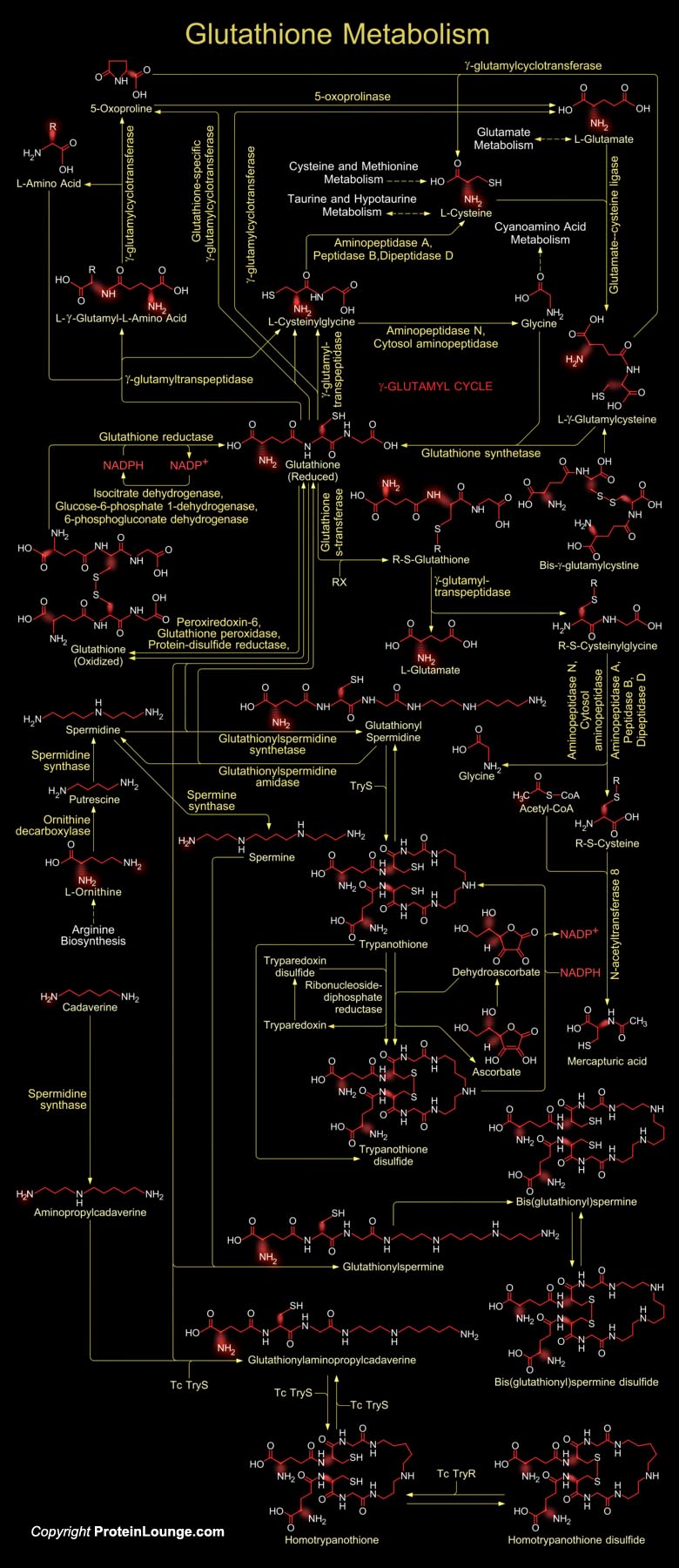
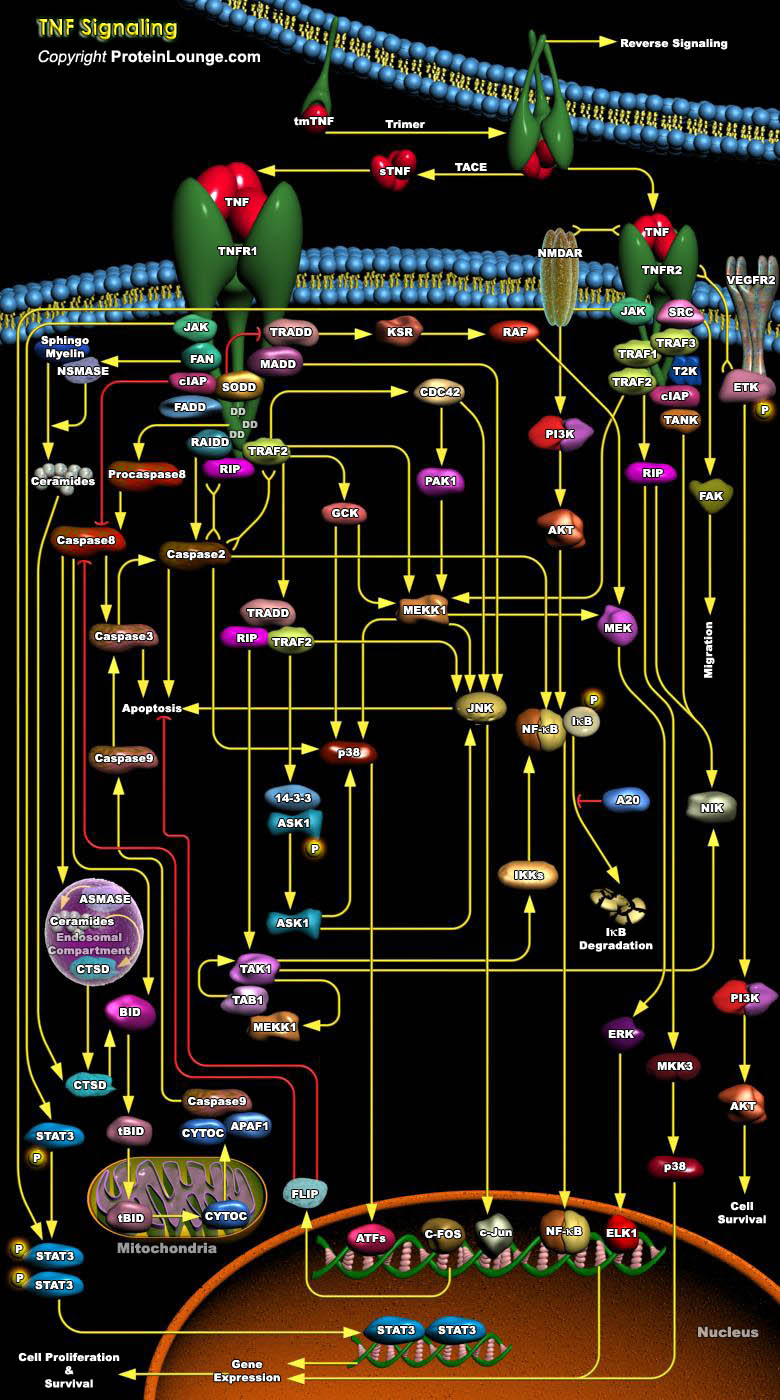
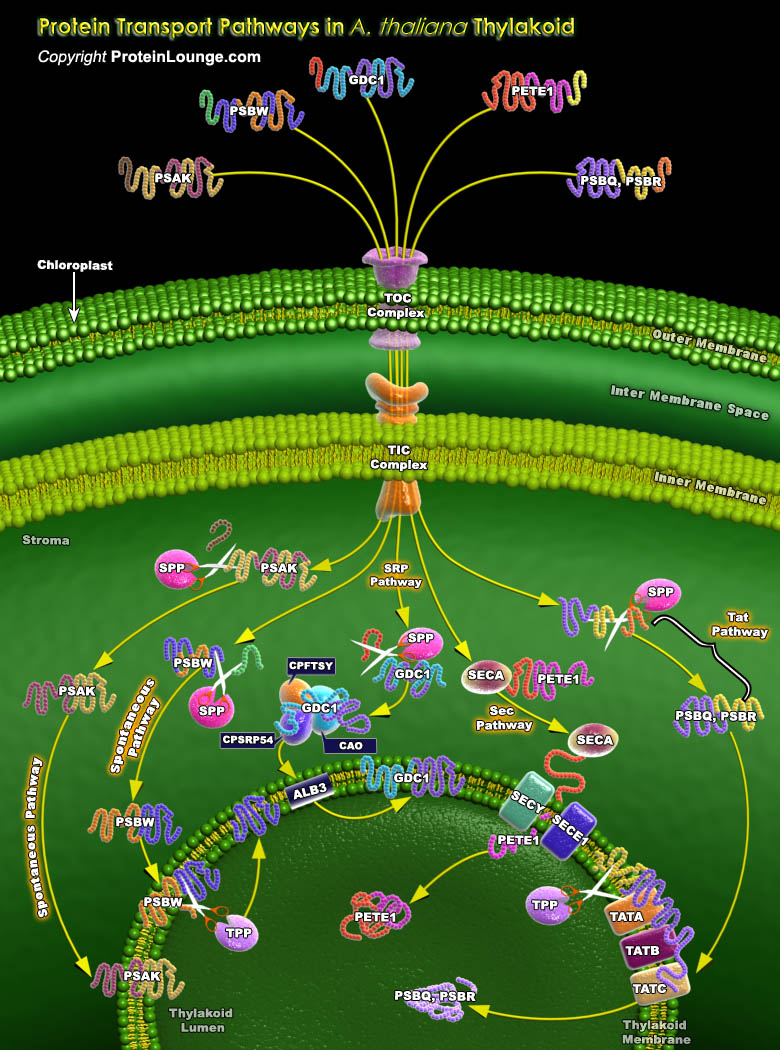
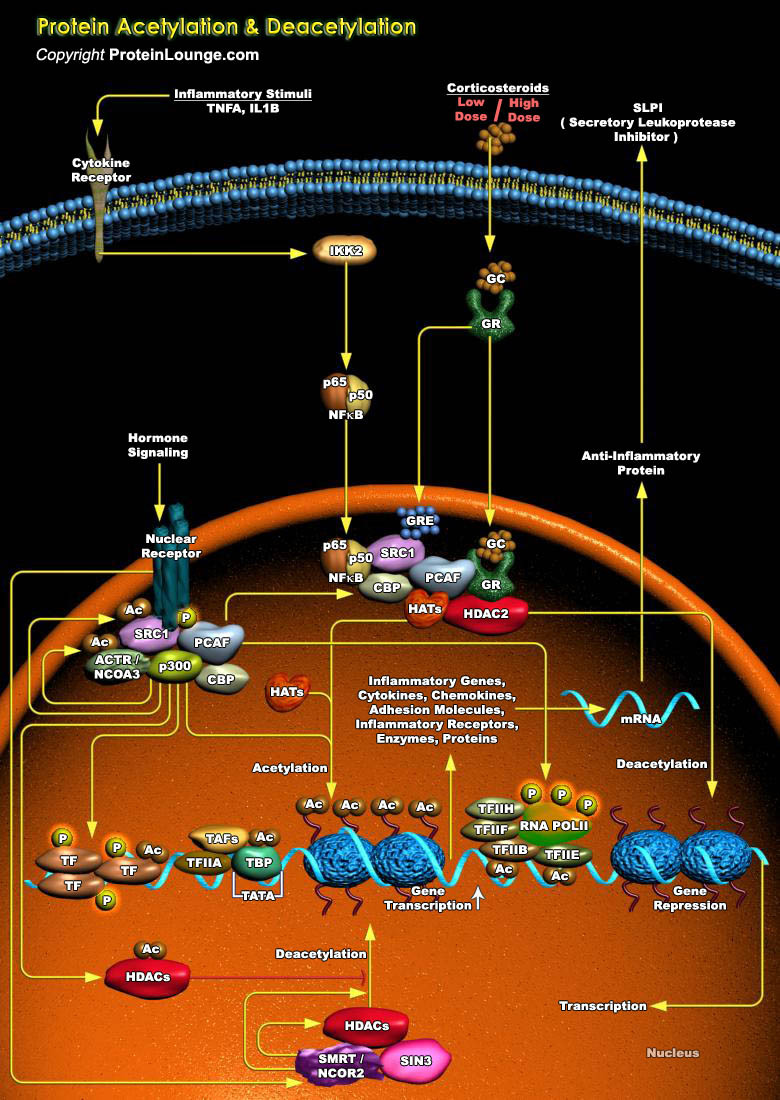
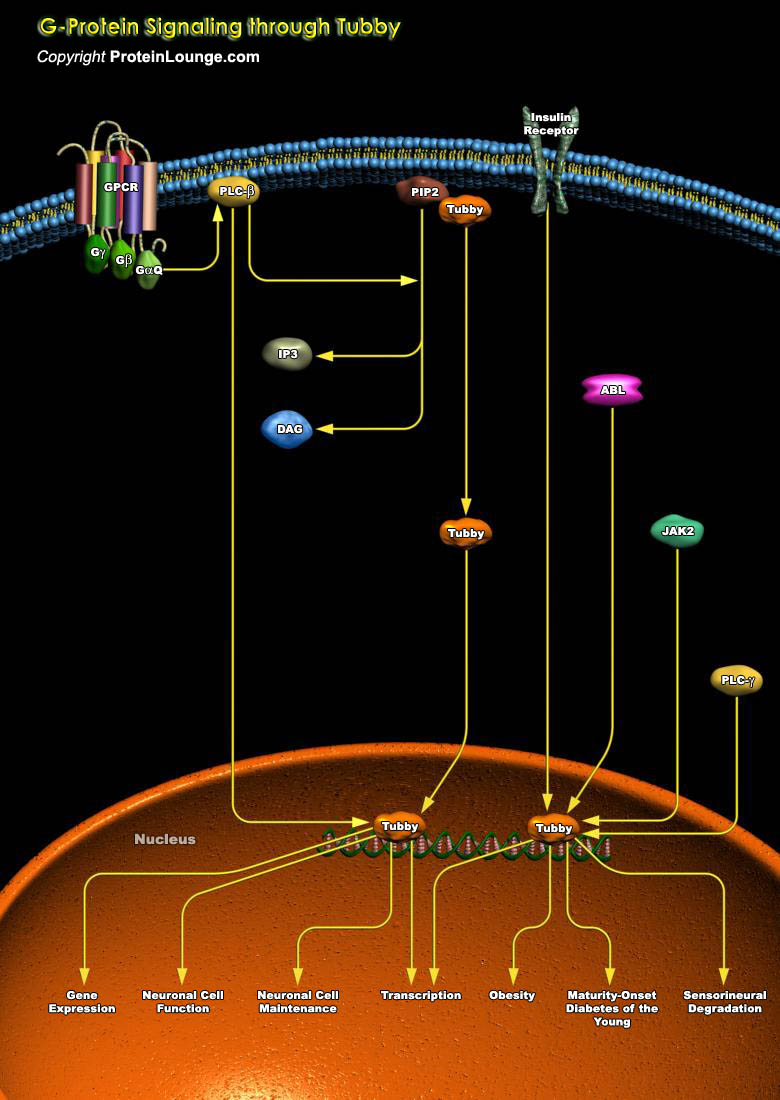
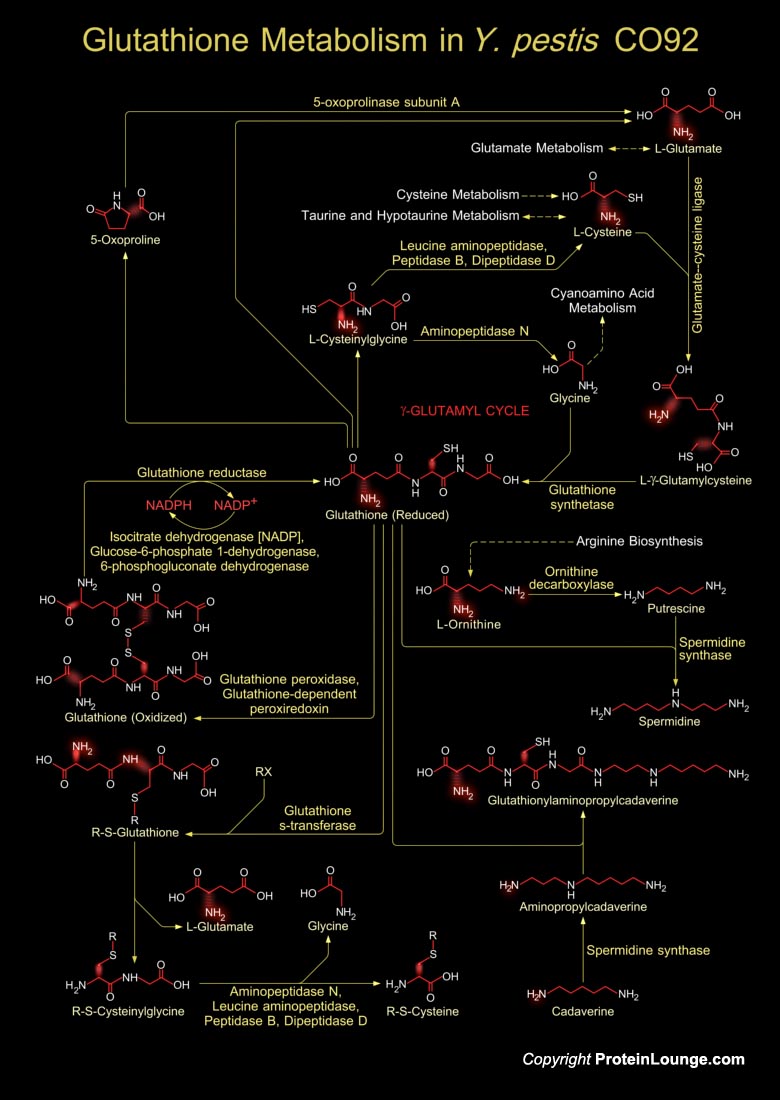
