Featured Pathways
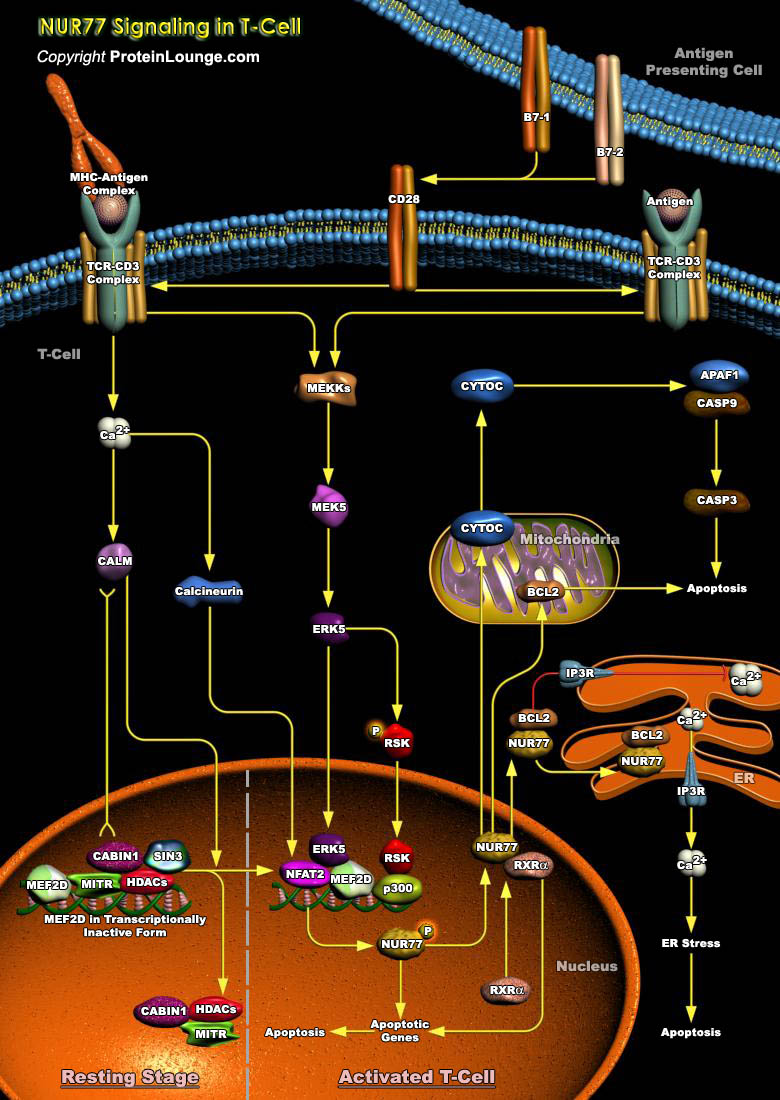
In the immune system, thymus acts as a primary lymphoid organ within which T cells referred to as thymocytes mature. During T cell development in the thymus, immature thymocytes expressing self-reactive TCR (T-Cell Receptor) are eliminated from the developing T-cell repertoire by clonal deletion, or negative[..]
