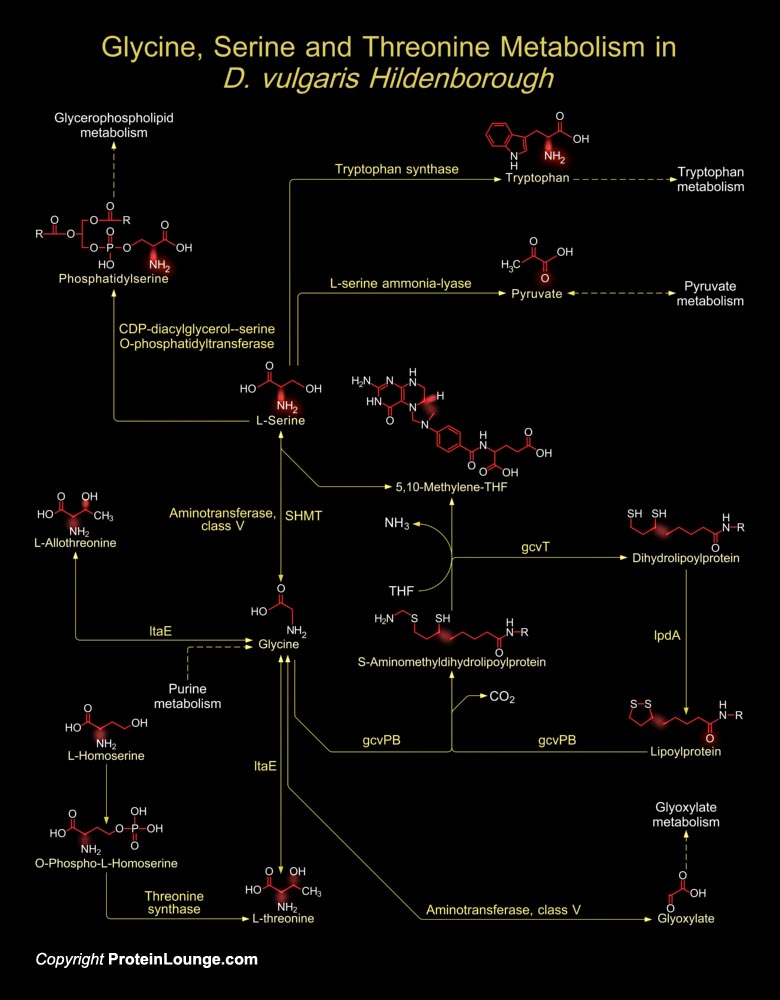
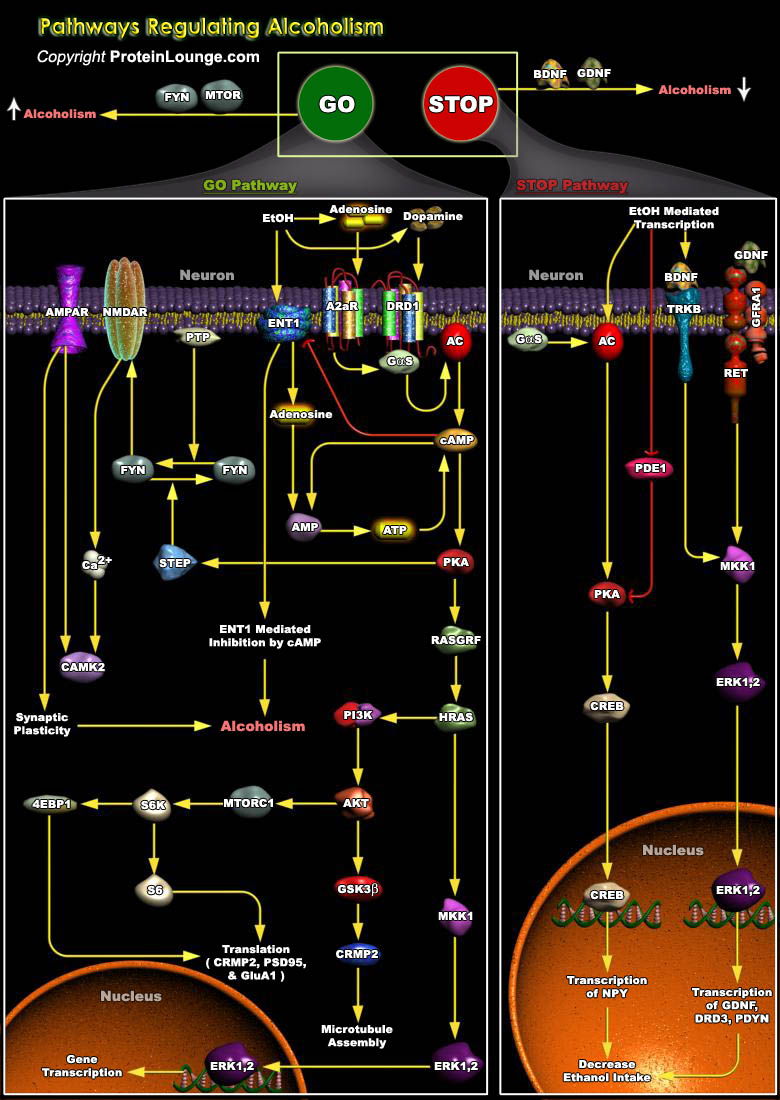
Featured Pathways
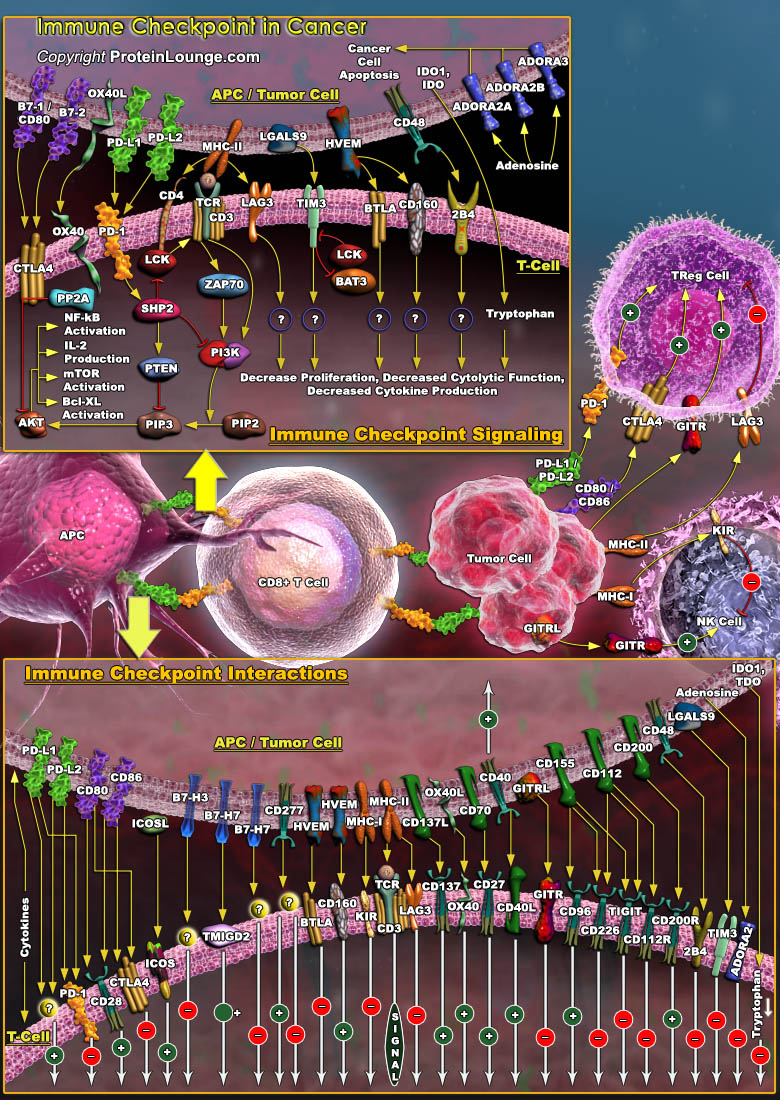
Immune checkpoints are co-stimulatory or inhibitory molecules that serve as regulators of T cells function in the tumor microenvironment. Inhibitory immune checkpoints maintain immune homeostasis, down-regulate anti-tumor responses and prevent autoimmunity (Ref.1). Checkpoint pathways involve costimulatory and inhibitory receptors and their ligands. Costimulatory receptors[..]
