Featured Pathways
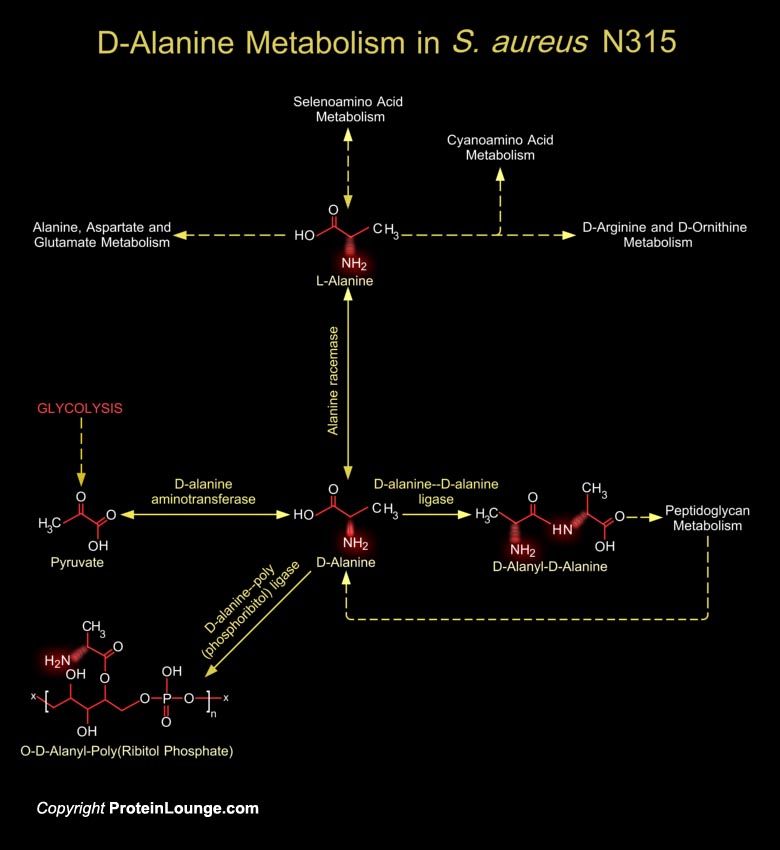
Staphylococcus aureus are Gram-positive nonmotile coccus that grows in aerobic and anaerobic conditions, in which it forms grape-like clusters. S. aureus is one of the major causes of community-acquired and hospital-acquired infections. It produces numerous toxins including superantigens that cause unique disease entities such as toxic-shock syndrome and staphylococcal[..]
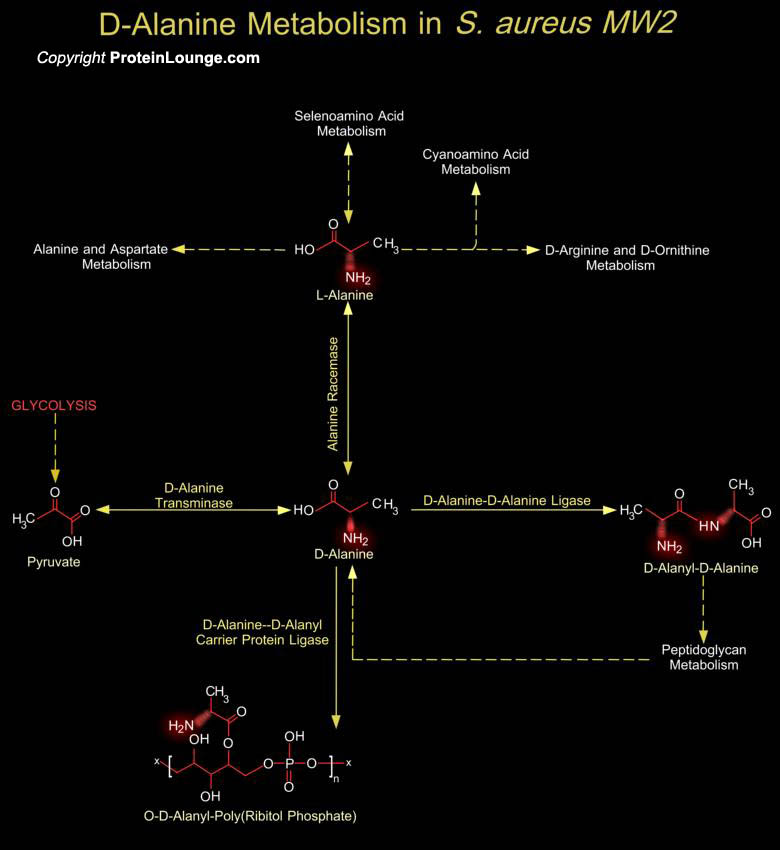
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacterium grouped with Bacillus sp on the basis of ribosomal RNA sequences. This immobile coccus grows in aerobic and anaerobic conditions, in which it forms grape-like clusters. Its main habitats are the nasal membranes and skin of warm-blooded animals, in which it causes a range of infections from mild, such as skin infections and food[..]
