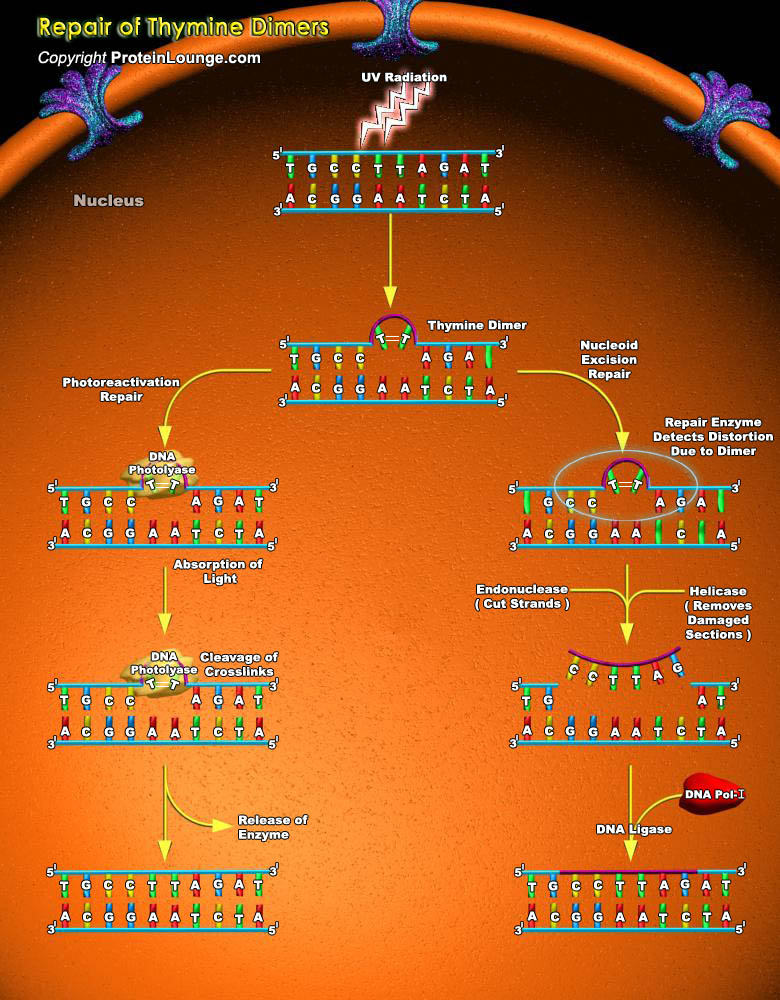
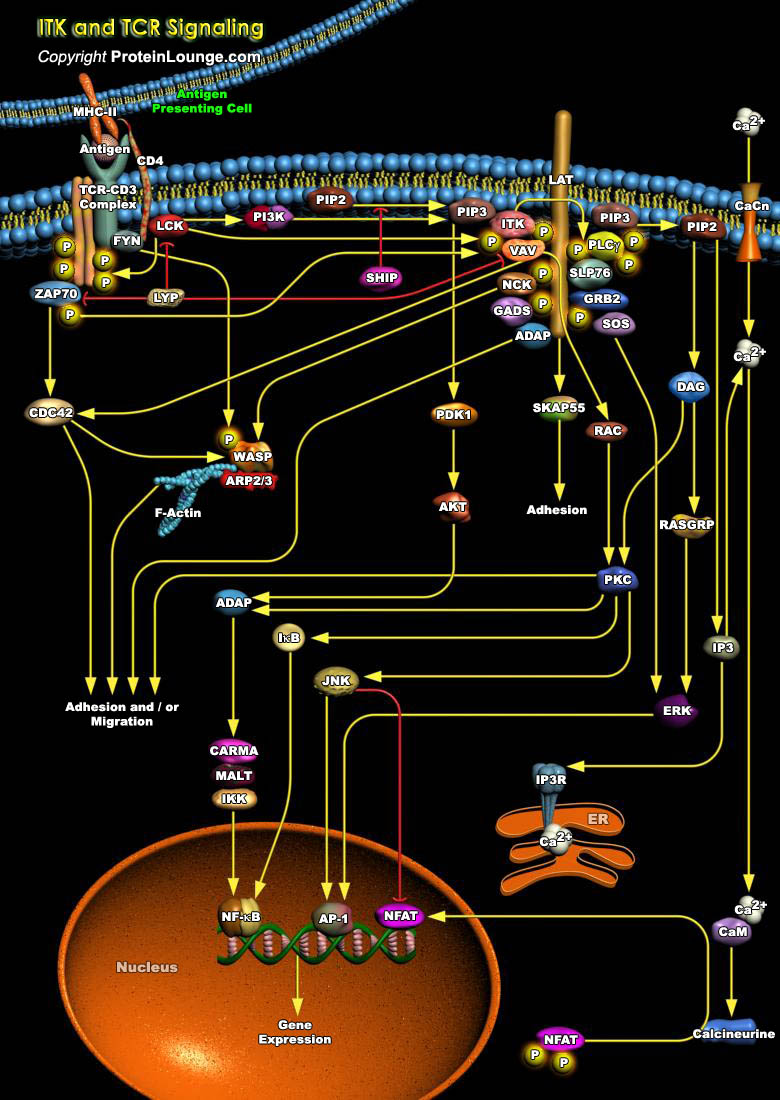
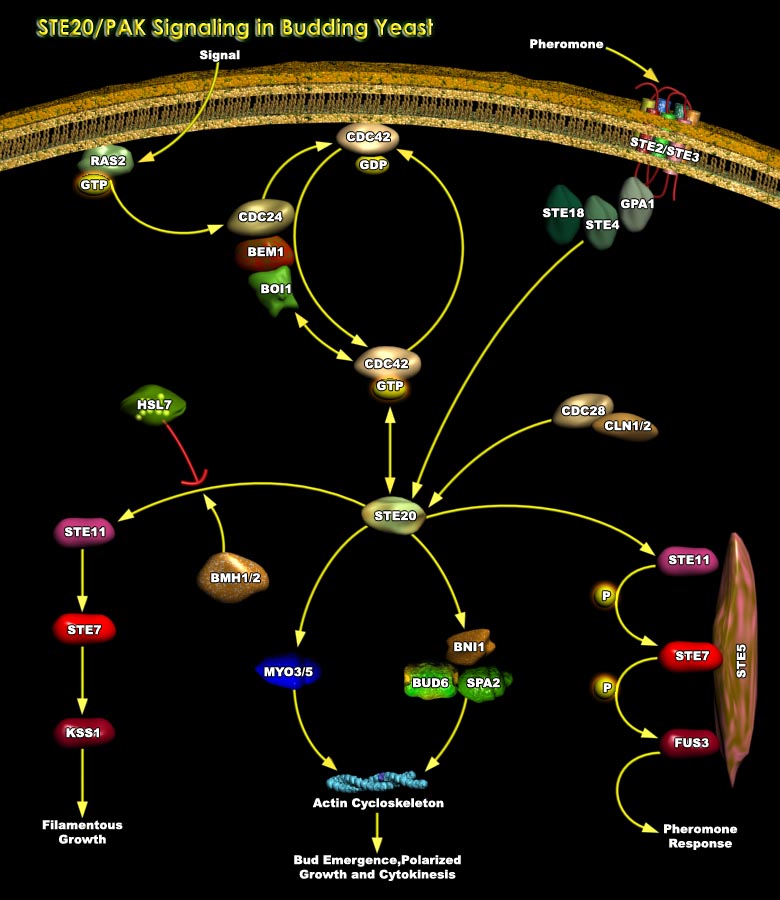
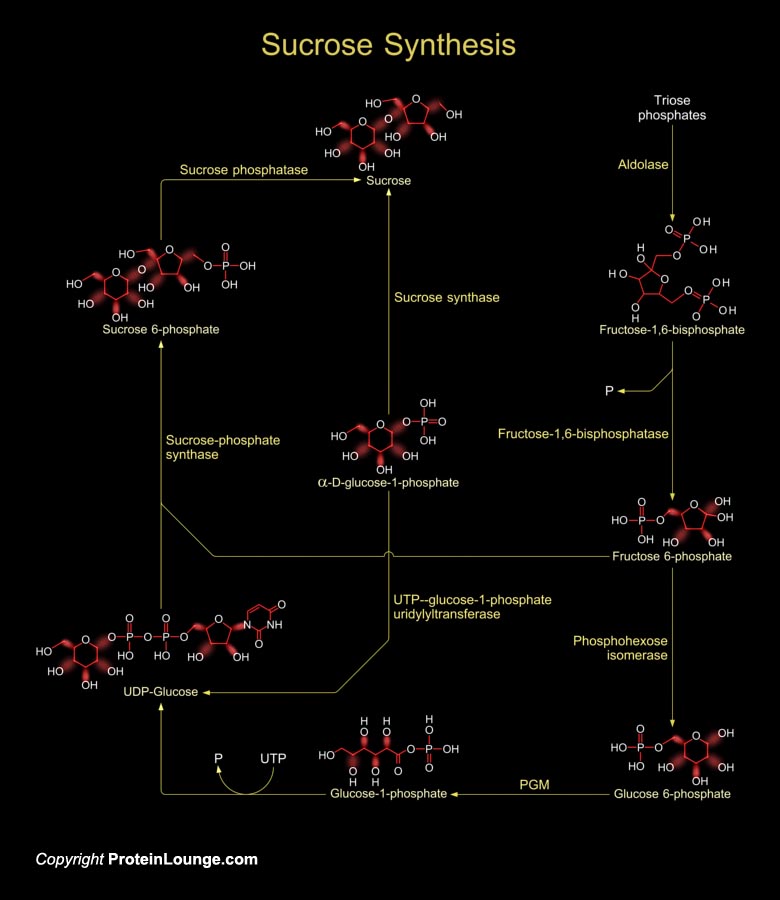
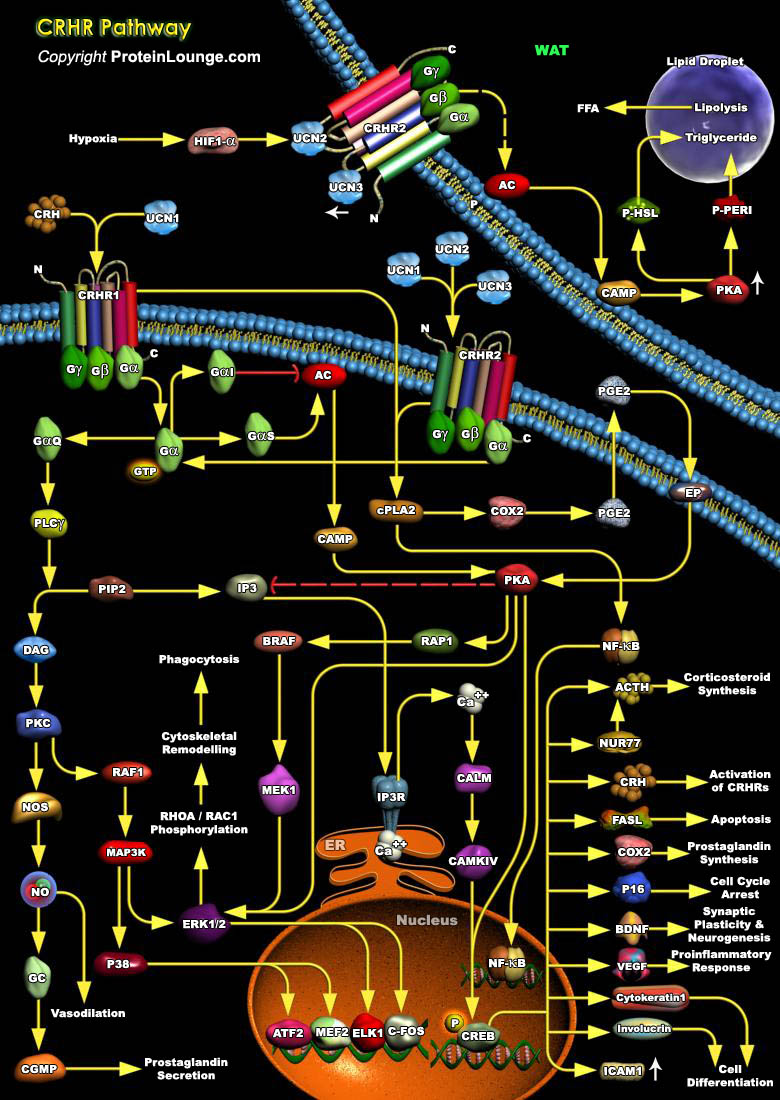
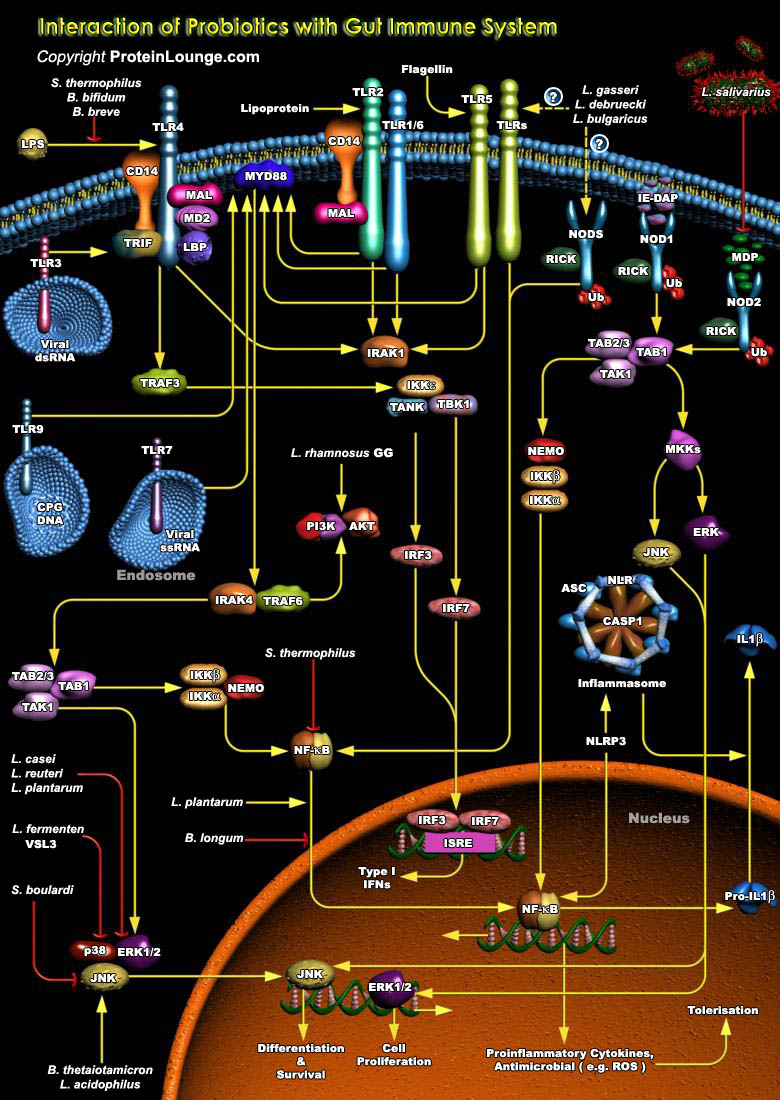
