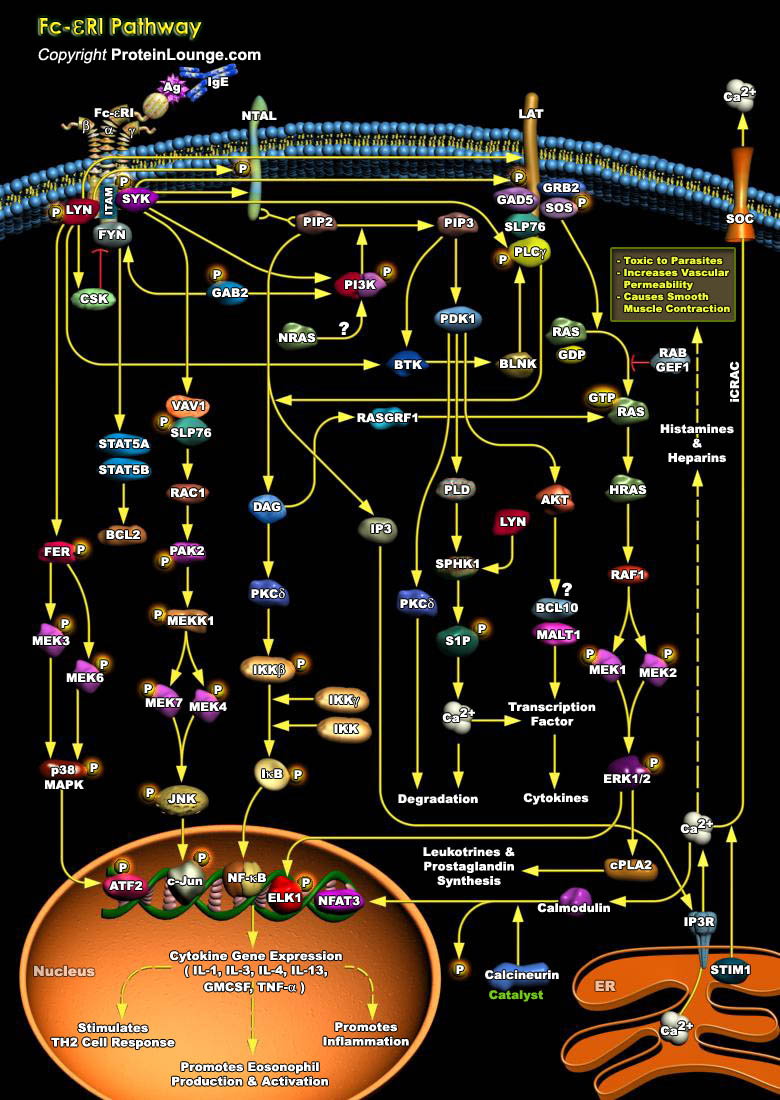
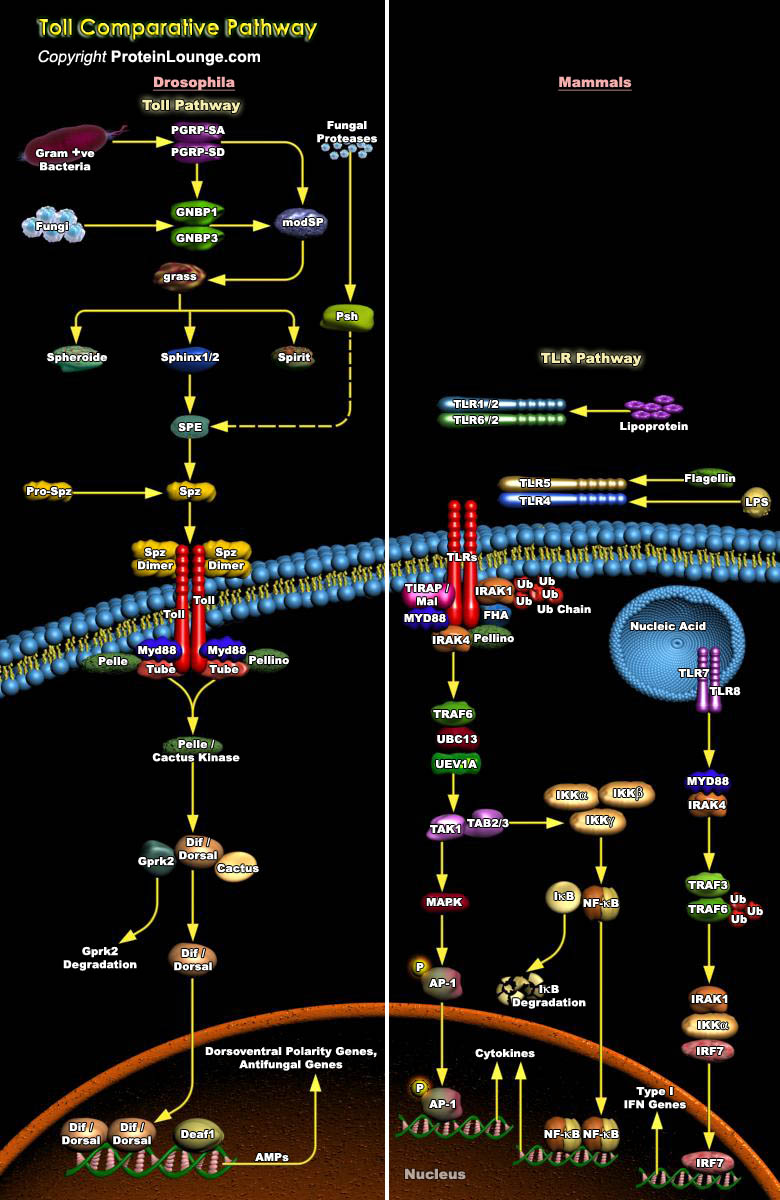
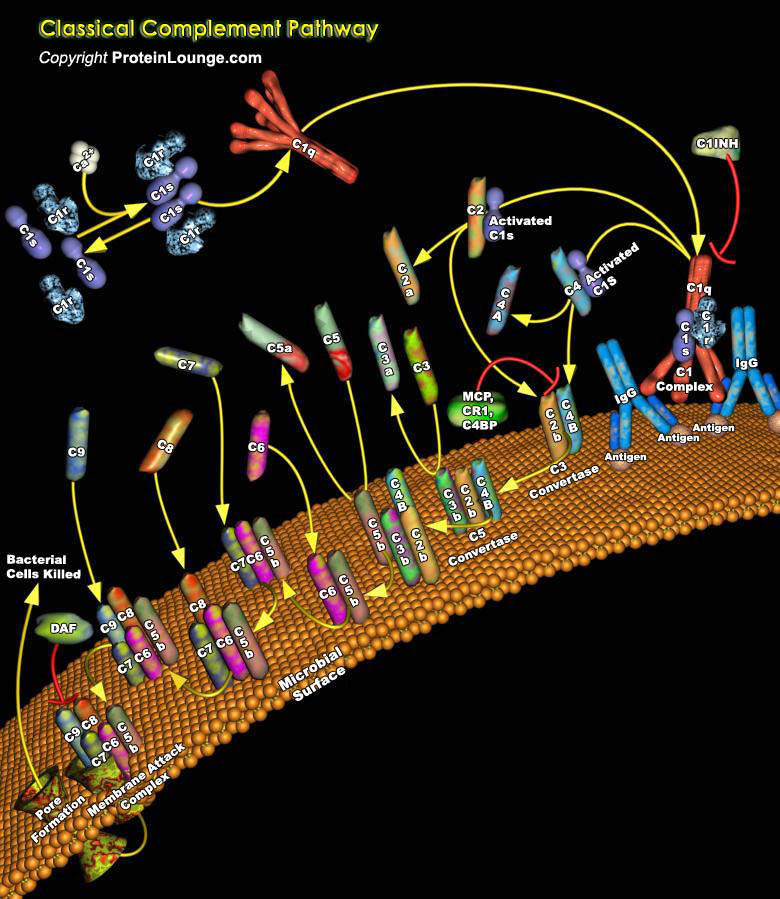
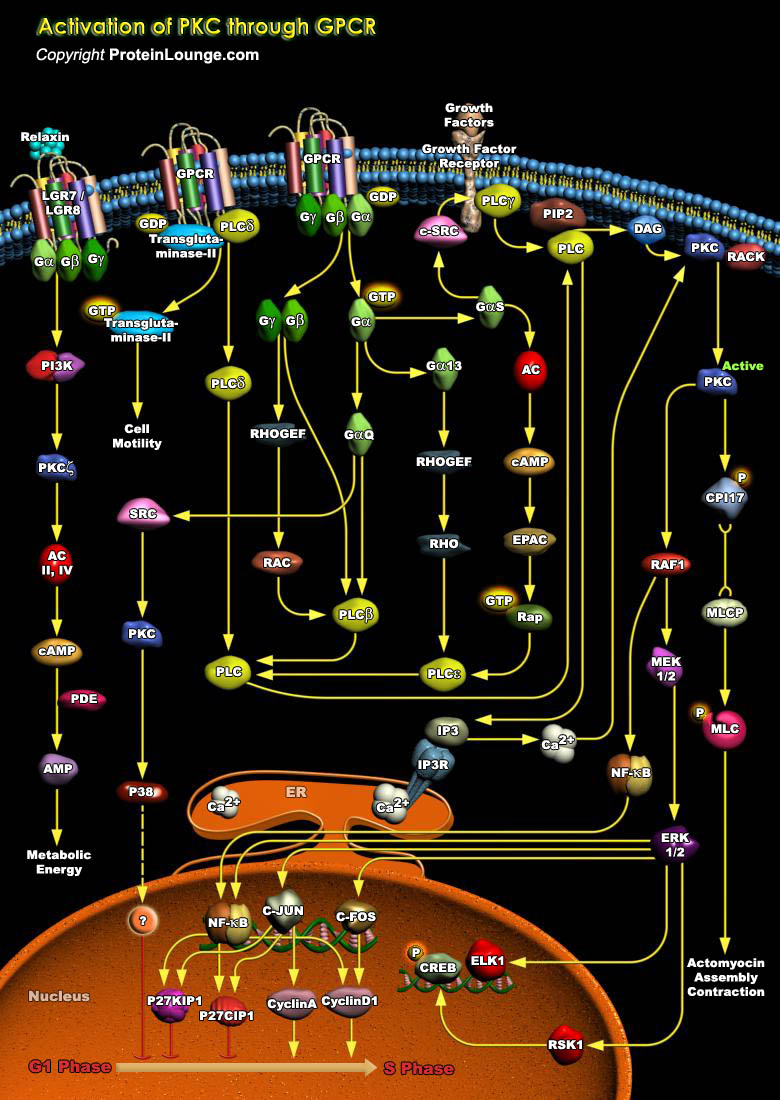
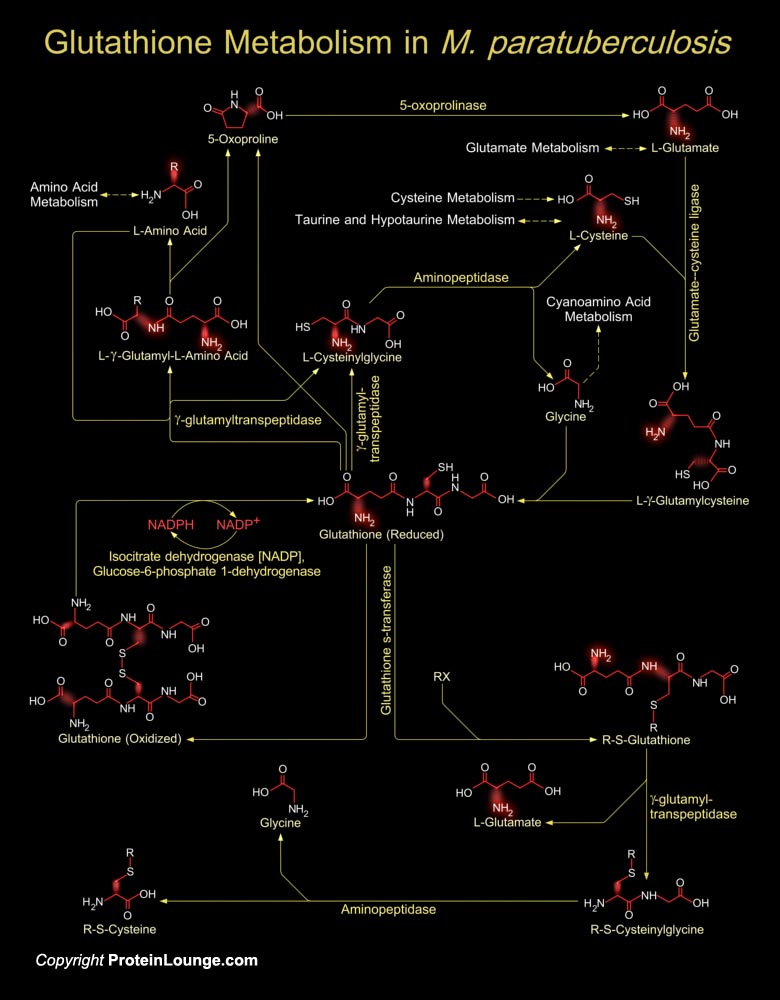
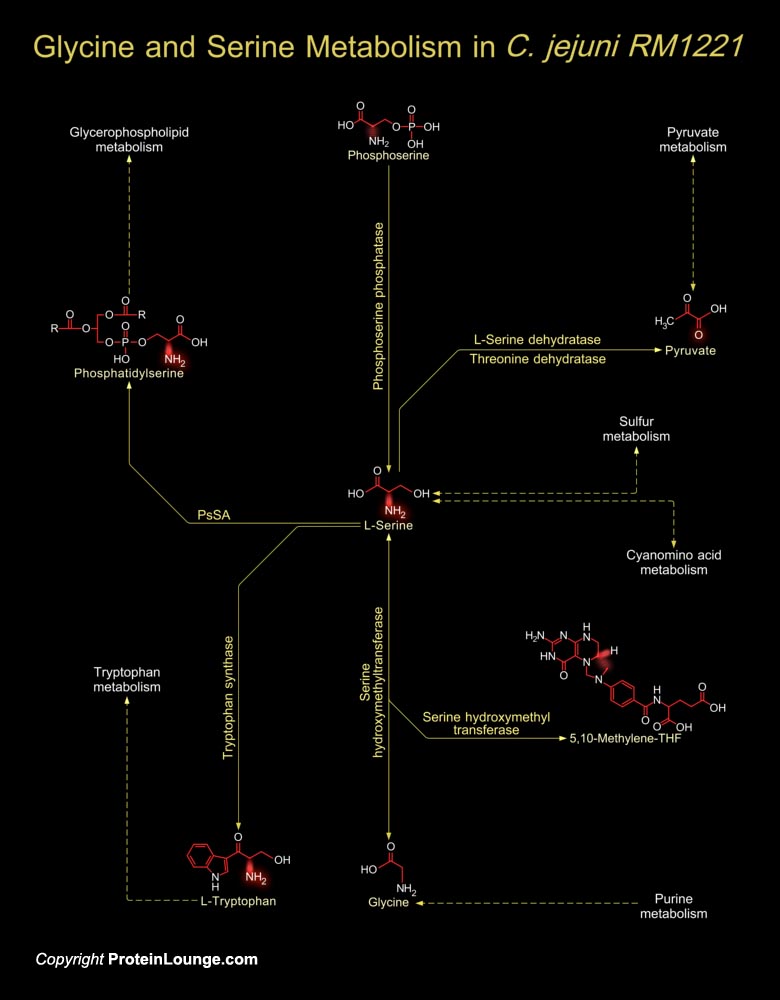
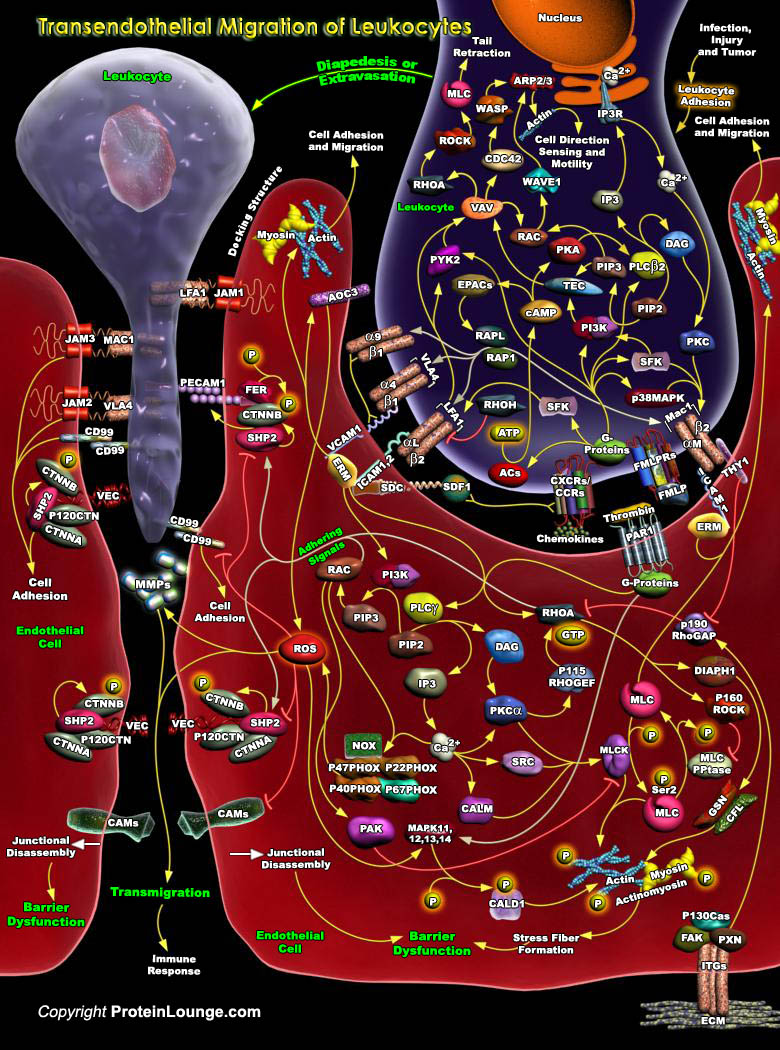
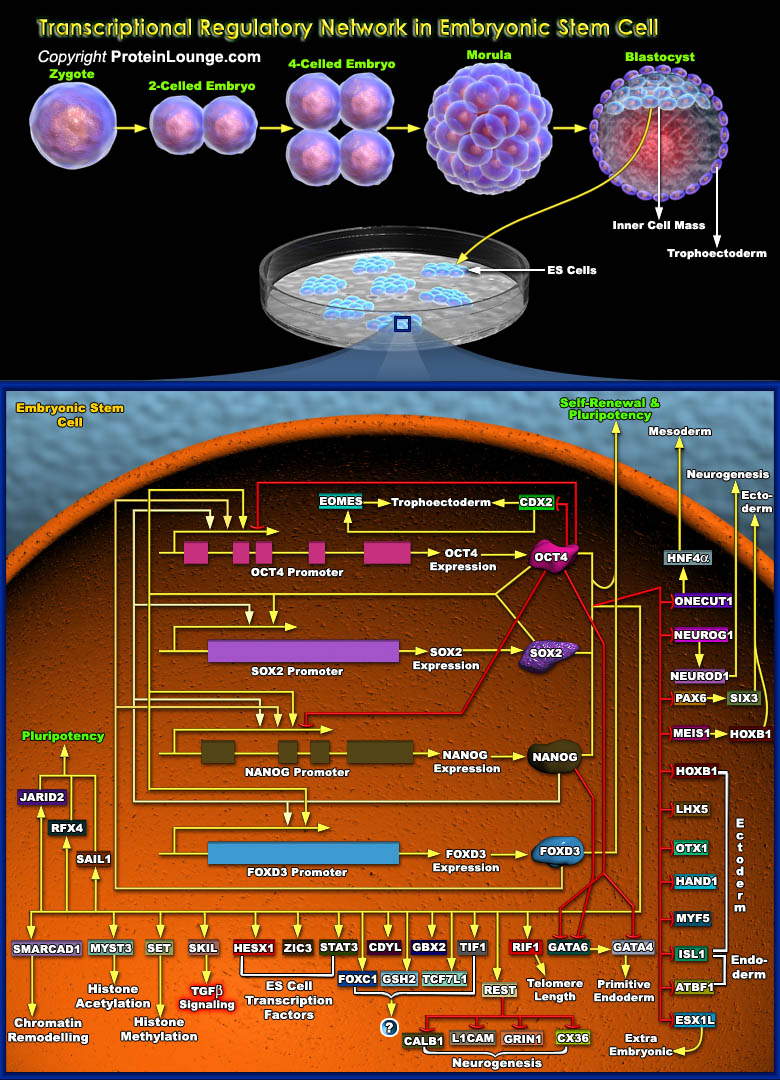
Featured Pathways
