Featured Pathways
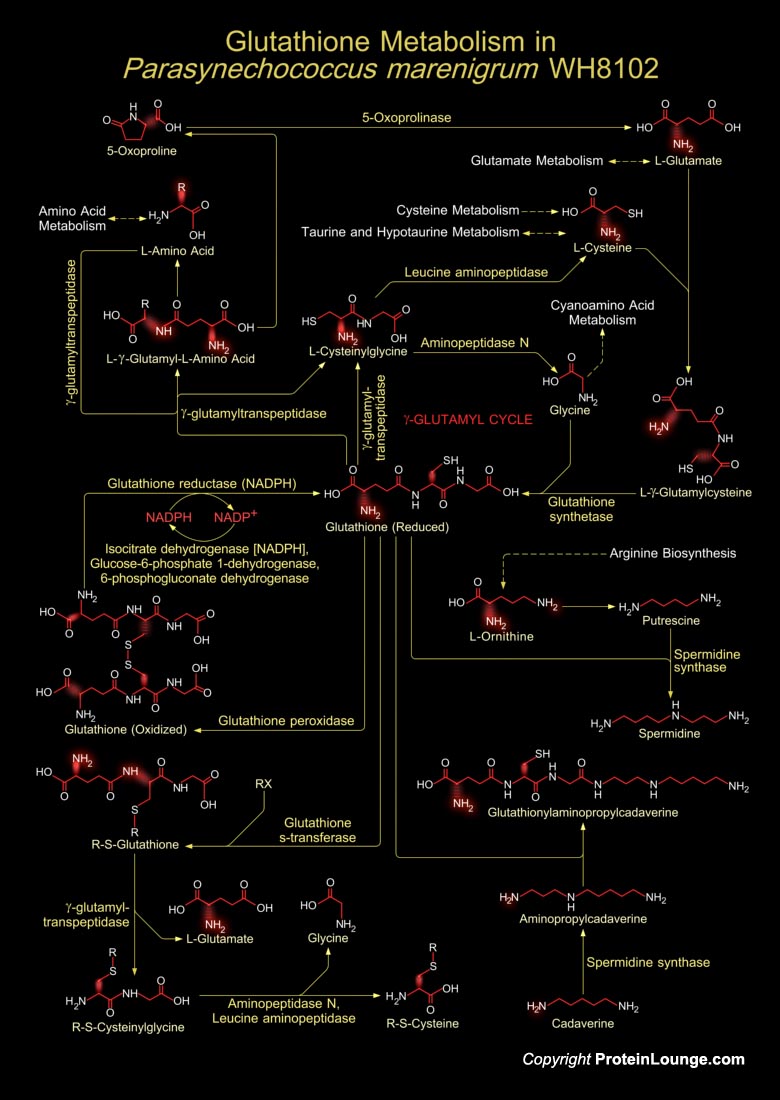
Marine unicellular Cyanobacteria of the Synechococcus group occupy an important position at the base of the marine food web. They are abundant in the world's oceans and as a result are major primary producers on a global scale and one of the most numerous genomes on earth Synechococcus is the main source of primary productin in oligotrophic, pelagic waters. Many genera of Cyanobacteria[..]
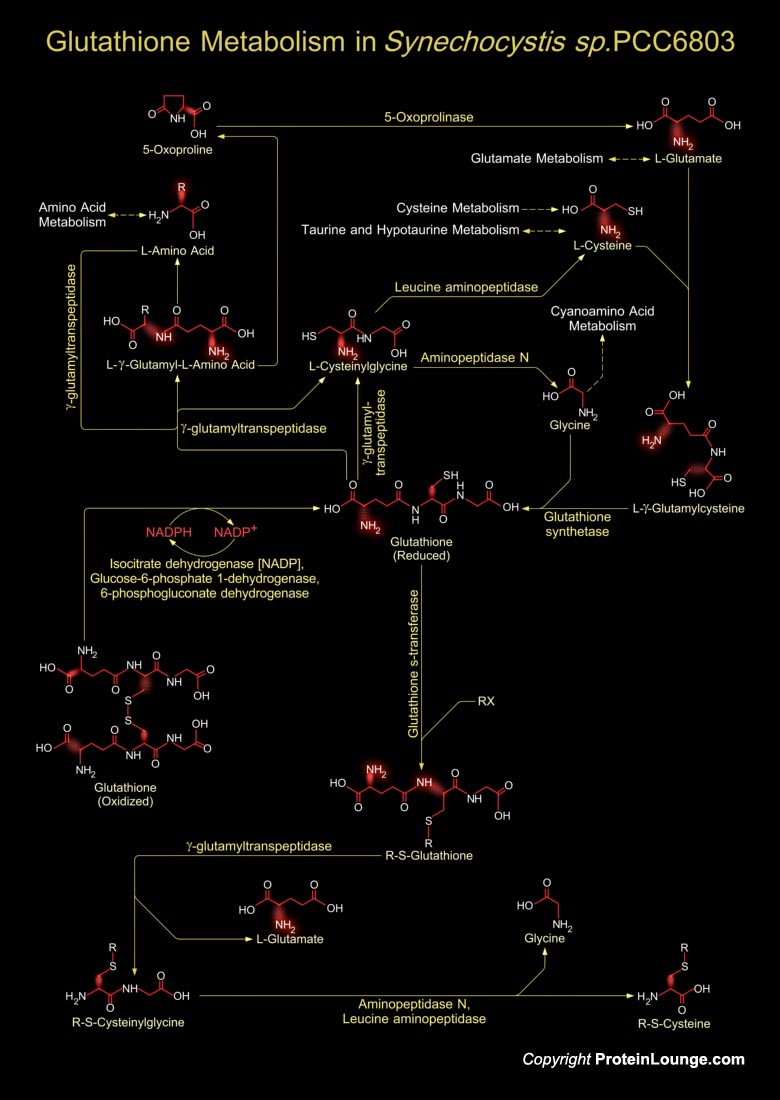
Synechocystiae are unicellular, photoautotrophic, facultative glucose-heterotrophic bacteria. They are oxygenic photosynthetic with two photosystems at their disposal, similar to those in algae and plants, and they can fix nitrogen. Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 can grow in the absence of photosynthesis if a suitable fixed-carbon source such as glucose is provided. The total length of[..]
