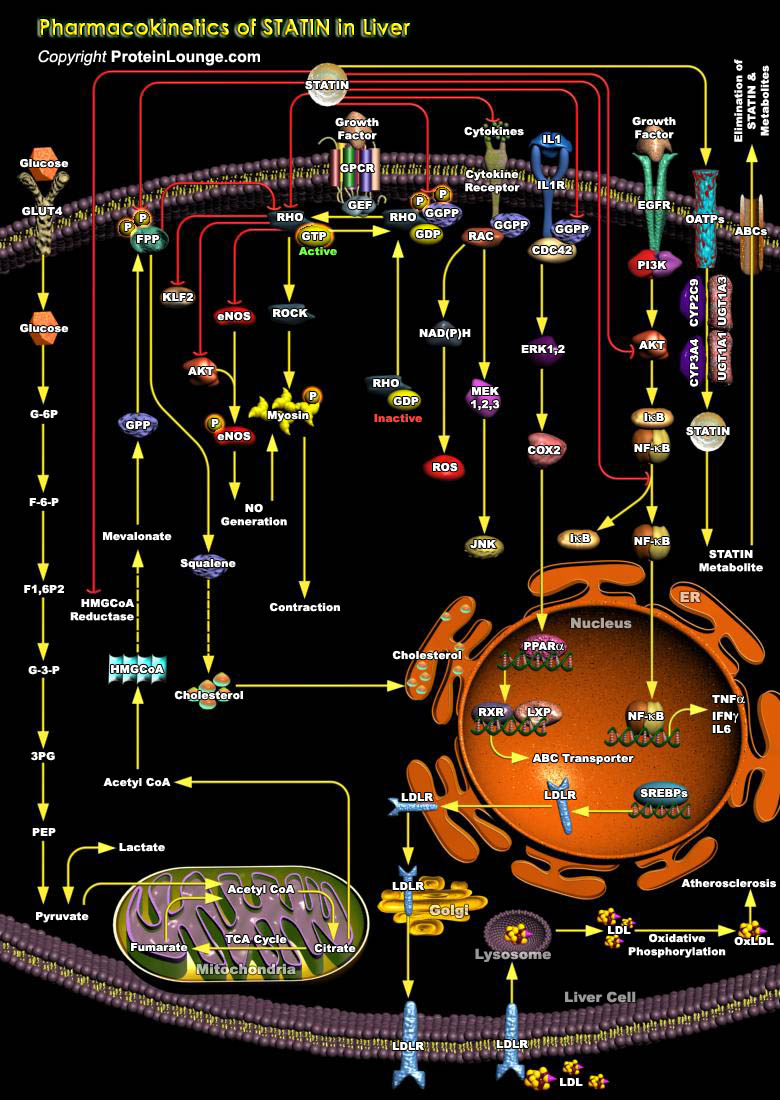
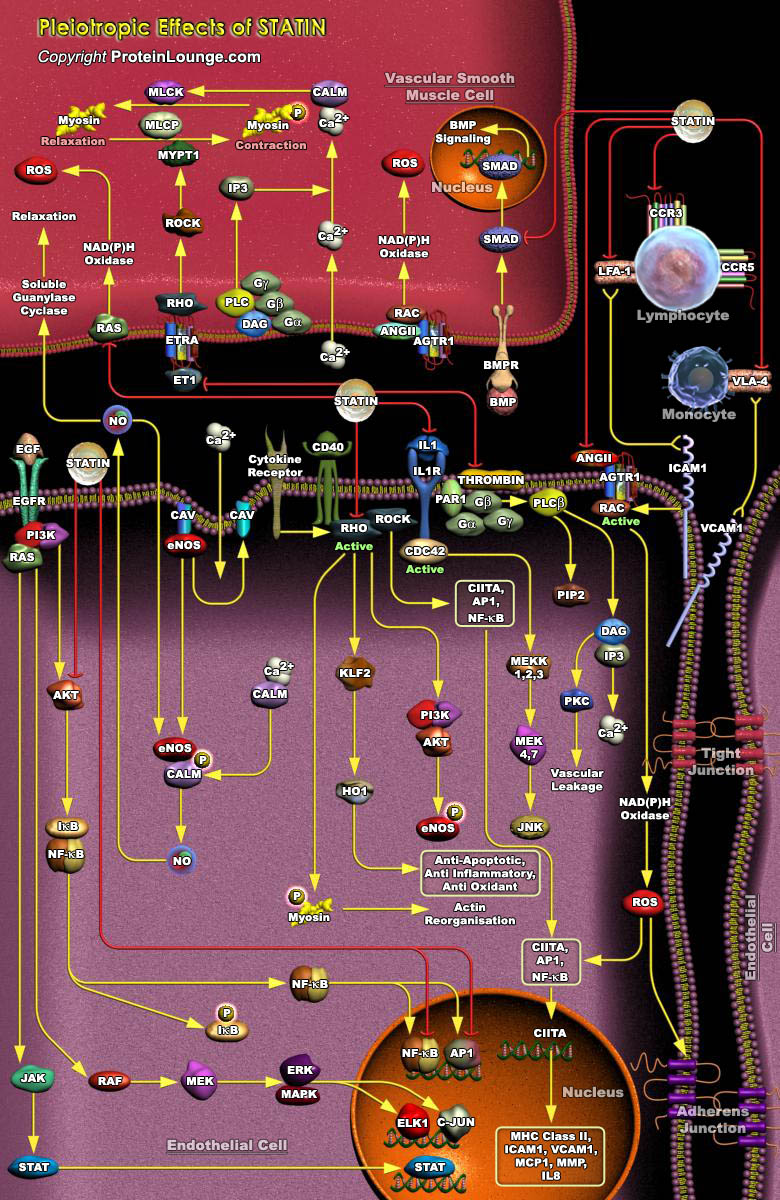
Atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease of the arterial wall, is the major cause of morbidity and mortality from CVD (Cardiovascular Disease) in much of the world’s population. The disease involves the formation of Plaques in arterial walls that narrow the arterial passage, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of occlusion of blood flow by a myocardial infarction.[..]