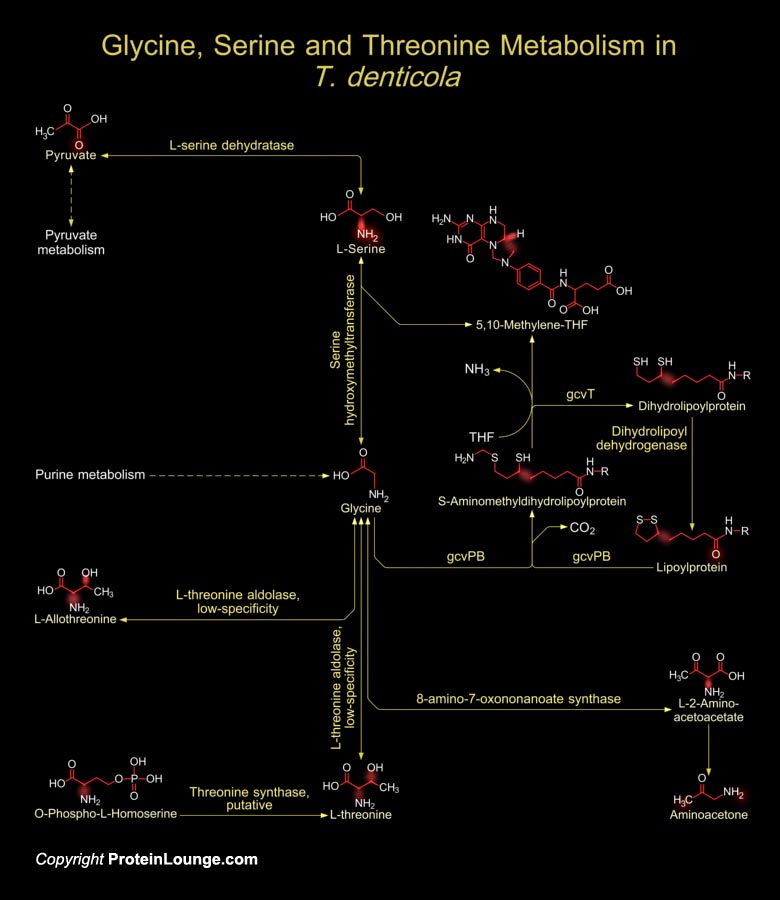
Featured Pathways
.jpg)
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease characterized by high blood glucose levels that requires long-term medical attention both to limit the development of its devastating complications and to manage them when they do occur. The pancreatic Beta-cell and its secretory product insulin are central in the pathophysiology of diabetes. There are two main types of diabetes, Type-I, which is insulin[..]

