Featured Pathways
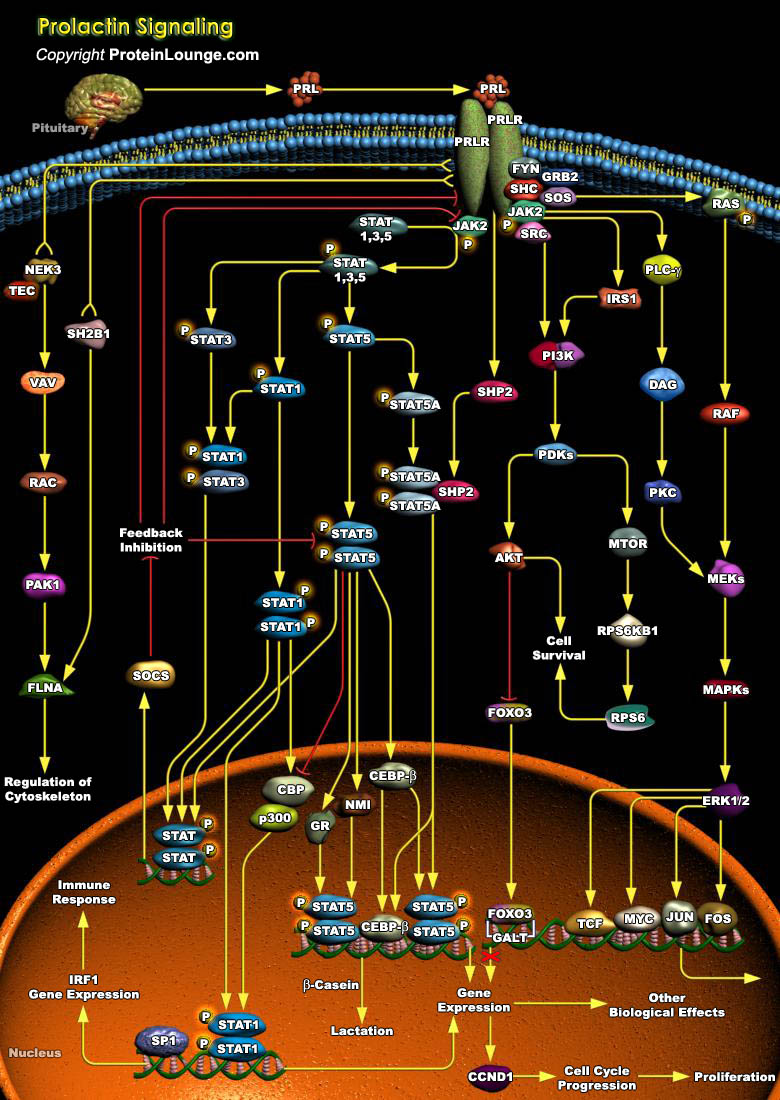
PRL (Prolactin), a multifunctional hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland and to a lesser extent by numerous extrapituitary tissues, affects more physiological processes than all other pituitary hormones combined. It was originally identified by its ability to stimulate the development of the mammary gland and lactation. However, this hormone has been established to be present in[..]
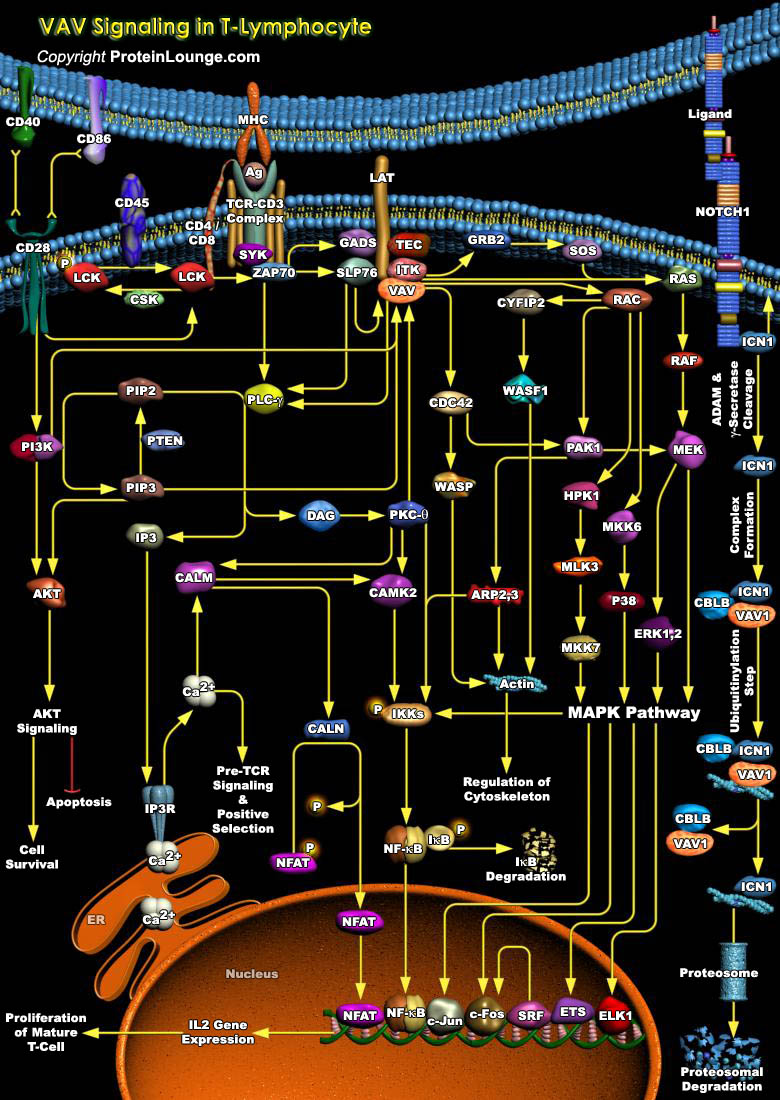
VAV(Oncogene Vav) family of proteins act as GEFs (Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors) and activators of Rho family