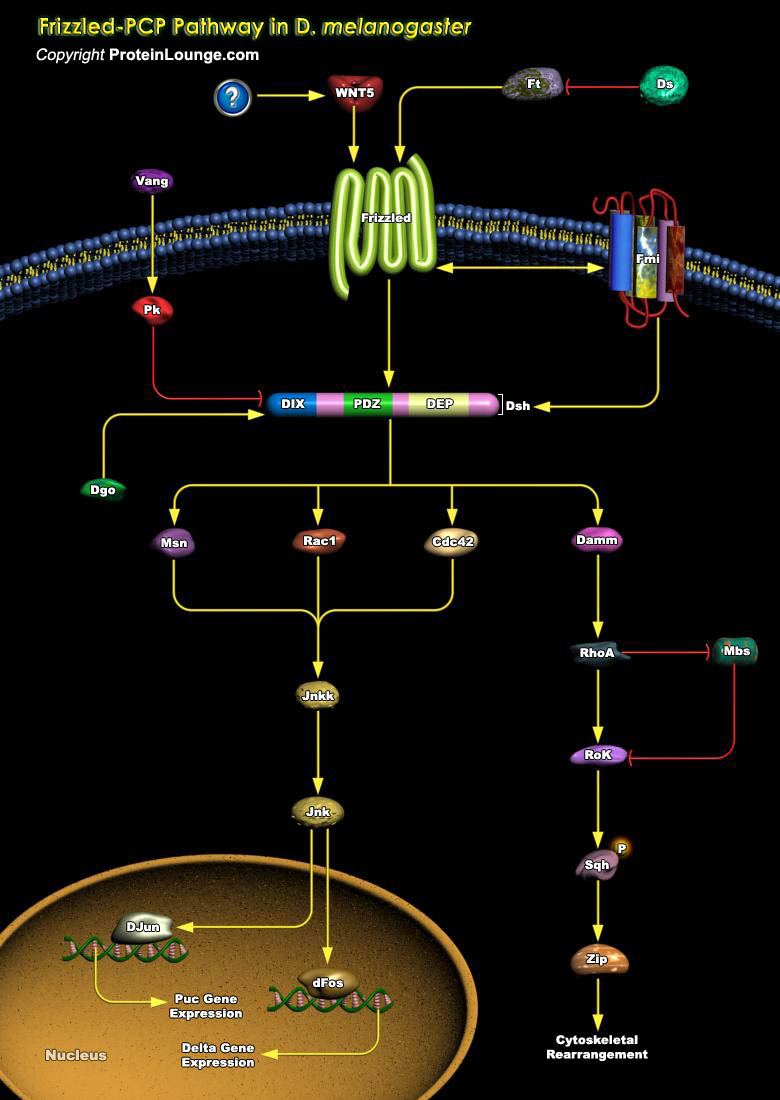
Epithelia are polarized along the apical–basal axis in order to allow for directional transport of proteins within a cell or secretion of factors into. In addition, most epithelia are also polarized within the epithelial plane. The latter polarization is called epithelial PCP (Planar Cell Polarity) or tissue polarity. Planar polarization provides a cell not only with positional[..]
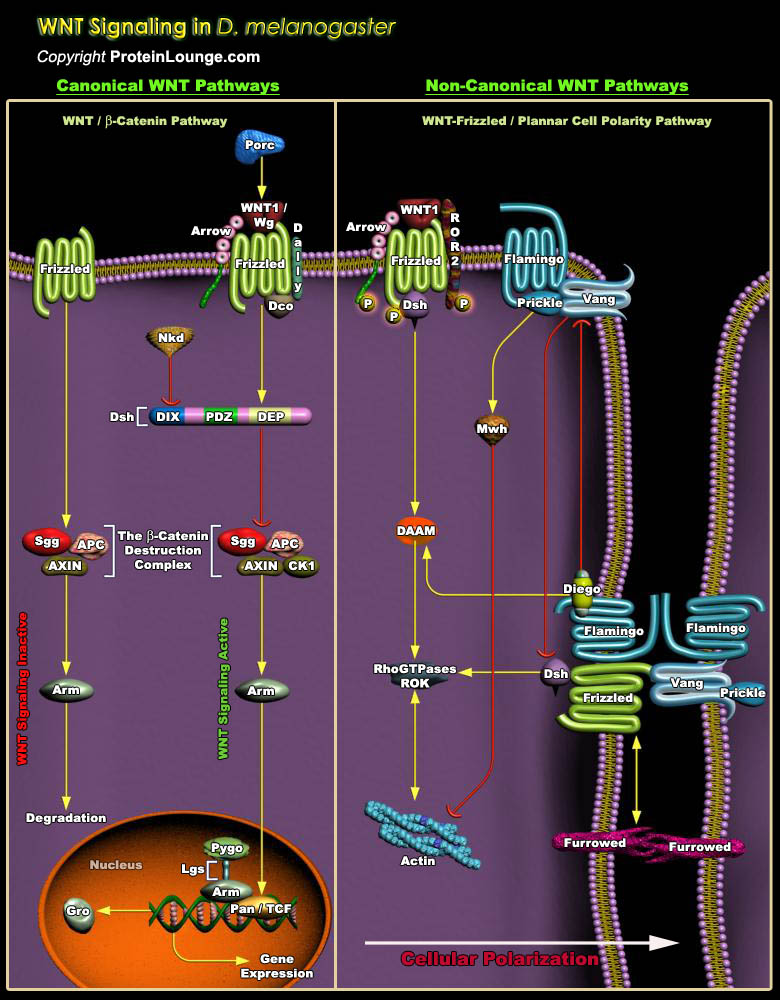
The Wg (wingless) pathway is highly conserved amongst various species and is important for embryonic development, including body axis patterning, cell fate specification, cell