Featured Pathways
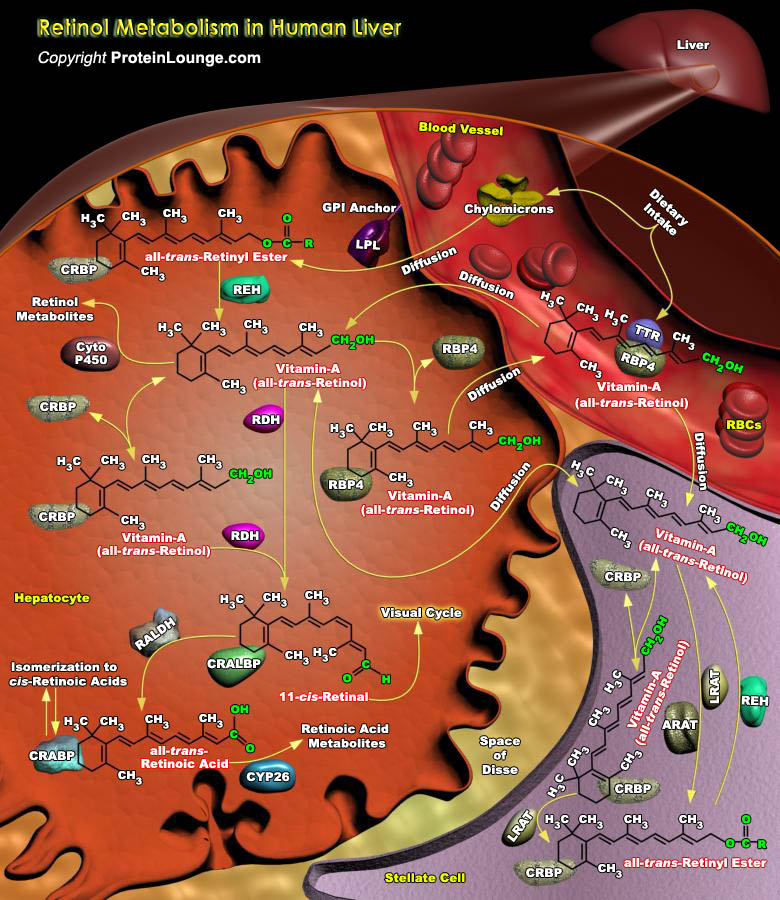
Vitamin-A (all-trans-Retinol), one of the essential micronutrient in the human is obtained chiefly in form of Retinyl Esters from meat, and Carotenoids, such as Beta-Carotene, from plant tissue. Beta-carotene and other Carotenoids are converted by the body into Retinol and are referred to as Provitamin-A Carotenoids. Hundreds of different Carotenoids are synthesized by plants, but only about 10[..]
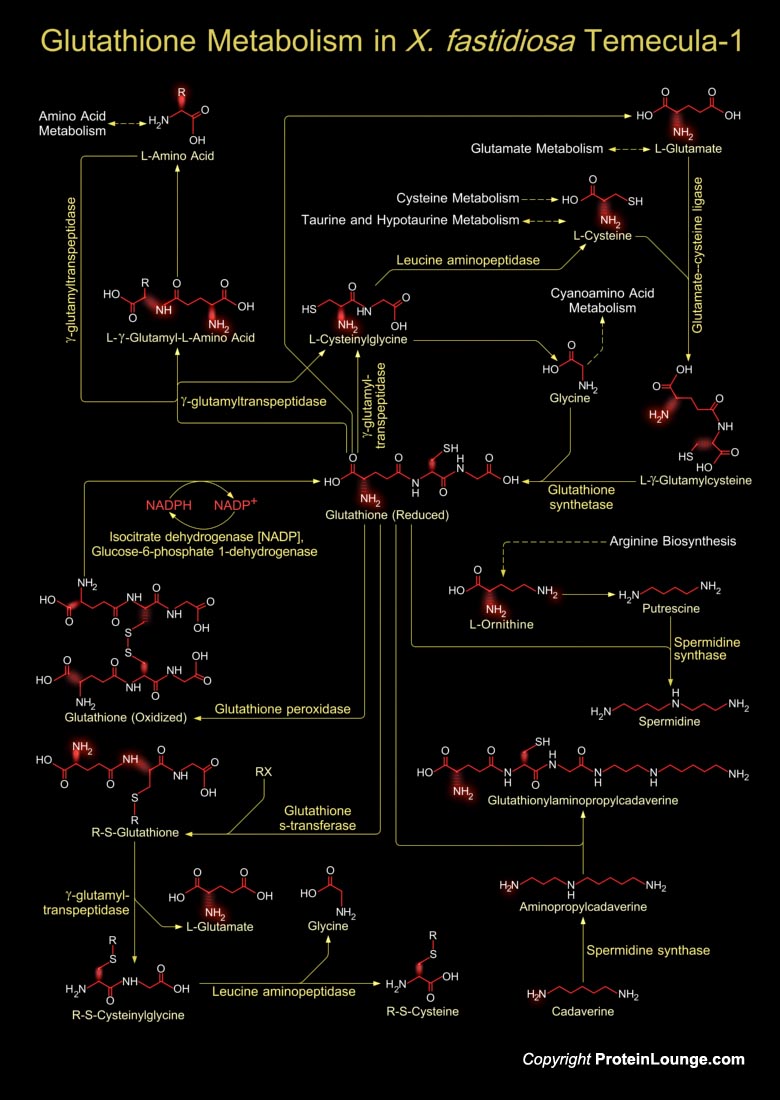
Xylella fastidiosa is a Gram-negative, fastidious, xylem-limited bacterium that causes a range of economically important plant diseases. It causes citrus variegated chlorosis-a serious disease of orange trees. It is responsible for pathogenicity and virulence involving toxins, antibiotics and ion sequestration systems (Ref.1 & 2). X. fastidiosa Temecula-1 is 2.52MB. It is[..]