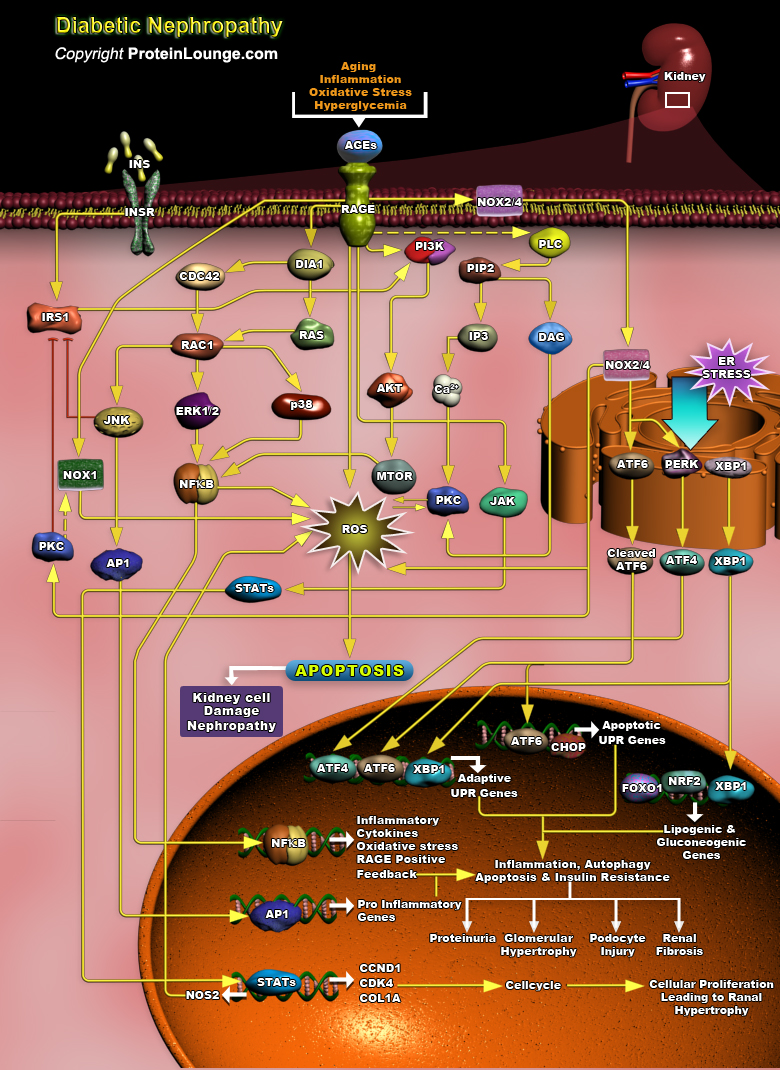
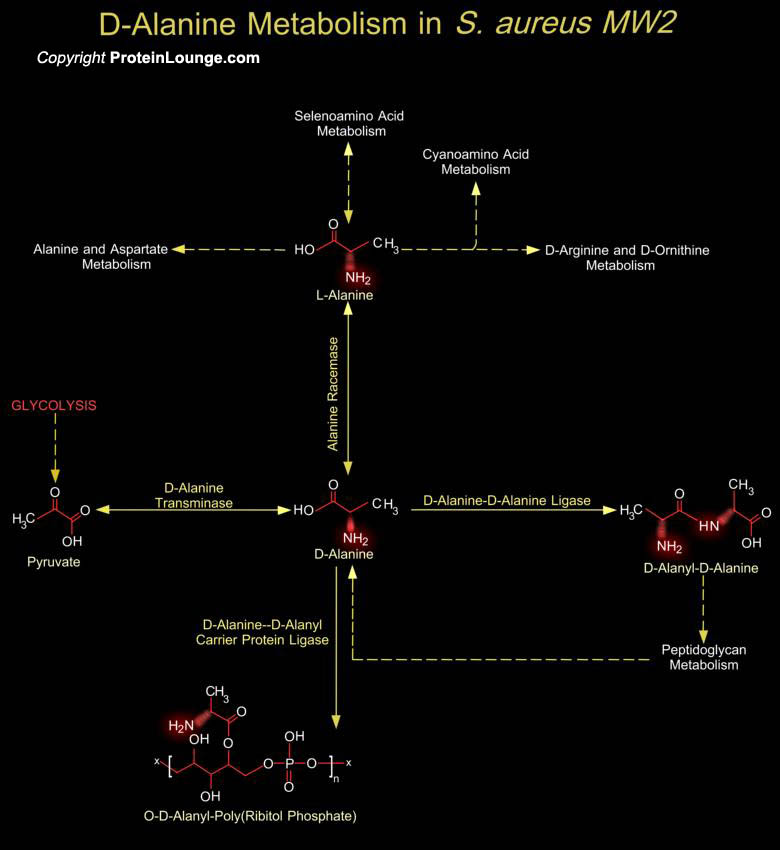
Featured Pathways
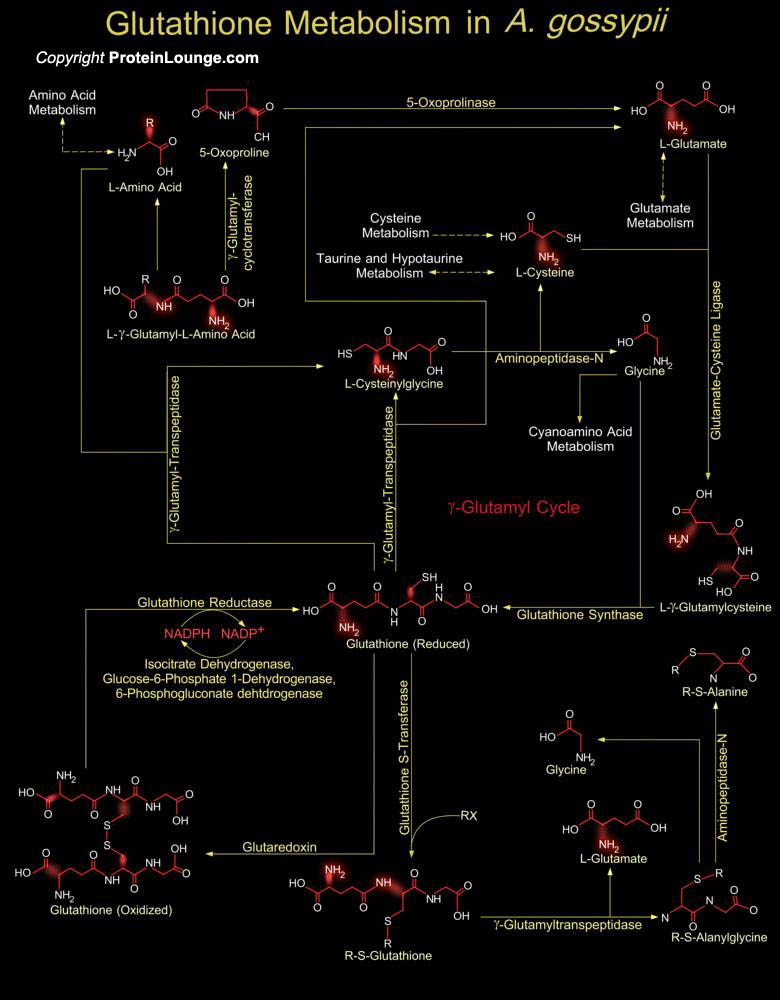
Eremothecium gossypii (also known as Ashbya gossypii) is a filamentous fungus or mold closely related to yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae. It was originally isolated from cotton as a pathogen causing stigmatomycosis and relies on heteropterous insects for its dispersal of spores or mycelia fragments. A. gossypii is also recognized for its ability to[..]
