Featured Pathways
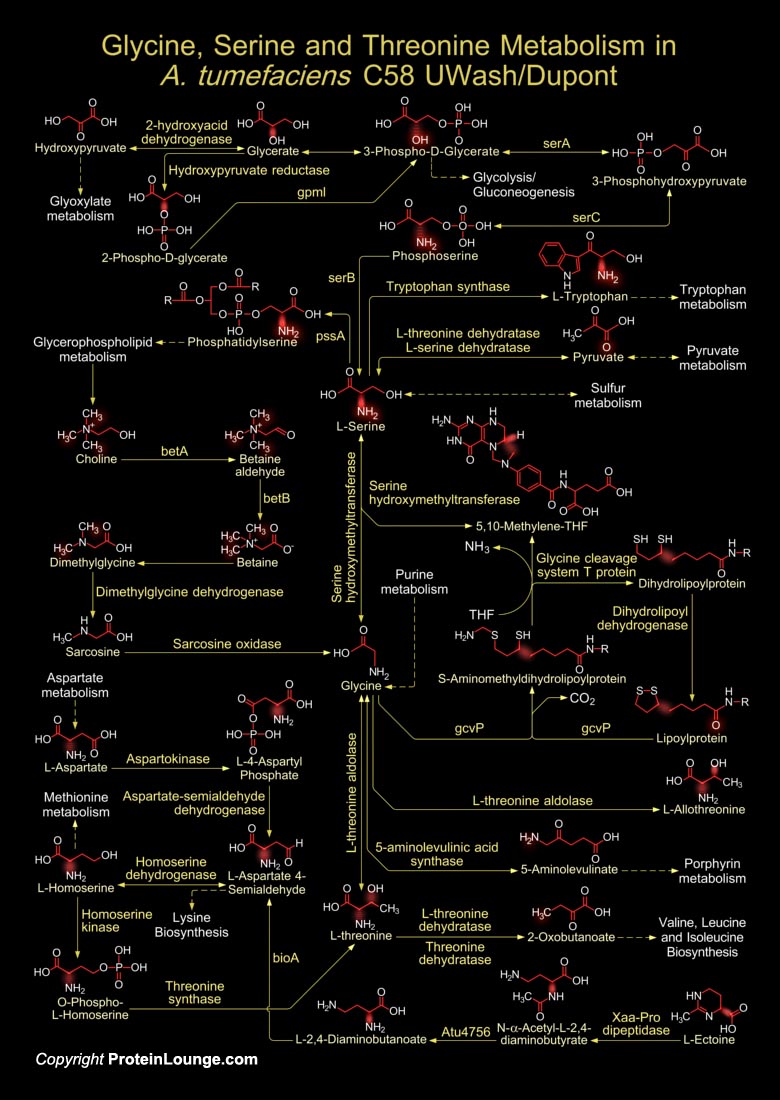
A. tumefaciens (Agrobacterium tumefaciens) is a species of bacteria that causes tumors (commonly known as ‘Galls’ or ‘Crown Galls’) in dicots. This Gram-negative bacterium form Crown Gall by inserting a small segment of DNA (known as the T-DNA, for ‘Transfer DNA’) into the plant cell, which is incorporated at a semi-random location into the[..]