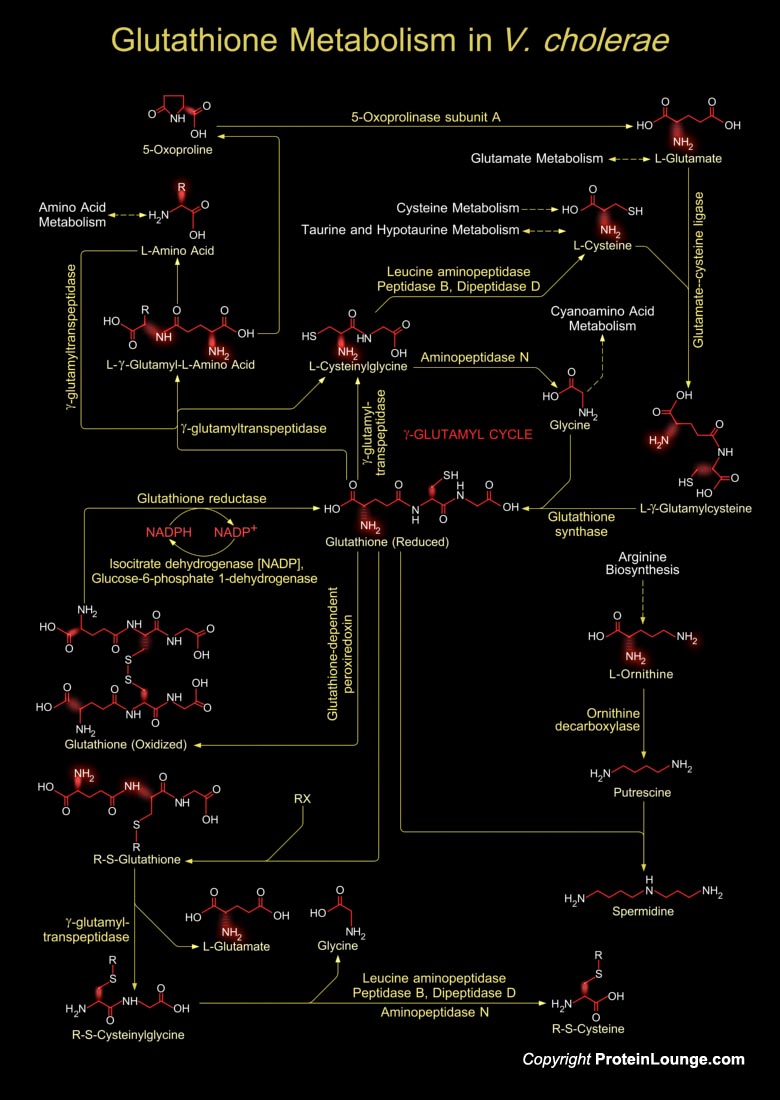
Vibrio cholerae is a facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative, crescent-shaped, motile rod like bacterium, and the causative infectious agent of the diarrheal disease, Cholera. It colonizes the mucosal surface of the human small intestine and secretes cholera toxin. The toxin stimulates secretion of water and electrolytes by the cells of the small intestine, leading to the severe watery diarrhoea[..]