proliferation and cell migration. Additionally, Wnt signaling also controls tissue regeneration in adult bone marrow, skin and intestine.Much of our understanding of the role of Wnt proteins during[..]
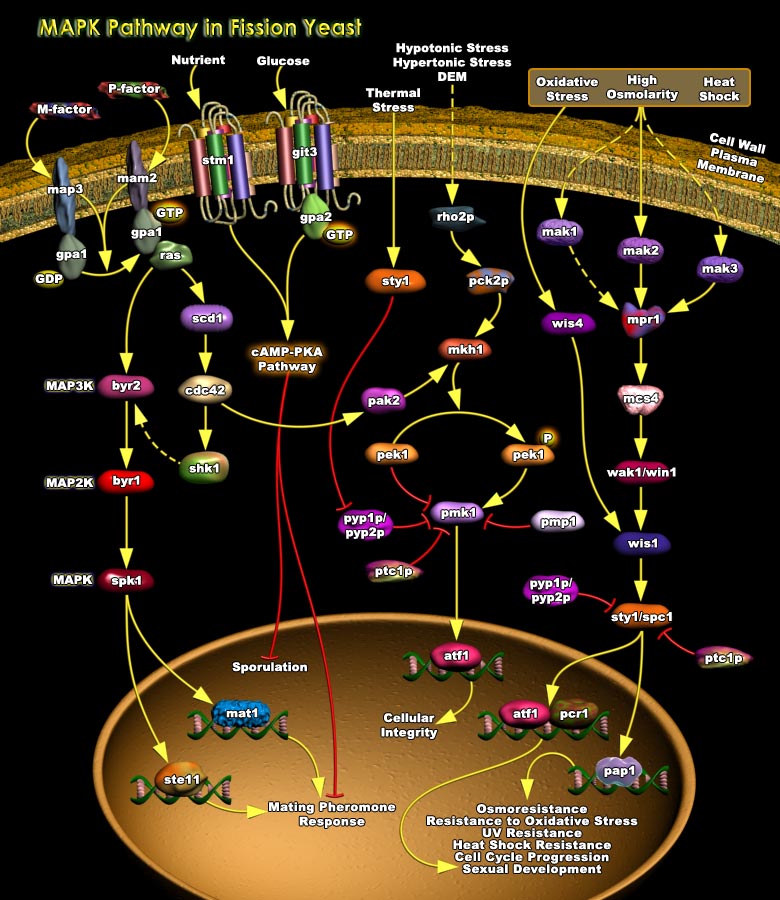
In both Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes, a major adaptive response to various Stress conditions is to change the repertoire of Gene expression. Prokaryotic cells commonly employ the two-component Signal Transduction Systems, where a “sensor” Histidine Kinase, often located in the Plasmamembrane, mediates environmental signals to a cytoplasmic “response regulator” that[..]