GTPases, and are known to orchestrate cytoskeletal changes and cell migration in response to extracellular stimuli by catalyzing the exchange of GDP for GTP. Of the three mammalian isoforms, Vav1 is[..]
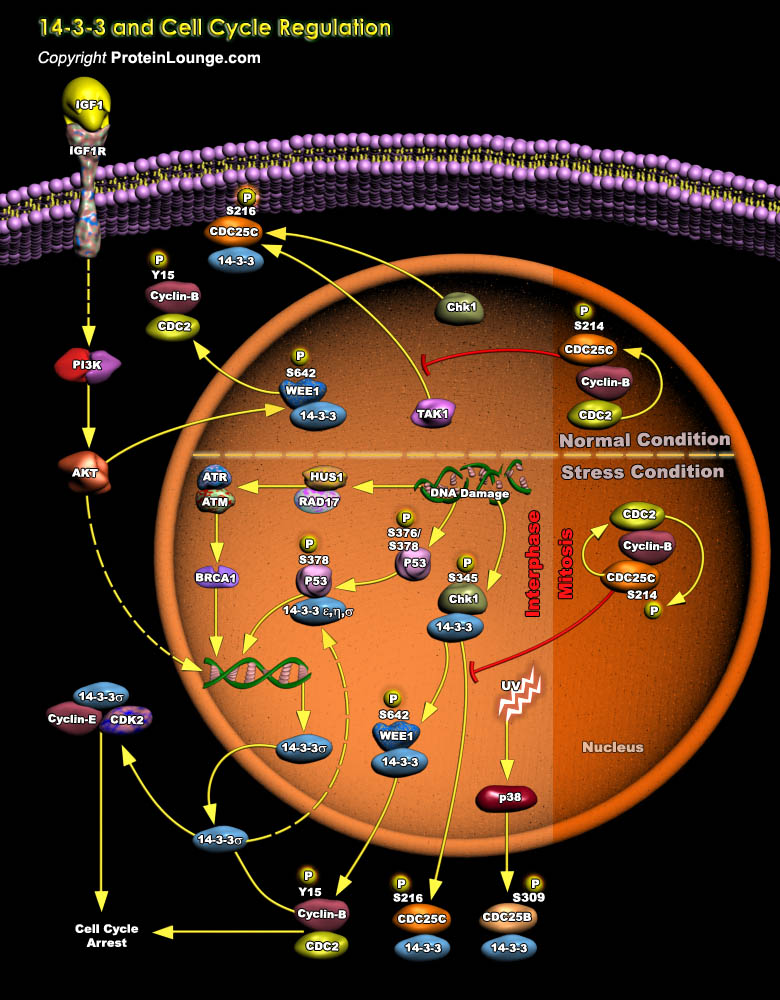
Co-ordinated progression through the cell cycle is essential for the maintenance of genomic integrity. 14-3-3 proteins play particularly important roles in coordinating progression of cells through the cell cycle, regulating their response to DNA damage, and influencing life-death decisions following internal injury or external cytokine-mediated cues. 14-3-3 proteins function at several key[..]