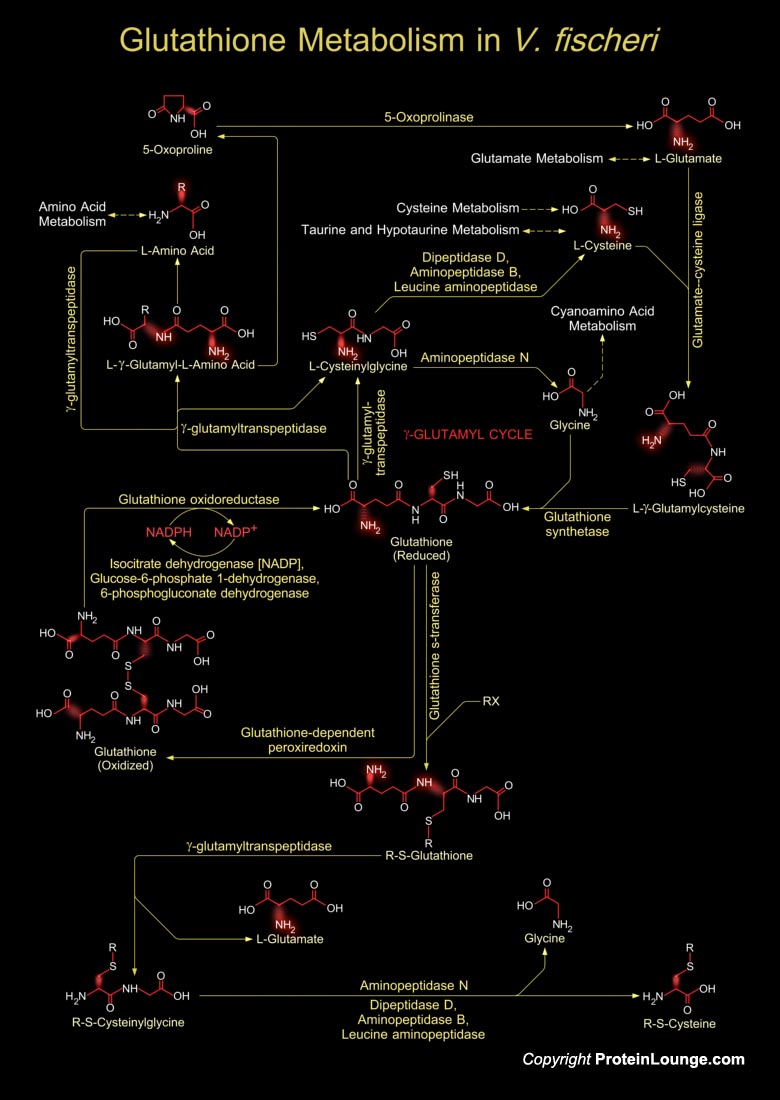
Vibrio fischeri is a Gram-negative heterotrophic bacterium, belonging to the Vibrionaceae, a large family within the Gamma-proteobacteria, consisting of many species that are characterized by both cooperative and pathogenic interactions with animal tissue. V. fischeri has a worldwide distribution, principally in temperate and subtropical waters, where it occupies a variety of niches. In[..]
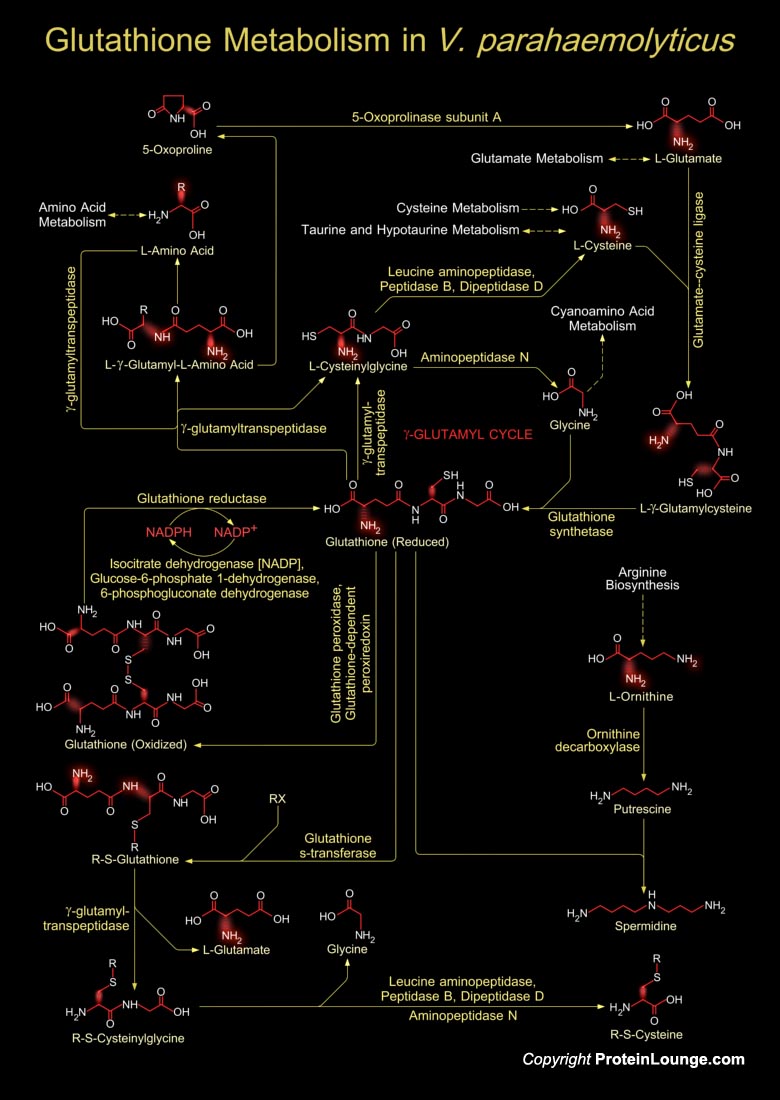
Vibrio parahaemolyticus, a Gram-negative marine bacterium, is a worldwide cause of food-borne gastroenteritis. The organism is phylogenetically close to V. cholerae, the causative agent of cholera. This universal marine pathogen is used as a bacterial model to clarify the various physiological phenomena of its native and host environments (Ref.1 & 2).
Glutathione in[..]