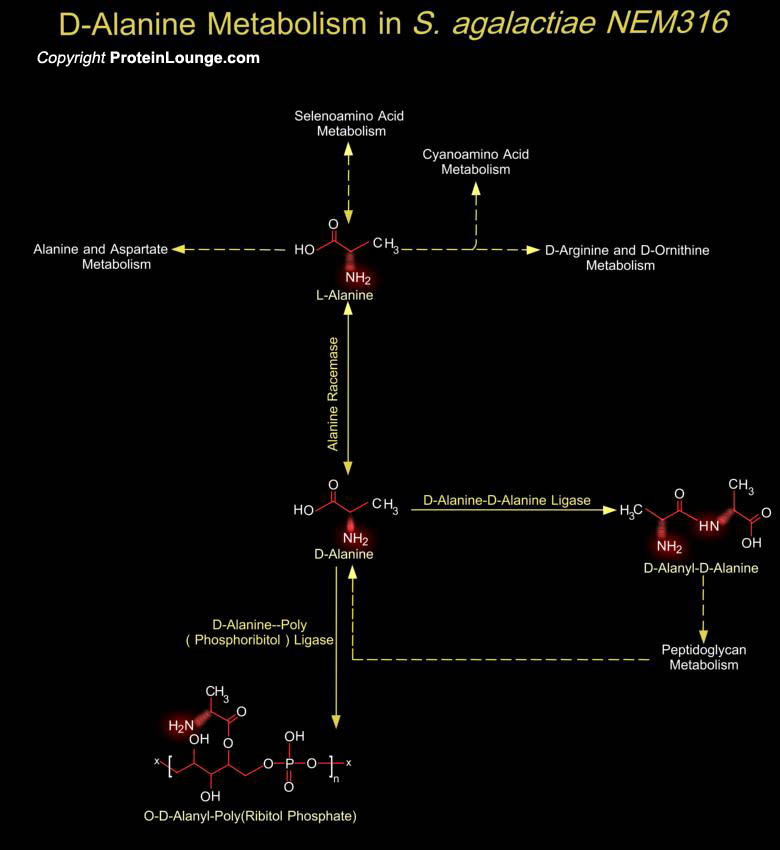
Streptococcus agalactiae, or Group-B Streptococcus is a Gram-positive nonmotile bacterium and is the leading cause of bacterial sepsis, pneumoniae and meningitidis in neonates in U.S. and Europe. It usually behaves as a commensal organism that colonizes the gastrointestinal or genital tract of 25-40% of healthy women, but it can cause life-threatening invasive infection in susceptible[..]