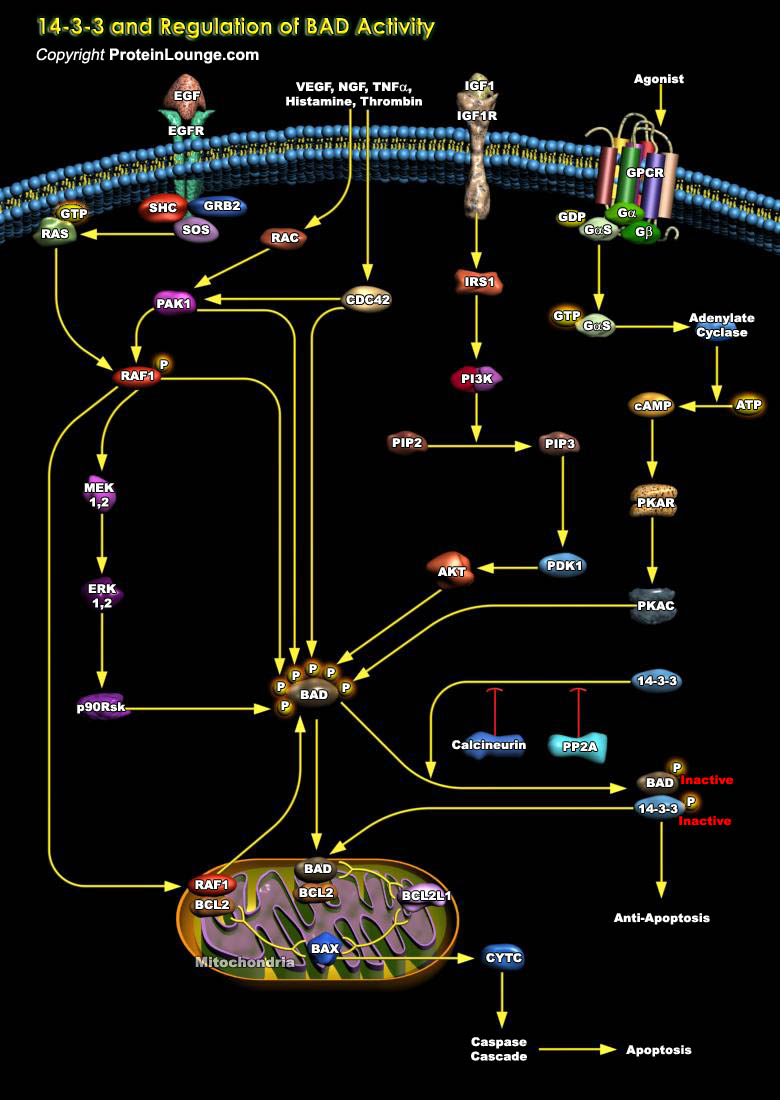
14-3-3 is a phosphoserine/phosphothreonine-binding protein that is being implicated in a wide range of cellular phenomena. 14-3-3 family members are found in all eukaryotes – from plants to mammals – and more than 100 binding partners have been identified to date. They regulate their activities by a number of different mechanisms, which include inter- and intracompartmental[..]
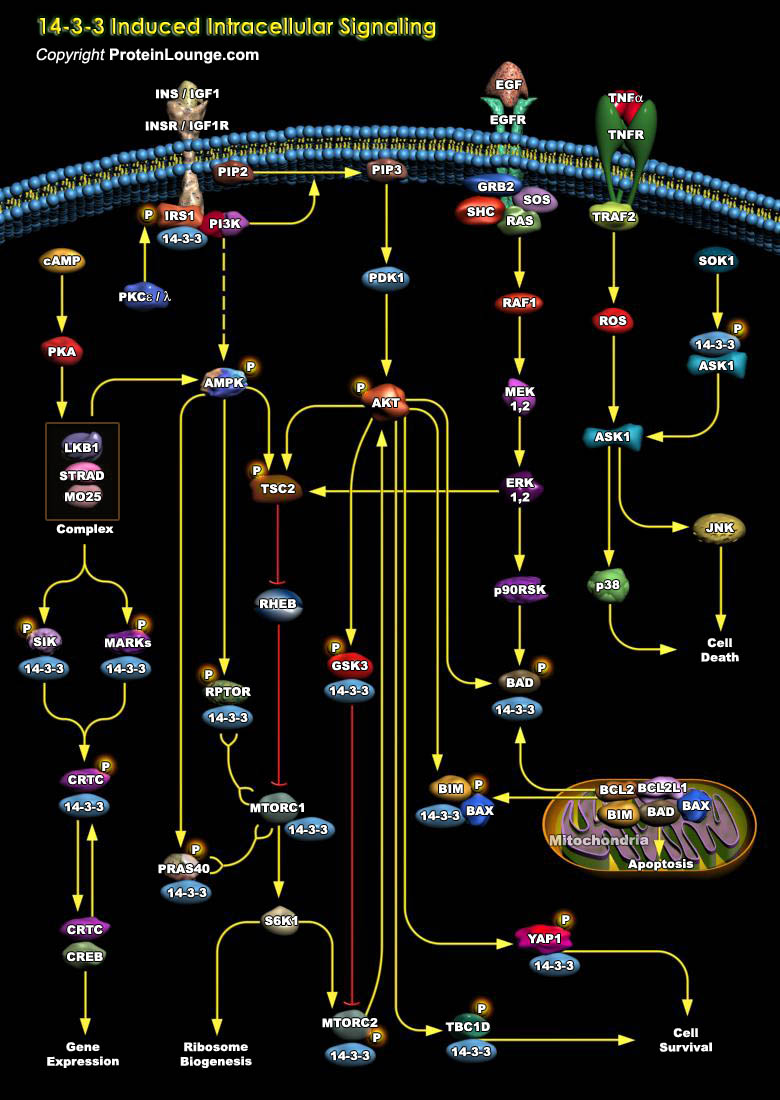
The 14-3-3 family of proteins consists of molecular adaptors that recognize phosphorylated proteins (e.g. kinases, transcription factors and receptors). They are able to coordinate almost