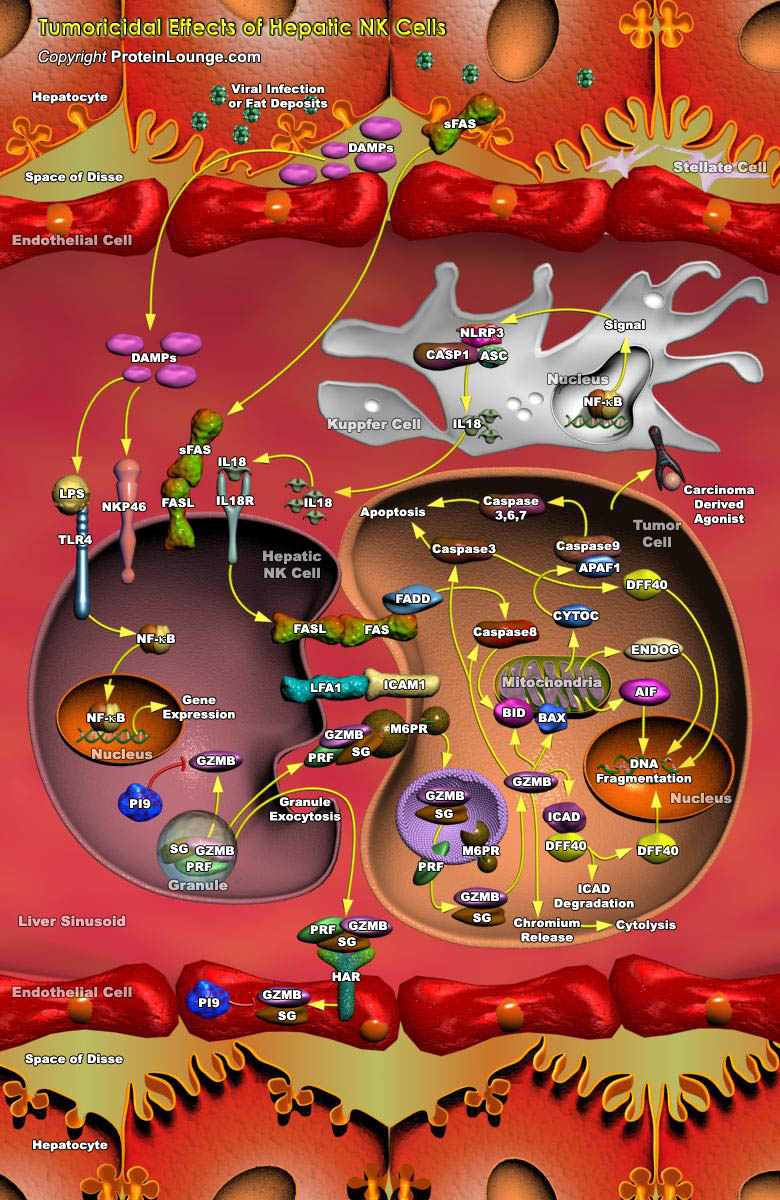
The liver is a major site for the formation and metastasis of Tumors. Malignant Liver Tumors fall into two types: Primary and Metastatic. While Primary Liver tumors such as HCC (Hepatocellular Carcinoma) originate in the liver itself, Metastatic or Secondary Liver Tumors commpnly known as “Liver Metastases” are cancerous tumors that originate at sites remote from the liver and spread to the[..]