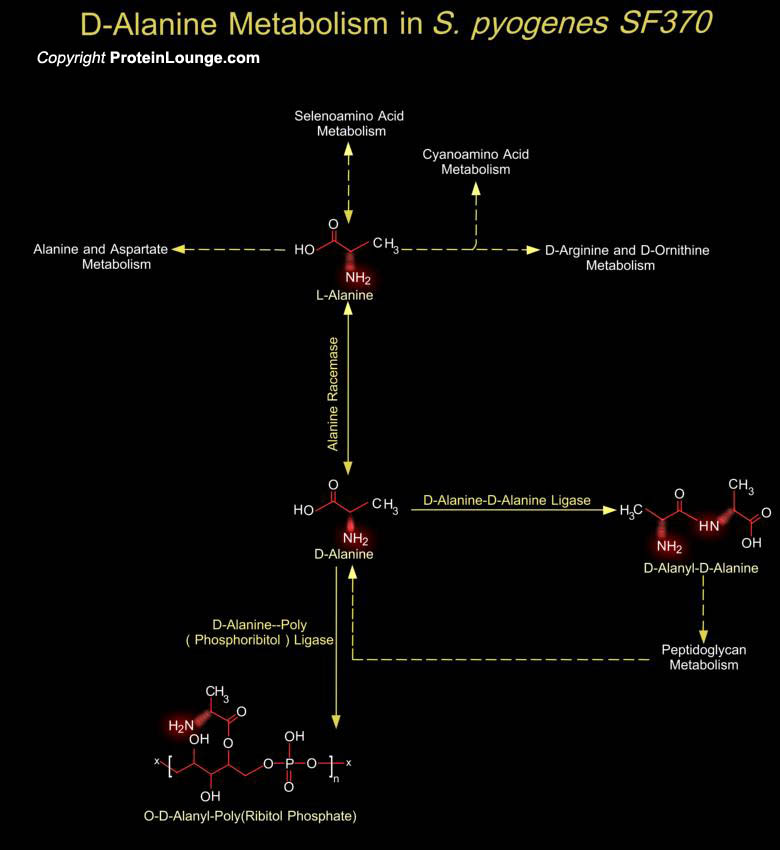
The Group-A Streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes) remains an important human pathogen, associated with a range of superficial skin and throat infections as well as a variety of more serious invasive infections and autoimmune sequelae such as acute rheumatic fever and post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (Ref.1). S. pyogenes strains are grouped into two classes on the basis of post infectious[..]
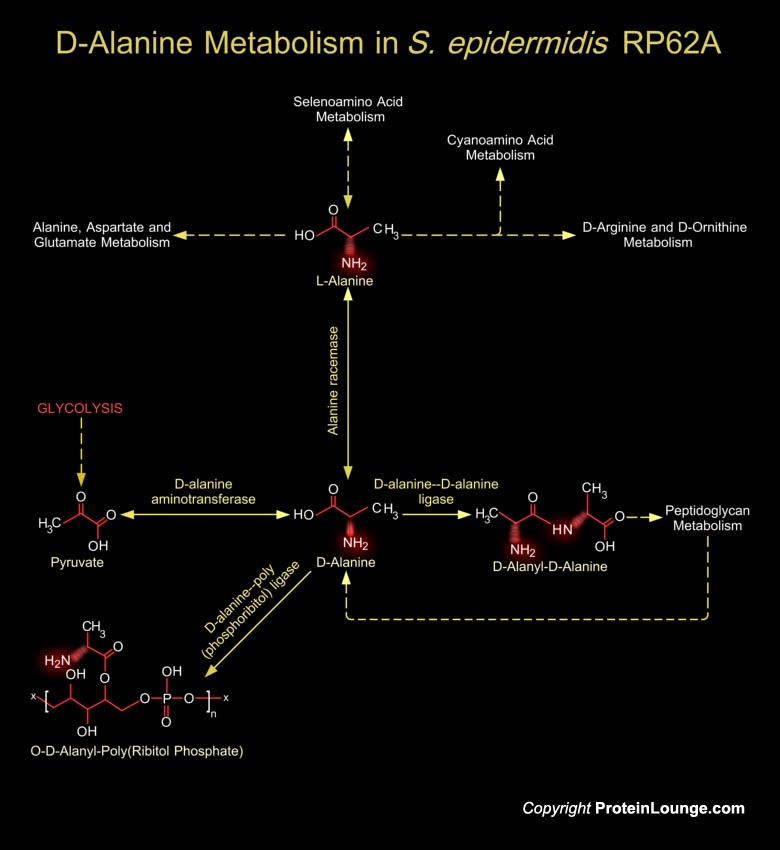
Staphylococci are known as clustering Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, non-spore forming facultatively anaerobic that classified in two main groups, coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative. Staphylococcus epidermidis with the highest percentage has the prominent role among coagulase-negative Staphylococci that is the most important reason of clinical infections.[..]