limitless combinations of protein complexes, which accounts for their functional diversity (Ref.1). This plethora of interacting proteins allows 14-3-3 to play important roles in a wide range of vital[..]
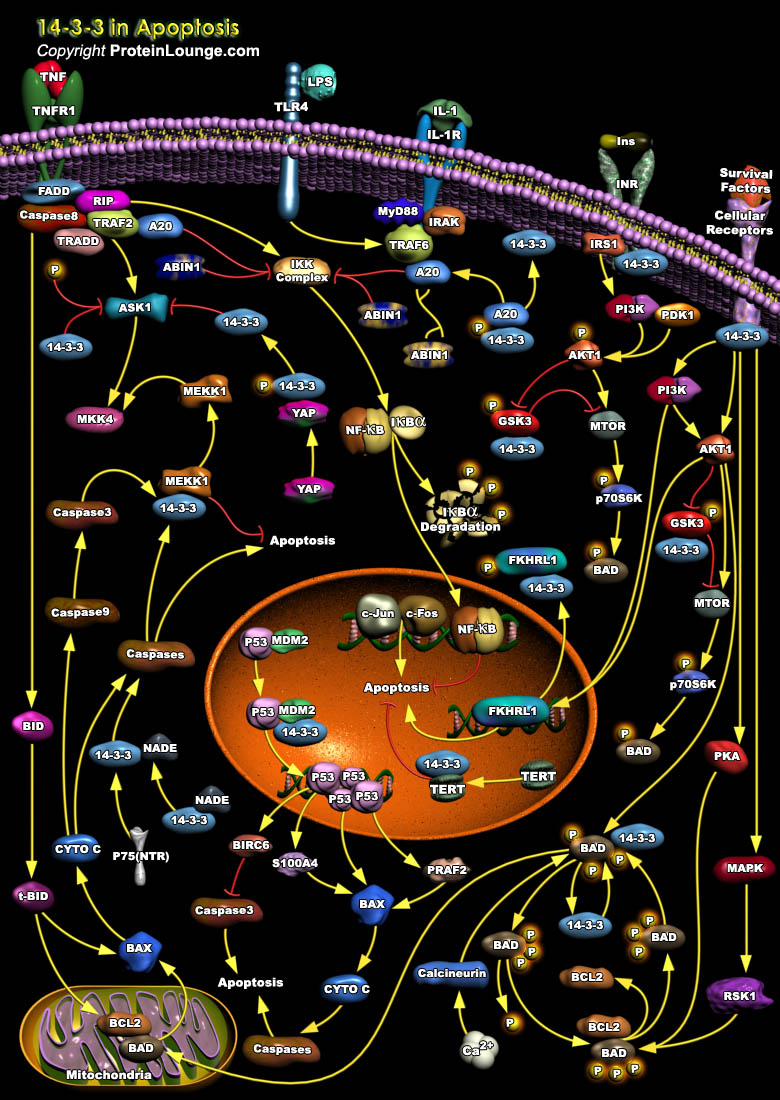
14-3-3 proteins are abundantly expressed adaptor proteins that interact with a vast number of binding partners to regulate their cellular localization and function. They regulate substrate function in a number of ways including protection from dephosphorylation, regulation of enzyme activity, formation of ternary complexes and sequestration. They are key regulators of major cellular processes[..]