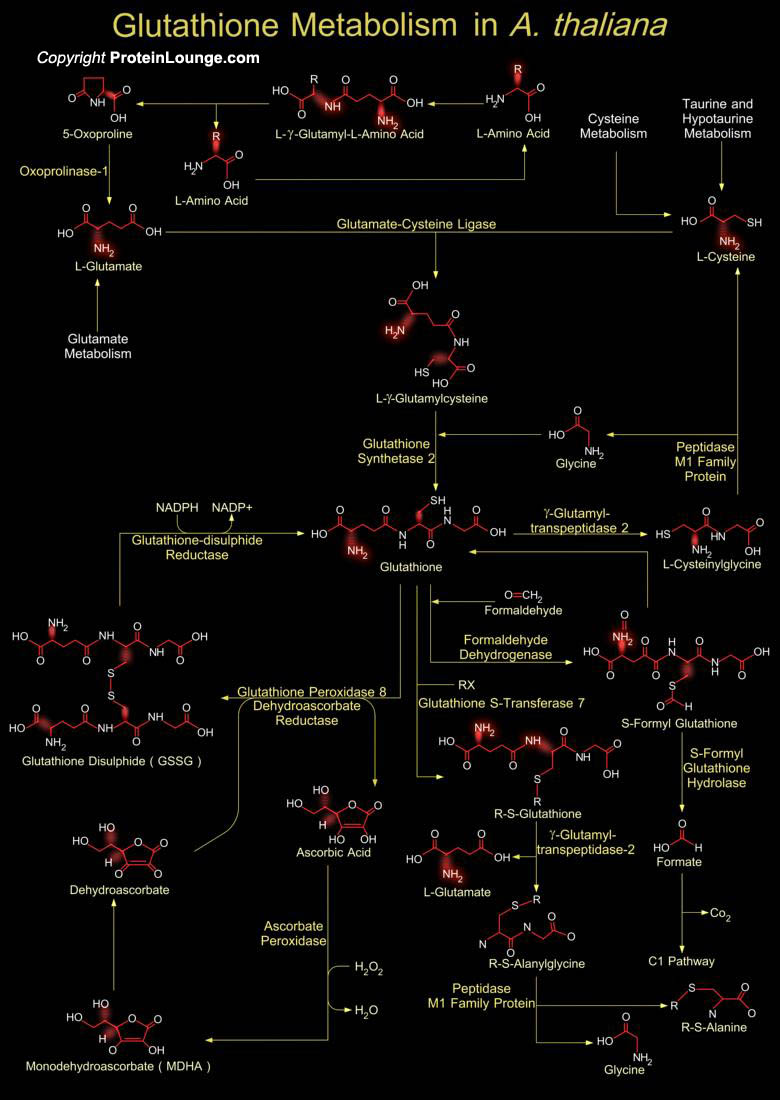
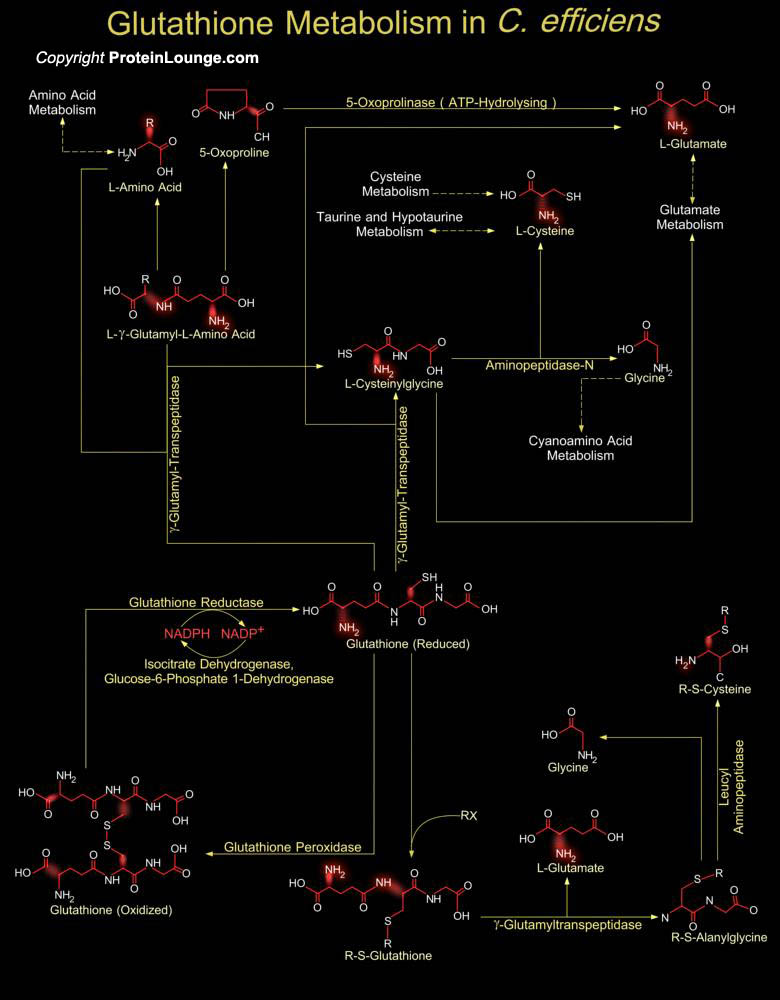
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. Glutathione is[..]