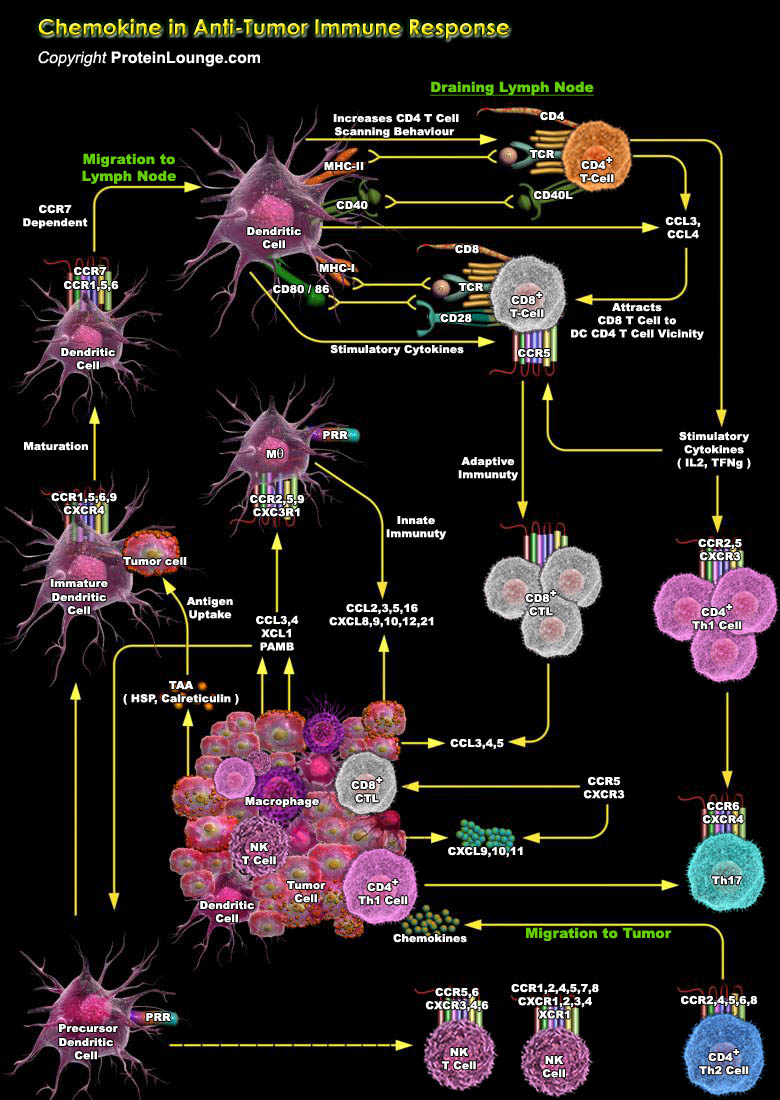
Chemokines are chemotactic cytokines belonging to a large family of small, secreted proteins that stimulate the cells migration and the positioning and interactions of cells within tissue. About 50 endogeneous chemokine ligands and 20 cell surface G protein-coupled heptahelicalchemokine receptors together form the chemokine superfamily. Chemokines regulate leukocyte migration into the tumor[..]
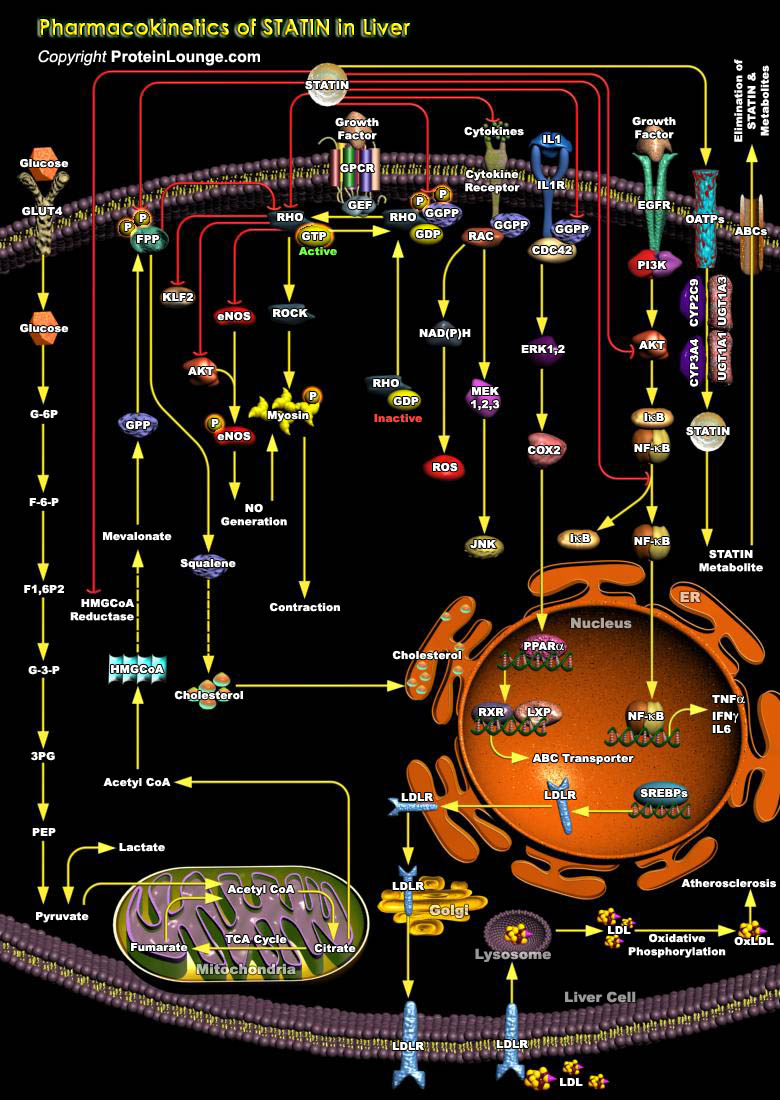
Cholesterol is the key component of the structure and function of cell membranes and is biosynthesized by all animal cells. Cholesterol biosynthesis occurs in the liver and the intestines. The liver has two sources of cholesterol either it can take up LDL particles from the blood, or it can synthesis cholesterol using HMG-CoA reductase adding to the cholesterol pool in[..]