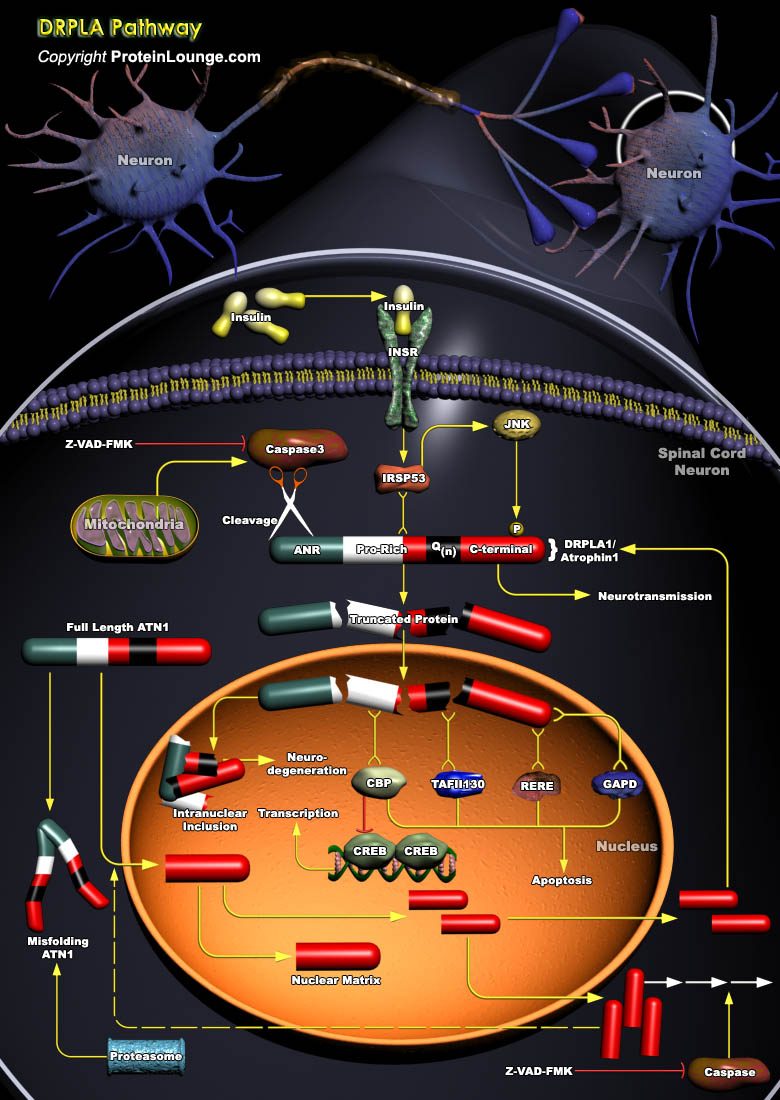
DRPLA (Dentatorubropallidoluysian Atrophy) is a Rare Neurodegenerative Disorder that usually is inherited in an Autosomal Dominant pattern. The Clinical symptoms are variable depending on the age of onset of the disease Myoclonus, Epilepsy, and Mental Retardation are the main symptoms in Juvenile Onset, whereas Cerebellar Ataxia, Choreoathetosis, and Dementia are seen in Adult Onset.[..]