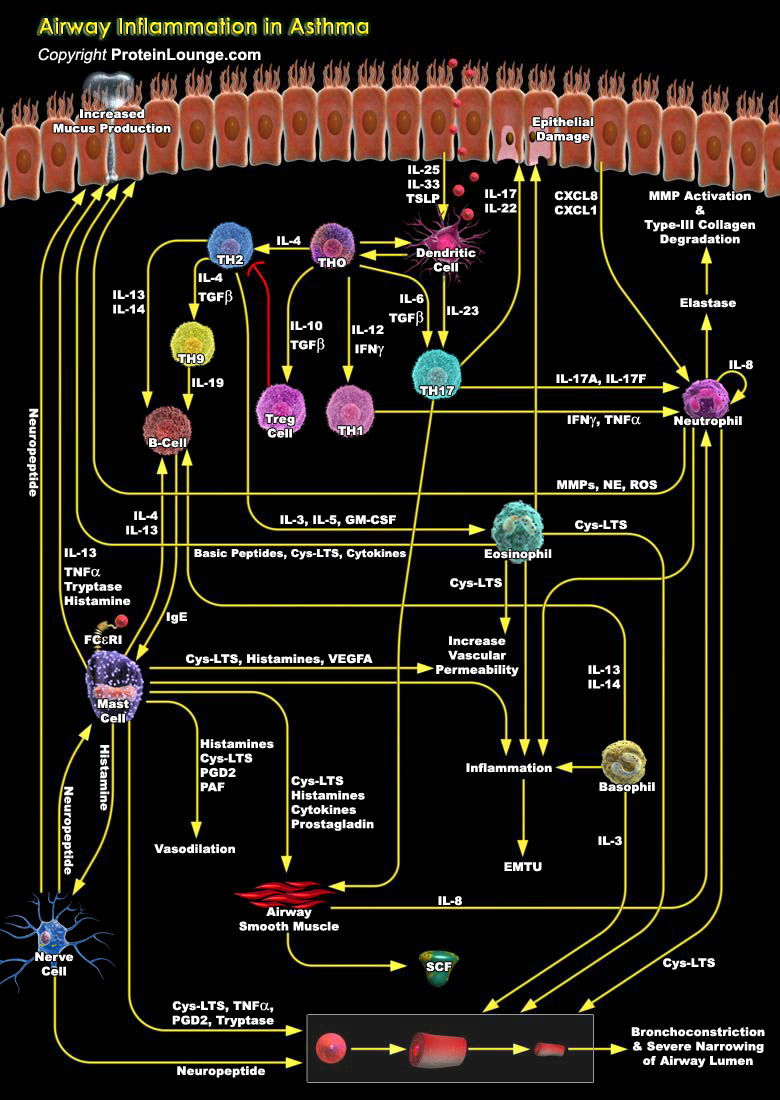
Asthma is a complex, chronic inflammatory lung disease which is characterized by persistent airway inflammation and airway wall remodeling, that includes the structural changes in the airway wall, epithelial cell shedding, hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the ASM (airway smooth muscle) bundles, basement membrane thickening and increased vascular density. Airway wall remodeling starts early in[..]