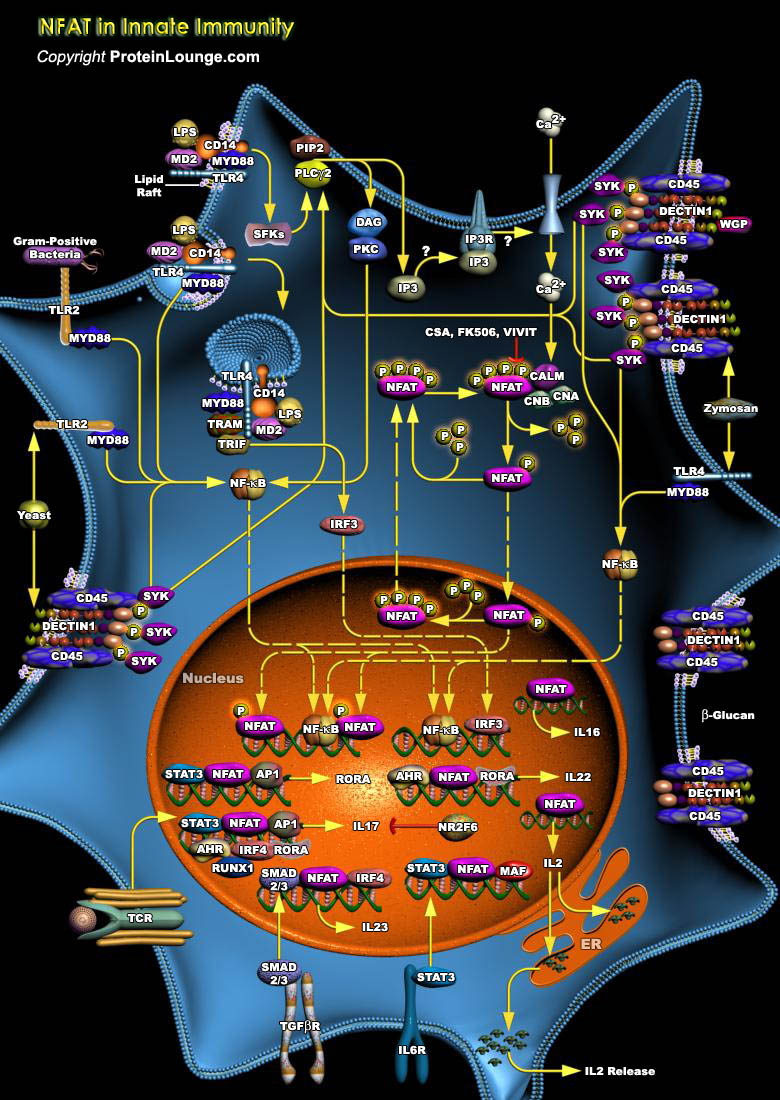
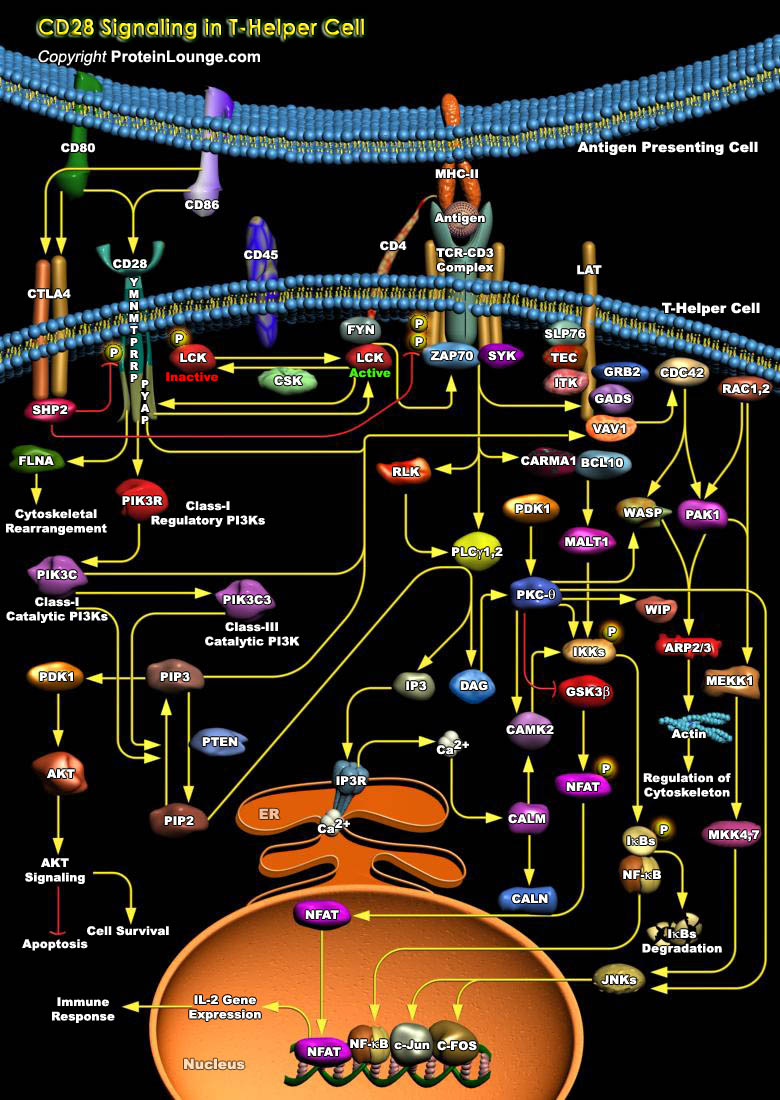
NFATs are basically calcium-dependent transcription factors, activated by stimulation of receptors coupled to calcium/calcineurin signals, such as the antigen receptors on T-Cells and B-Cells, FcEpsilonR (Fc-Epsilon Receptors) on mast cells and basophils, the Fc-Gamma receptors on macrophages and NK cells, the platelet collagen receptors, and receptors coupled to heterotrimeric G-Proteins[..]