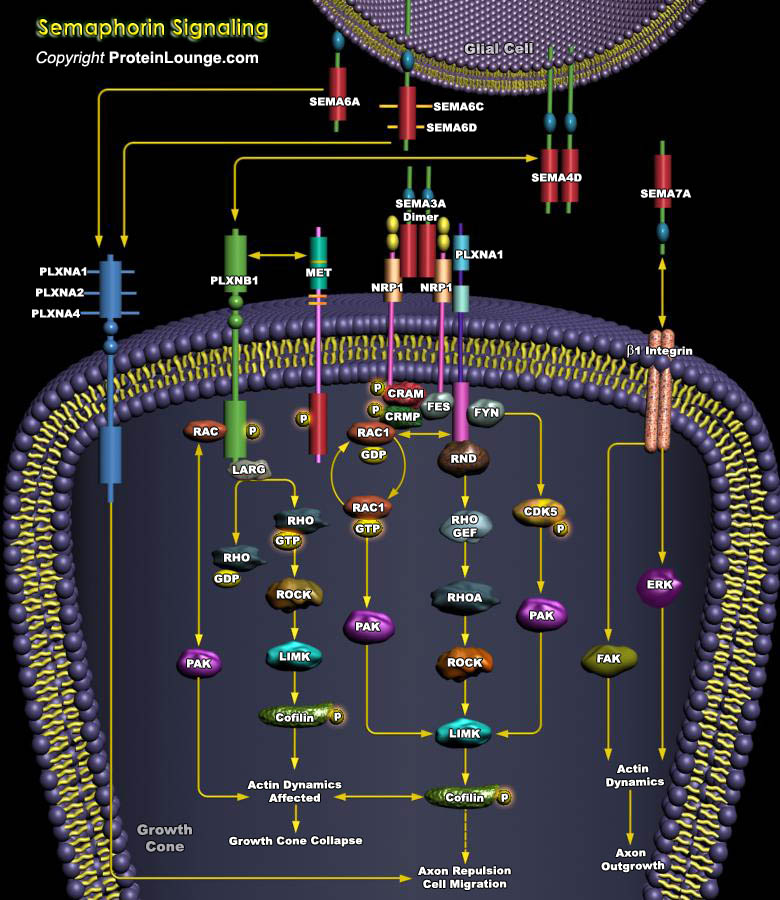
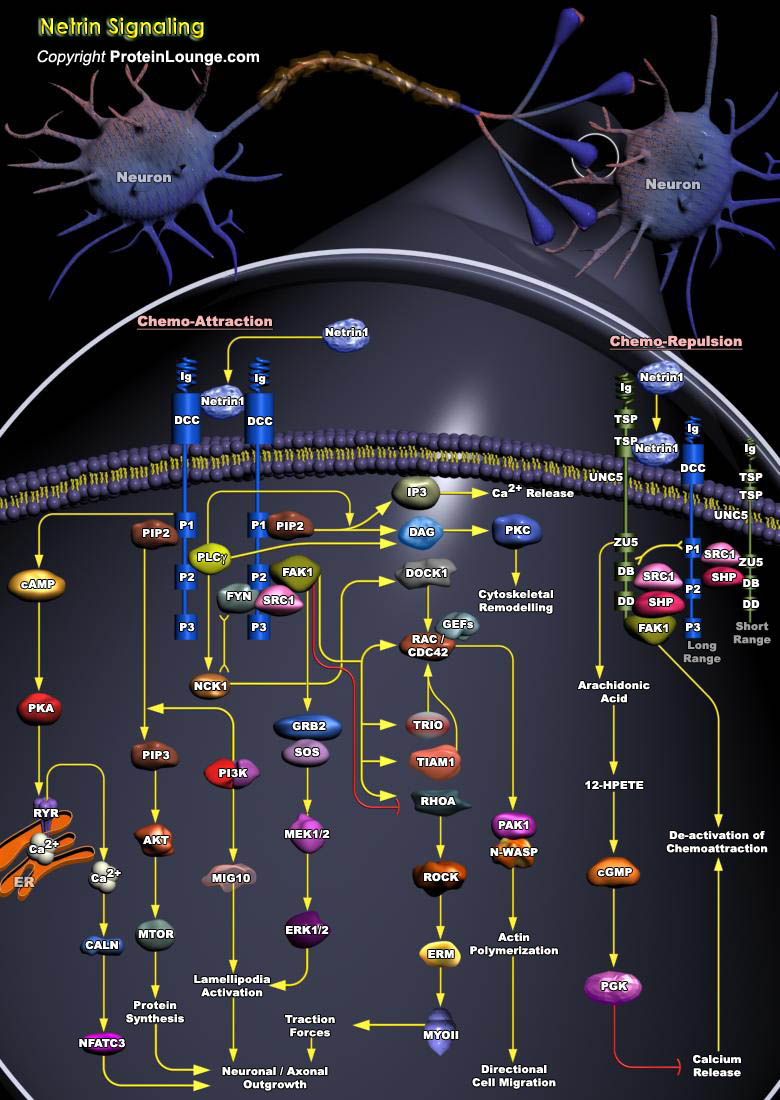
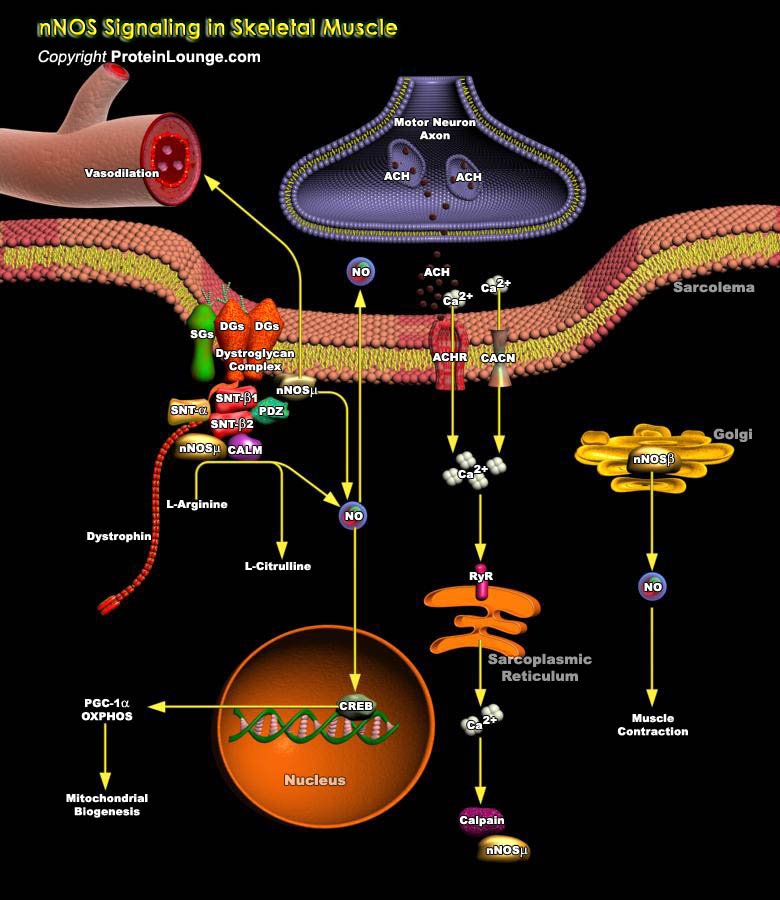
NO (Nitric Oxide) is formed endogenously by a family of enzymes known as NOS (NO Synthases). The distribution of different isoforms of NOS is largely related to their respective functions. Three distinct isoforms of NOS have been identified: nNOS (also known as NOSI and NOS-1) being the isoform first found (and predominating) in neuronal tissue, iNOS (also known as NOSII and NOS-2) which is[..]