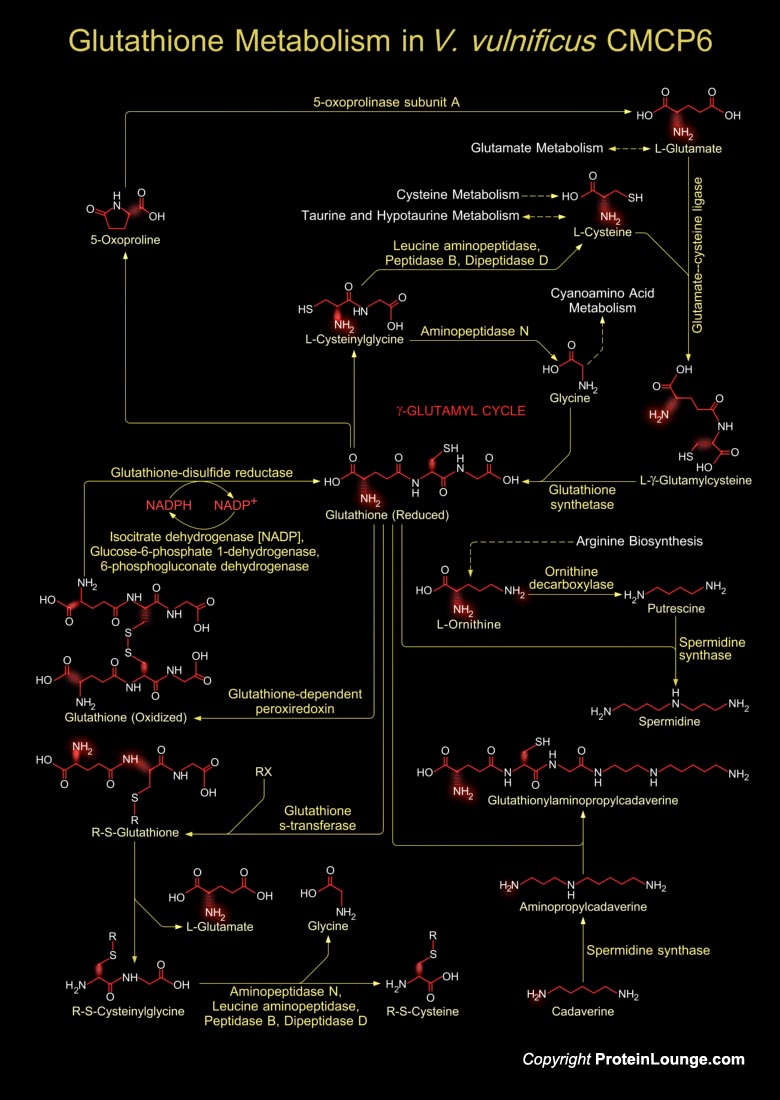
Vibrio vulnificus is an etiologic agent for severe human infection acquired through wounds or contaminated seafood. This is a lactose-fermenting, halophilic, Gram-negative, opportunistic pathogen, is found in estuarine environments and is associated with various marine species such as plankton, shellfish (Oysters, Clams, and Crabs), and finfish (Ref.1). V. vulnificus belong[..]
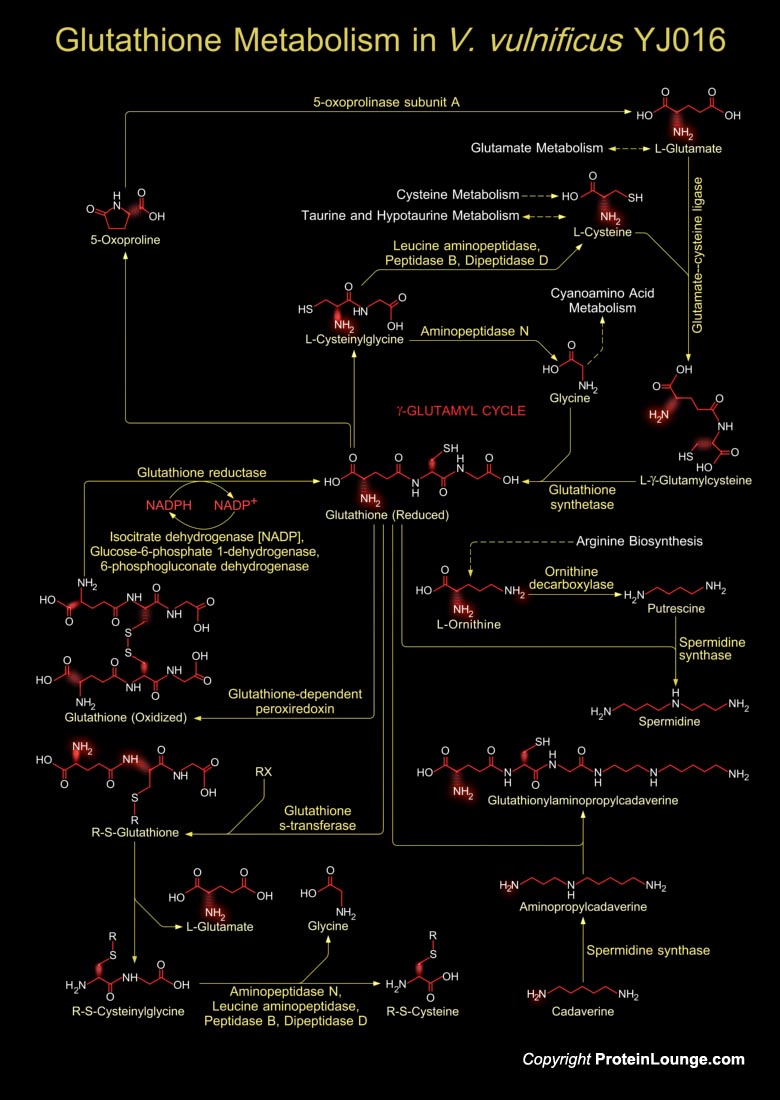
Vibrio vulnificus is an etiologic agent for severe human infection acquired through wounds or contaminated seafood. This is a lactose-fermenting, halophilic, Gram-negative, opportunistic pathogen, is found in estuarine environments and is associated with various marine species such as plankton, shellfish (Oysters, Clams, and Crabs), and finfish (Ref.1). V. vulnificus belong[..]