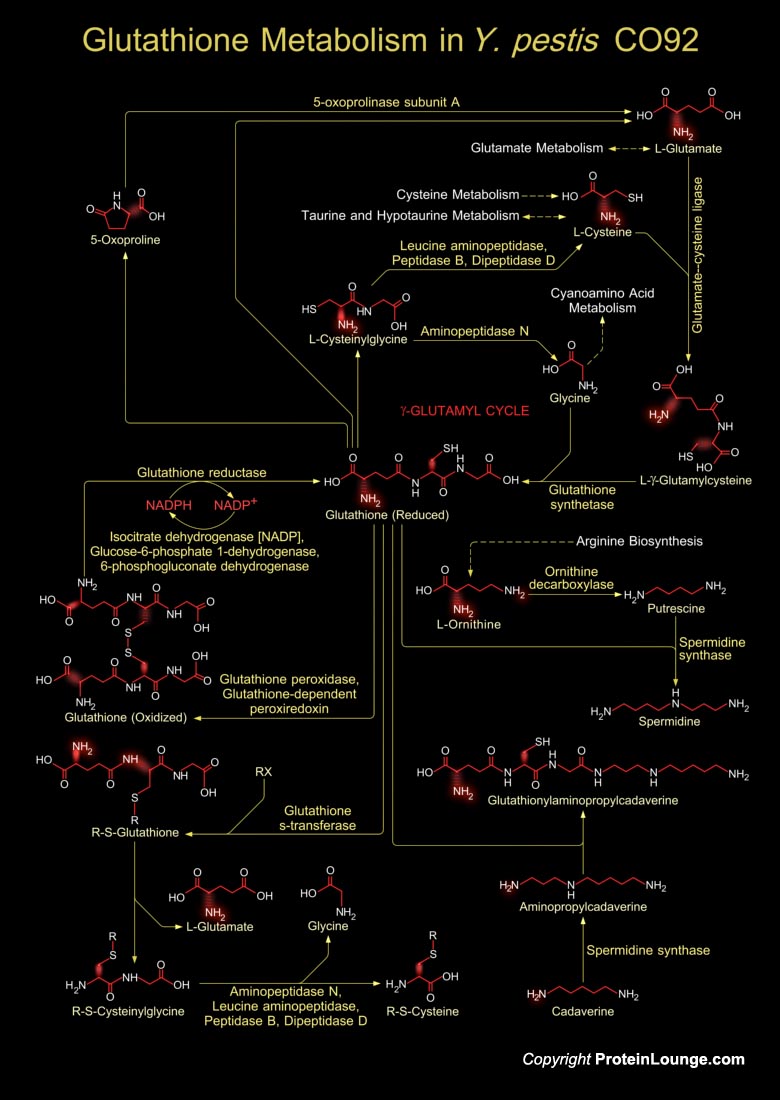
Yersinia sp. is responsible for disease syndromes ranging from gastroenteritis to plague. Y. pestis is categorized into three subtypes or biovars; Antiqua, Mediaevalis, and Orientalis, each associated with a major pandemic. Y. pestis strain CO92 belongs to biovar Orientalis that are responsible for the current pandemic (modern plague). Glutathione is a tripeptide[..]