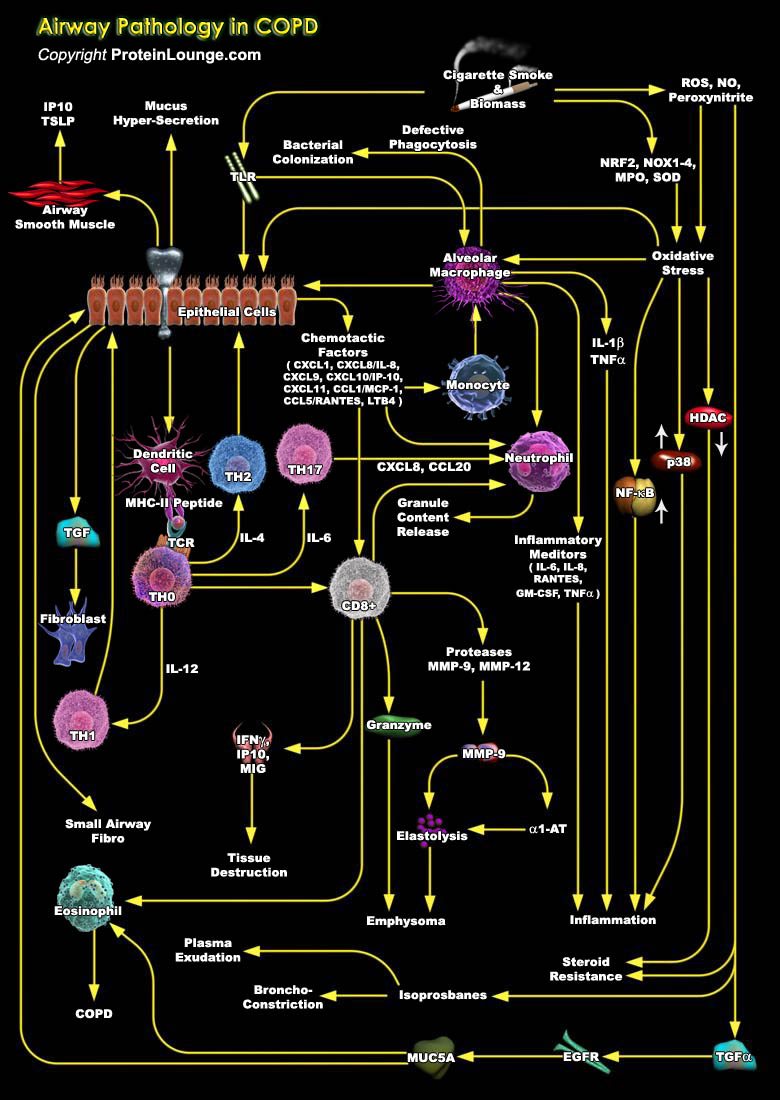
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major global health problem that is becoming preva¬lent, particularly in developing countries [Ref.1]. It is one of the most common diseases in the world, with a lifetime risk estimated to be as high as 25%, and now equally affects both men and women [Ref.2]. COPD is greatly under¬ diagnosed and often diagnosed late in its course, so[..]
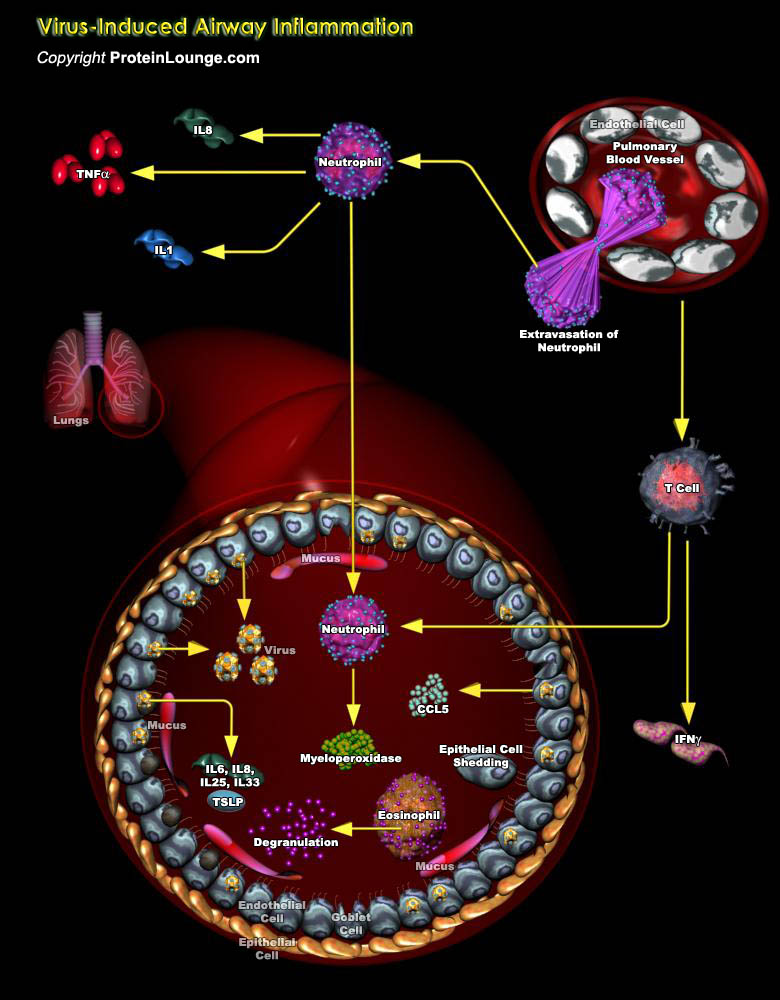
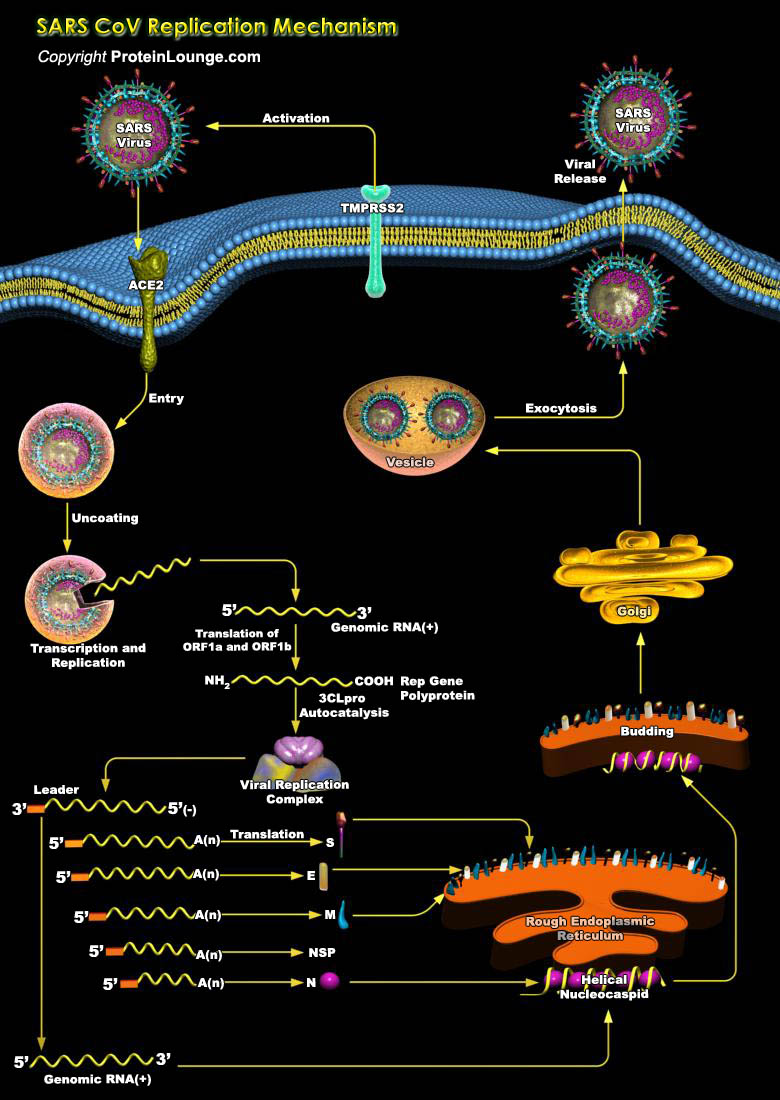
More than 200 different types of viruses, such as human Rhinovirus (HRV), human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), and human