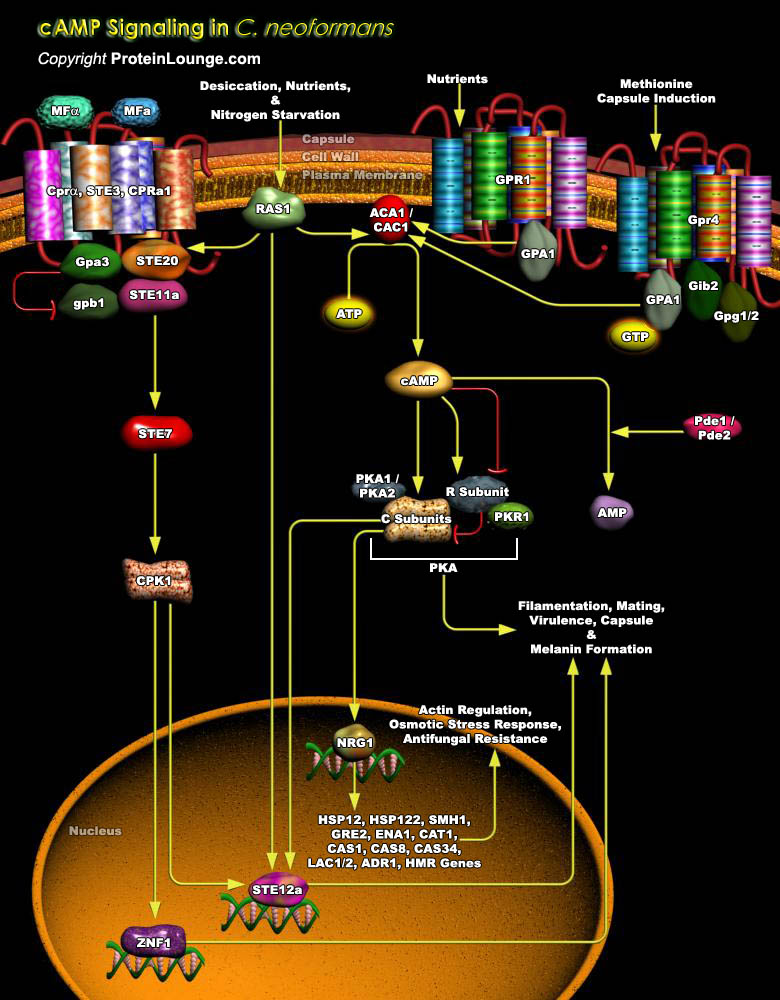
C. neoformans (Cryptococcus neoformans) is an encapsulated yeast-like basidiomycetous fungus and a significant human pathogen responsible for fungal meningoencephalitis in immune-compromised individuals. It has emerged as a model organism to study the molecular mechanisms of fungal pathogenesis (Ref.1). Desiccated yeast cells or basidiophores of C. neoformans[..]
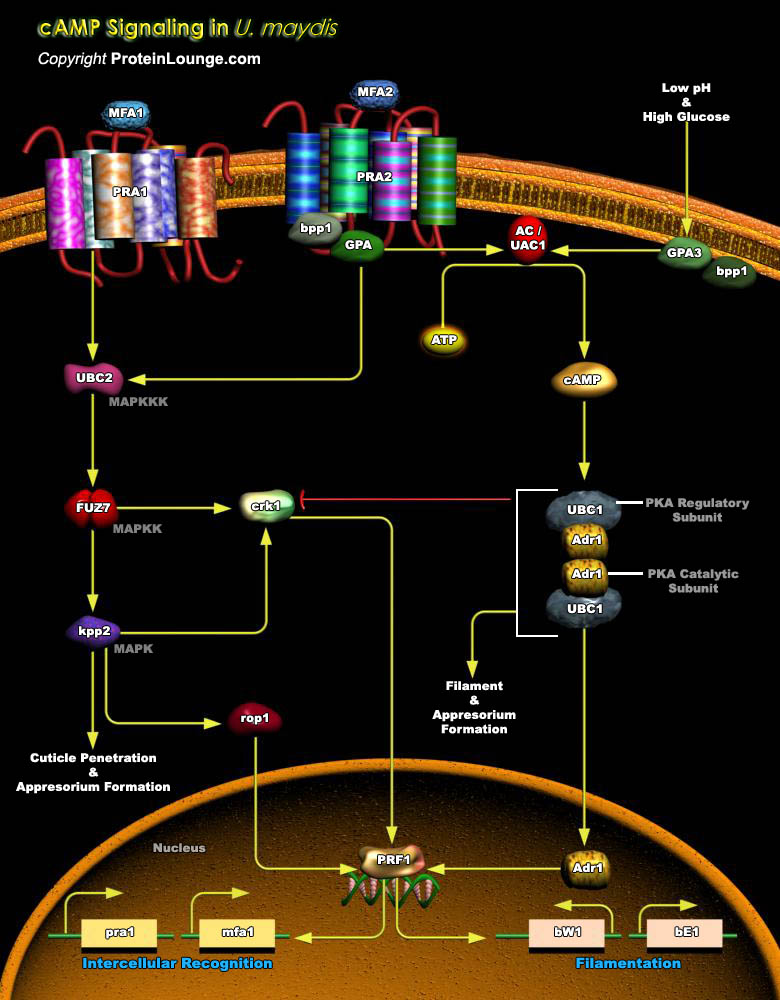
Ustilago maydis (U.maydis) belongs to the phyla Basidiomycetes (smut fungi) that infects maize. Dimorphism is linked to pathogenicity in U.maydis, where the budding haploid cells are saprobic in nature that converts to a dikaryotic filamentous pathogenic form after mating. cAMP signaling pathway regulates the dimorphic transition in U.maydis (Ref.1 and 2).[..]