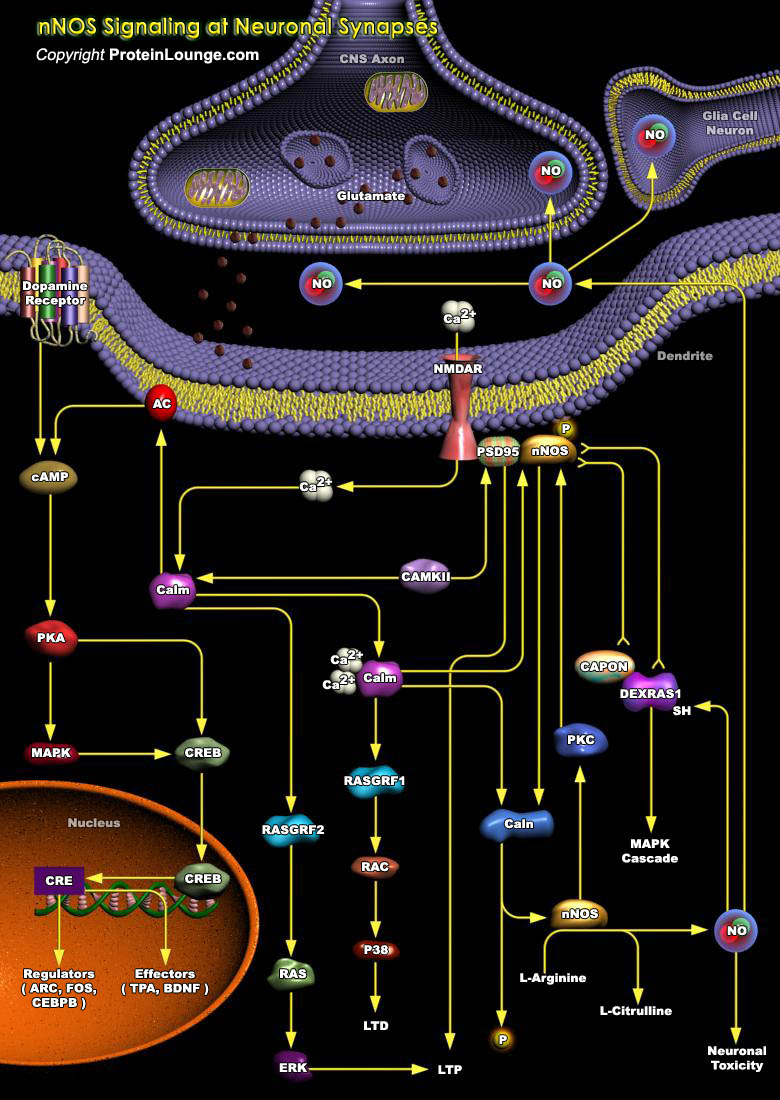
NO (Nitric Oxide) is formed endogenously by a family of enzymes known as NOS (NO Synthases). The distribution of different isoforms of NOS is largely related to their respective functions. Three distinct isoforms of NOS have been identified: nNOS (also known as NOSI and NOS-1) being the isoform first found (and predominating) in neuronal tissue, iNOS (also known as NOSII and NOS-2) which is[..]