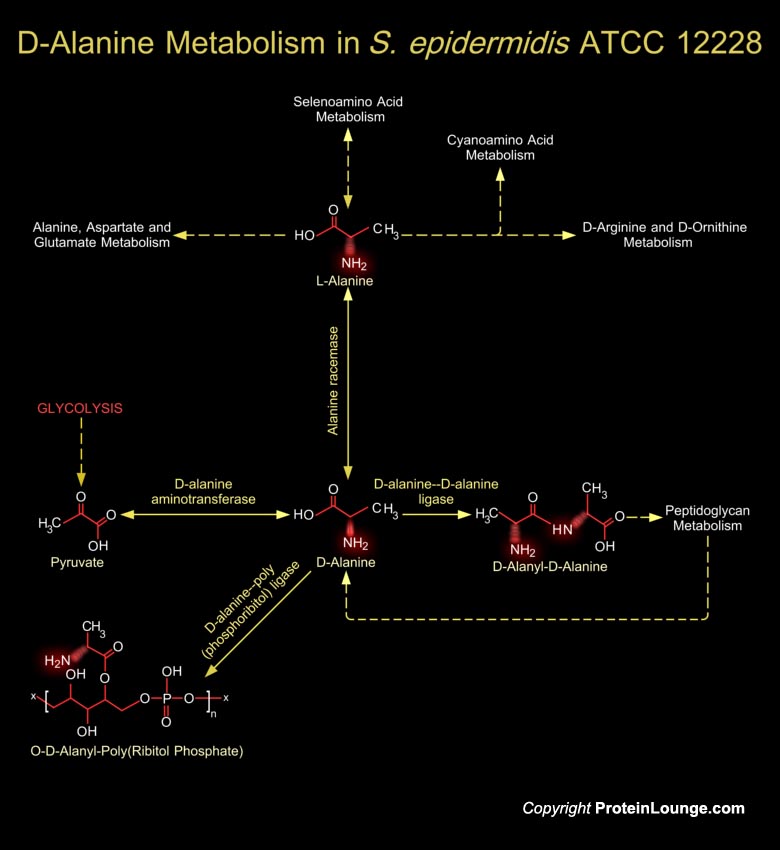
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a Gram-positive non motile bacterium that grows in aerobic and anaerobic conditions, in which it forms grape-like clusters. It produces numerous toxins including superantigens that cause unique disease entities and has emerged as a causative agent of infections often associated with implanted medical devices. The S. aureus and S. epidermidis genomes are[..]
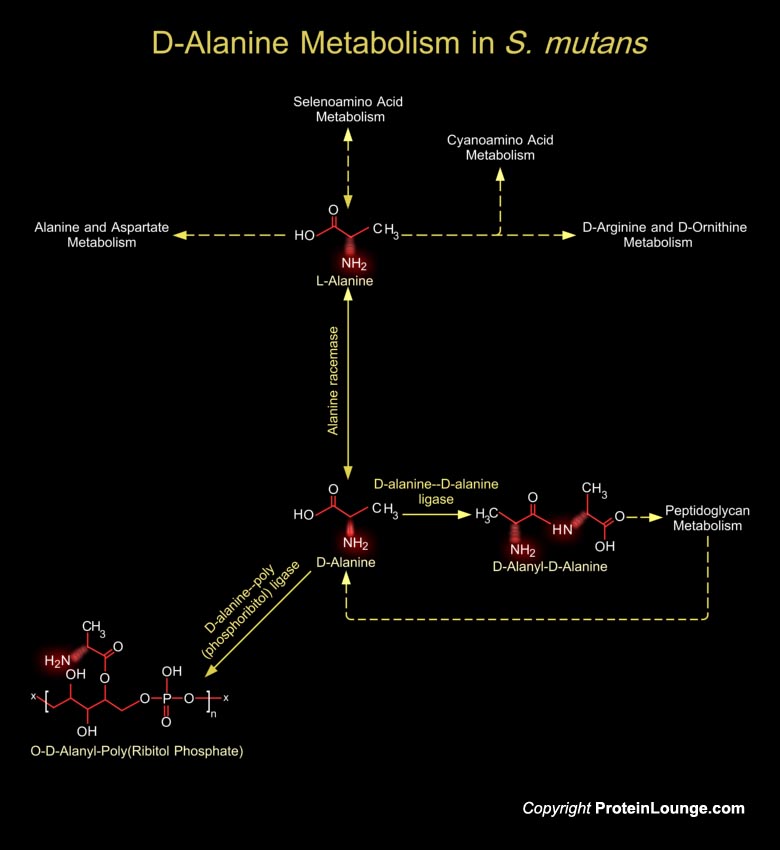
Based on differences in their compositions and the linkages of cell wall polysaccharides, Streptococci are classified into eight serotypes as follows; Streptococcus mutans (Serotypes c, e, and f), Streptococcus sobrinus (Serotypes d and g), Streptococcus cricetus (Serotype a), Streptococcus rattus (Serotype b), Streptococcus ferus (Serotype c),[..]
