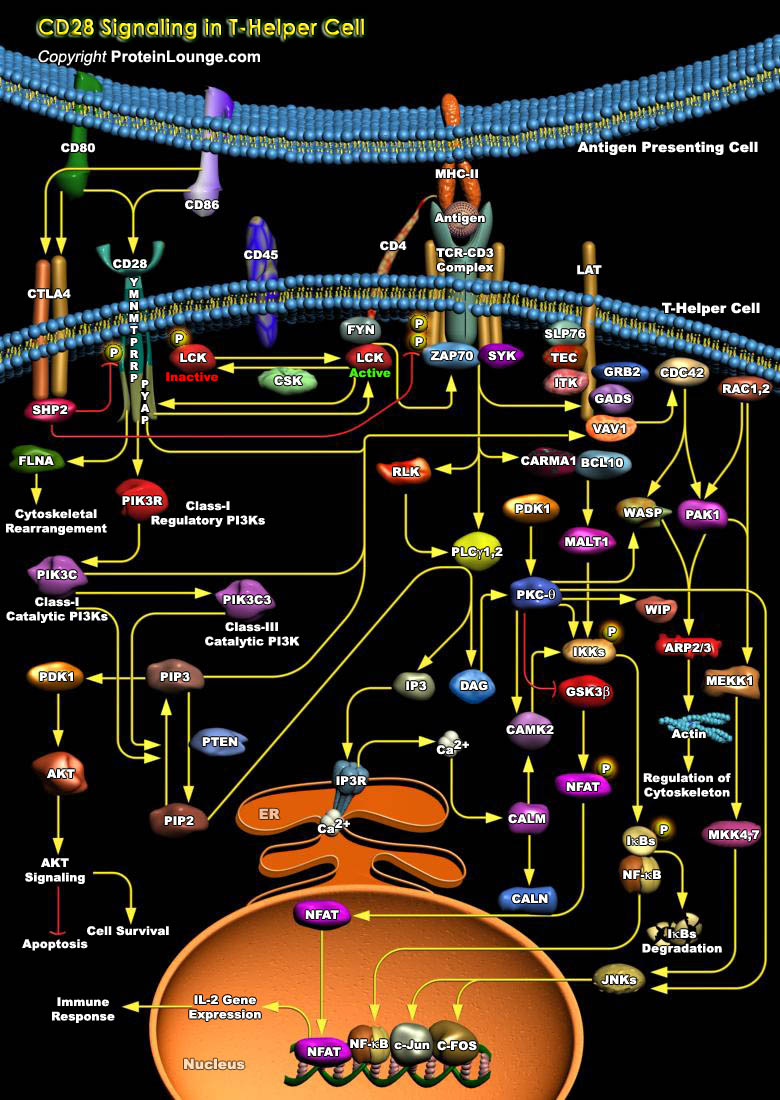
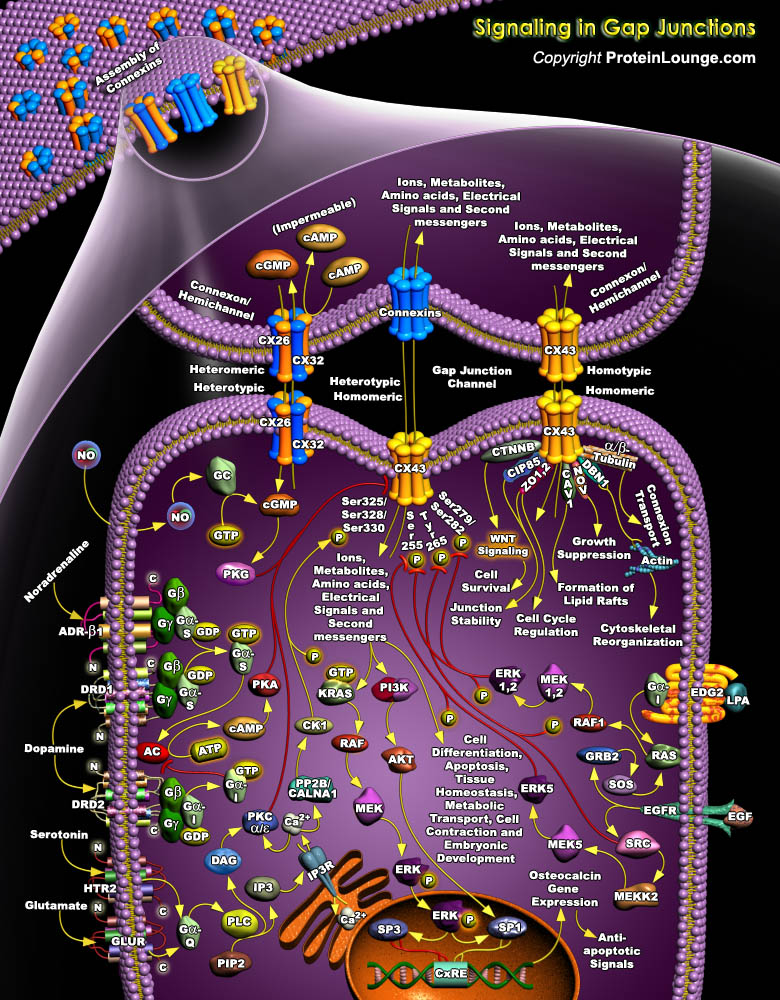
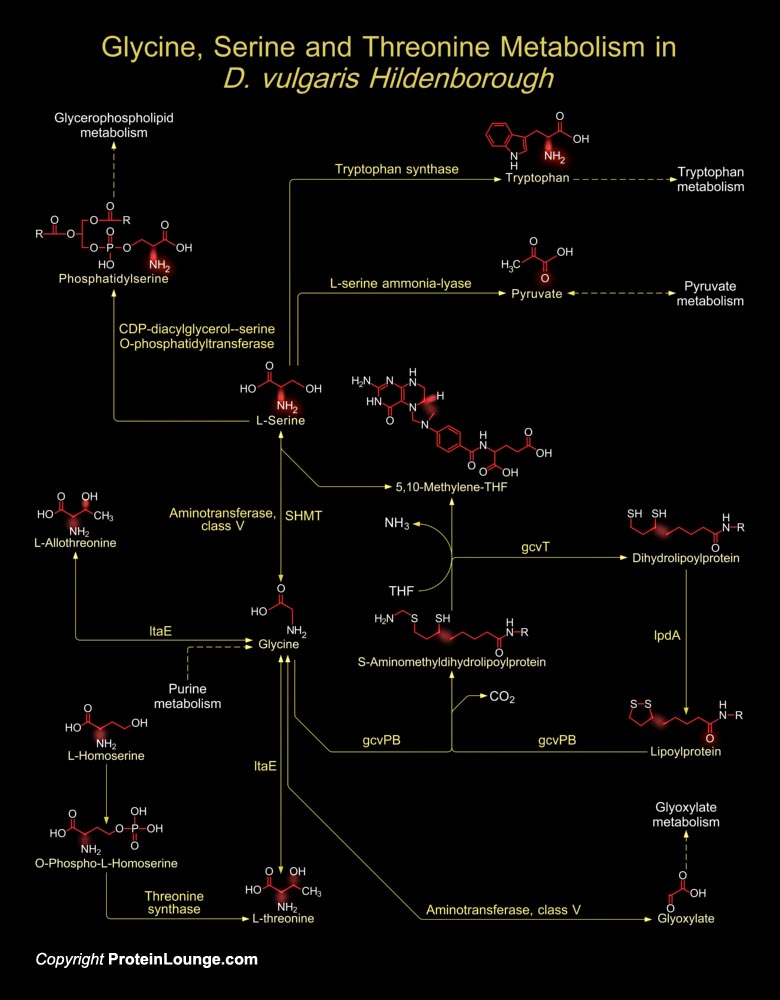
Featured Pathways
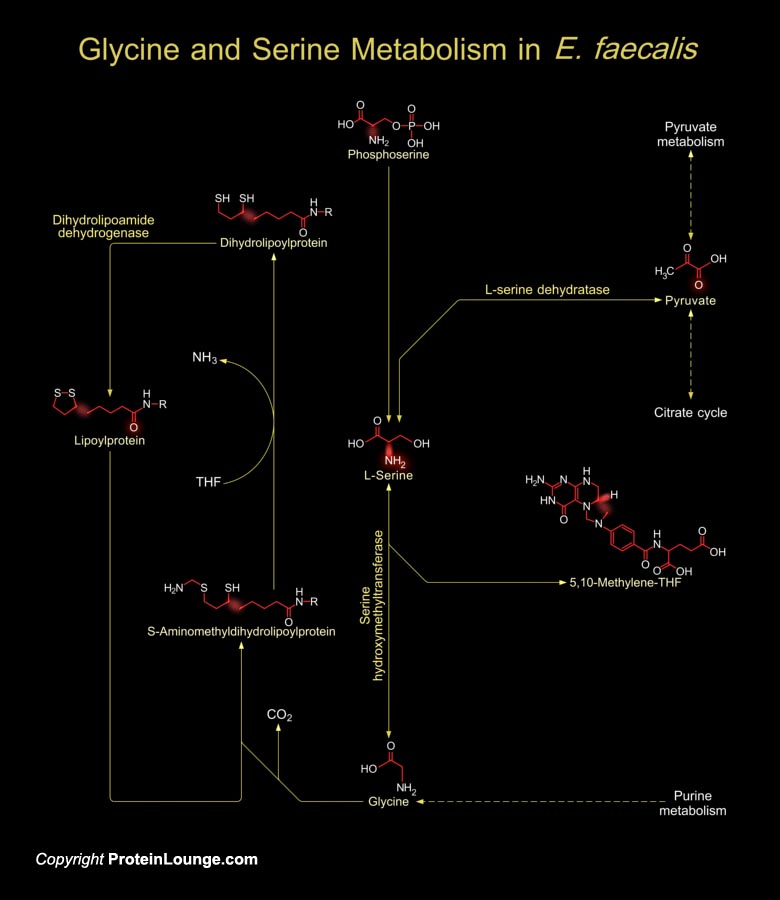
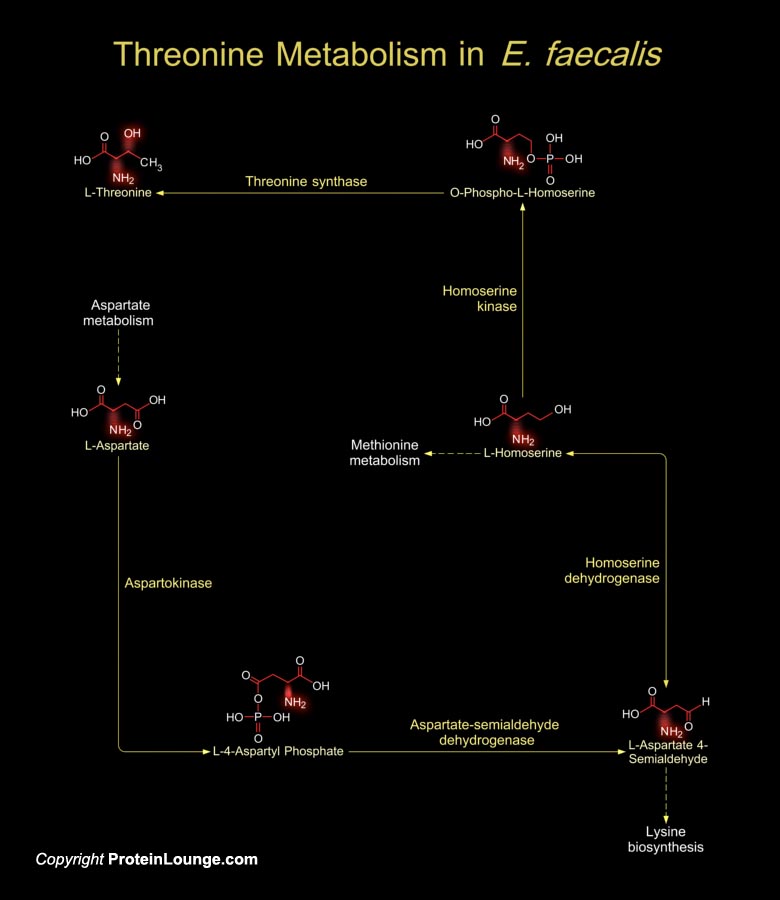
Enterococci are Gram-positive, facultative anaerobic and Lactic acid producing bacteria. Most strains are non-hemolytic. E. faecalis (Enterococcus faecalis), also known as S. faecalis (Streptococcus faecalis), the second most frequent enterococcal species, is a saprophytic commensal that inhabits the oral cavity and gastrointestinal flora of humans and animals and[..]