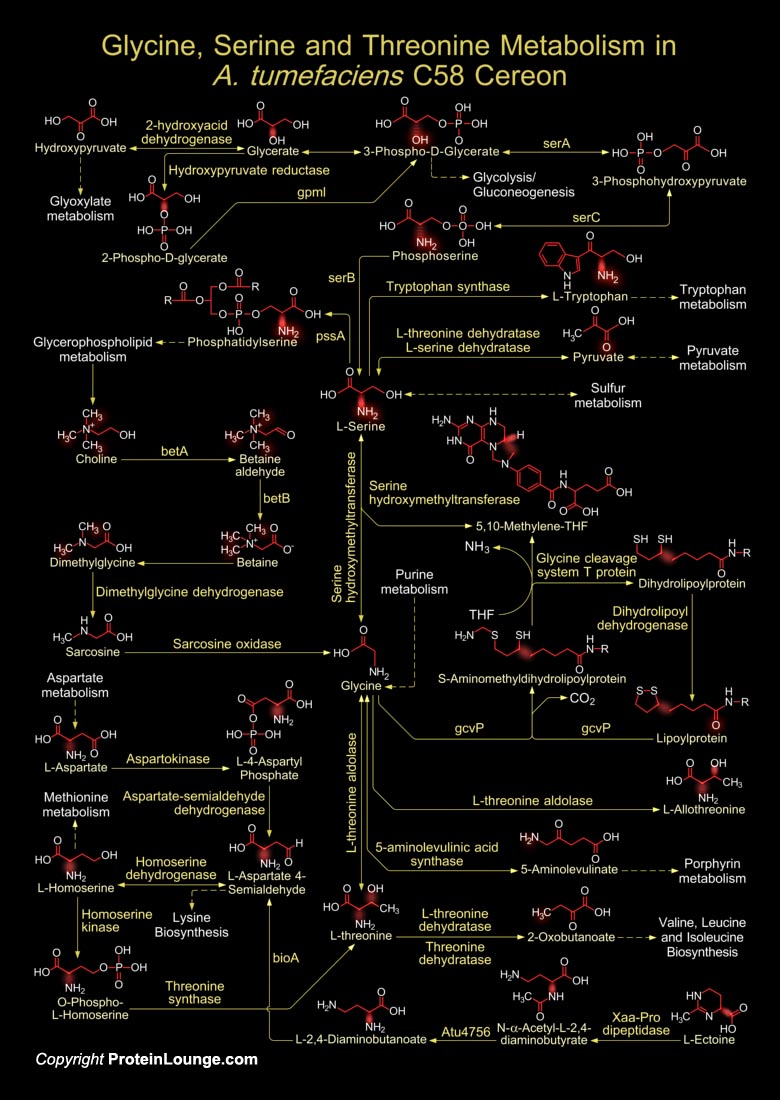
A. tumefaciens (Agrobacterium tumefaciens) is a plant pathogen with the unique ability to transfer a defined segment of DNA to eukaryotes, where it integrates into the eukaryotic genome. It is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes tumors commonly known as ‘Galls’ or ‘Crown Galls’ in dicots. Crown Gall is formed by inserting a small segment of DNA[..]
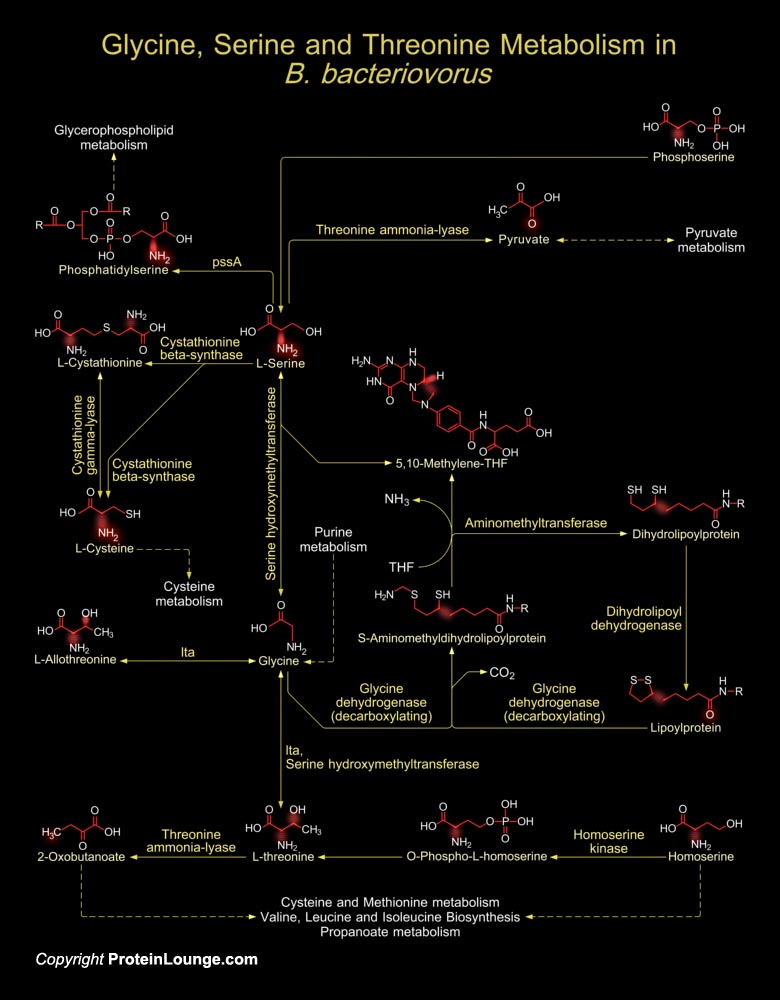
Members of the bacterial genus Bdellovibrio are obligately predacious upon other Gram-negative bacteria. Bdellovibrio are ubiquitous in nature and their prey includes plant, animal, and human pathogens. Despite the small dimensions of Bdellovibrio cells, its genome consists of 3,782,950 base pairs on a single circular chromosome. B. bacteriovorus[..]