Poliovirus is a member of the Picornaviridae family, which includes a number of significant pathogens of humans (e.g., Rhinoviruses, Coxsackieviruses, Echoviruses, Enteroviruses, and Hepatitis-A virus) and livestock (e.g., foot-and-mouth disease viruses). Poliovirus has three known serotypes: PV1, PV2, and PV3 and all three serotypes can cause poliomyelitis, a paralytic disease resulting from[..]
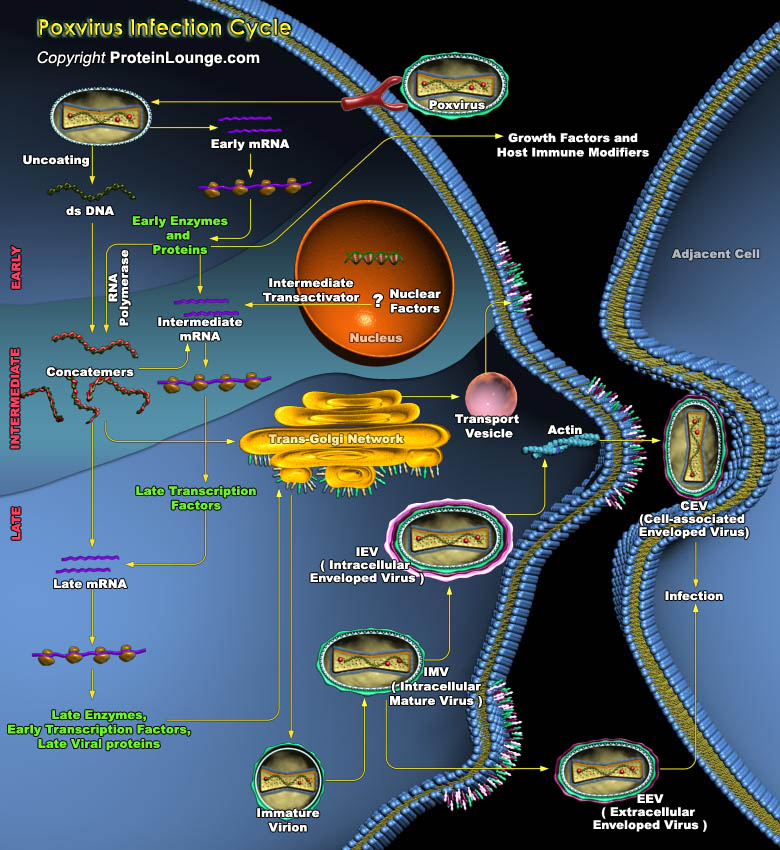
Poxviridae is a family of viruses containing large double-stranded DNA genomes of 130,000 to >300,000 nucleotides. Humans, vertebrates, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. Poxviridae viral particles (virions) are generally enveloped (external enveloped virion), though the intracellular mature virion form of the virus, which contains different envelope, is also infectious. They vary[..]
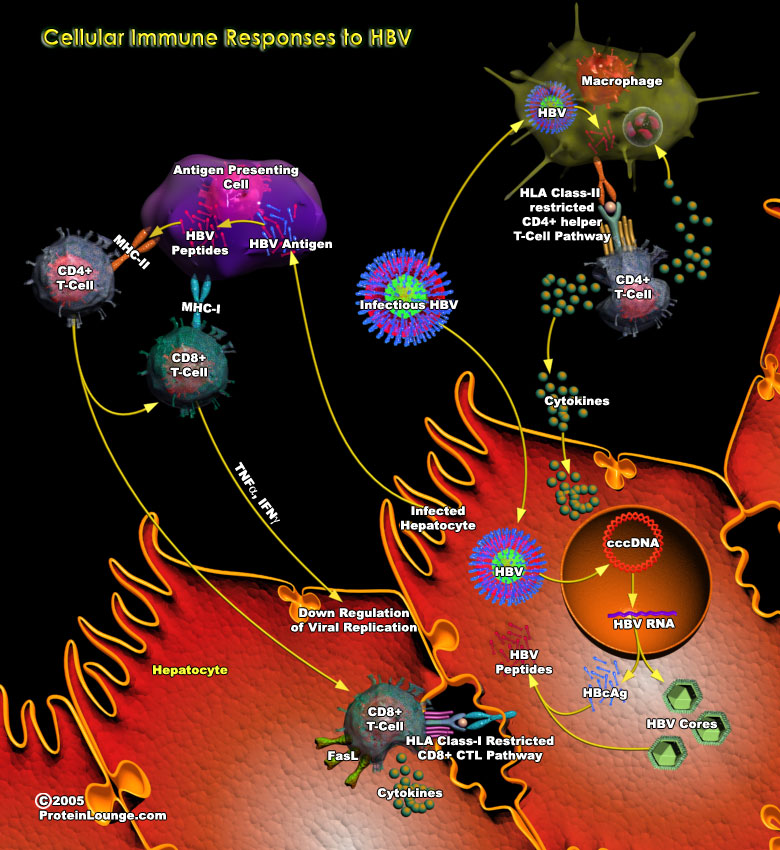
HBV(Hepatitis B virus) is a member of the family Hepadnaviridae. It is a hepatotropic non-cytopathic DNA virus and is a major cause of acute and chronic hepatitis in humans. As HBV itself is currently viewed as a non-cytopathic virus, the liver pathology associated with hepatitis B is mainly thought to be due to immune responses directed against HBV antigens. The outcome of HBV infection is[..]
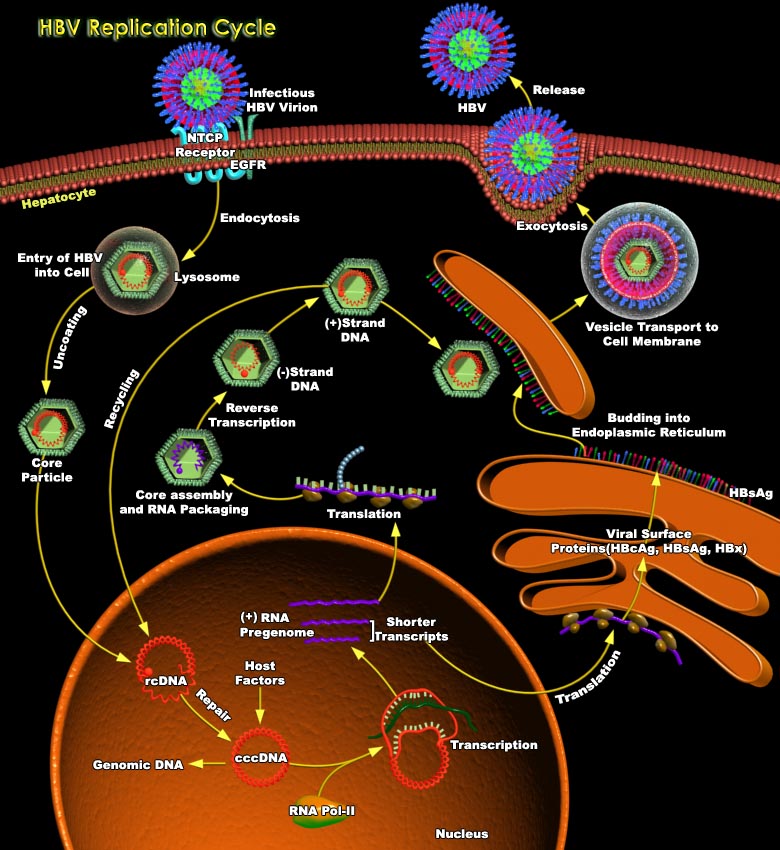
HBV (Hepatitis-B Virus) belongs to a family of closely related DNA viruses called the Hepadnaviruses. Included in this family are the WHV (Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus), the DHBV (Duck Hepatitis-B Virus) and several other avian and mammalian variants. Hepadnaviruses have a strong preference for infecting liver cells, but small amounts of hepadnaviral DNA can be found in kidney, pancreas, and[..]