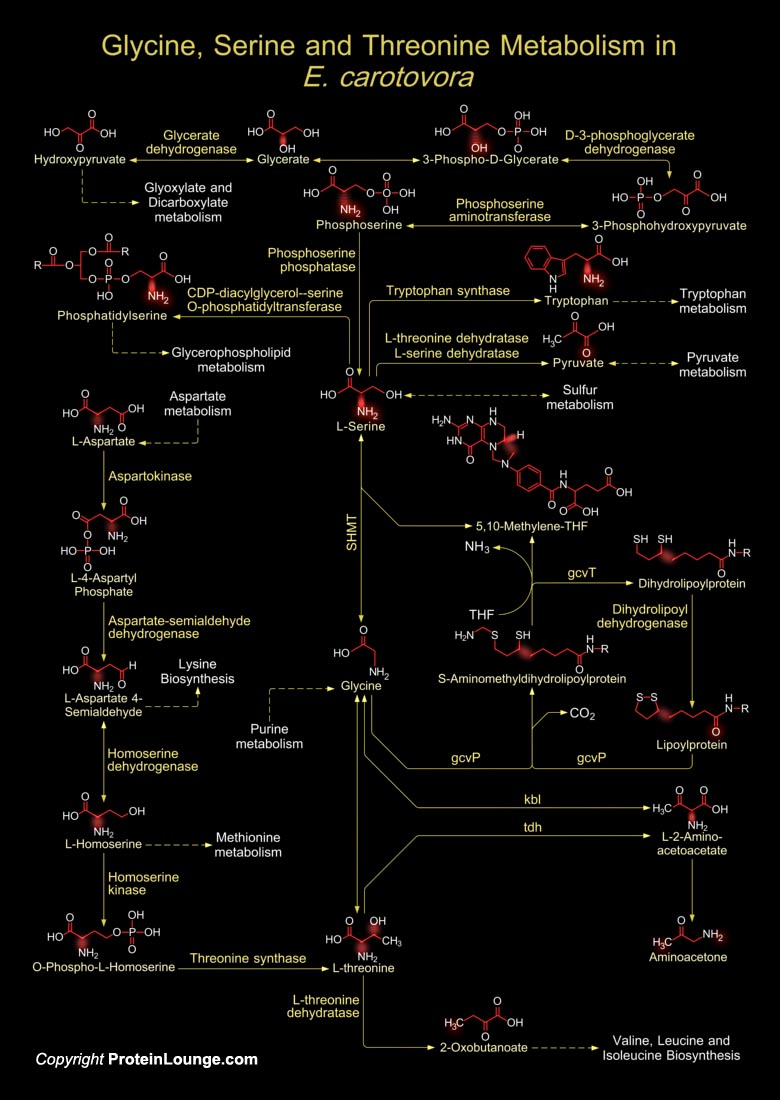
E. carotovora (Erwinia carotovora) is a species of plant pathogenic, Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria which gets its name from carrots, but it affects many other vegetables, including potatoes, cucumbers, onions, tomatoes, lettuce and even some ornamental plants like Iris. The bacterial family Enterobacteriaceae is notable for its well studied human[..]