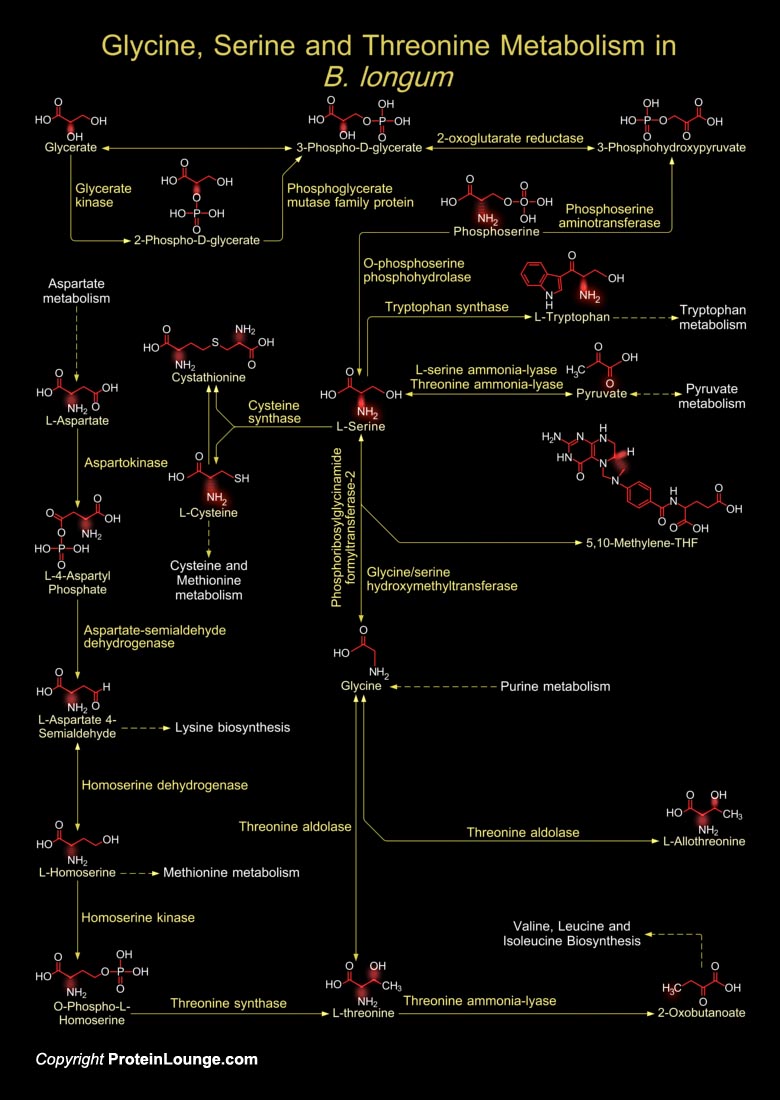
B. longum (Bifidobacterium longum) is among the first colonizers of the sterile digestive tract of newborns and predominate in breast-fed infants. Bifidobacteria including B. longum are Gram-positive, anaerobic and branched rod-shaped bacteria that naturally colonize in the human gastrointestinal tract and vagina. These are beneficial bacteria that[..]