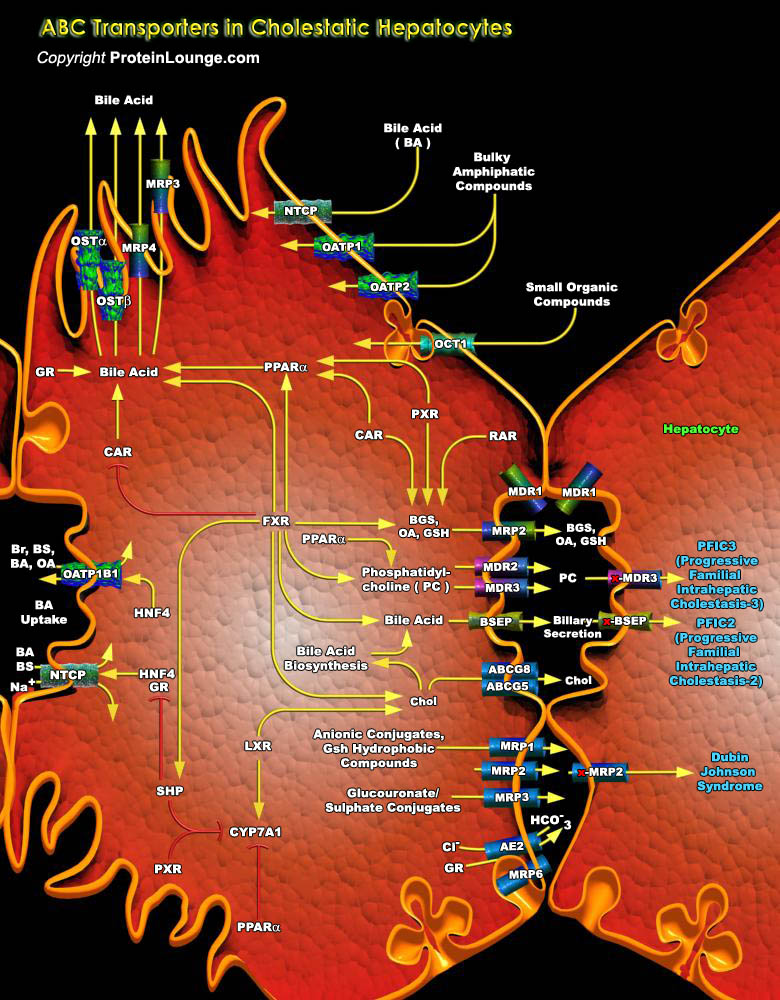
A cell must selectively translocate molecules across its plasma membrane to maintain the chemical composition of its cytoplasm distinct from that of the surrounding milieu. The most intriguing and, arguably, the most important membrane proteins for this purpose are the ABC (ATP-Binding Cassette) transporters. These proteins, found in all species, use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to translocate[..]
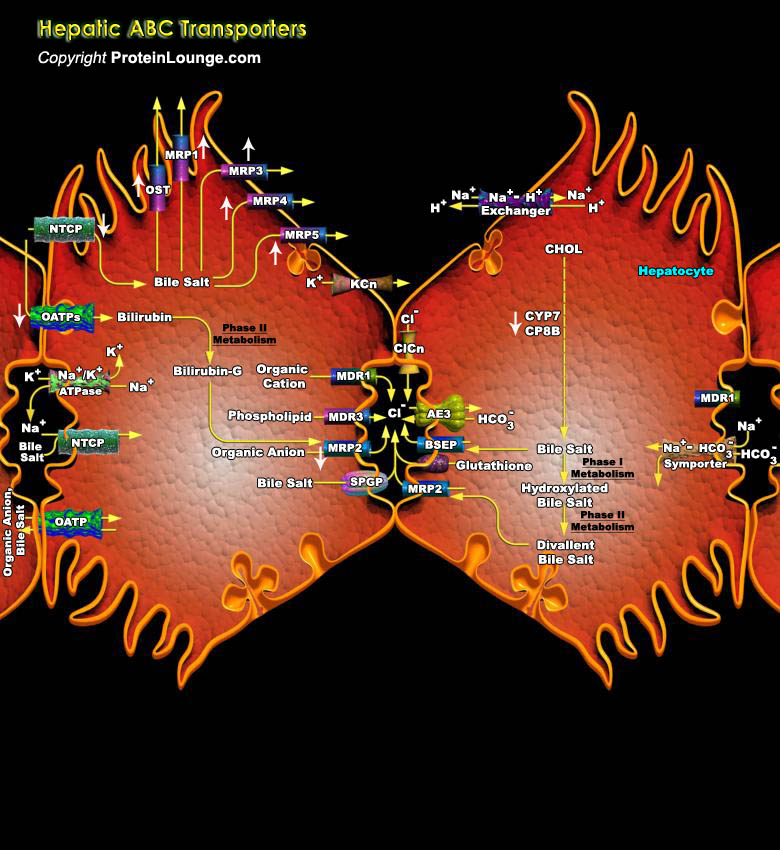
ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporters are a large superfamily of integral membrane proteins involved in the cellular export or import of a wide variety of different substances, including ions, lipids, cyclic nucleotides, peptides, and proteins. ABC transporters are systemically classified into eight subfamilies by sequence similarity, i.e., ABCA (ABC1), ABCB (MDR/TAP), ABCC (MRP/CFTR),[..]