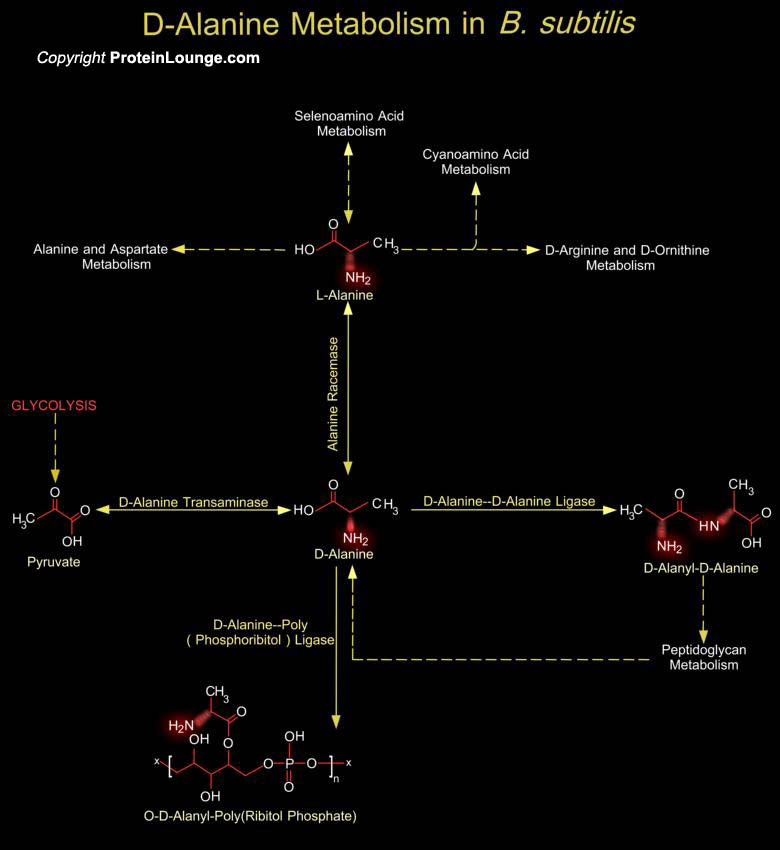
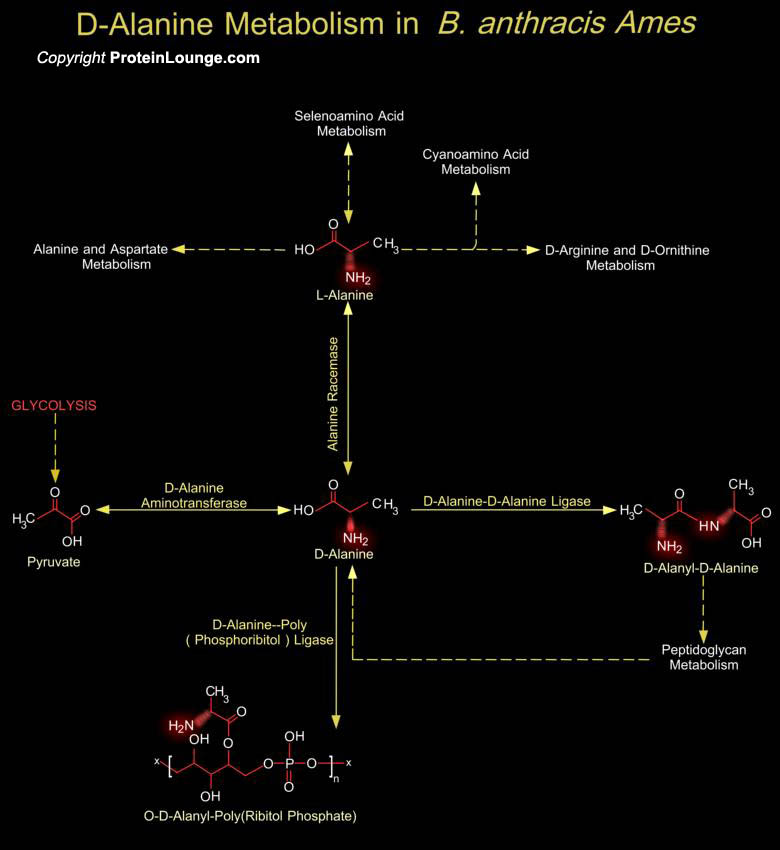
Bacilli are an extremely diverse group of bacteria that include both the causative agent of anthrax (Bacillus anthracis) as well as several species that synthesize important antibiotics. Bacilli are rod-shaped, Gram-positive, sporulating, aerobes or facultative