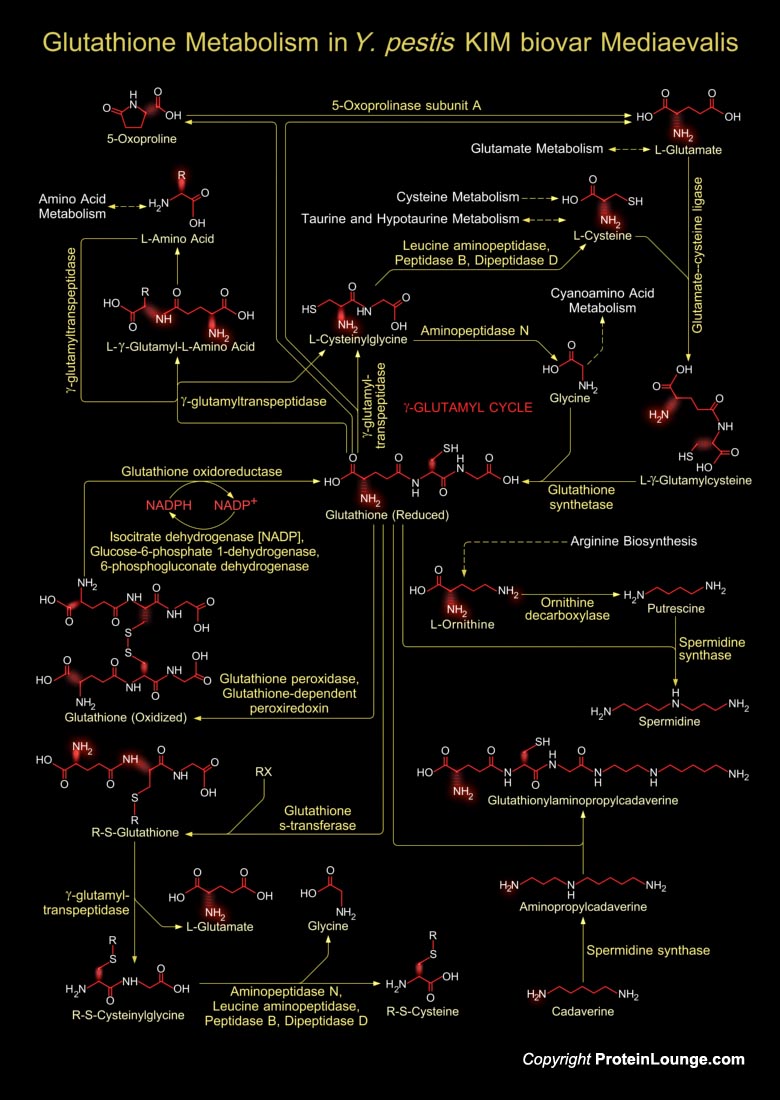
Glutathione is a tripeptide present in Yersinia sp., which is composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine, and has numerous important functions within cells. Yersinia sp. is responsible for disease syndromes ranging from gastroenteritis to plague. Y. pestis is categorized into three subtypes or biovars; Antiqua, Medievalis, and Orientalis, each associated with a major pandemic. The strain Y.[..]
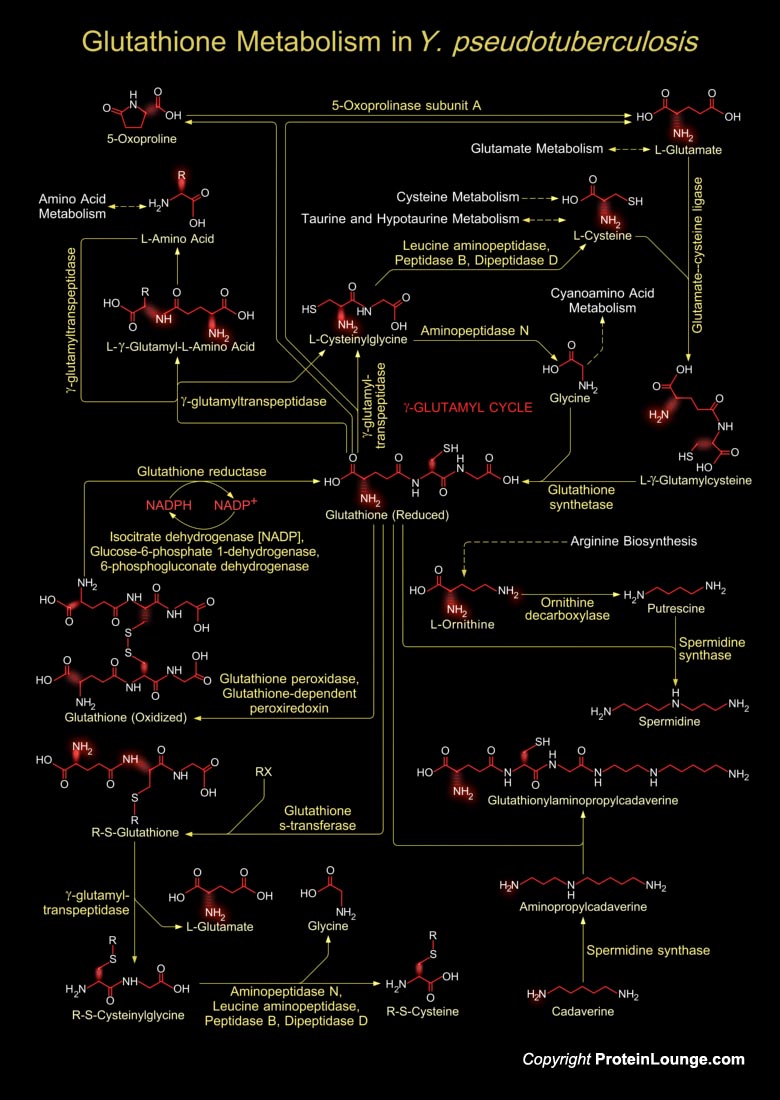
Yersinia sp. is responsible for disease syndromes ranging from gastroenteritis to plague. Y. pestis is categorized into three subtypes or biovars; Antiqua, Mediaevalis, and Orientalis, each associated with a major pandemic. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is the least common of the three main Yersinia species to cause infections in humans. It is primarily a zoonotic infection with variable hosts,[..]
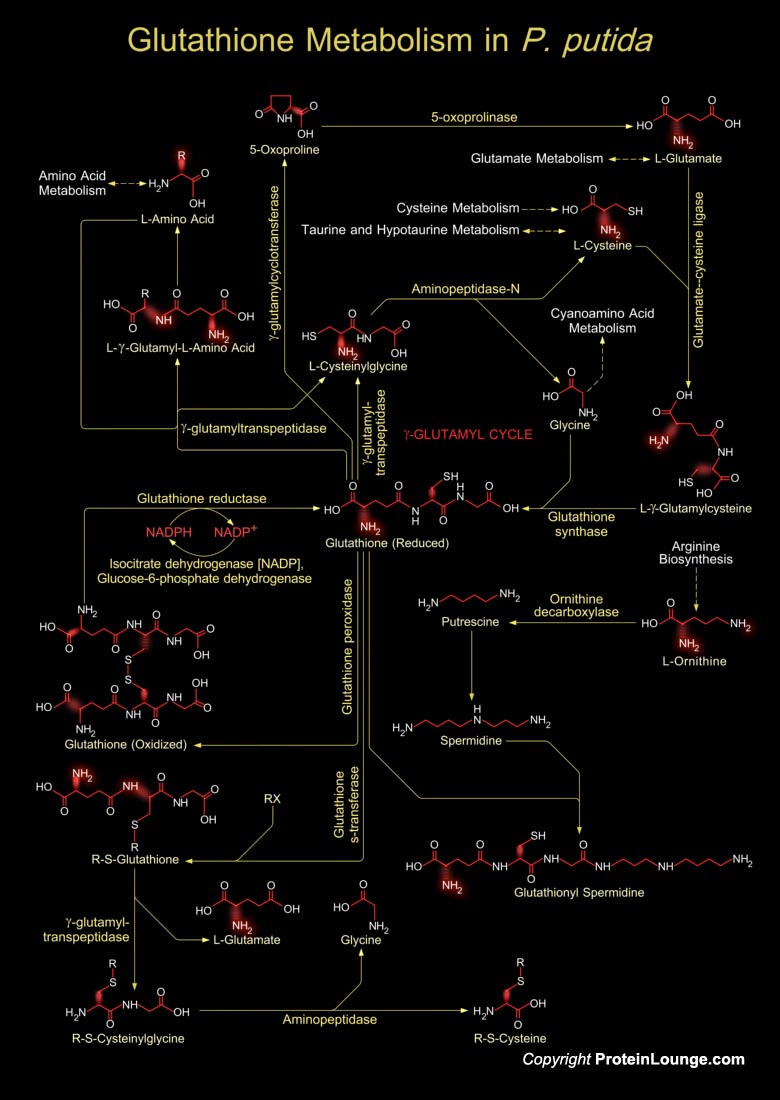
Pseudomonas putida is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, saprotrophic soil bacterium (Ref.1). It has been reported as opportunistic human pathogens capable of causing nosocomial infections. P. putida exhibits an amazing ability to metabolize a wide range of biogenic and xenobiotic compounds (Ref.2). As a frequent inhabitant of sites polluted with toxic chemicals,[..]