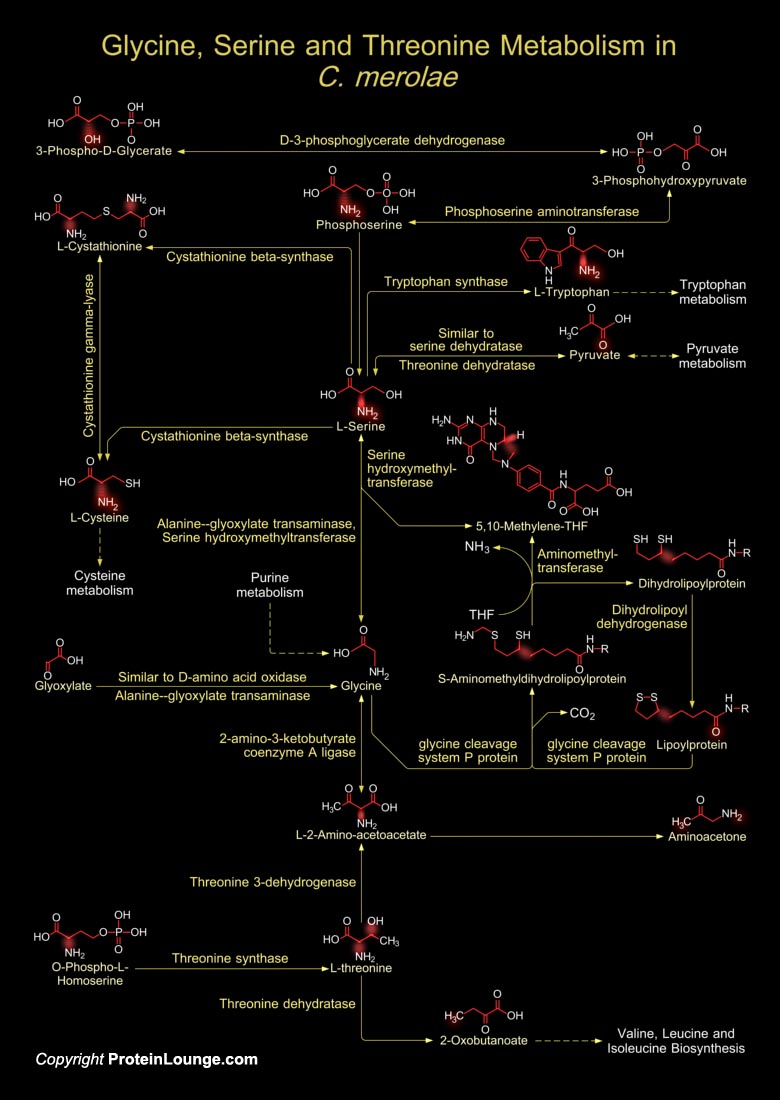
The Cyanidiophyceae, including C. merolae (Cyanidioschyzon merolae), are a basal clade within the red lineage plastids. The red algae are thought to be one of the basal eukaryotic lineages, and may possess ancestral features of eukaryotic phototrophs. C. merolae is the first species of algae to be