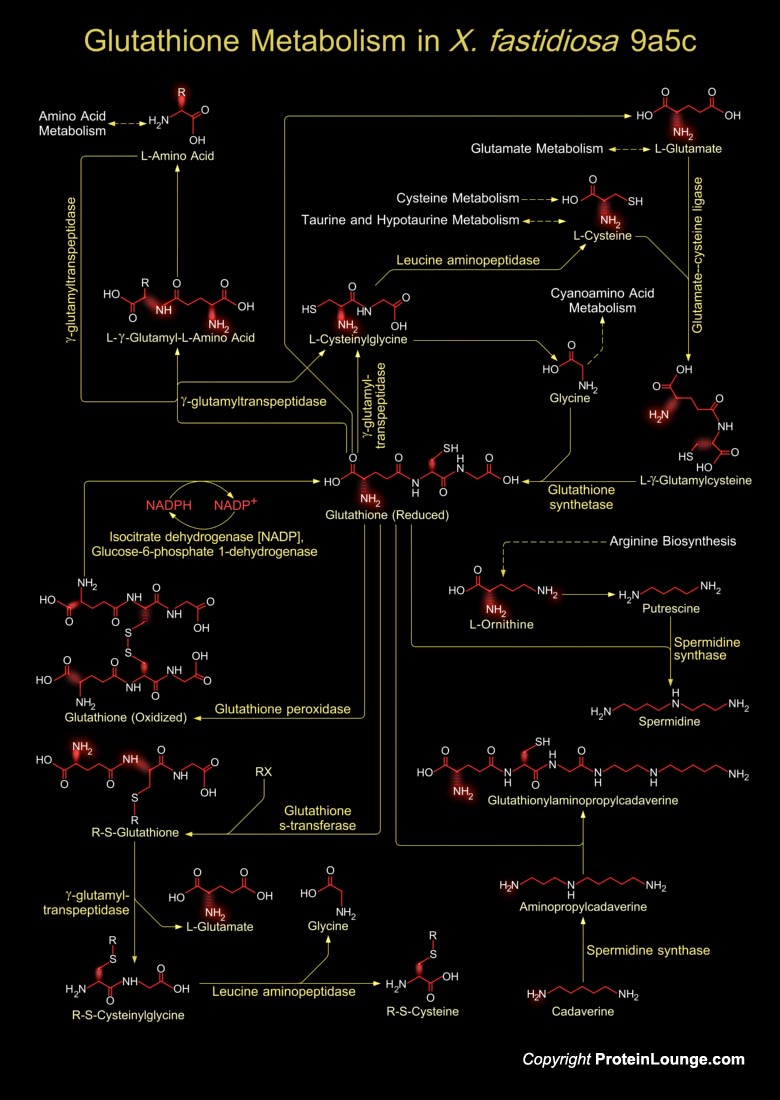
Xylella fastidiosa is a Gram-negative, fastidious, xylem-limited bacterium that causes a range of economically important plant diseases. It causes citrus variegated chlorosis-a serious disease of orange trees. It is responsible for pathogenicity and virulence involving toxins, antibiotics and ion sequestration systems. Glutathione is a tripeptide present in Xylella sp., which[..]