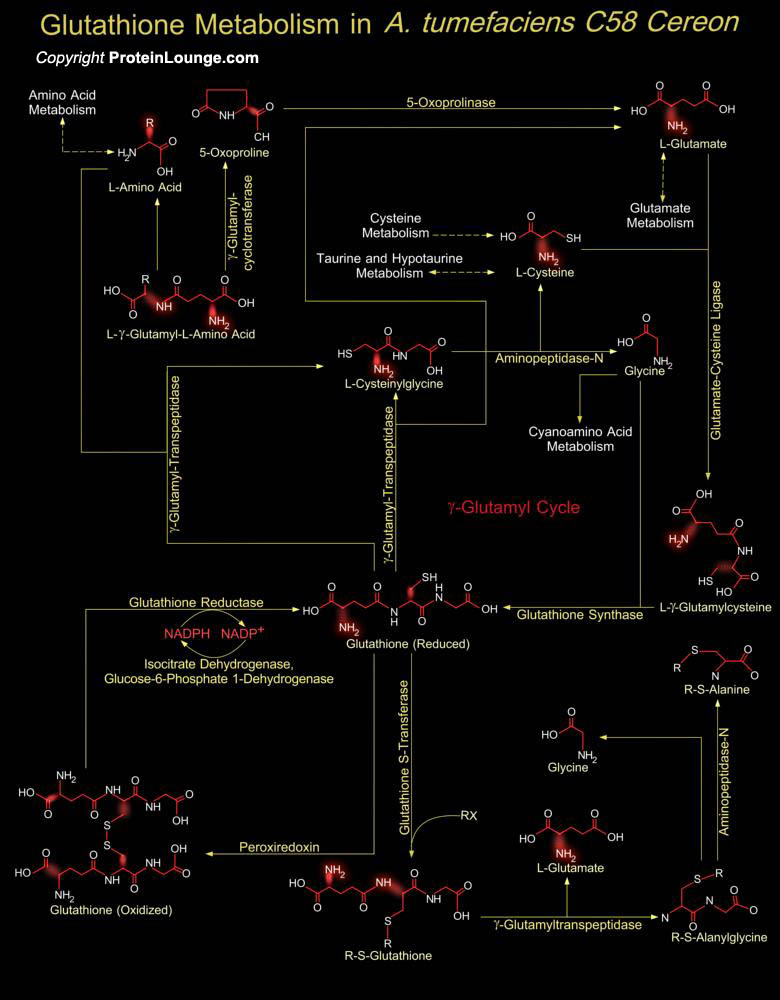
Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 Cereon is a Gram-negative, non-sporing, motile, rod-shaped bacterium. It is a plant pathogen capable of transferring a defined segment of DNA to a host plant replacing the transferred tumor-inducing genes with exogenous DNA generating a gall tumor. A. tumefaciens strain C58 has an unusual structure consisting of one circular and one linear[..]
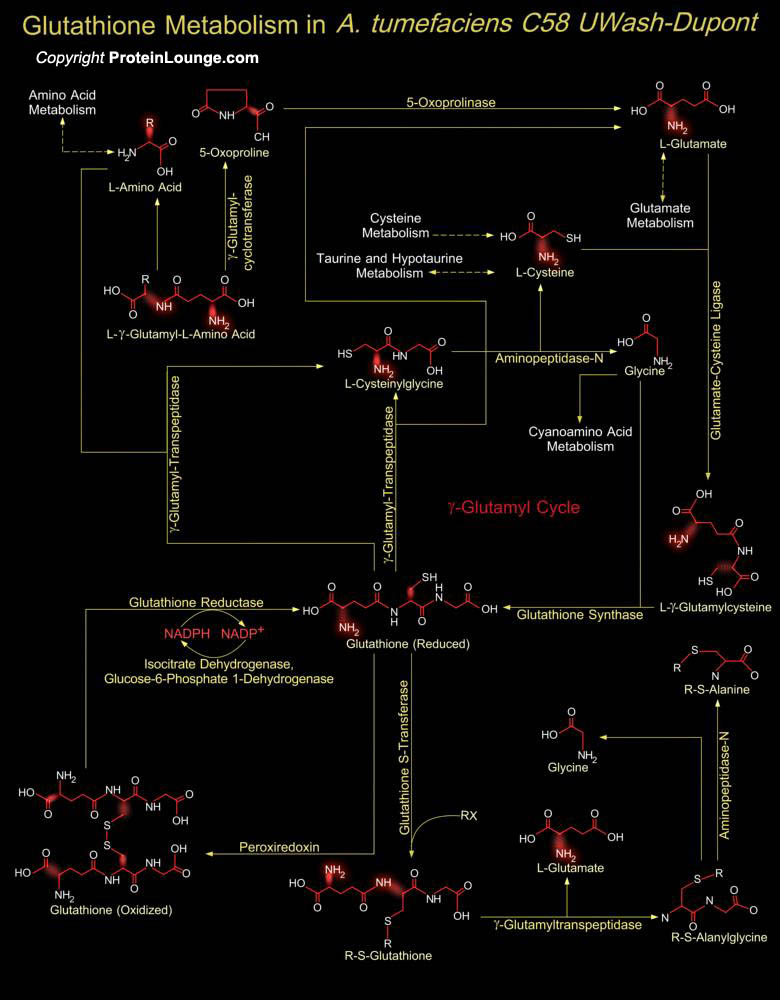
Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 (UWash/Dupont) is a Gram-negative, non-sporing, motile, rod-shaped bacterium. It is a plant pathogen capable of transferring a defined segment of DNA to a host plant replacing the transferred tumor-inducing genes with exogenous DNA generating a gall tumor. A. tumefaciens strain C58 has an unusual structure consisting of one circular and one[..]
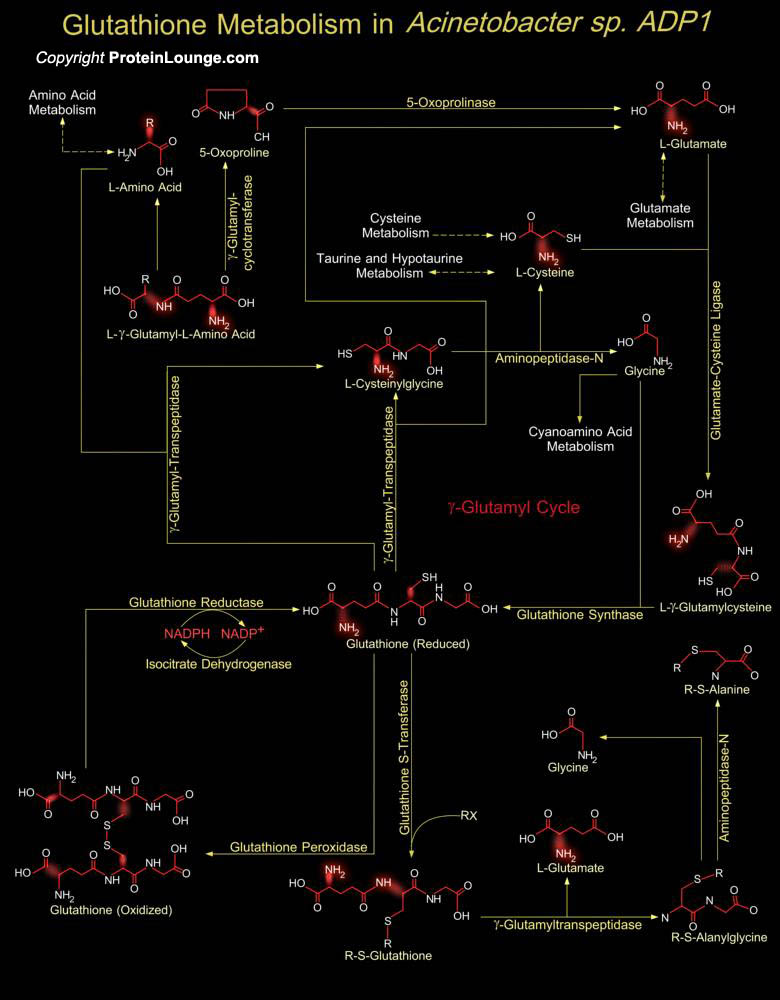
Gram-negative bacteria of the genus Acinetobacter are classified in the gamma subdivision of the Gram-negative proteobacteria and more precisely on the Moraxellaceae branch. Isolates of Acinetobacter are characterized as strictly aerobic non-motile heterotrophic mesophiles, capable of utilising a great variety of substrates as carbon sources, from alkanes to organic acids, especially aromatic[..]