Parainfluenza Virus (HPIV), are known to cause acute respiratory illness. Virus-induced cytokine production and inflammatory cell activation are instrumental in the development of neurogenic inflammatory responses, and[..]
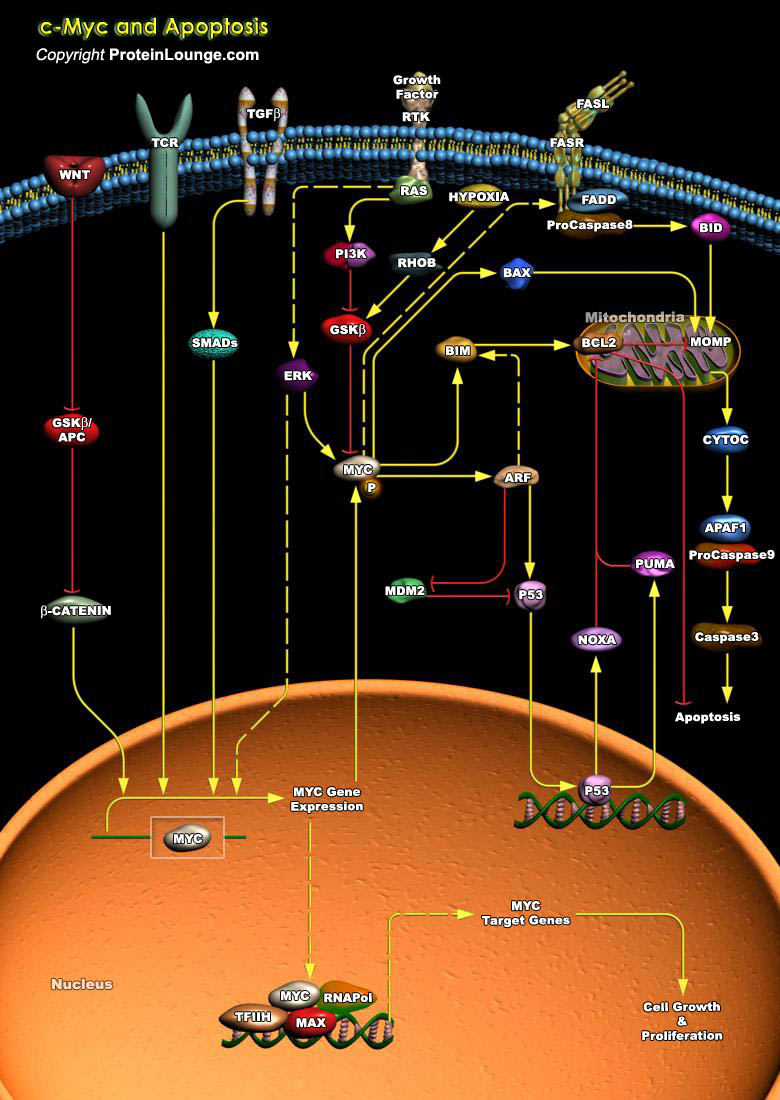
Many proto-oncogenes participate in the regulation of apoptosis and closely intertwined with their actions are various growth factors and other genes that participate in the control of cellular growth. The proto-oncogene c-Myc encodes a transcription factor c-Myc that plays a critical role in multiple cellular processes including cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and[..]