anaerobes. Bacilli exhibit an array of physiologic abilities that allow them to live in a wide range of habitats, including many[..]
Bacilli are rod-shaped, Gram-positive, sporulating, aerobes or facultative anaerobes. Bacilli exhibit an array of physiologic abilities that allow them to live in a wide range of habitats, including many extreme habitats such as desert sands, hot springs, and Arctic soils. Species in the genus Bacillus can be thermophilic, psychrophilic, acidophilic, alkaliphilic, halotolerant, or halophilic[..]
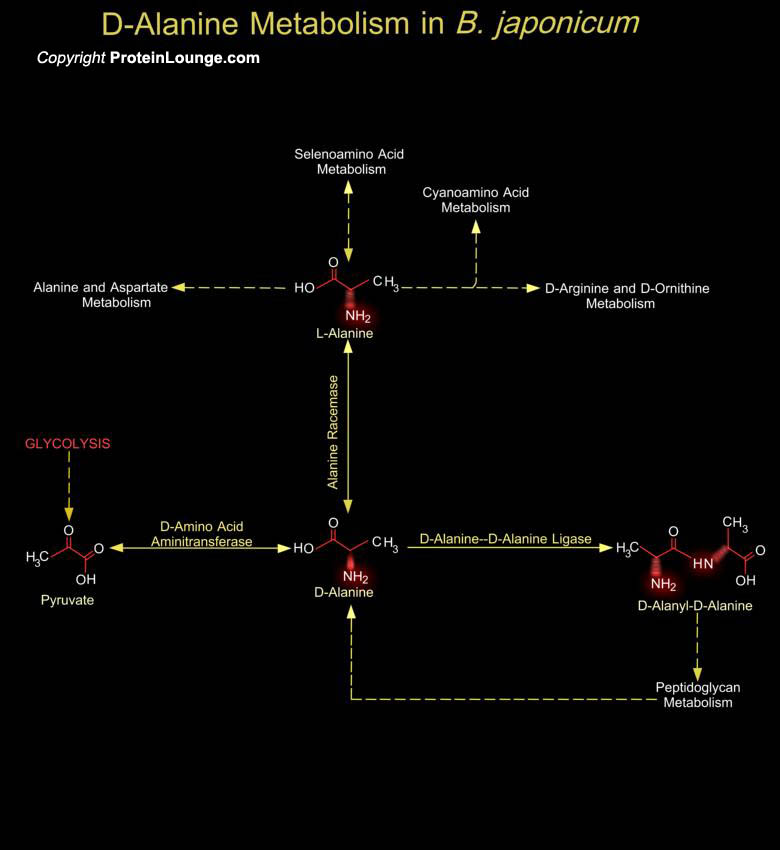
Rhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Sinorhizobium and Azorhizobium-known as Rhizobia-are Gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing bacteria of agronomic importance because they perform nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with leguminous plants. They are responsible for the world’s largest portion of fixed atmospheric nitrogen. Bradyrhizobium japonicum(B. japonicum) has been used since 1957 in[..]