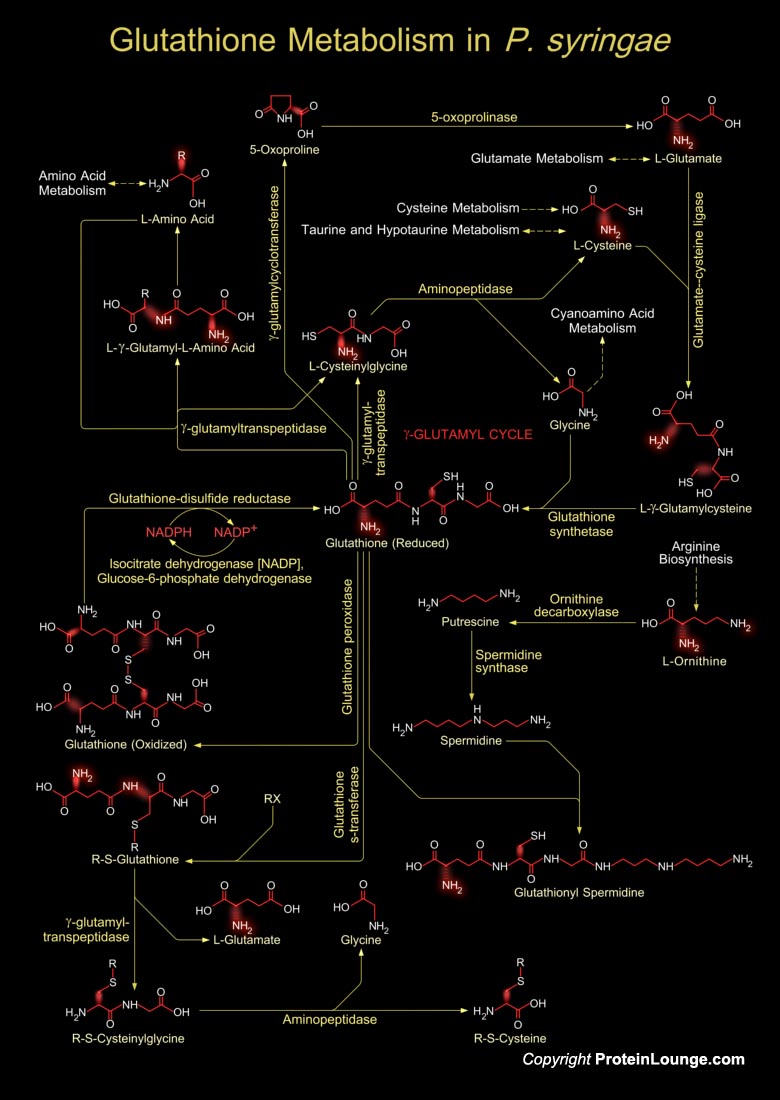
Pseudomonas syringae is one of the best studied plant pathogen with more than 50 pathovars. Each pathovar is known to infect a characteristic group of host plant species (Ref.1). P. syringae is a Gram-negative bacterium and its different strains are known for their diverse interactions with plants. Among these strains, P. syringae pv. tabaci is a non-host pathogen of[..]
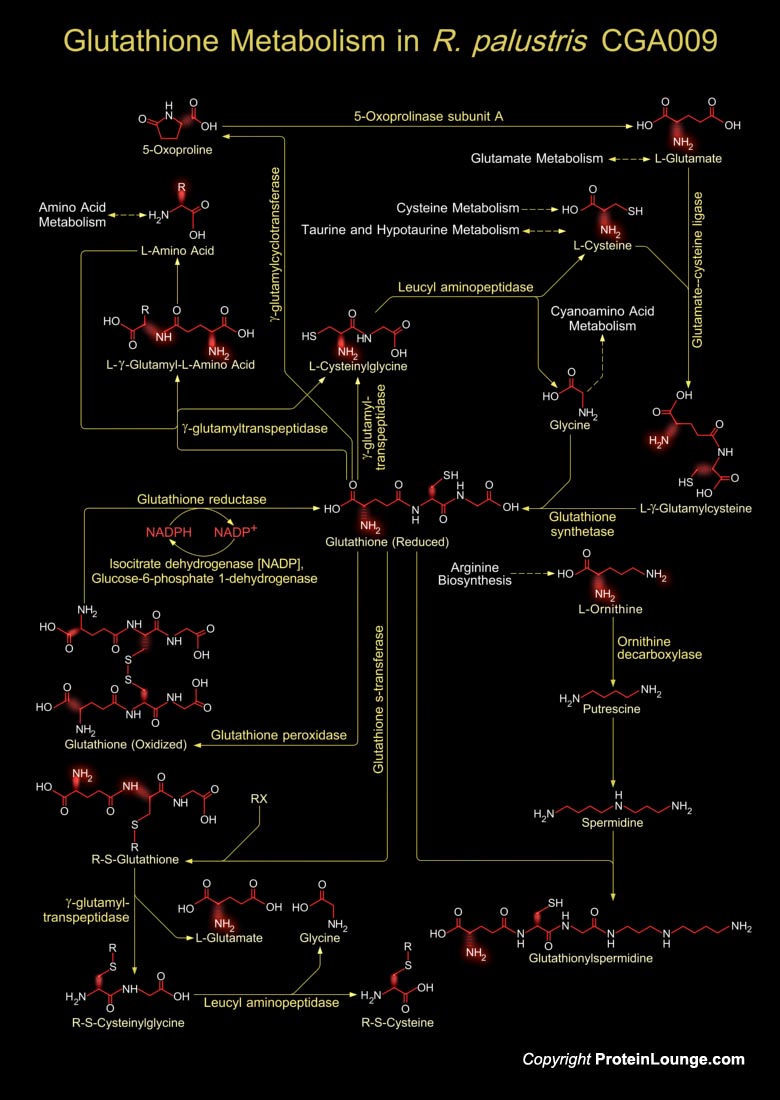
Rhodopseudomonas palustris is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative purple nonsulfur bacterium. It is an alphaproteobacterium that serves as a model organism for