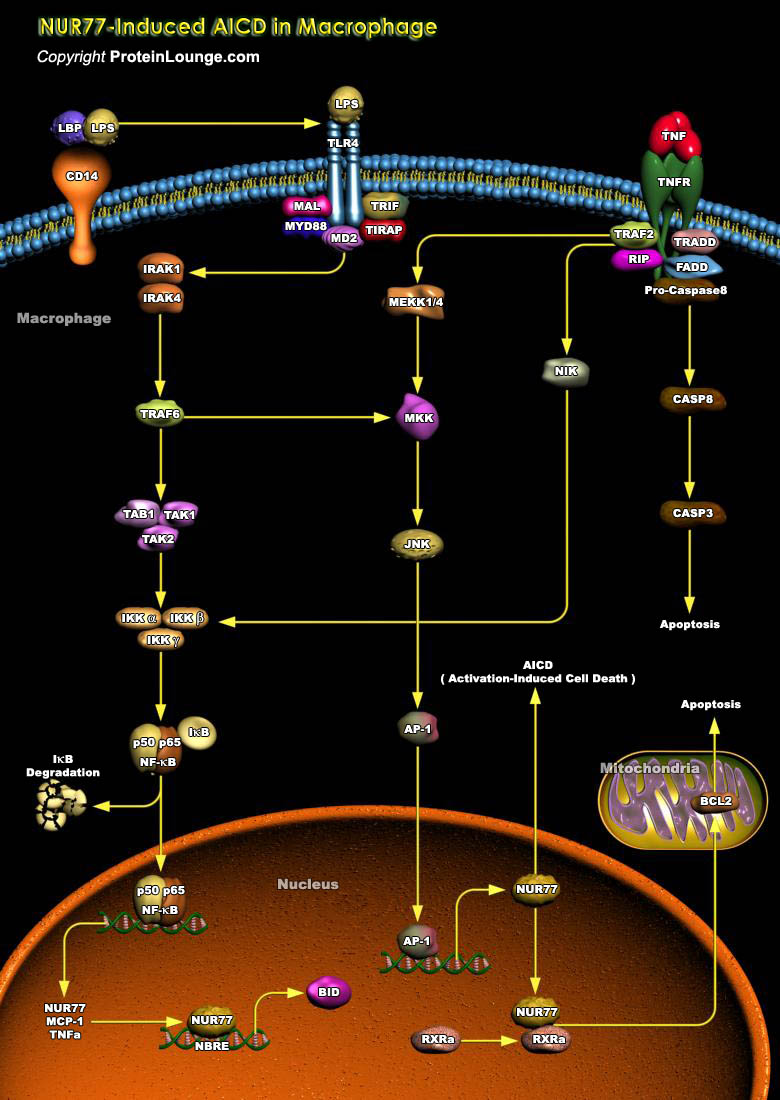
PCD (Programmed Cell Death) or Apoptosis, is a genetically regulated, self-destructive cellular process found in metazoans to eliminate individual cells when they are no longer needed in development, tissue remodeling, or immune regulation, as well as in various diseases. Macrophages are specialized phagocytes responsible for ingesting and digesting senescent,[..]
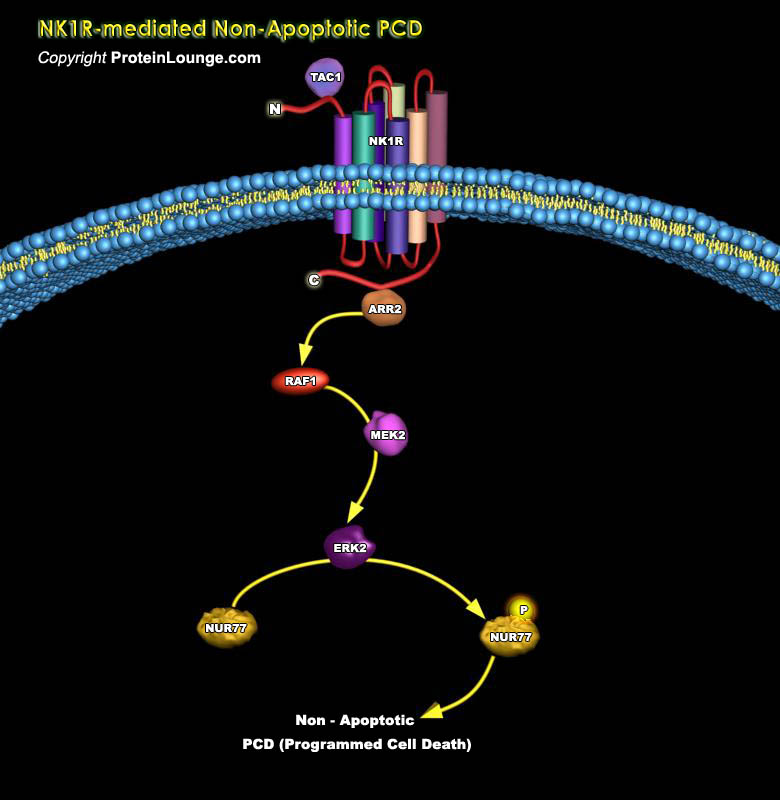
Cell death has been divided into two main types: PCD (Programmed Cell Death), in which the cell plays an active role, and Necrotic (passive) cell death. PCD is a form of cell death in which the cell plays an active role in its own demise. In contrast, Necrosis is characterized by swelling of the cell and its organelles; that results in disruption of the cell membrane and cell lysis. The PCD[..]