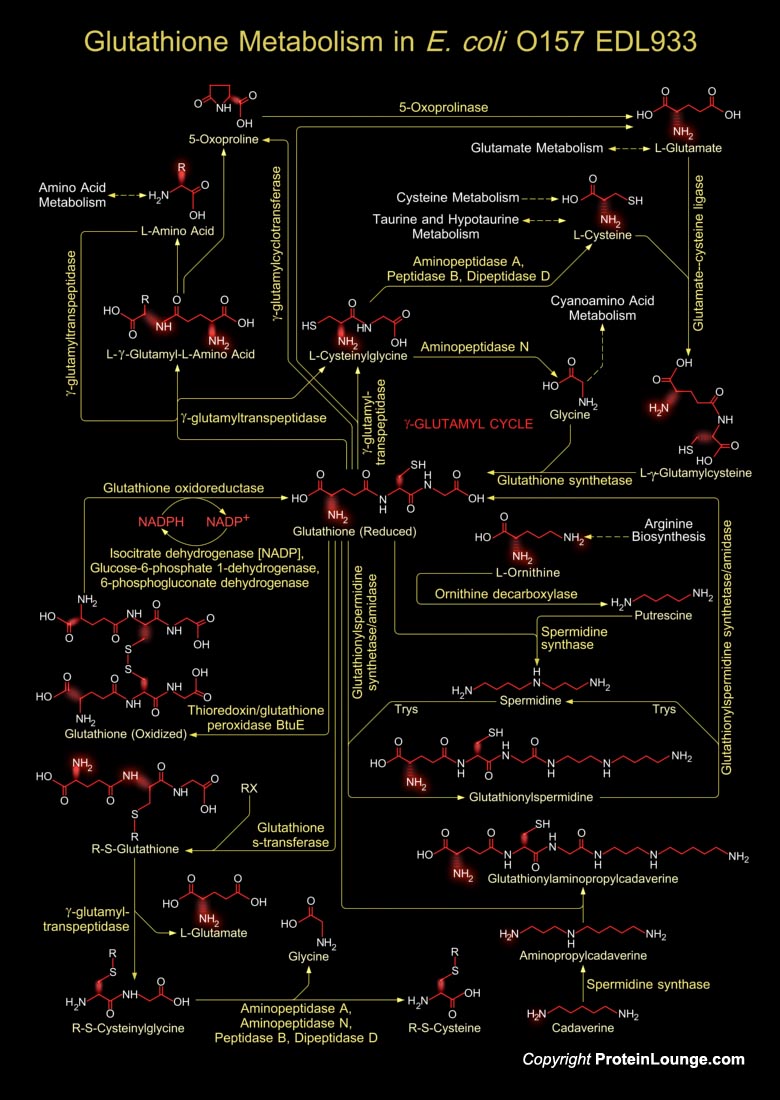
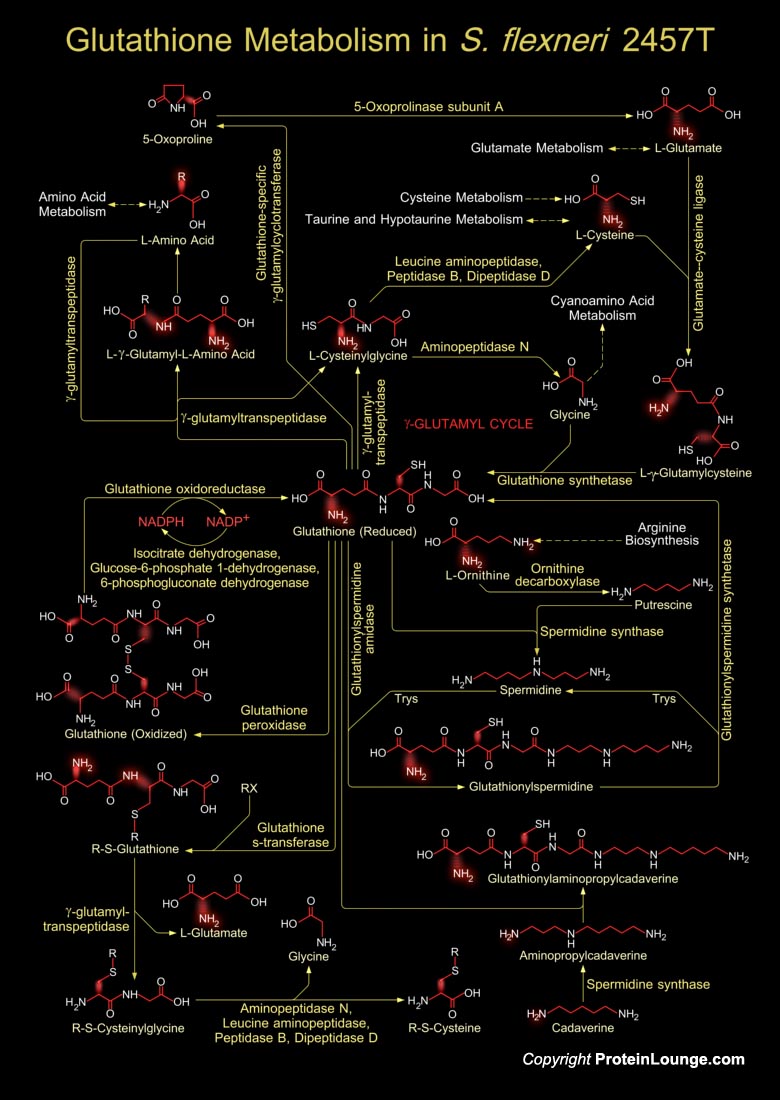
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. It is homeostatically[..]