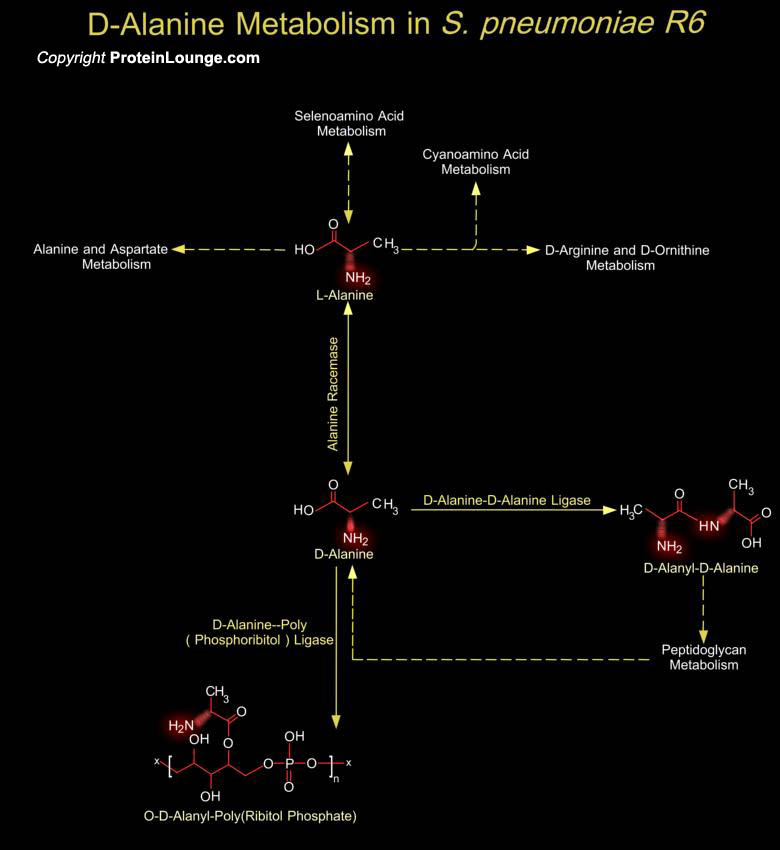
Streptococcus pneumoniae (also known as Pneumococcus or Diplococcus pneumoniae) is a Gram-positive coccus and is among the most significant causes of bacterial disease in humans. It is responsible for a high proportion of cases of pneumonia, acute otitis media, acute sinusitis, bacteremia and meningitis. There are 90 known serotypes of S. pneumoniae, each of[..]
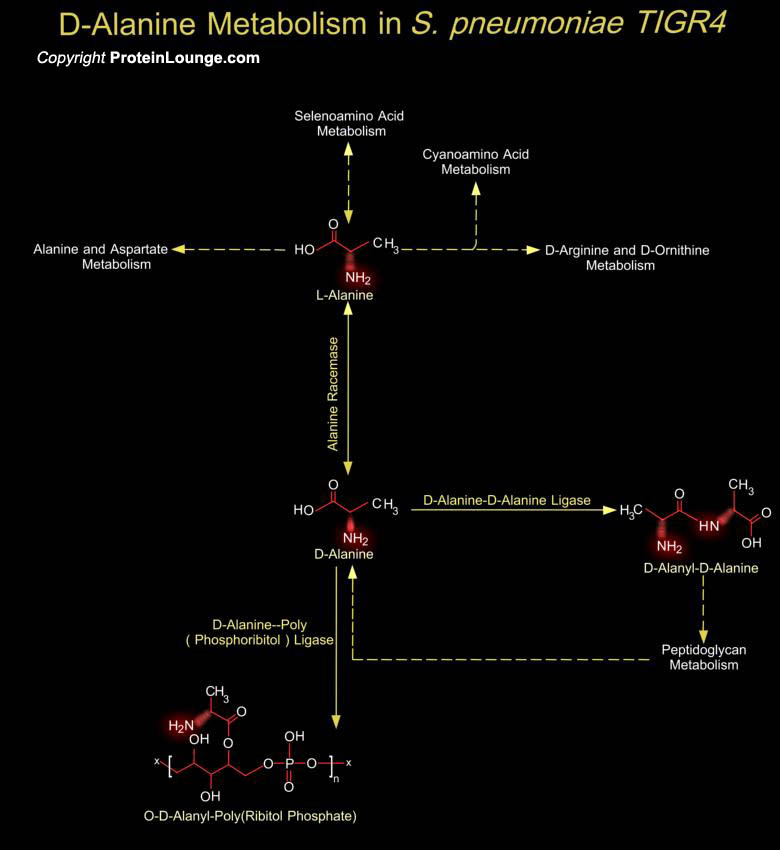
Streptococcus pneumoniae (also known as Pneumococcus or Diplococcus pneumoniae) is a Gram-positive coccus and is among the most significant causes of bacterial disease in humans. It is responsible for a high proportion of cases of pneumonia, acute otitis media, acute sinusitis, bacteremia and meningitis. There are 90 known serotypes of S. pneumoniae, each of[..]