Brucella is a Gram-negative aerobic pathogen that is distringuished from most other pathogens because it does not have "obvious virulence factors" like capsules, fimbriae, flagella, exotoxins, exproteases, or other exoenzymes, cytolysins, resistance forms, antigenic variation, plamids, or lysogenic phages. Brucella sp. causes a "zoonotic disease endemic in many[..]
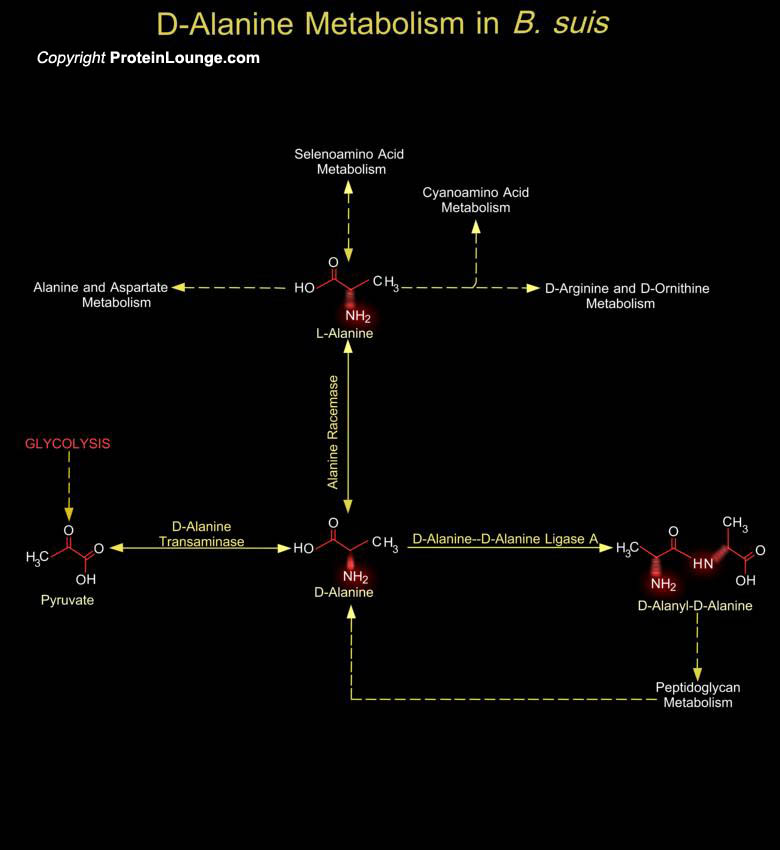
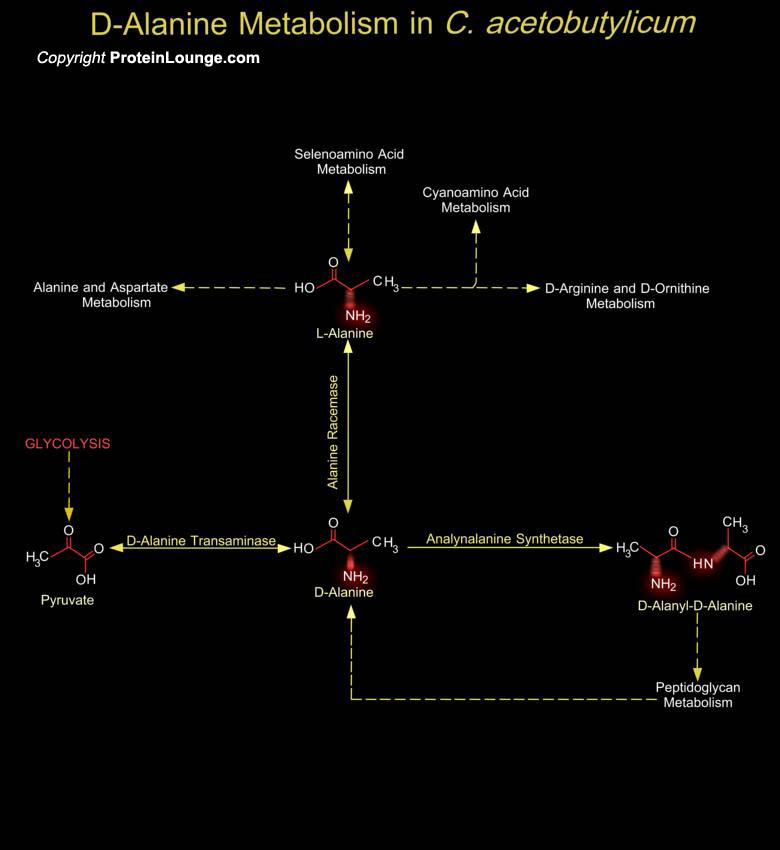
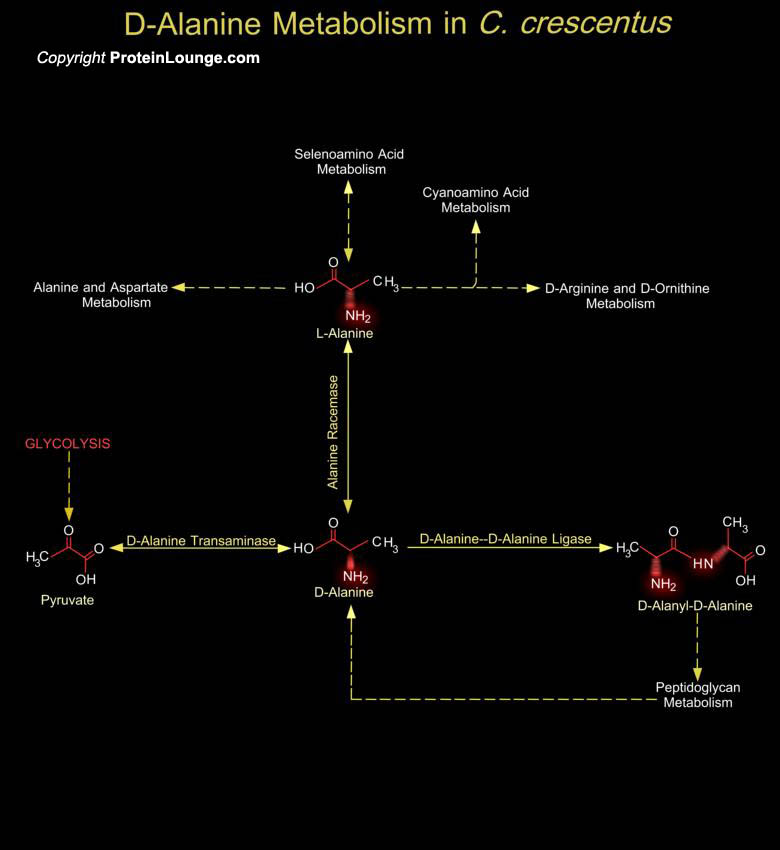
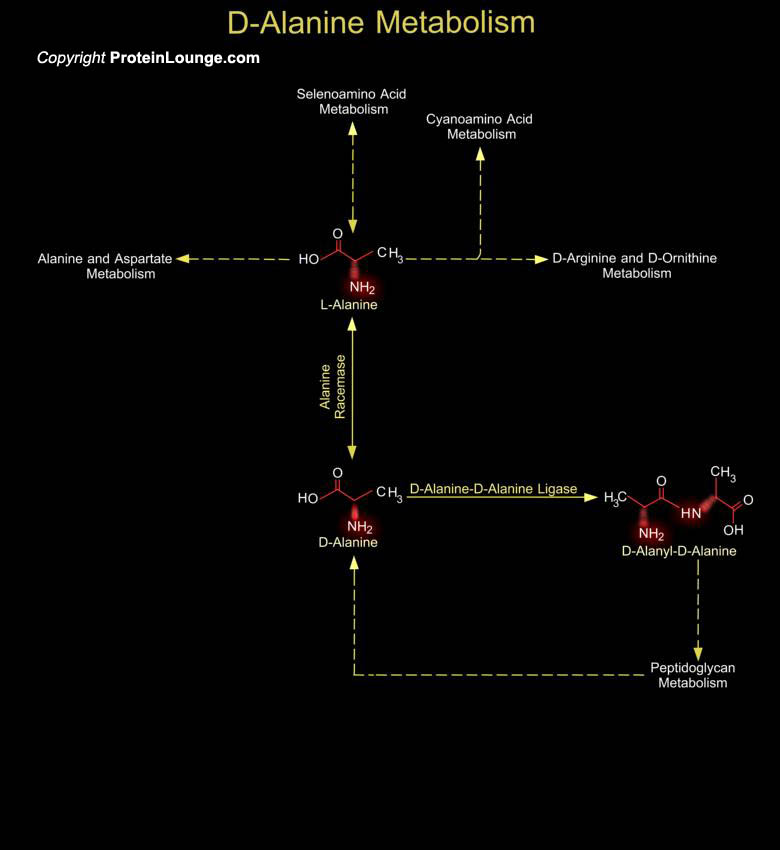
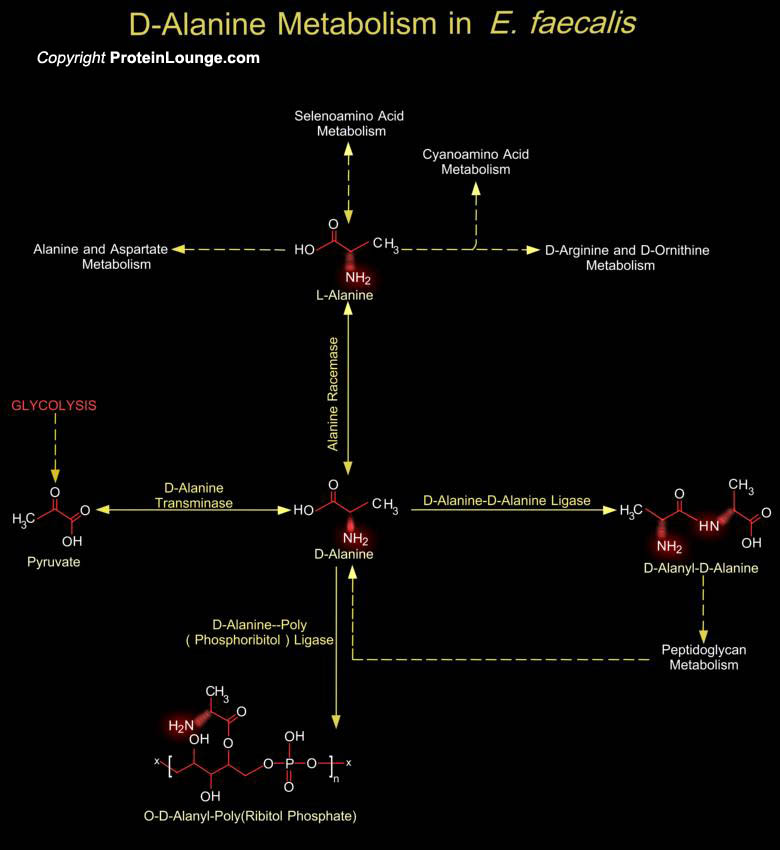
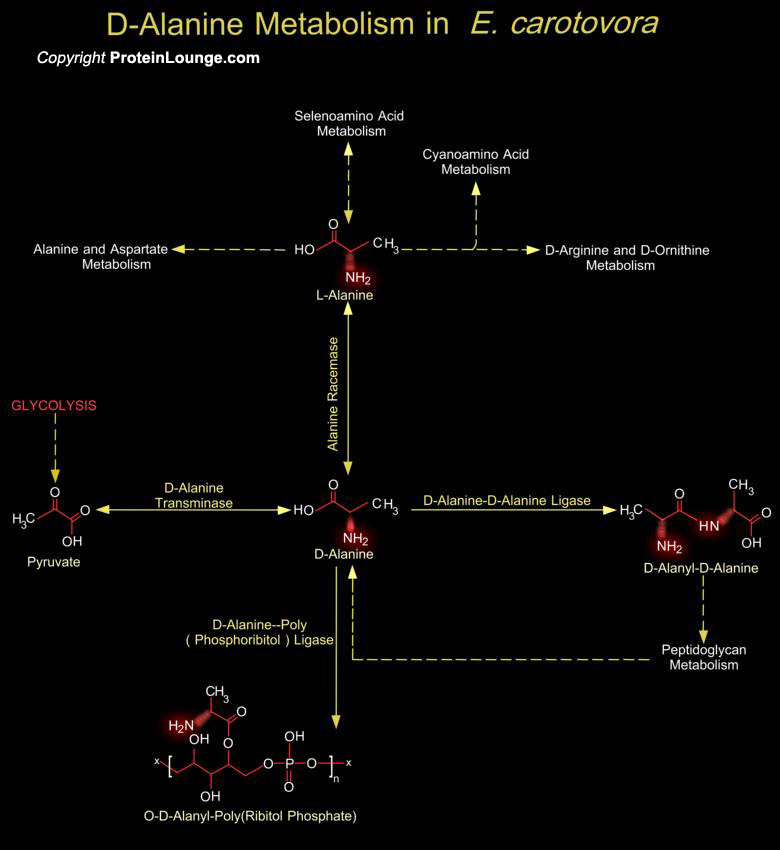
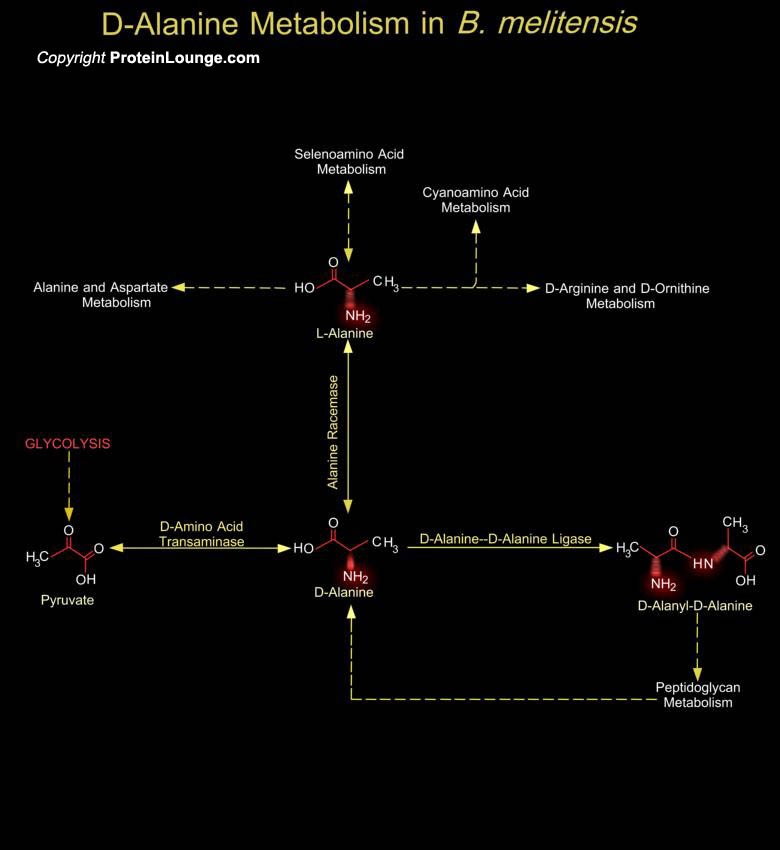
The bacterial cell wall is a unique biopolymer, containing both D- and L-Amino acids. Its basic structure is a carbohydrate backbone of alternating units of N-Acetyl Glucosamine and N-Acetyl Muramic Acid. The N-Acetyl Muramic Acid residues are cross-linked with oligopeptides. The terminal peptide is D-Alanine although other amino acids are present as D- isomers and this is the only known[..]