sequenced; the organism consists of a single cell that has three[..]
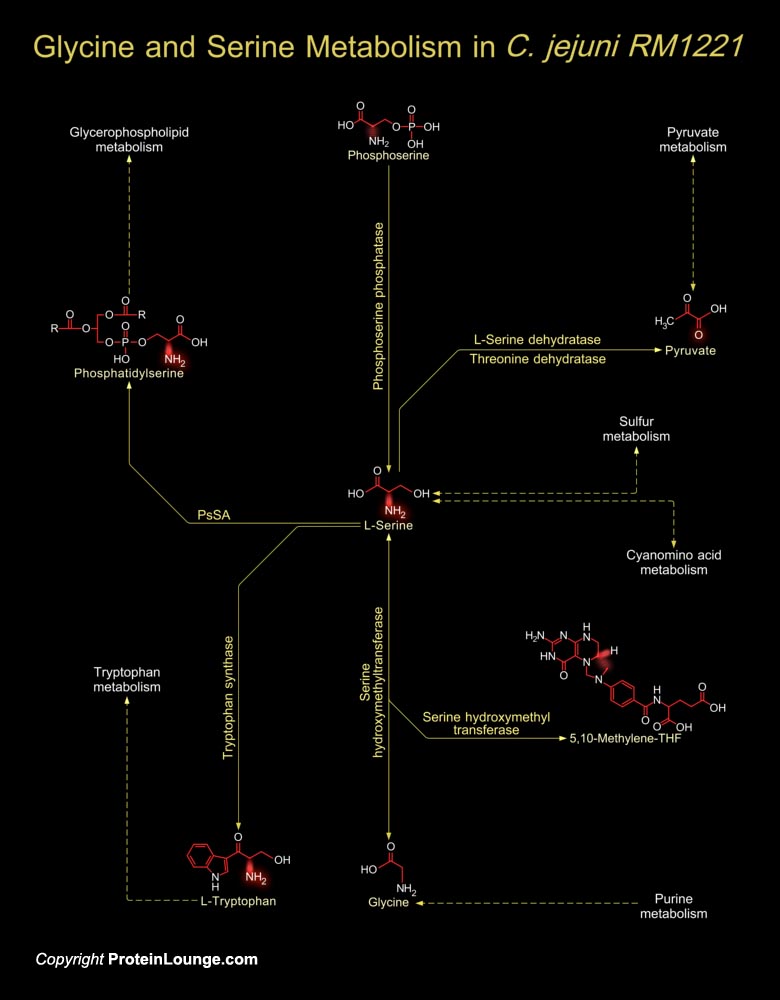
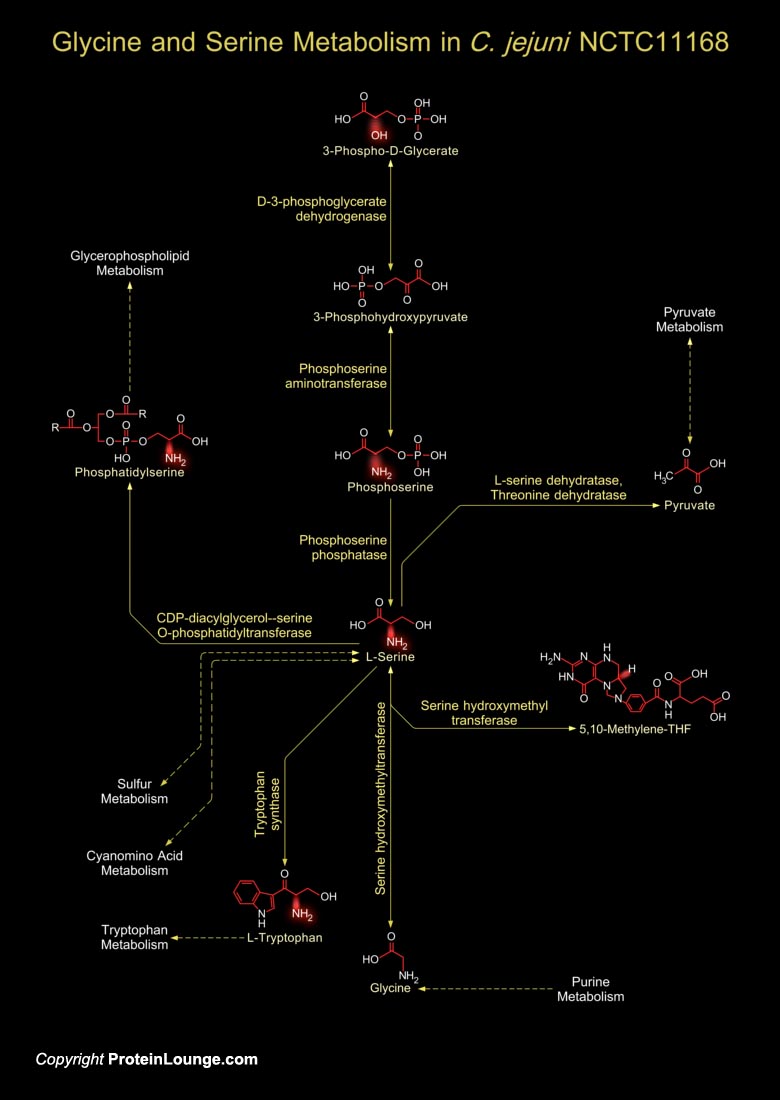
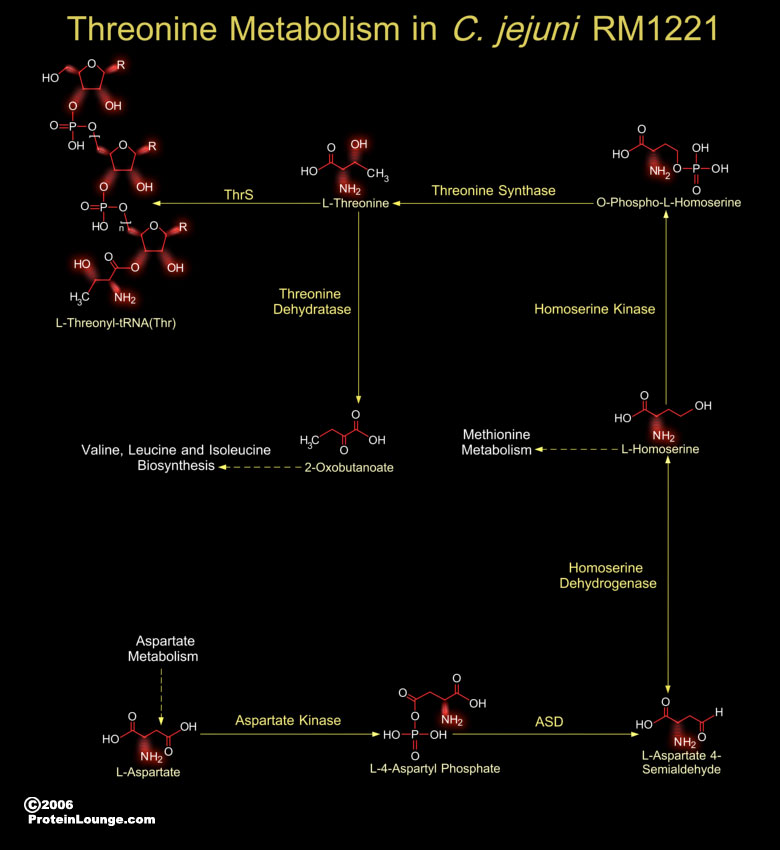
The genome of C. jejuni RM1221 (Campylobacter jejuni RM1221) is a single circular chromosome, 1,777,831 bp in length, with an average G+C content of 