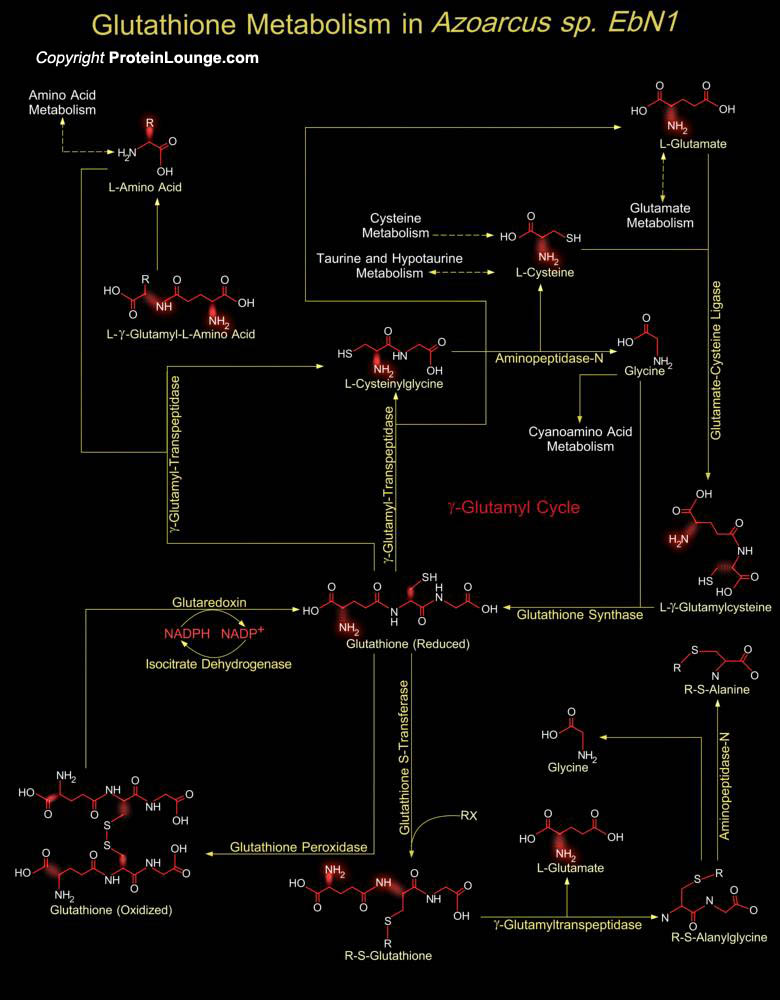
Aromatoleum aromaticum (strain EbN1) now known as Azoarcus sp. (strain EbN1) is a proteobacteria with one chromosome and two plasmids, encoding for 10 anaerobic and 4 aerobic aromatic degradation pathways. It is associated with microbial degradation of aromatic and other refractory compounds, including hydrocarbons in anoxic waters and soils. Strain EbN1 is an aromatic-degrading[..]
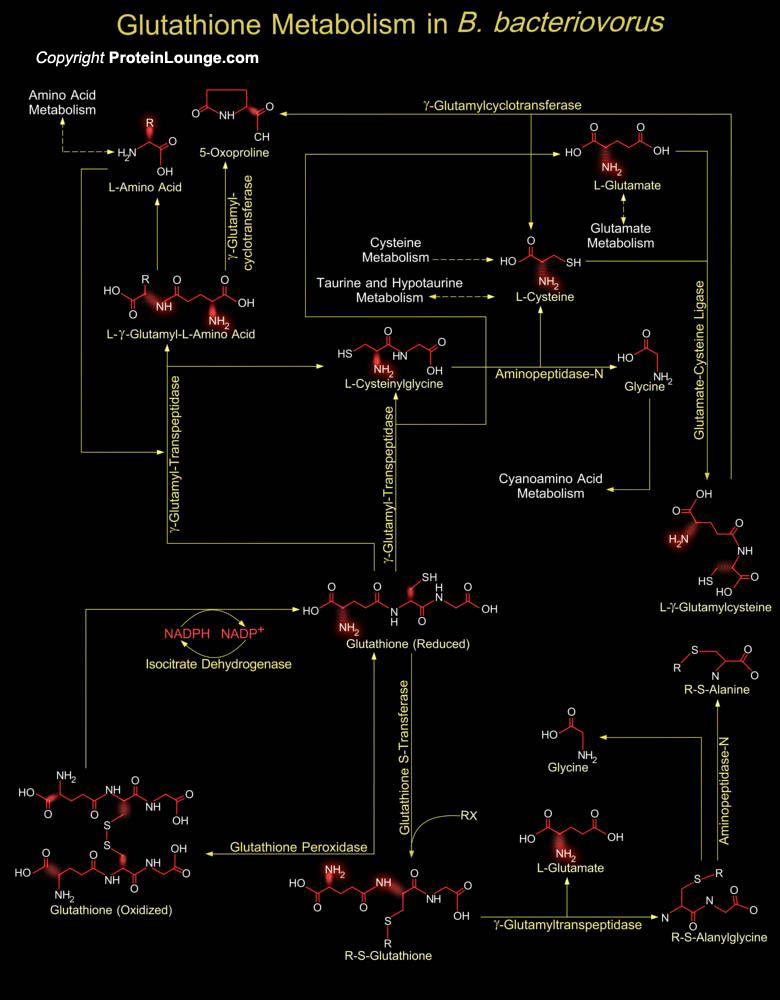
Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus is a tiny and highly motile Delta-Proteobacterium that preys on other Gram-negative bacteria. B. bacteriovorus attaches itself to the cell wall of its prey and invades the cell where it goes through a full-life cycle. After it reproduces, the offspring burst out of the cell. Despite its small size, it has a relatively large genome encoding more than[..]