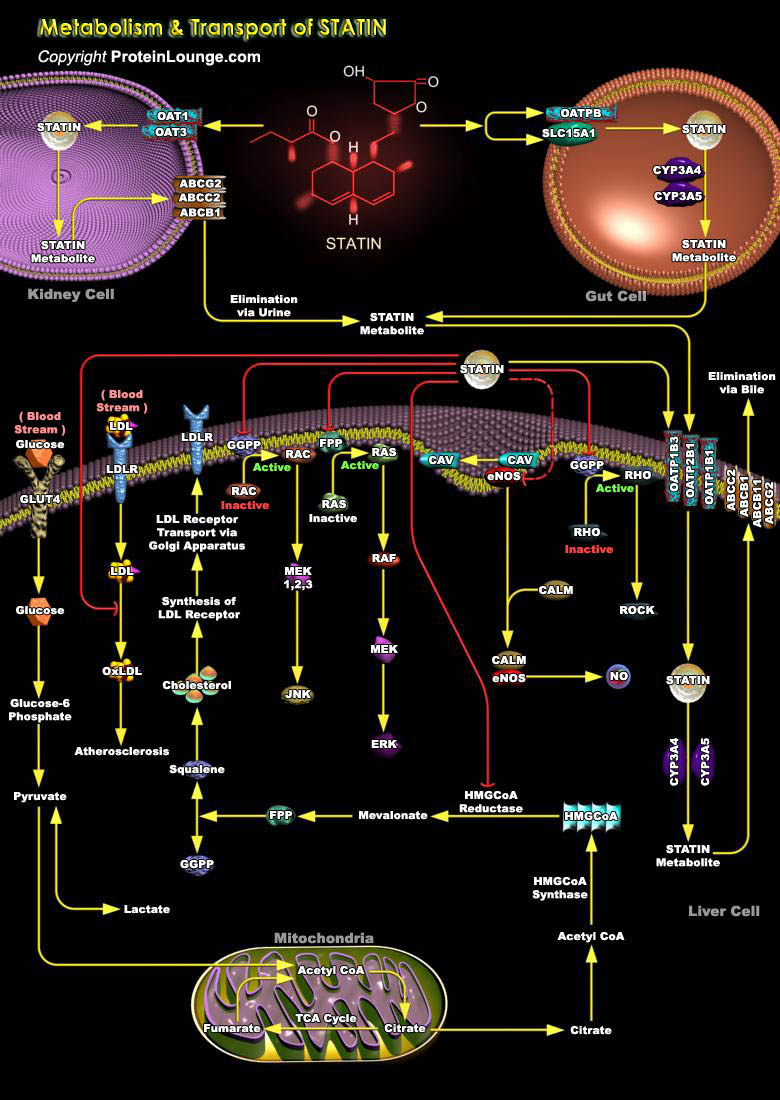
Cholesterol is an important structural component of cell membranes. They not only act as precursor of steroid hormones, bile acids and vitamin D but are essential for posttranslational modification of membrane proteins involved in cellular processes such as cell growth/differentiation, gene expression, and protein glycosylation and cytoskeletal assembly. Cholesterol biosynthesis occurs in the[..]