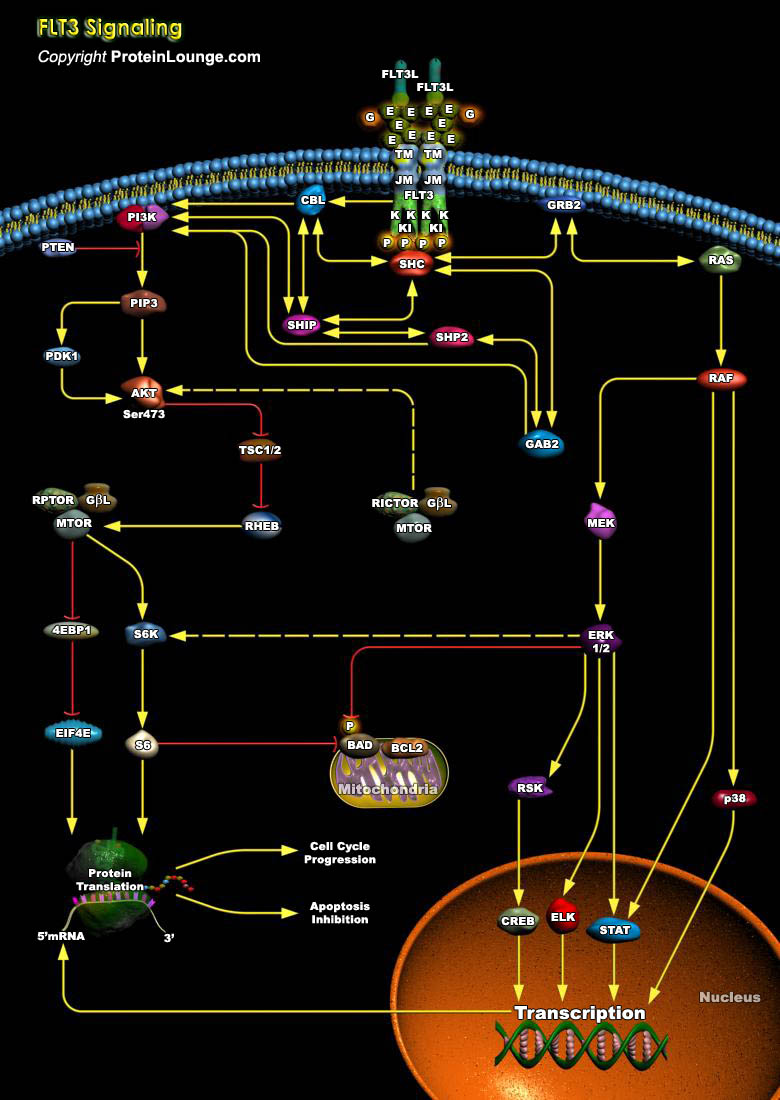
FLT3 (Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase-3), also known as FLK2 (Fetal Liver Kinase-2) and STK1 (human Stem Cell Kinase-1) was originally isolated as a hematopoietic progenitor cell-specific kinase, and belongs to the Class-III RTK (Receptor Tyrosine Kinase) family to which c-Fms, c-Kit, and the PDGFR (Platelet Derived Growth Factor Receptor) also belong (Ref.1). Normal expression of FLT3 is restricted to[..]