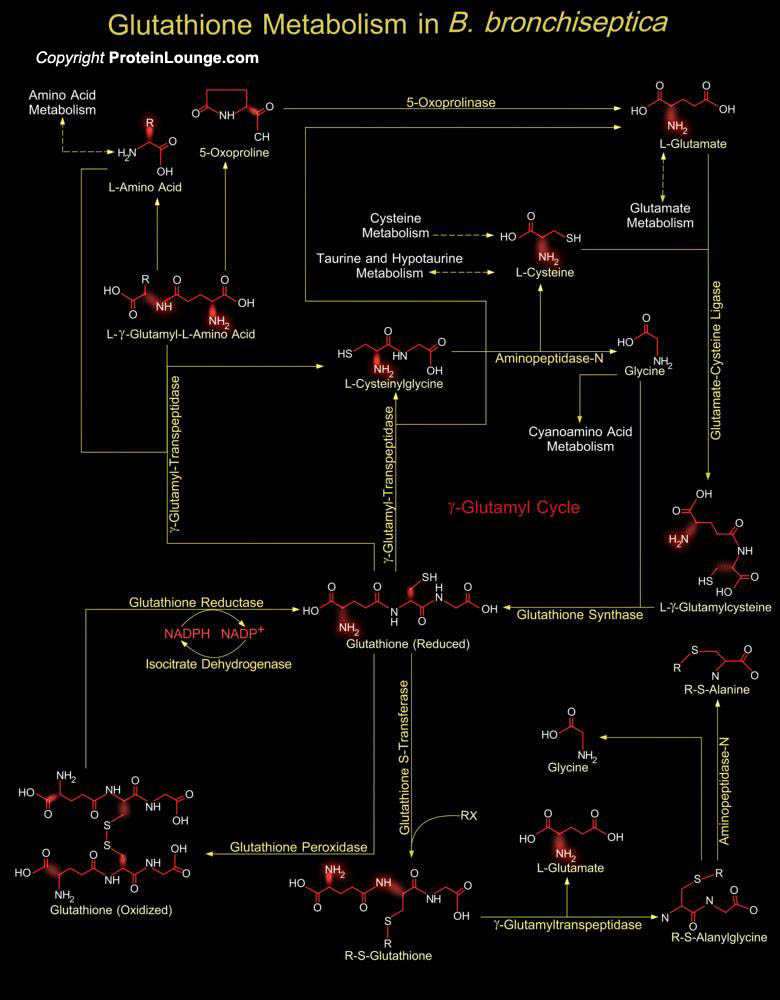
Bordetella bronchiseptica, Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis and are closely related Gram-negative Beta-proteobacteria that colonize the respiratory tracts of mammals. B. bronchiseptica causes chronic respiratory infections in a wide range of animals. B. bronchiseptica is encountered as a commensal or colonizer of the respiratory[..]
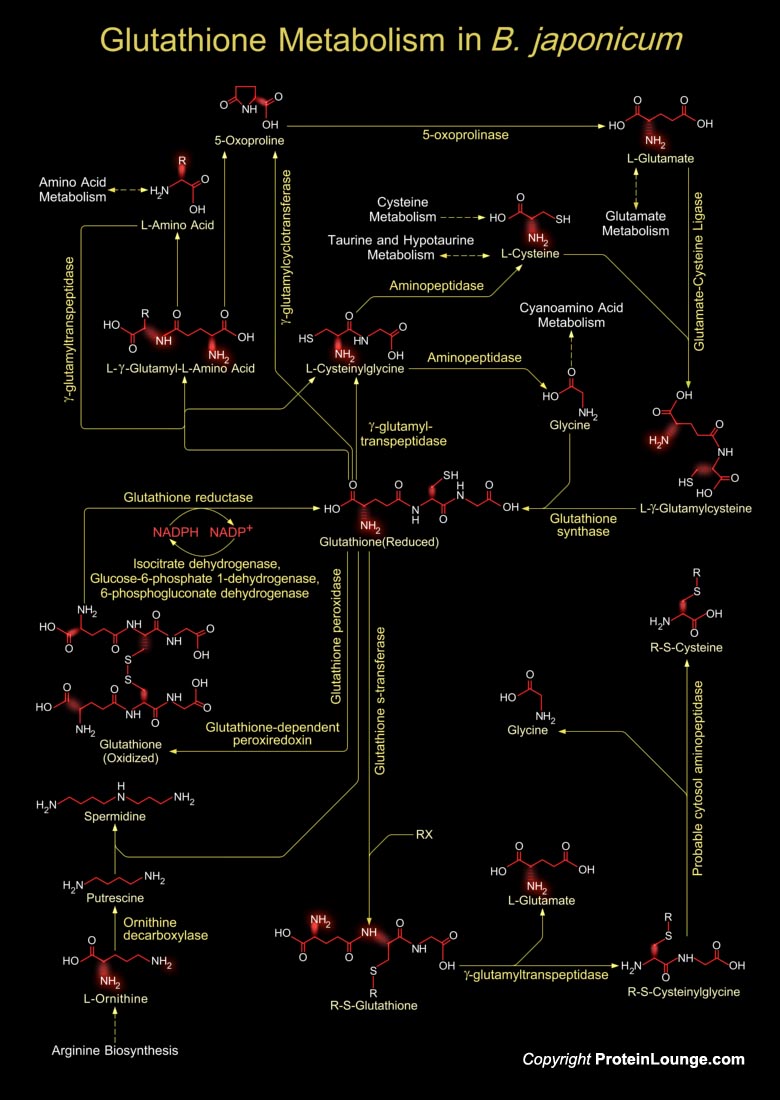
Rhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Sinorhizobium and Azorhizobium-known as Rhizobia-are Gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing bacteria of agronomic importance because they perform nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with leguminous plants. They are responsible for the world’s largest portion of fixed atmospheric nitrogen. Bradyrhizobium japonicum has been used since 1957 in molecular[..]
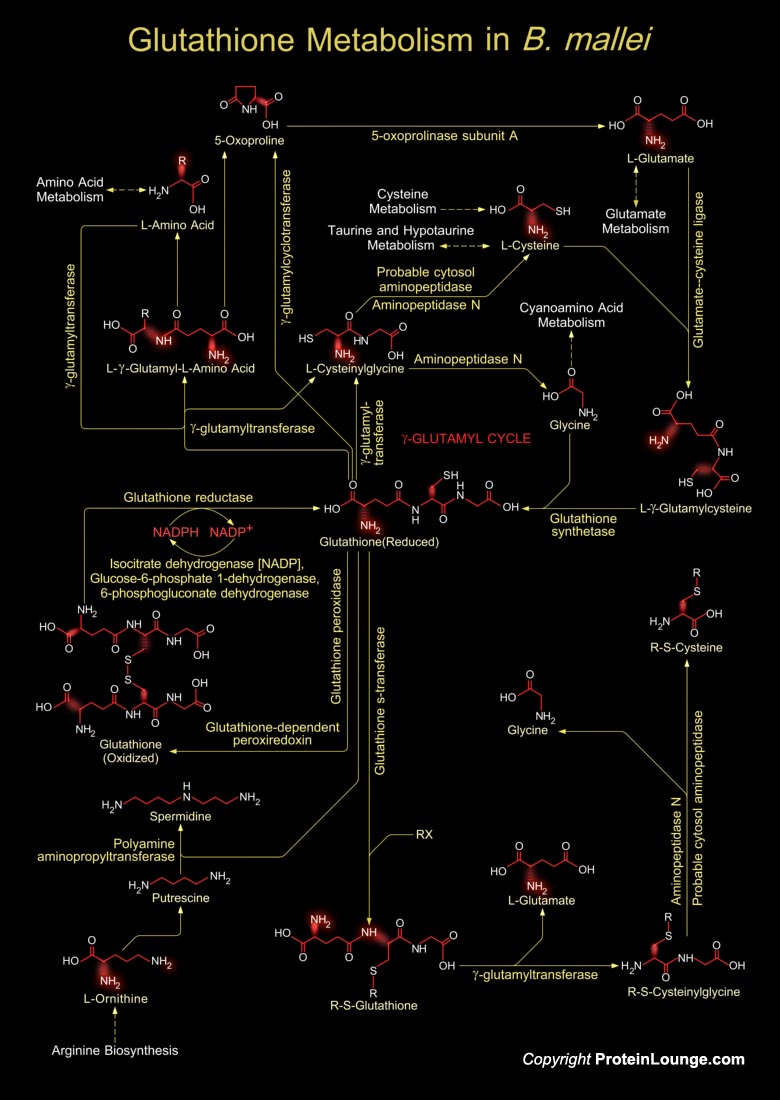
Burkholderia mallei are gram negative bacteria and are evolved as obligate parasite of horses, mules, and donkeys with no other known natural reservoir. B.mallei is regarded as a potential biological weapon because it is highly infectious as an aerosol and results in a disease that is painful, incapacitating, difficult to diagnose, and often fatal. Glutathione is a tripeptide[..]