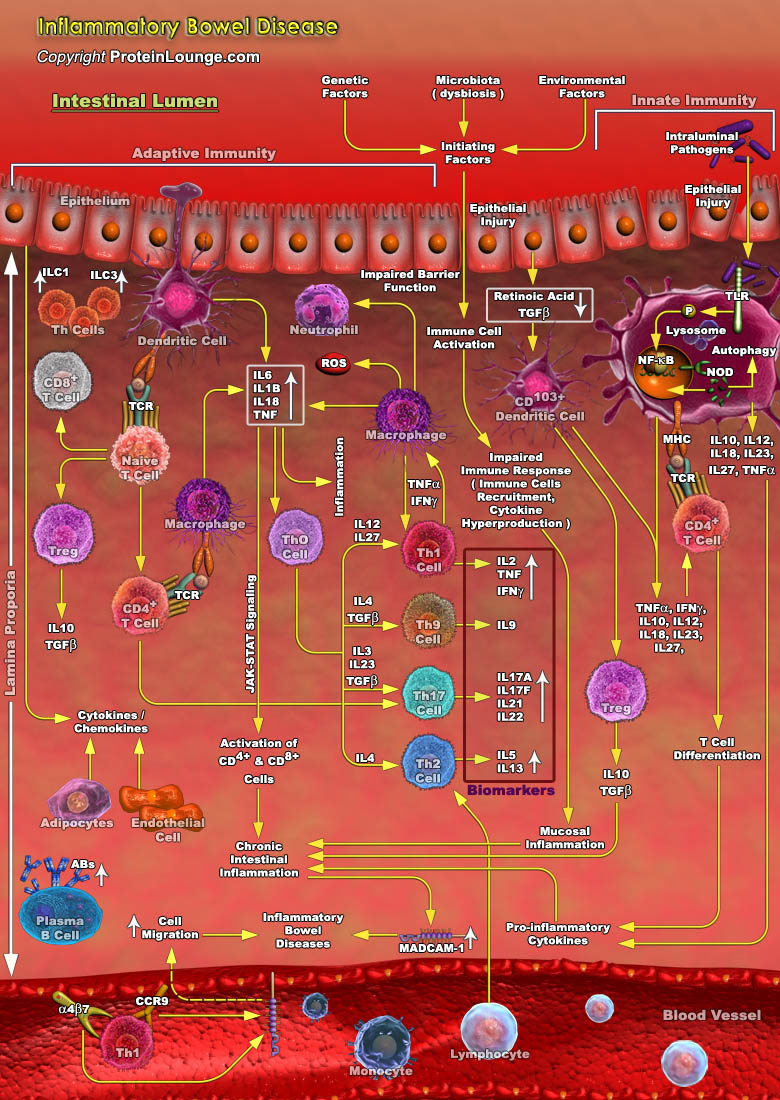
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract plays a central role in maintaining immune homeostasis, i.e., tolerance to non-pathogenic commensal bacteria, self-antigens, and food antigens, while also protecting the host against pathogenic organisms by mounting an inflammatory response. The fine line between tolerance and inflammation of the GI immune system, when disrupted, may result in diseases such as[..]
.jpg)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer of the blood and bone marrow in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes. This is a type of slow-growing leukaemia that affects developing B-lymphocytes. CLL is a malignancy of mature CD5+ B-cells that is characterized by apoptosis resistance and dysfunctional immune system. Within a complex cellular network in bone marrow and[..]
 & Interaction with Environment.jpg)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer of the blood and bone marrow in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes. This is a prototypic malignancy that not only depends on intrinsic genetic defects, but also depends on the interactions with cells present in microenvironment such as T cells, monocyte-derived cells (MDC), and stromal cells (such as endothelial cells,[..]
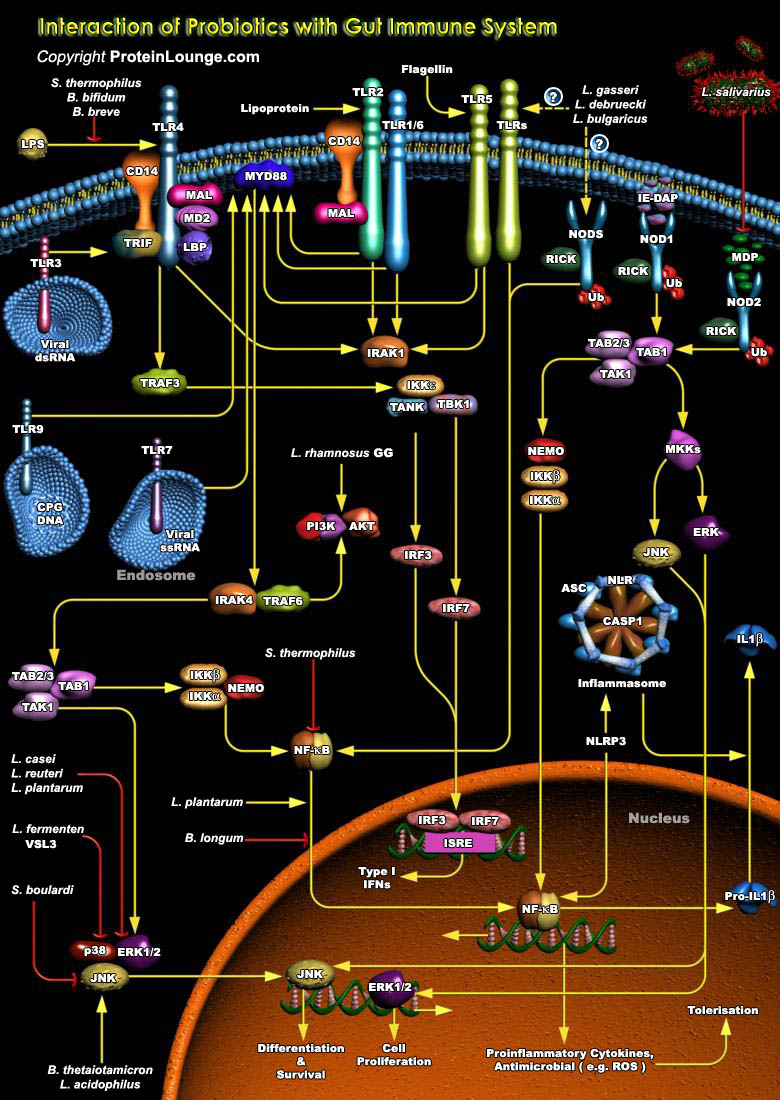
The immune response is initiated by innate immunity following exposure to foreign substances or tissue injury. Innate immunity exerts protective roles in host homeostasis in part by priming adaptive immune responses against persisting insults and inducing inflammation. However, the unbalanced immune response leads to severe inflammation and uncontrolled tissue damage and disease. Sensing of[..]