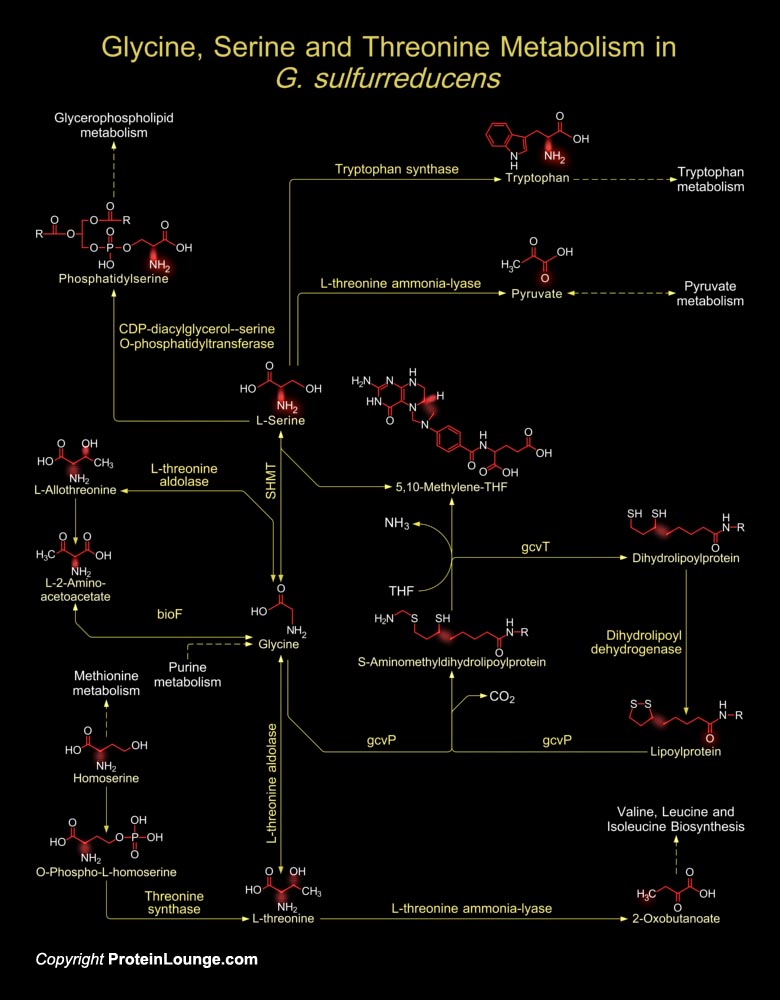
G. sulfurreducens (Geobacter sulfurreducens), a delta-proteobacterium, is an obligately anaerobic, non-fermentative, non-motile, Gram-negative rod. Geobacter species are of interest because of their novel electron transfer capabilities, impact on the natural environment and their application to the Bioremediation of contaminated environments and harvesting electricity from[..]
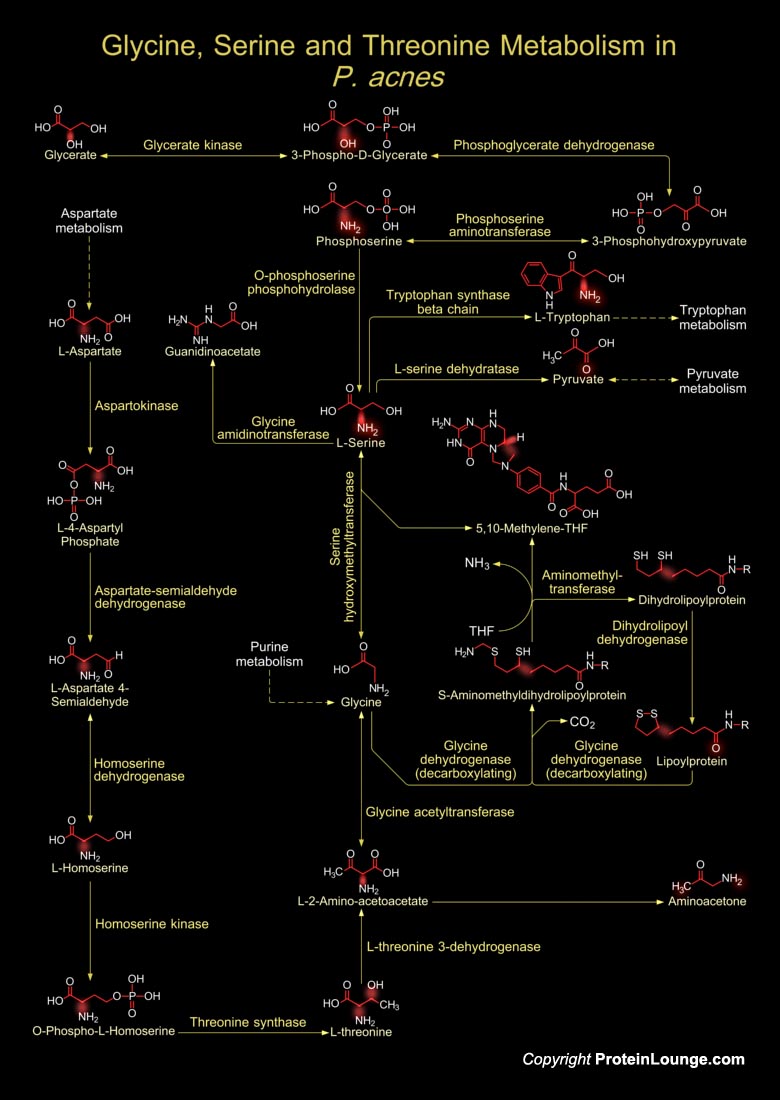
P. acnes (Propionibacterium acnes) is the most common Gram-positive, non-spore forming, anaerobic rod and a major inhabitant of adult human skin, where it resides within sebaceous follicles, usually as a harmless commensal, even though it has been implicated in Acne Vulgaris (Pimples) formation. P. acnes typically grows as an obligate anaerobe, however, some strains[..]