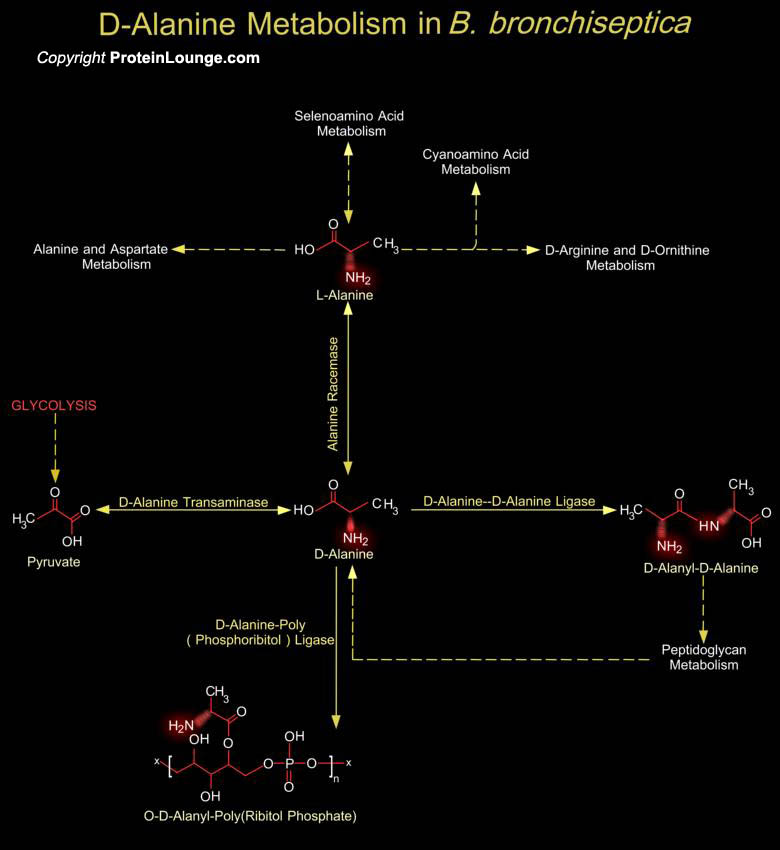
Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica are closely related Gram-negative Beta-proteobacteria that colonizes the respiratory tracts of mammals. B. bronchiseptica causes chronic respiratory infections in a wide range of animals. D-Alanine is a necessary precursor in the biosynthesis of cell wall in this bacterium[..]