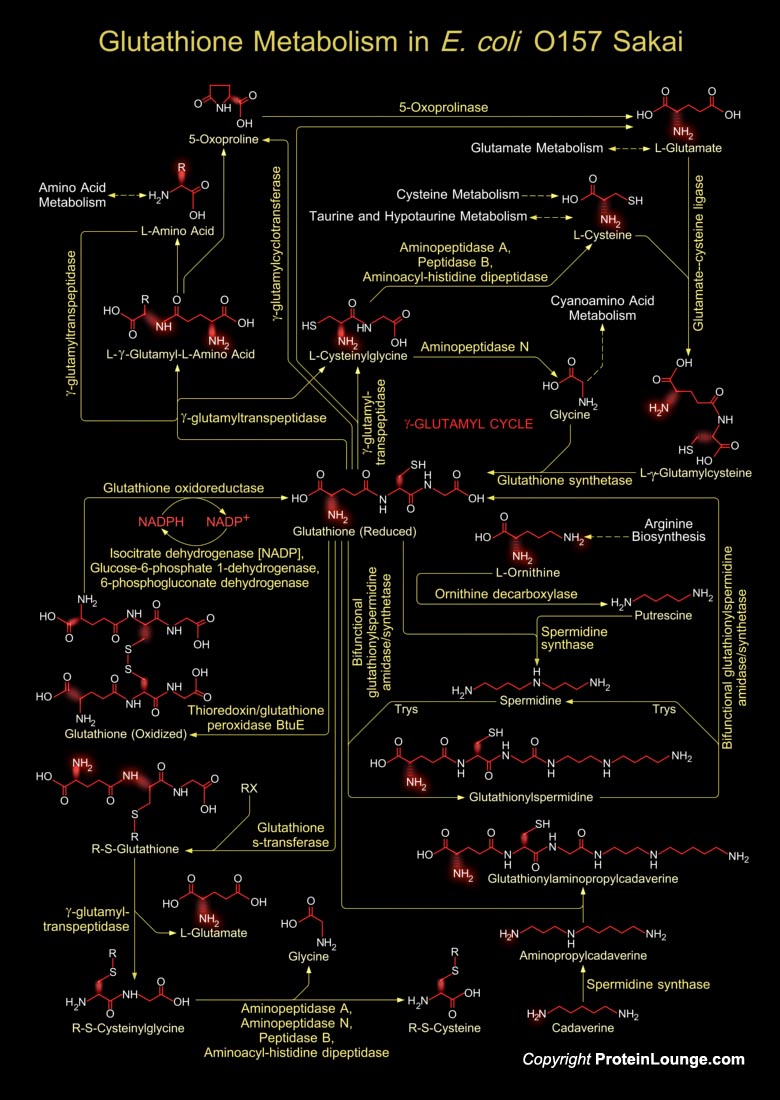
Glutathione is a sulfhydryl (-SH) antioxidant, antitoxin, and enzyme cofactor. It is ubiquitous in animals, plants, and microorganisms, and being water soluble is found mainly in the cell cytosol and other aqueous phases of the living system. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of Glutamate, Cysteine and Glycine that has numerous important functions within cells. It is homeostatically[..]
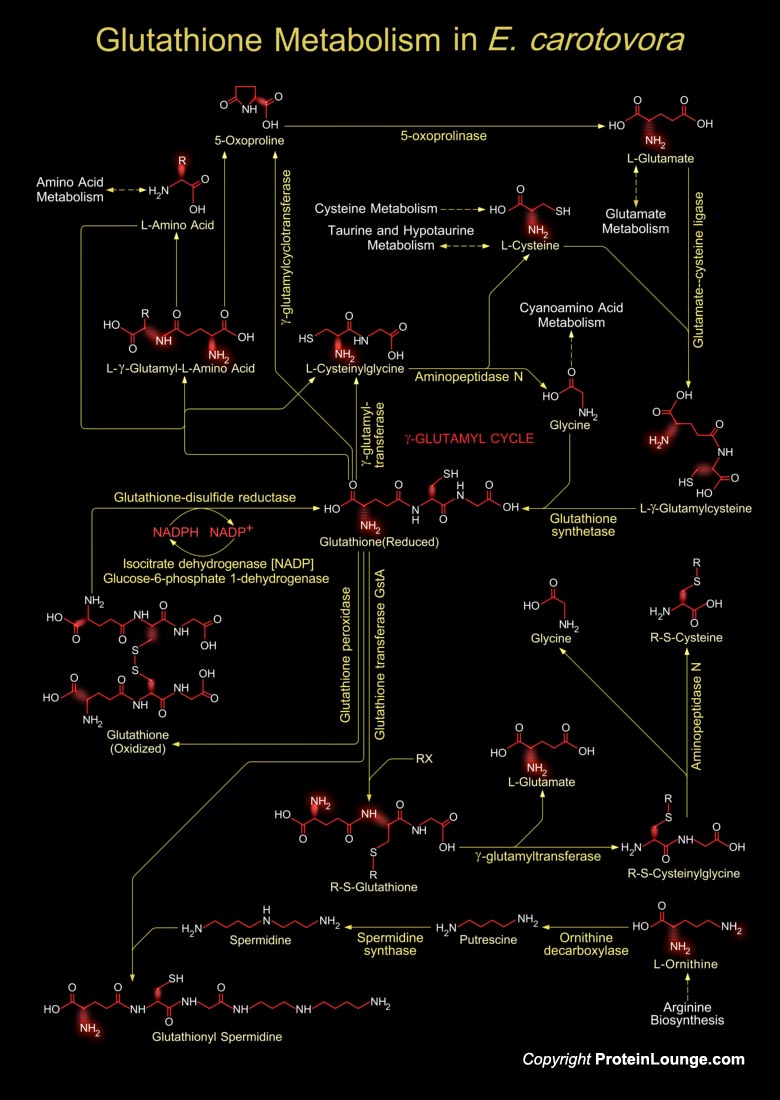
Pectobacterium carotovorum is a bacterium of the family Pectobacteriaceae. It used to be a member of the genus Erwinia. The bacterium is also known as Erwinia carotovora It is a ubiquitous plant pathogen with a wide host range and is able to cause disease in almost any plant tissue it invades. P. carotovorum is a very economically important pathogen in[..]