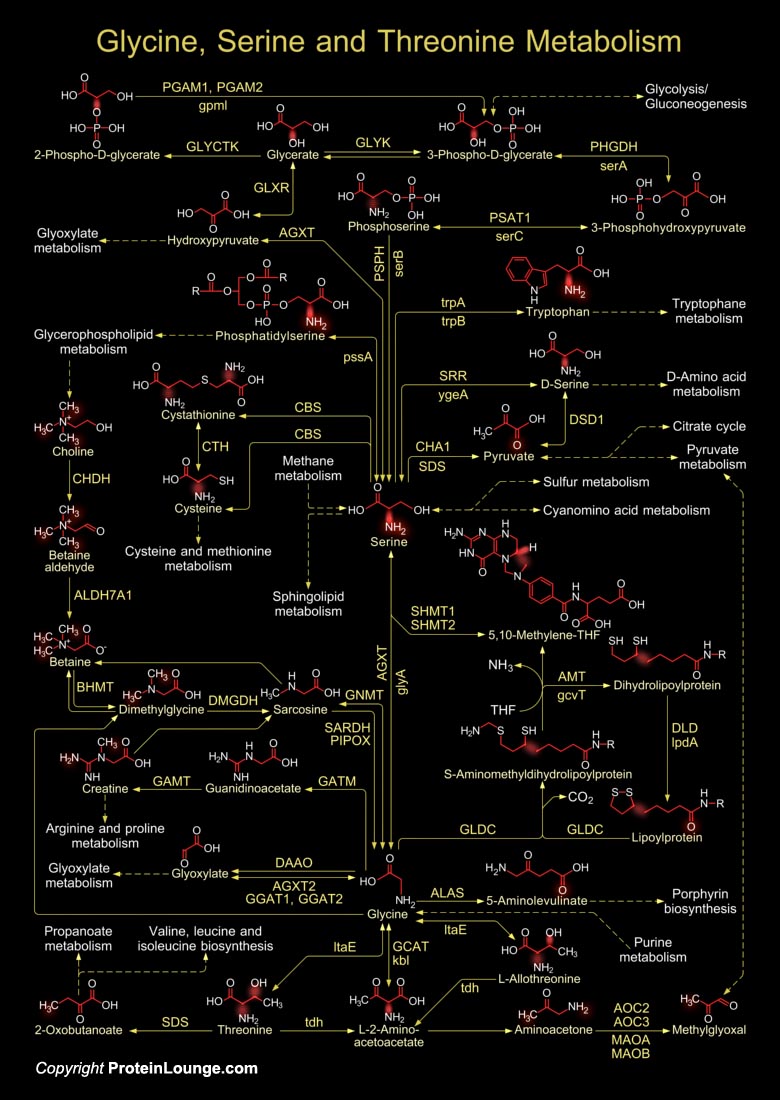
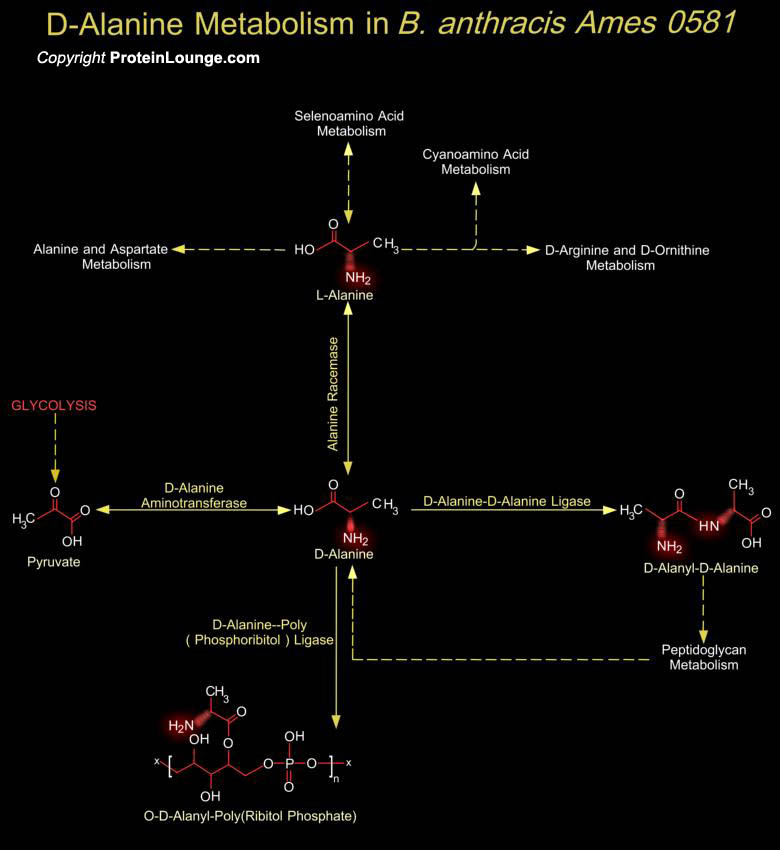
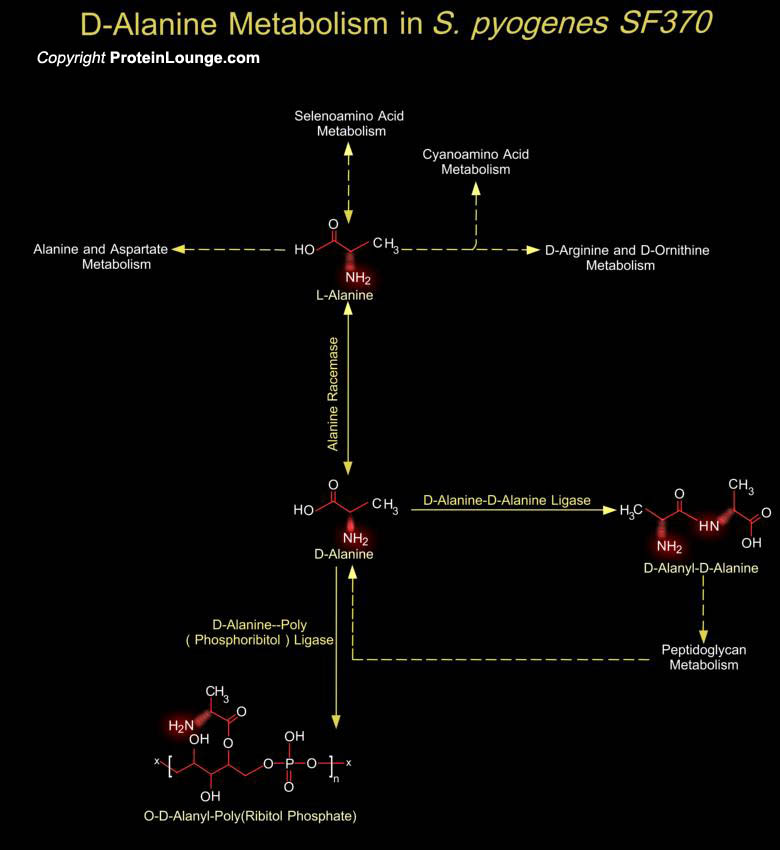
Organisms vary widely in their ability to metabolize amino acids. Based on metabolic requirements amino acids are grouped as essential amino acids (that must be provided in as nutrient) and non-essential amino acids (biosynthesized in adequate amounts). Except for Glycine, all amino acids occur in two possible optical isomers, called D and L. Because of the two hydrogen atoms at the[..]