studies of photophosphorylation, regulation of nitrogen fixation, production of hydrogen as a biofuel, and anaerobic degradation of aromatic compounds. This bacterium is able to transition between anaerobic photoautotrophic growth, anaerobic[..]
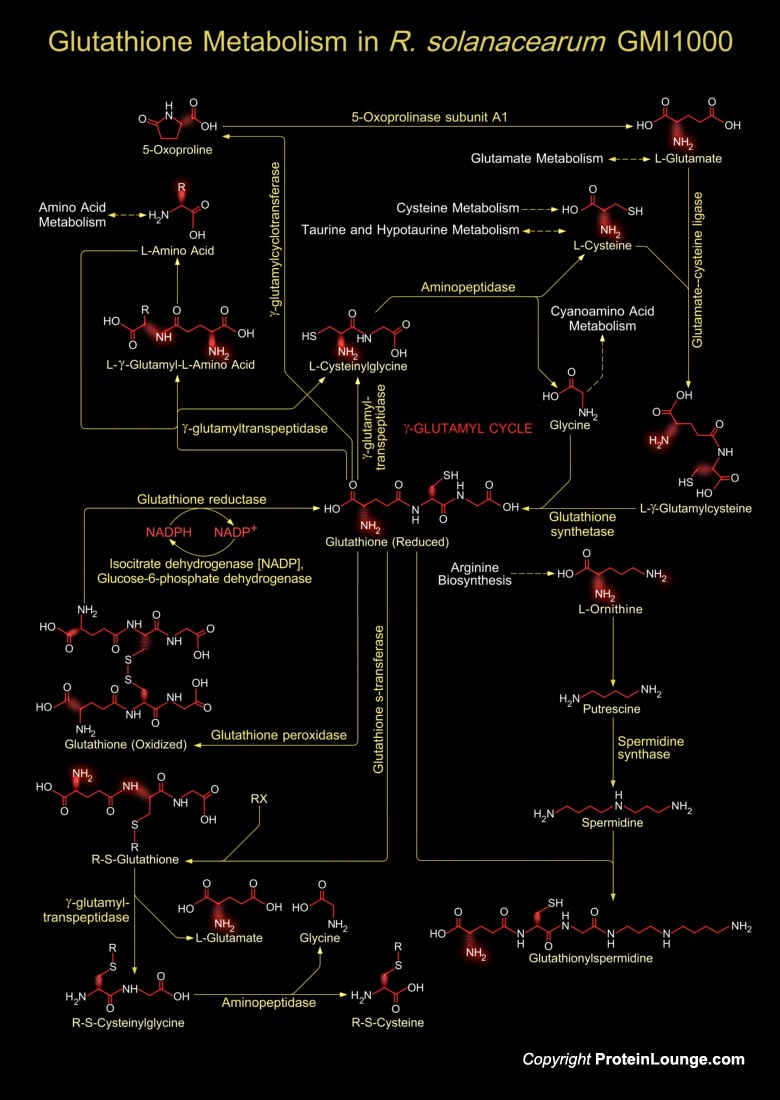
Ralstonia solanacearum is a Gram negative β-proteobacteria. It is an aerobic non-spore-forming, Gram-negative, plant pathogen. R. solanacearum is soil-borne and motile with a polar flagellar tuft. It colonises the xylem, causing bacterial wilt in a very wide range of potential host plants (Ref.1). Although R. solanacearum is considered a plant[..]