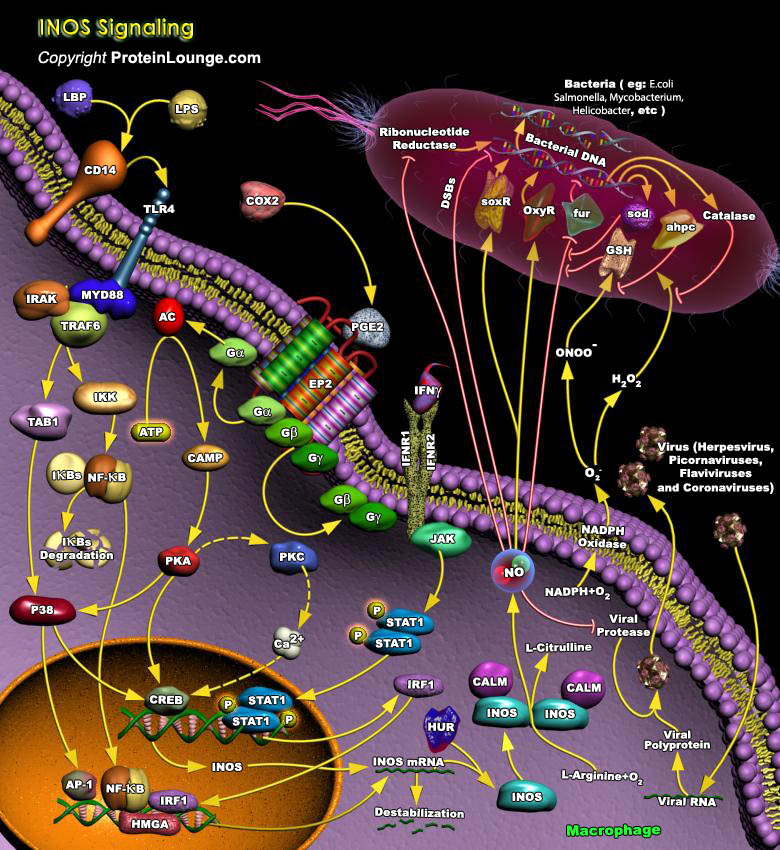
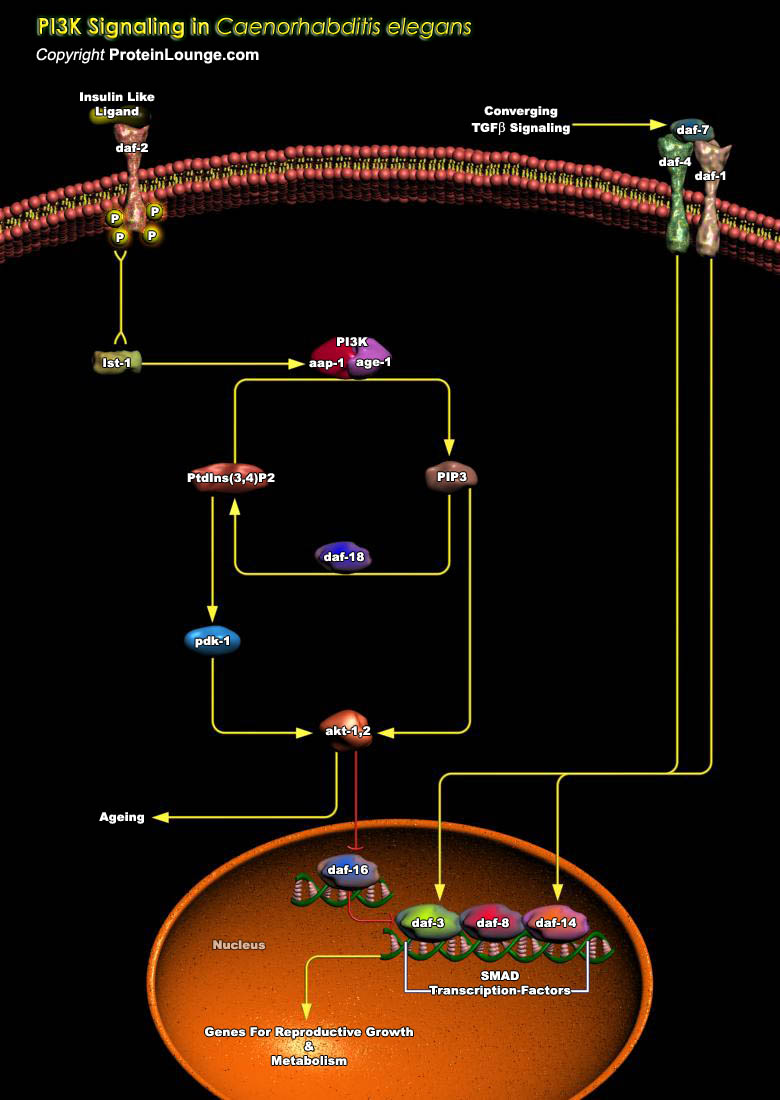
Microorganisms have developed several mechanisms to survive in their hosts' environments. These include competition with their hosts for metal acquisition and resistance to host defenses such as NO (Nitric Oxide), a cytotoxic weapon generated by macrophages. In eukaryotic cells, NO is metabolically produced by NOS (NO Synthase) from L-Arginine, O2 (Molecular Oxygen), and NADPH[..]