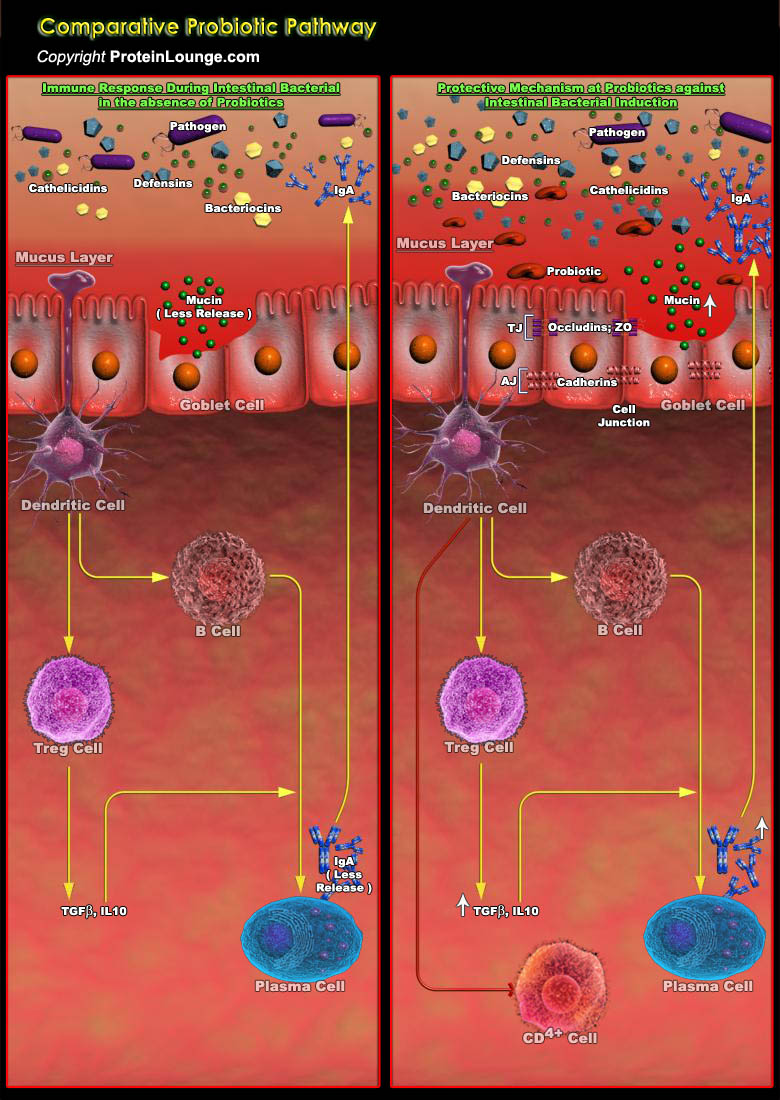
Probiotics are living microorganisms that confer health benefits to the host when administered in adequate amounts; however, dead bacteria and their components also exhibit probiotic properties. Bifidobacterium and strains of lactic acid bacteria are the most widely used bacteria that exhibit probiotic properties and are included in many functional foods and dietary supplements[..]