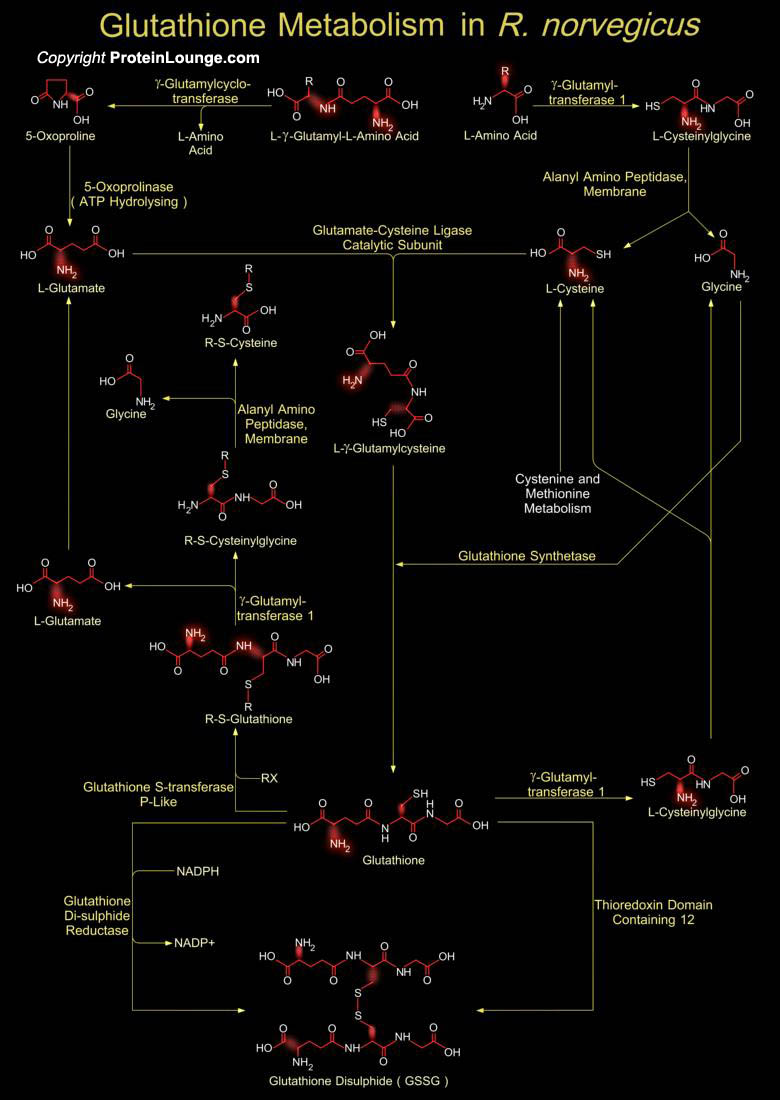
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. The tripeptide Glutathione is part of[..]
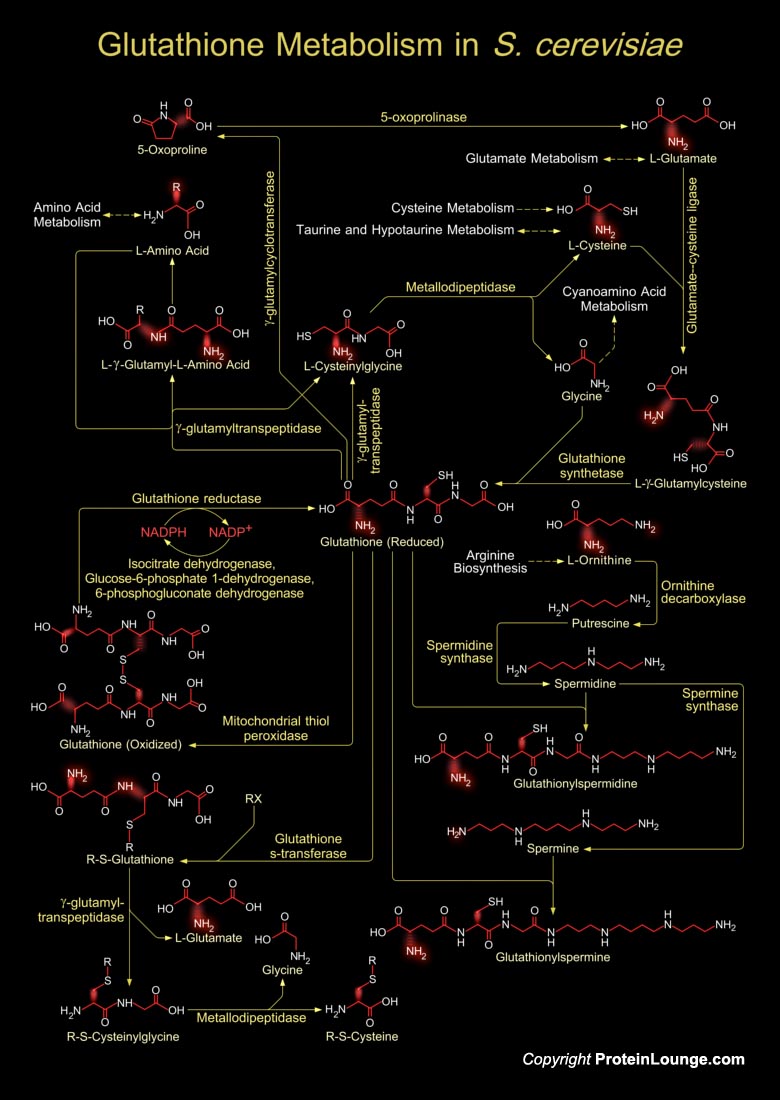
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) is a unicellular fungus, possessing a nuclear genomic DNA of 12068 kilobases (kb) organized in 16 chromosomes. Its genome has been completely sequenced by Goffeau et al. 1996 and was found to contain approximately 6000 genes, of which, 5570 are predicted to be protein-encoding genes. S. cerevisiae has been an essential component of[..]