30.31 percent. There are a total of 1,884 predicted coding regions in the genome with an average ORF (Open Reading Frame) length of 885 bp. The genomic structure of C. jejuni RM1221 is syntenic with the genome of C.[..]
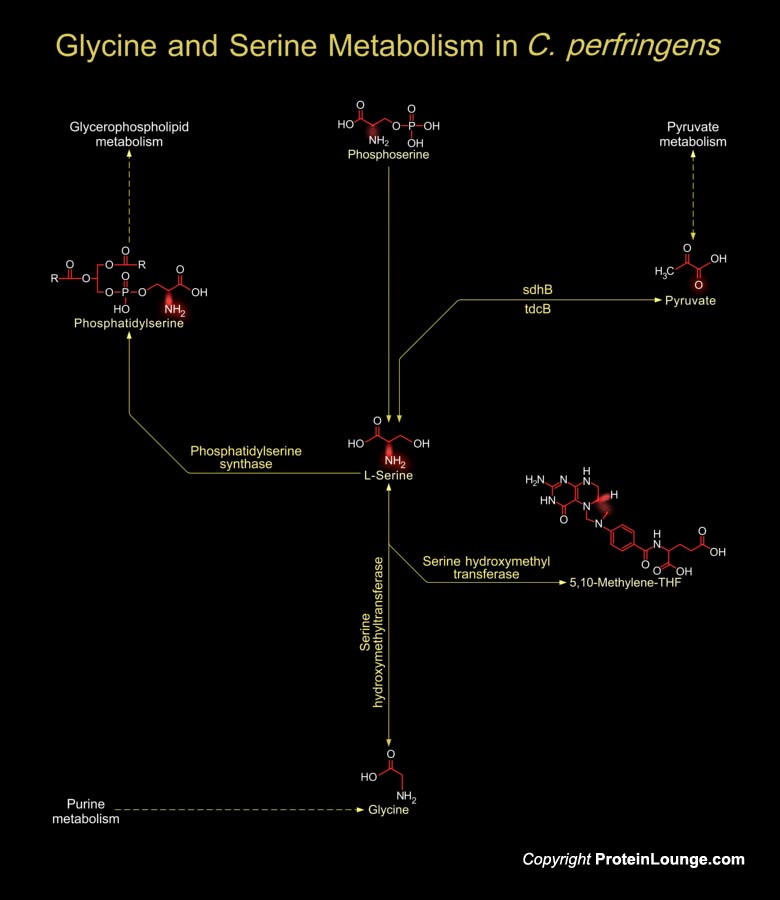
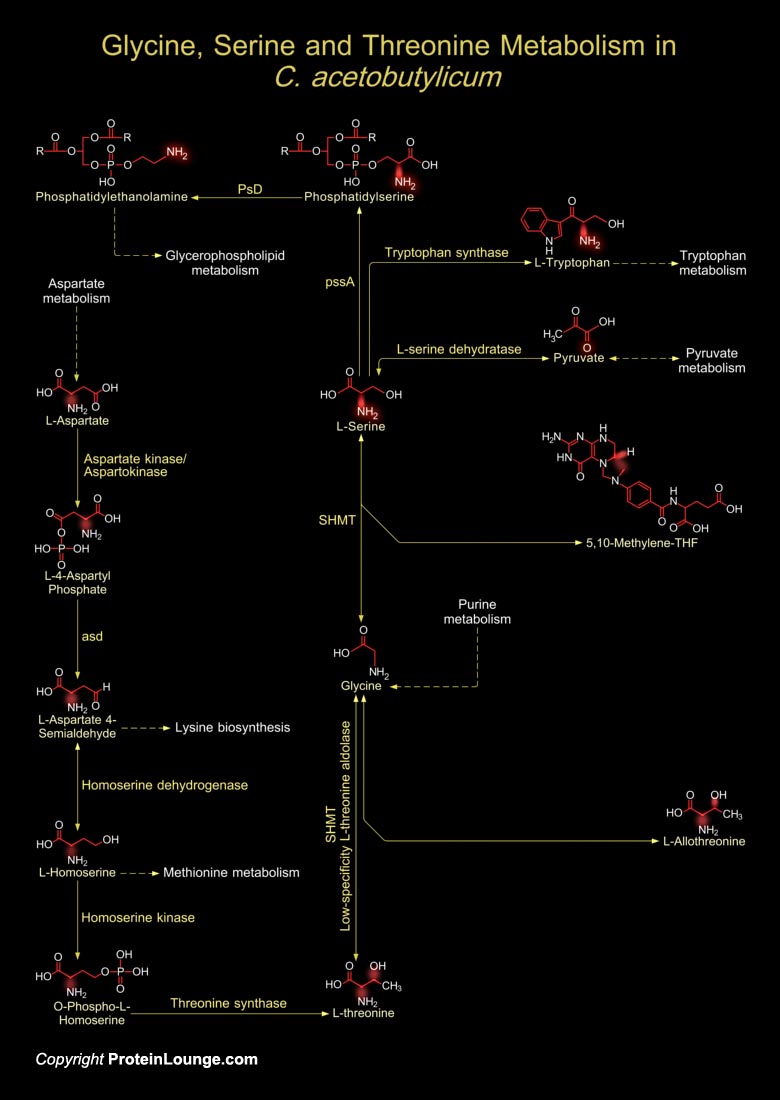
Members of genus Clostridium are Gram-positive, spore-forming rods that are anaerobic. These bacteria includes both motile and non-motile bacillus with ubiquitous distribution in nature and are especially fond of soil. Clostridium shows optimimum growth when plated on blood agar at human body temperatures. When the environment becomes stressed, however, the bacteria produce[..]