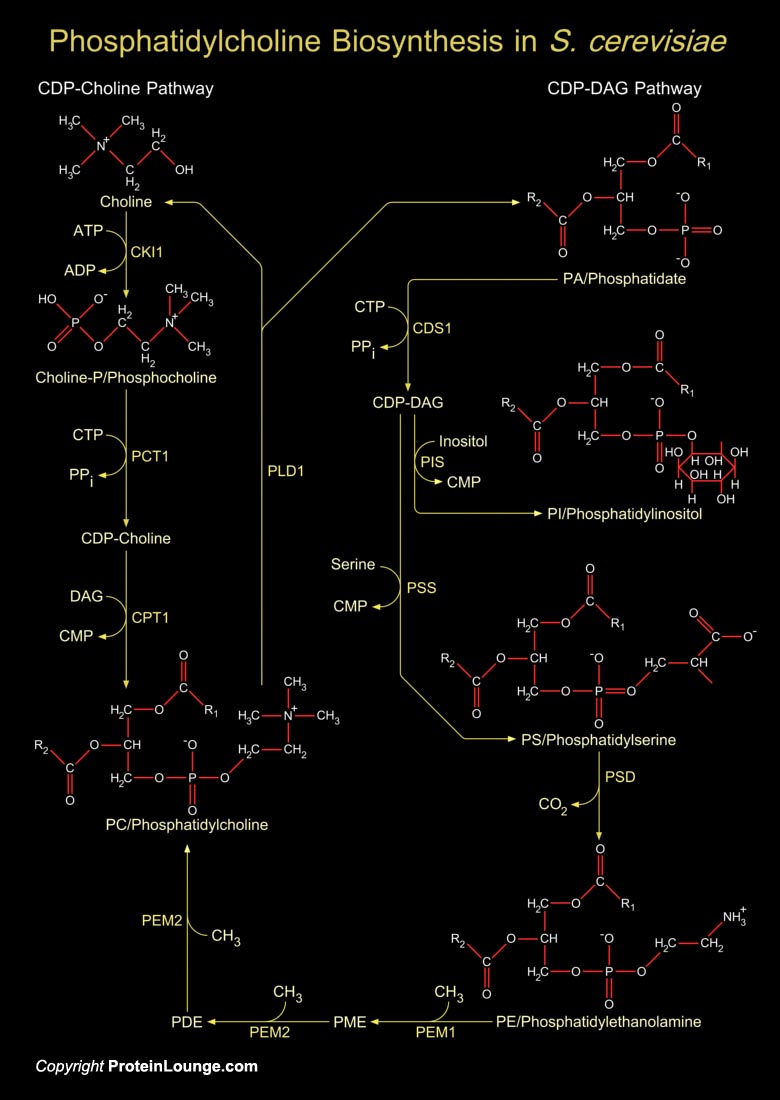
PC (Phosphatidylcholine) is the most abundant Phospholipid in the yeast S. cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and the major Phospholipid present in eucaryotic cell membranes. It serves as a major structural component of cellular membranes and as a source of several lipid messengers. There are two pathways for PC synthesis in yeast, the CDP-Choline (Cytidine[..]