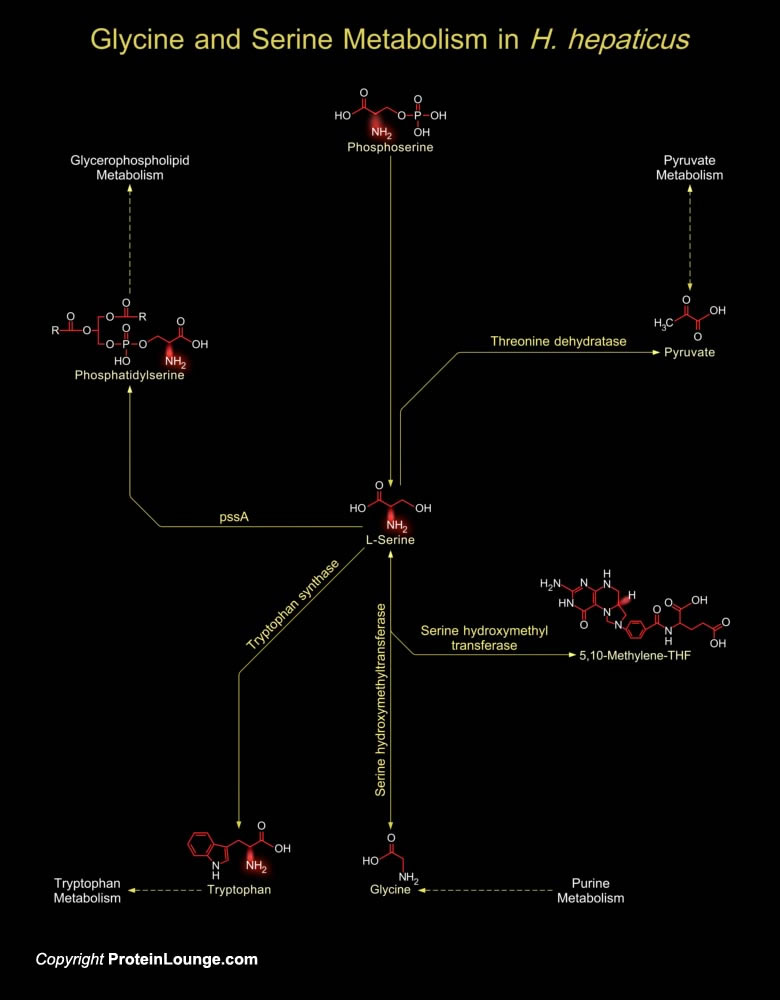
H. hepaticus (Helicobacter hepaticus) causes chronic Hepatitis and liver cancer in mice. It is the prototype enterohepatic Helicobacter species and a close relative of H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori), also a recognized carcinogen. H. hepaticus have a circular chromosome encoding 1,875 proteins. A total of 938, 953, and 821 proteins have orthologs in[..]
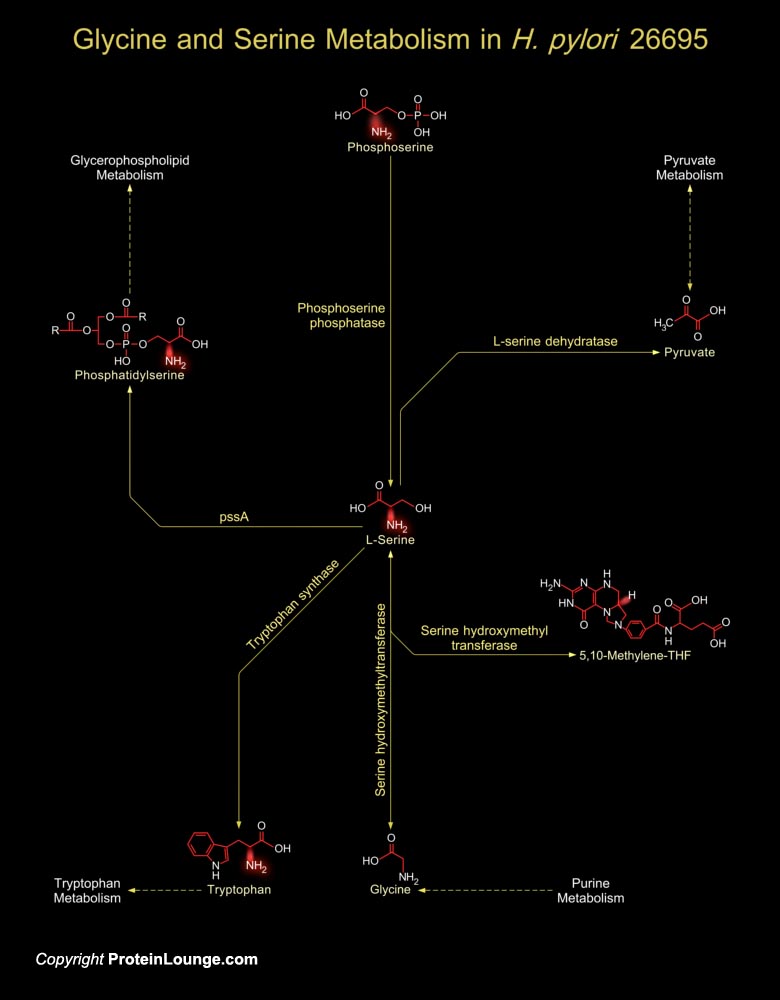
H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori) are Gram-negative, micro-aerophilic, spiral-shaped and flagellated bacteria that remains associated with Gastric inflammation and Peptic ulcer disease. As a human pathogen, H. pylori’s presence in the gastric mucosa is associated with Gastritis and is often implicated in Peptic ulceration and Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue[..]