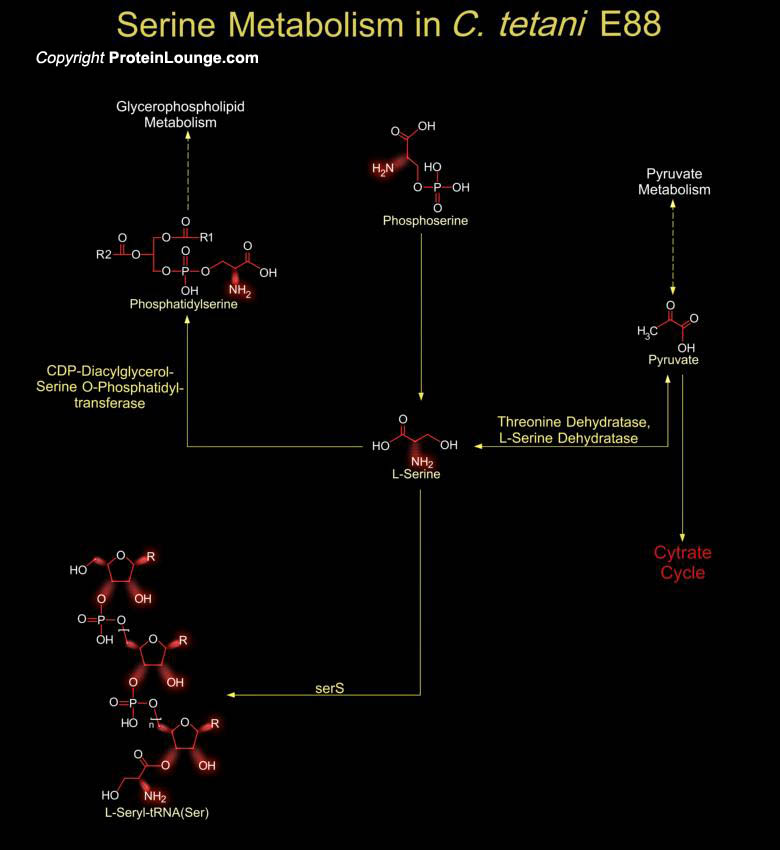
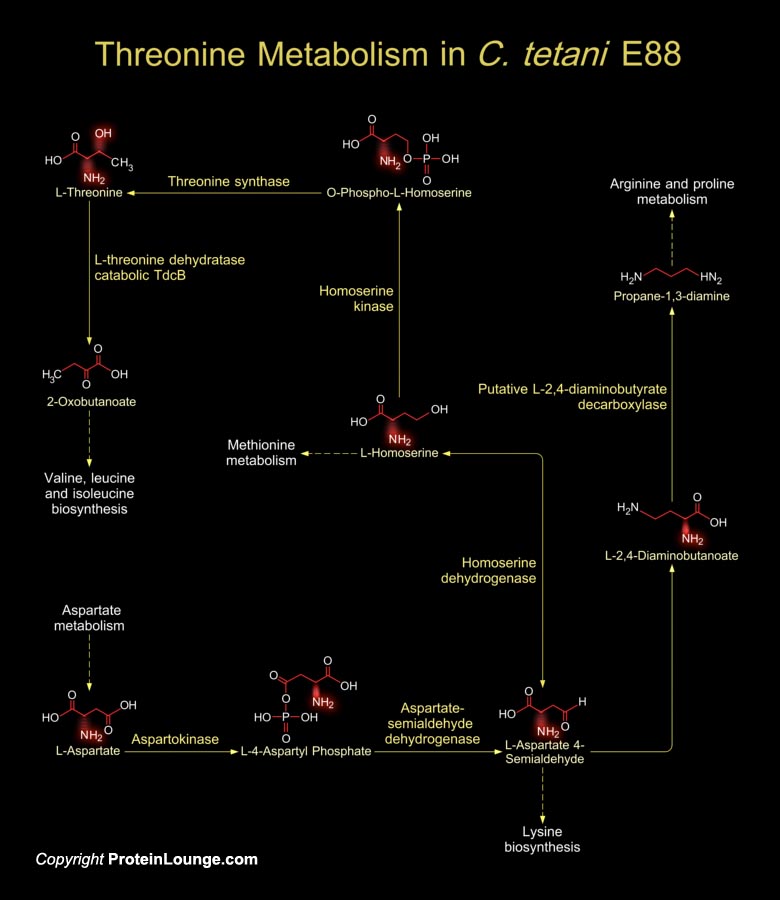
Tetanus disease is one of the most dramatic and globally prevalent diseases of humans and vertebrate animals. The manifestation of the disease, spastic paralysis, is caused by the second most poisonous substance known, the Tetanus toxin (Ref.1). The causative agent of Tetanus disease is C. tetani (Clostridium tetani), an anaerobic Gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium, whose[..]