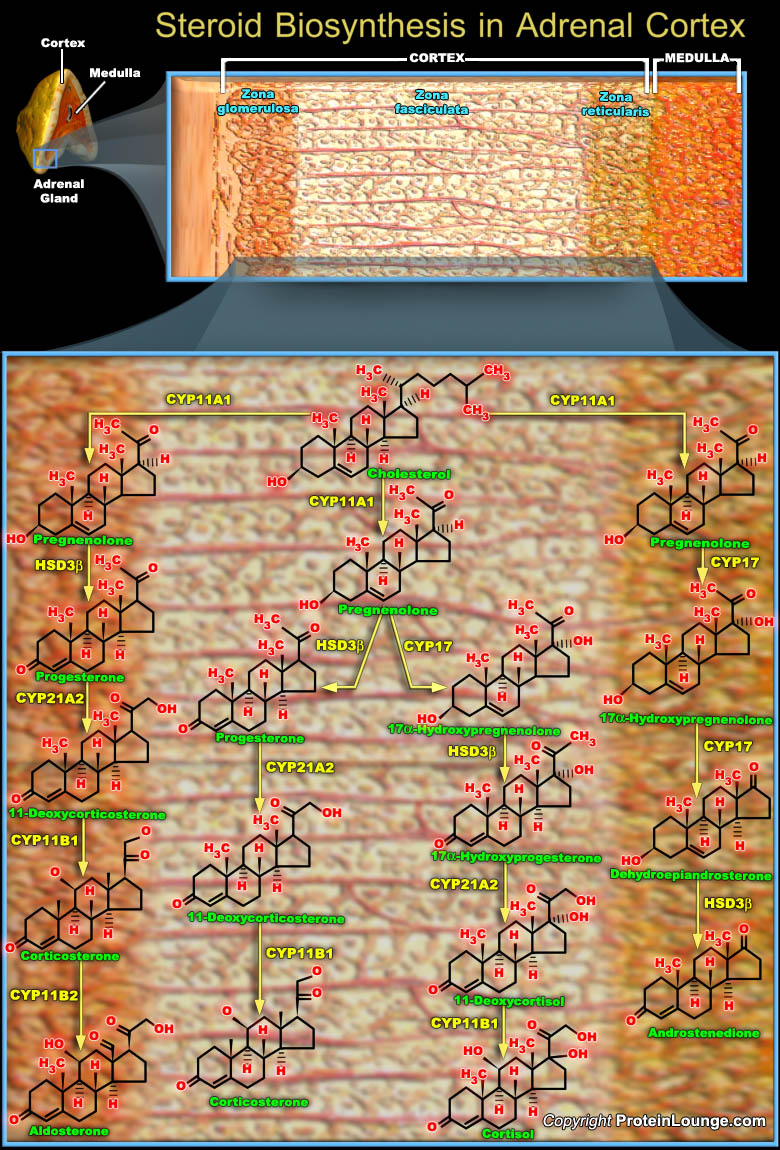
Steroid hormones are lipophilic, low-molecular weight compounds derived from Cholesterol that play important physiological roles. The steroid hormones are synthesized mainly by Endocrine Glands such as the the Adrenal Cortex and the Gonads (Ovary and Testes), and are then released into the blood circulation. There are five major classes of steroid hormones. They are the (i) Glucocorticoids[..]
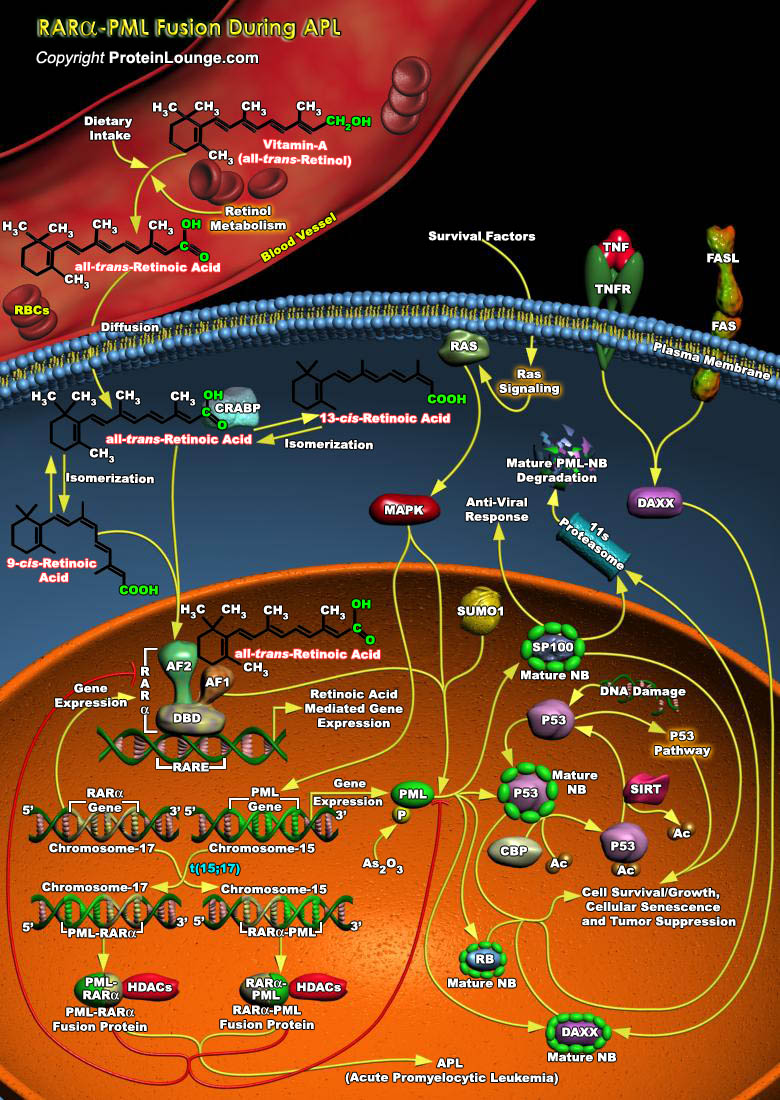
AMLs (Acute Myeloid Leukemias) are characterized with chromosomal translocations resulting in the formation of fusion proteins. Understanding PML (Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Inducer) function has become an area of intense research because of its involvement in the pathogenesis of APL (Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia), a distinct subtype of Myeloid Leukemia. In the[..]