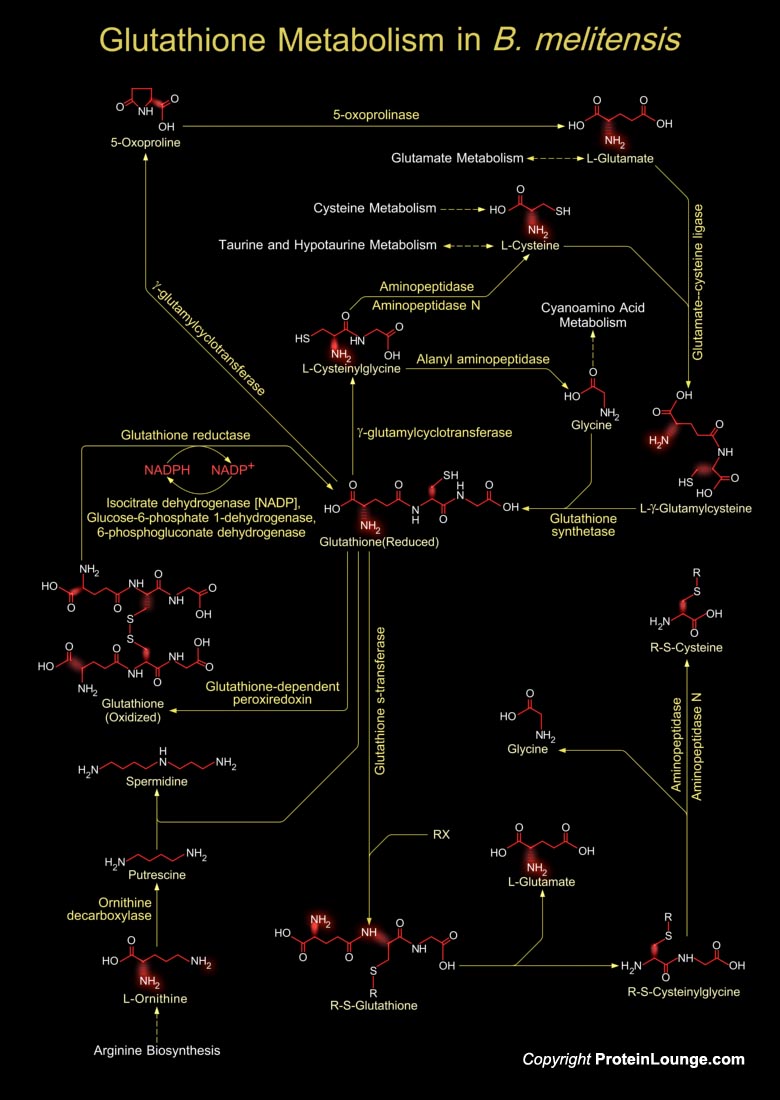
Brucella is a Gram-negative aerobic pathogen that is distringuished from most other pathogens because it does not have "obvious virulence factors" like capsules, fimbriae, flagella, exotoxins, exproteases, or other exoenzymes, cytolysins, resistance forms, antigenic variation, plamids, or lysogenic phages (Ref.1). Brucella sp. causes a "zoonotic disease endemic[..]
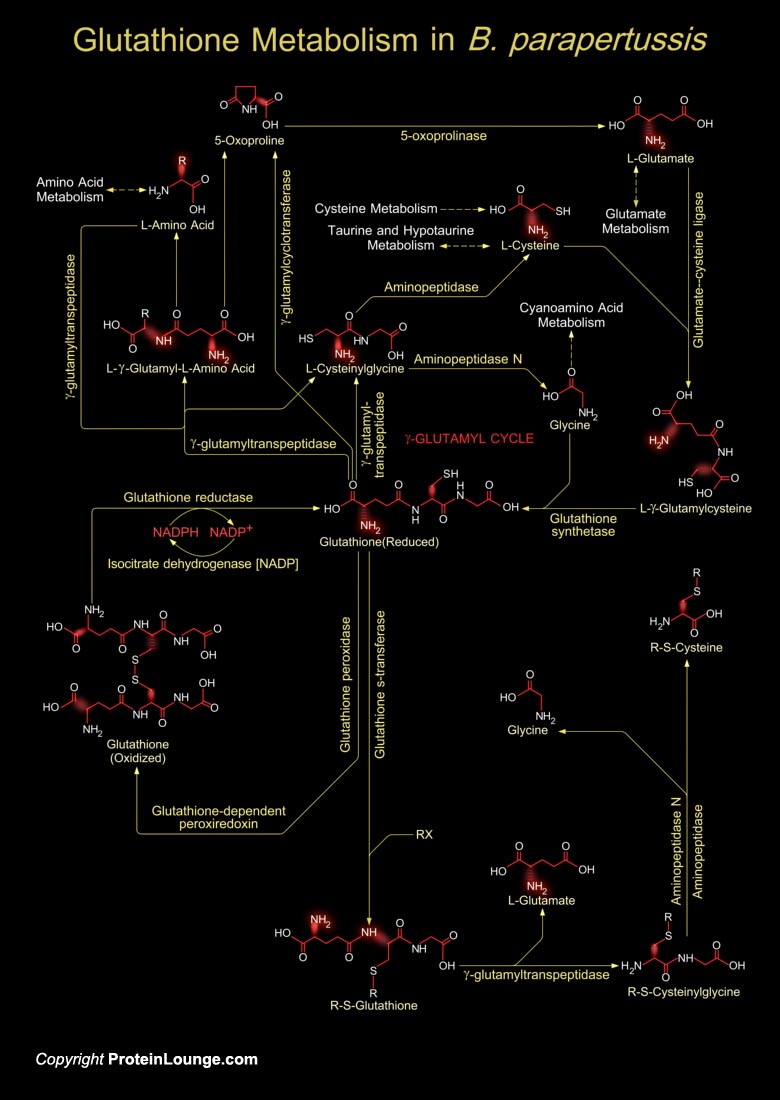
Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica are closely related Gram-negative Beta-proteobacteria that colonizes the respiratory tracts of mammals. B. parapertussis causes whooping cough in a wide range of animals. It produces a complex array of adhesins, aggressins and toxins that are presumed to be important in the[..]