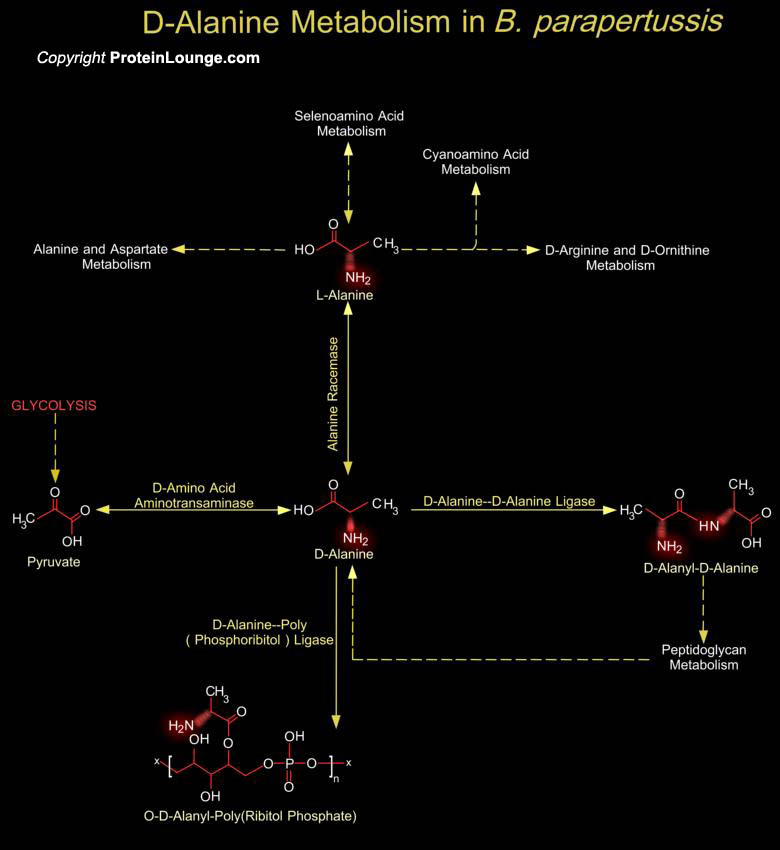
The genus Bordetella in the family Alcaligenaceae, comprises five species(Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica, Bordetella hinzii and Bordetella avium ), four of which cause infections of the upper respiratory tract in different host organisms. They are closely related Gram-negative Beta-proteobacteria Bordetella pertussis is[..]
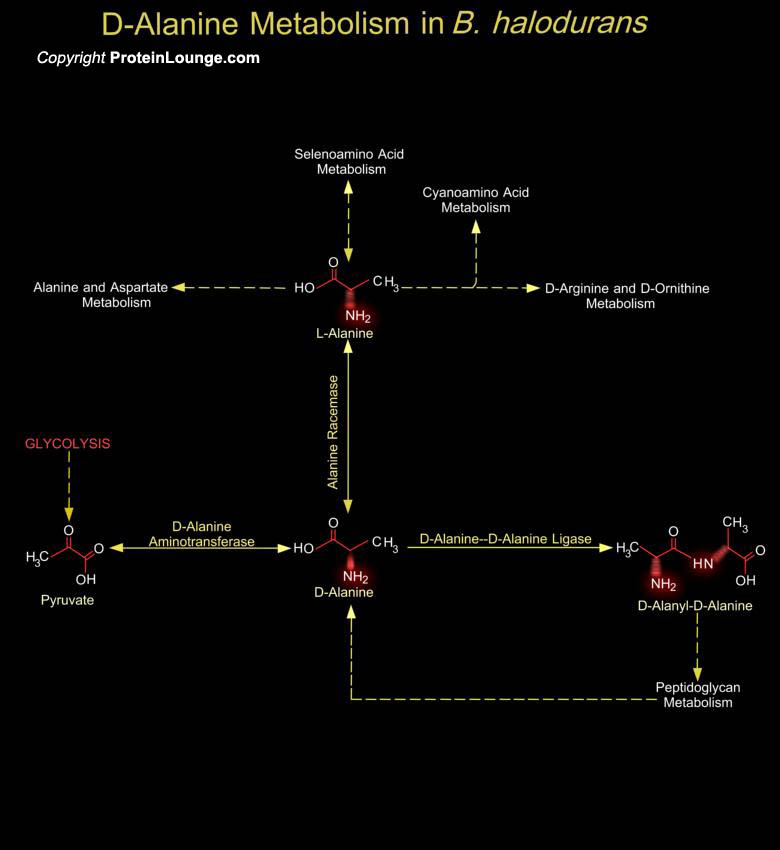
Bacillus species and other microbes with pH optima for growth higher than pH 9 are defined as alkaliphiles. A large number of alkaliphilic Bacillus strains producing useful enzymes, have been isolated from various environments. Bacillus halodurans(B. halodurans) is an alkaliphilic Bacillus species that grows optimally above pH 9.5. It is the second Bacillus species whose entire[..]