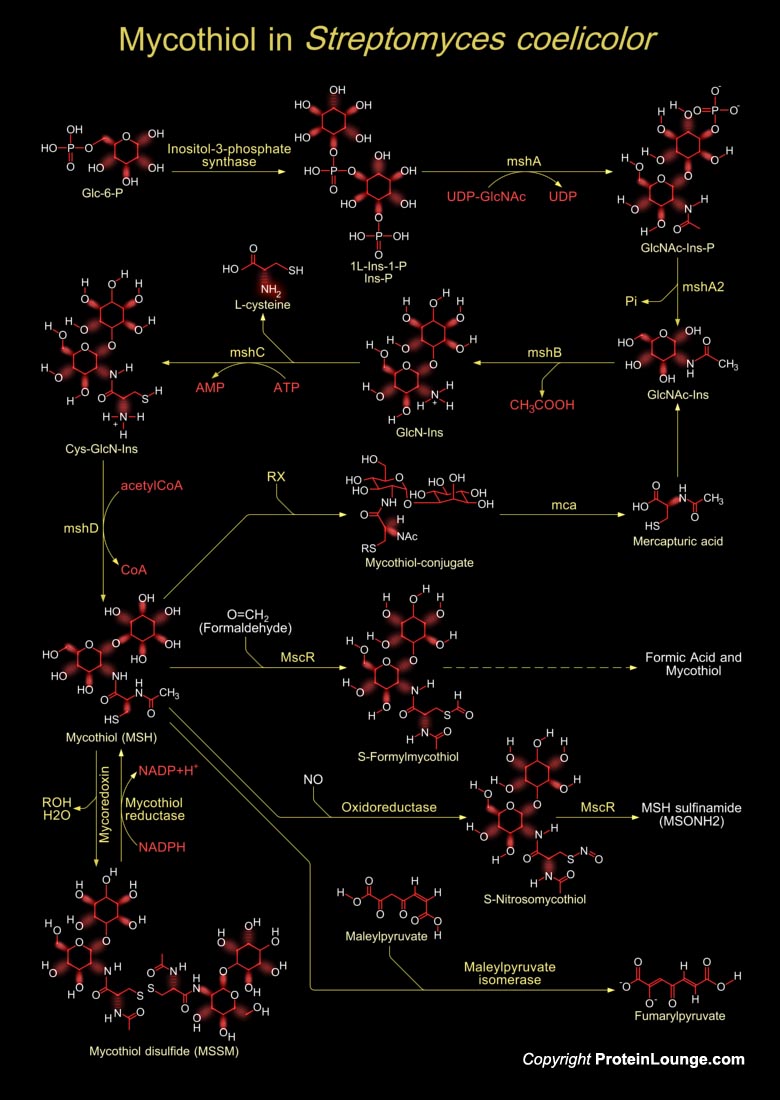
Streptomycetes are soil dwelling, Gram-positive, GC-rich bacteria belonging to the class Actinobacteria. They have a unique capacity to produce novel bioactive compounds and are the most known to produce metabolites like antibiotics, immunosuppressants, antivirals and herbicides. Filamentous Streptomyces bacteria produce bioactive secondary metabolites that account for more than half of all[..]