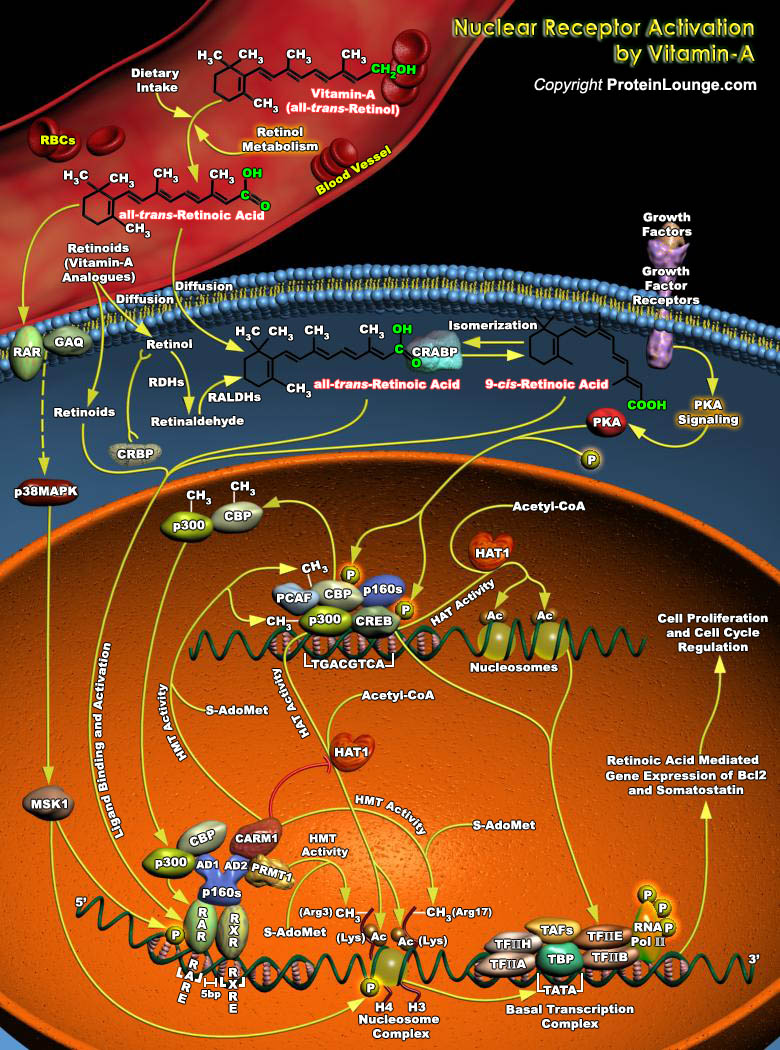
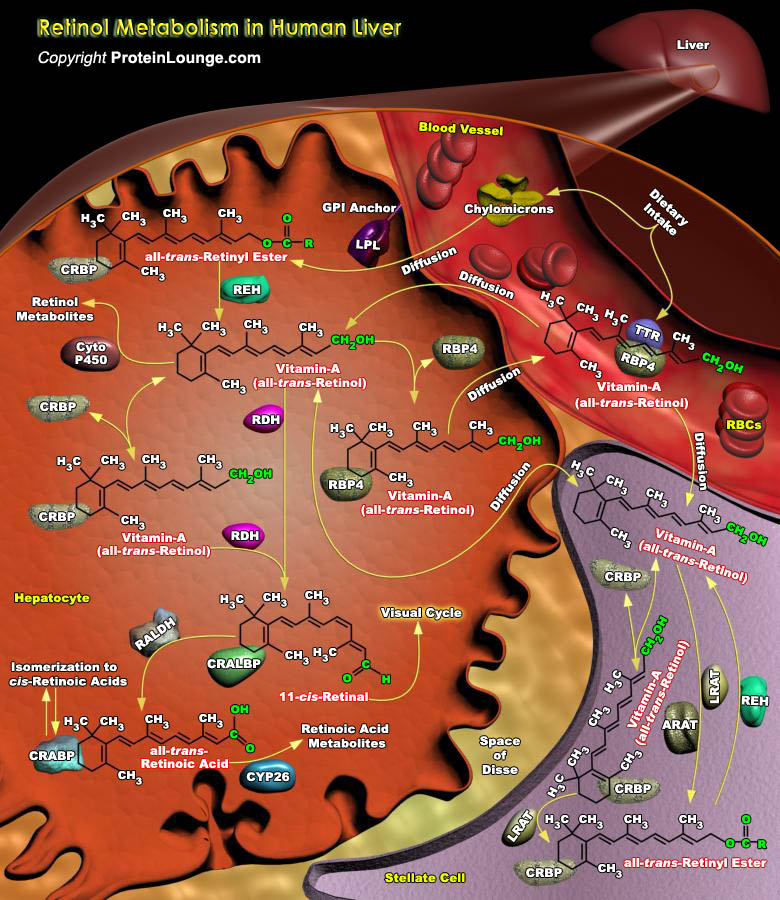
Vitamin A and its analogs, collectively termed retinoids, have a profound effect on cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and morphogenesis. Retinol, the lipid-soluble vitamin A, is an absolute requirement for normal growth, vision and differentiation of epithelial tissues in mammals. Retinol must be obtained directly through dietary intake, but may also be derived in its provitamin A forms[..]
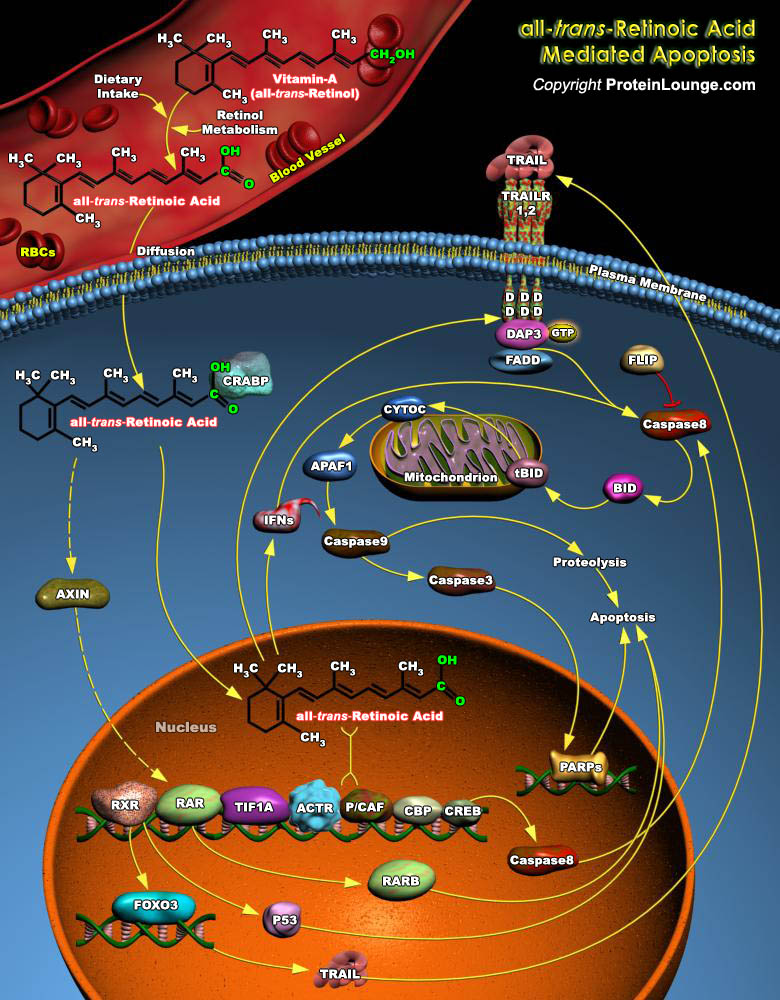
Retinoic Acid, a lipophilic molecule and a metabolite of Vitamin-A (all-trans-Retinol), affects gene transcription and modulates a wide variety of biological processes like Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, including Apoptosis. Retinoic Acid mediated gene transcription depends on the rate of transport of Retinoic Acid to target cells and the timing of exposure of Retinoic Acid to RARs[..]