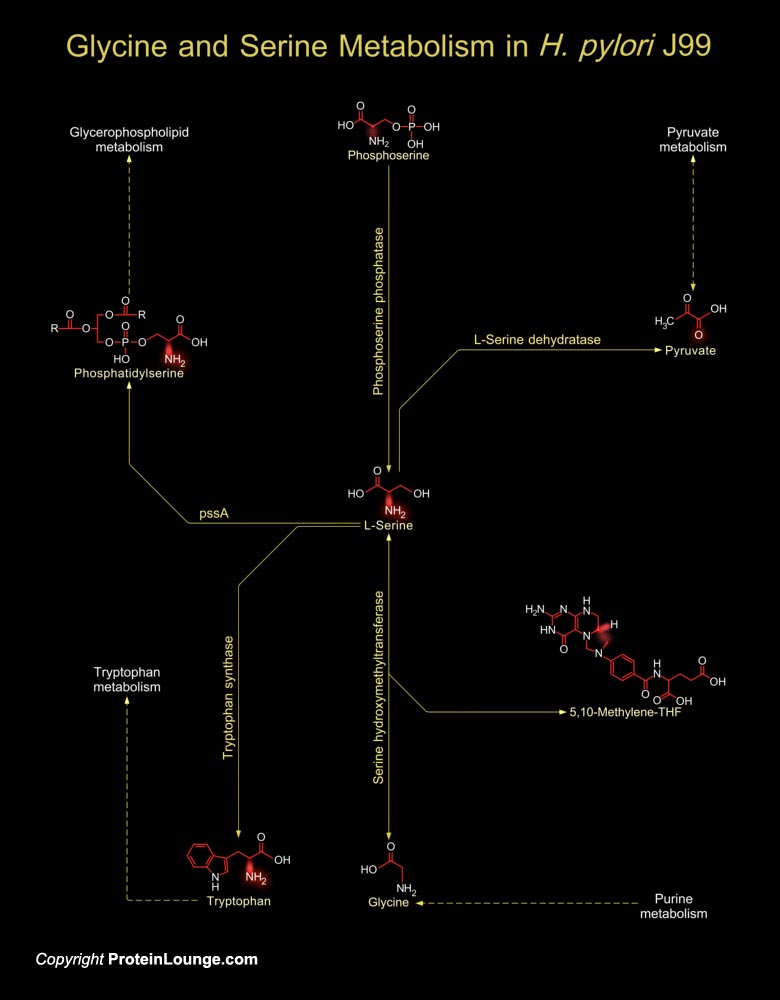
The human pathogen, H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori) present in the gastric mucosa is associated with Gastritis and is often implicated in Peptic ulceration and Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue Lymphomas (Ref.1). The H. pylori genome is important for drug discovery and vaccine development and this is exemplified by the genome analysis of not only H. pylori Strain 26695 but[..]
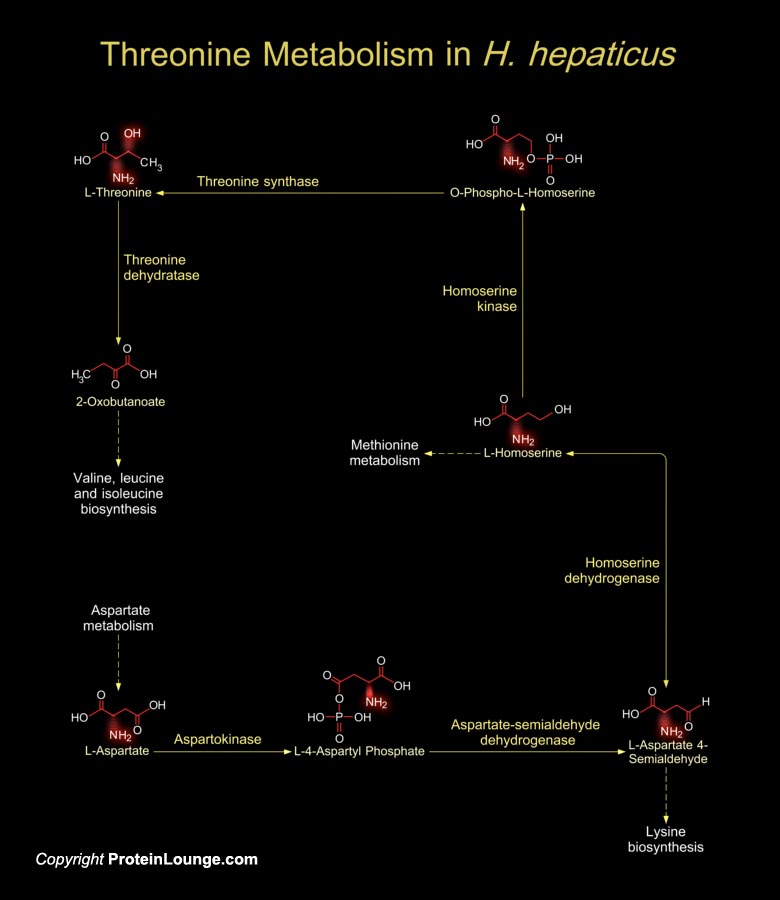
H. hepaticus (Helicobacter hepaticus) are motile and Gram-negative, curved to spiral in shape, with one to several spirals; and it has bipolar sheathed flagella (one at each end) but lacks the periplasmic fibers that envelope the bacterial cells in other mouse Helicobacter species. It grows microaerobically at 37ºC but not at 25ºC or 42ºC. H. hepaticus[..]