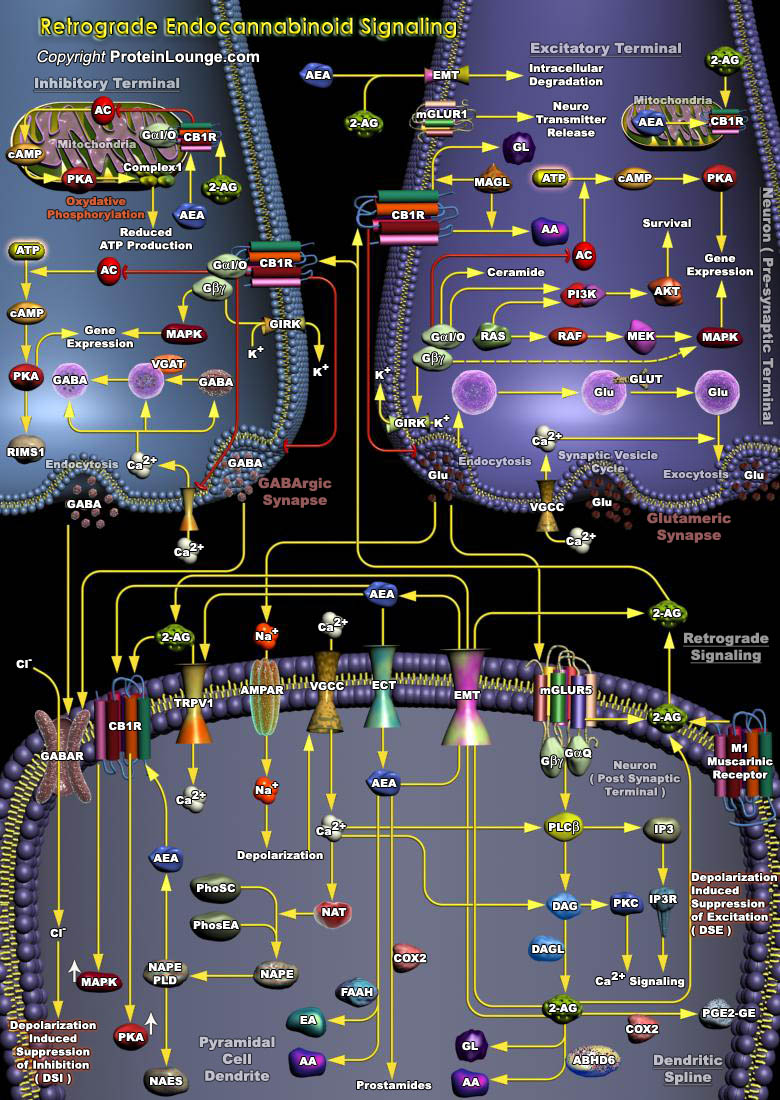
Endocannabinoids are endogenous ligands of cannabinoid receptors that bind as the principal biologically active component of Cannabis sativa, D9-tetrahydrocannabinol (D9-THC), and also comprise amides, esters and ethers of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Endogenous cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) serve as retrograde messengers at synapses in various regions of the brain. The[..]
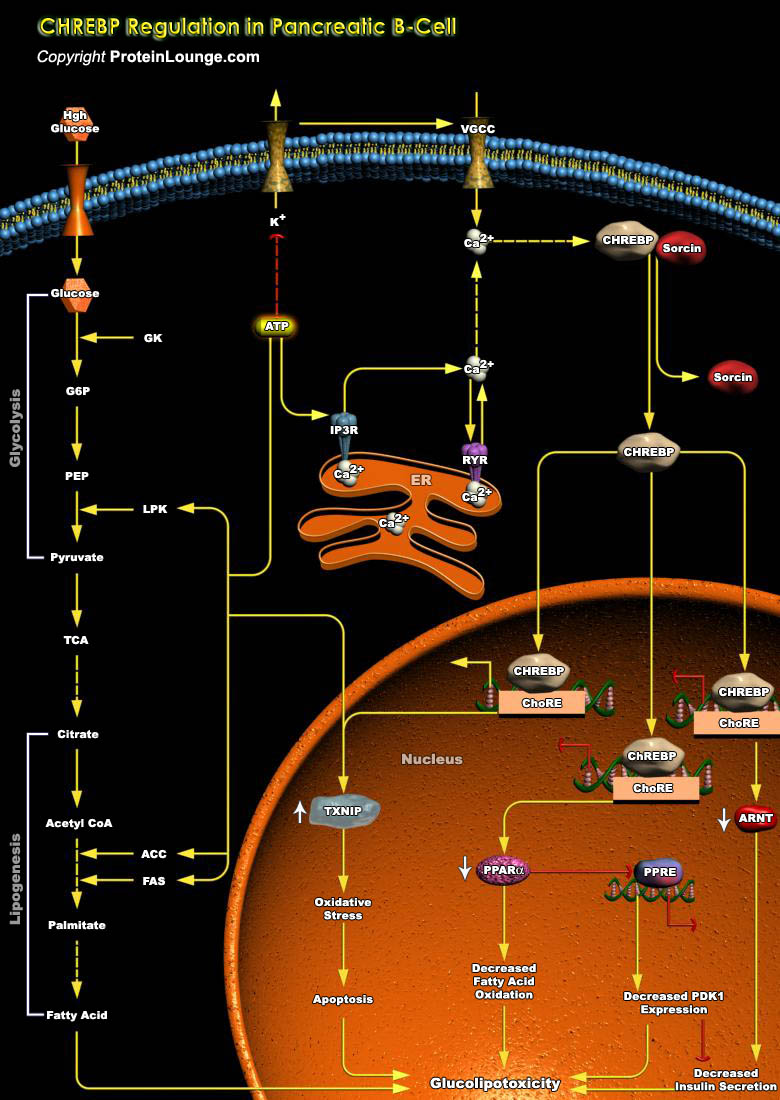
CHREBP (Carbohydrate-response element-binding protein) is the major transcription factor conferring glucose-induced gene expression in pancreatic islets, liver and adipose tissue. To date, only two natural isoforms, CHREBPα and CHREBPβ, have been identified. CHREBP-β was identified in adipose tissue and found to be also expressed in islets and involved in[..]