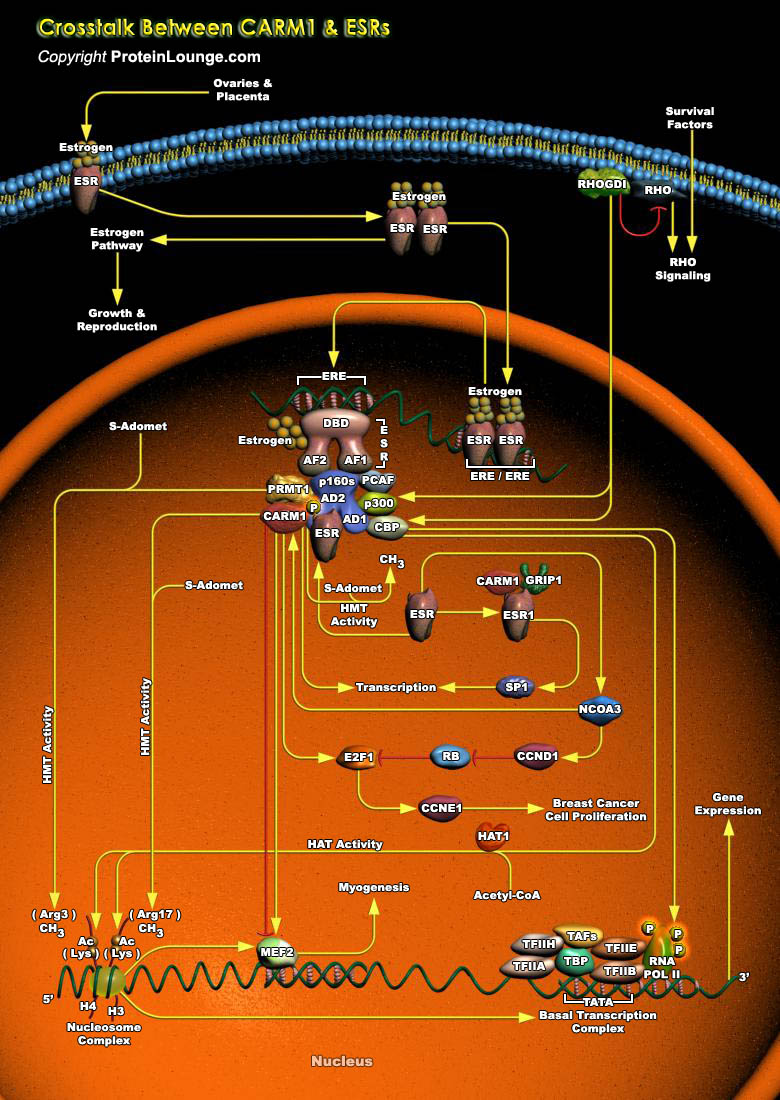
The ESRs (Estrogen Receptors) are ligand-dependent transcription factors and are important Nuclear Hormone Receptors that act as regulators of cell growth, differentiation and malignant transformation. Transcriptional activation by ESRs is accomplished through specific and general cofactor complexes that assemble with the receptor at target promoters to regulate transcription. The chief ligand[..]








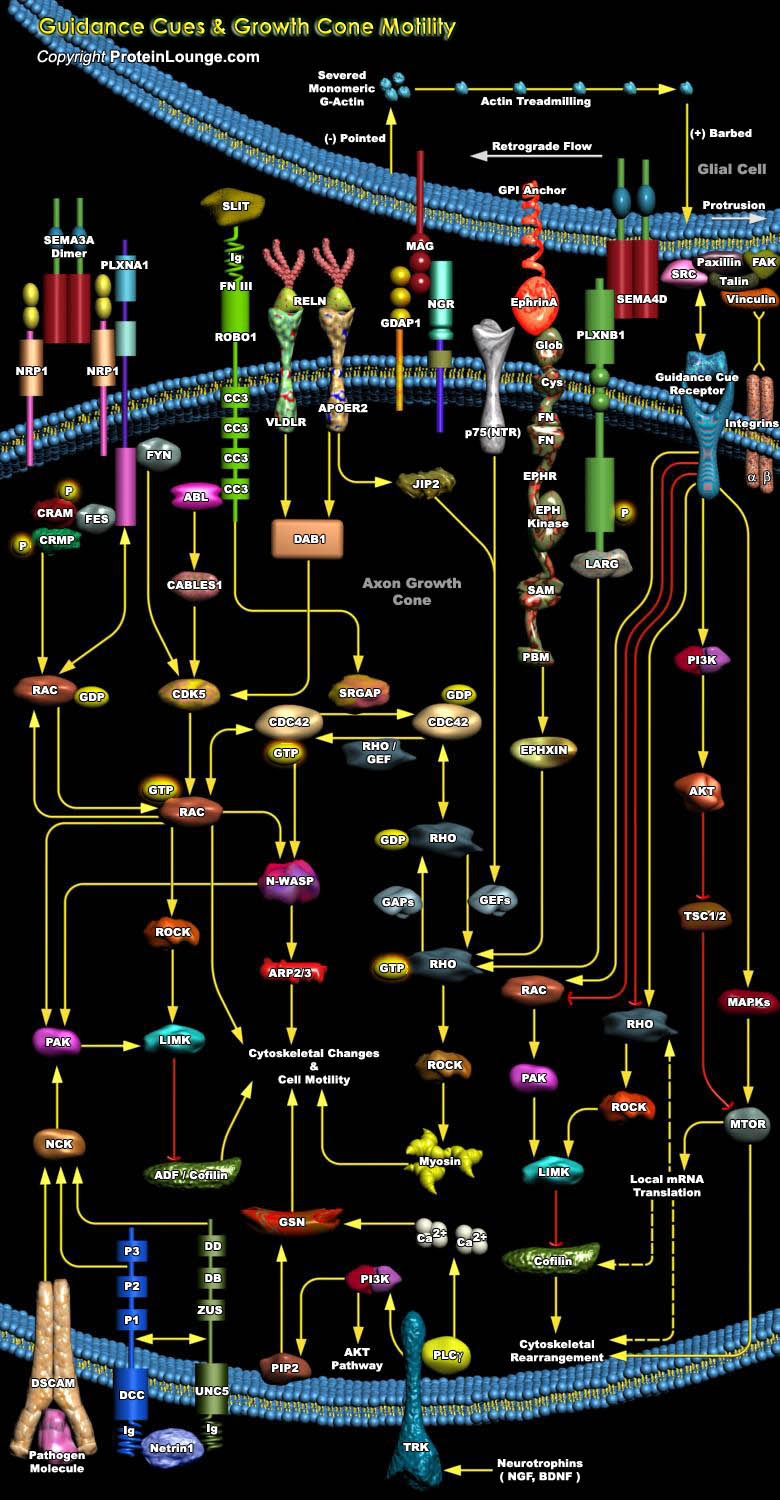
-Mediated Signaling.jpg)