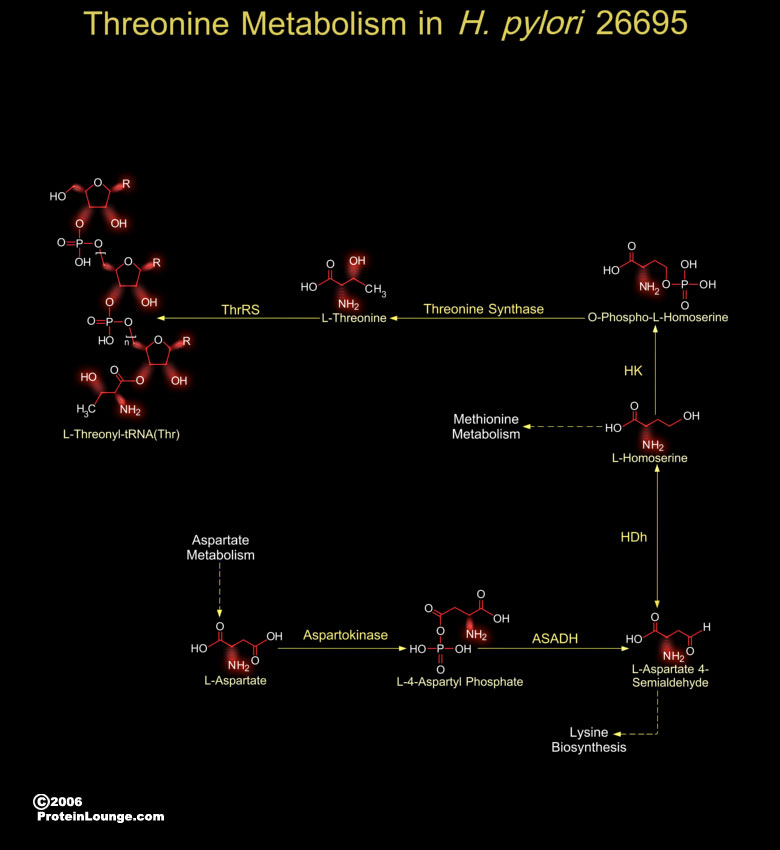
The Gram-negative, micro-aerophilic, spiral-shaped and flagellated bacteria, H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori) are associated with the pathogenesis of Gastric inflammation and Peptic ulcer disease. Presence of H. pylori in the gastric mucosa is associated with Gastritis and is often implicated in Peptic ulceration and Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue Lymphomas. The[..]
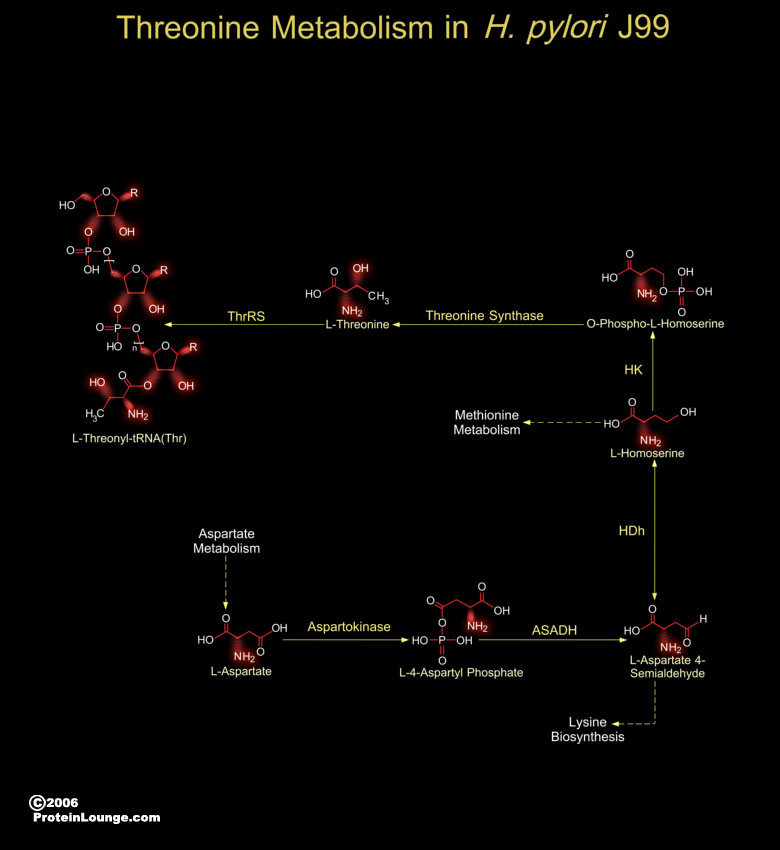
The H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori) J99 strains are Gram-negative, micro-aerophilic, spiral-shaped and flagellated bacteria, are associated with the pathogenesis of Gastric inflammation and Peptic ulcer disease (Ref.1). Presence of H. pylori J99 in the gastric mucosa is associated with Duodenal ulcers. The H. pylori genome is important for drug discovery and[..]