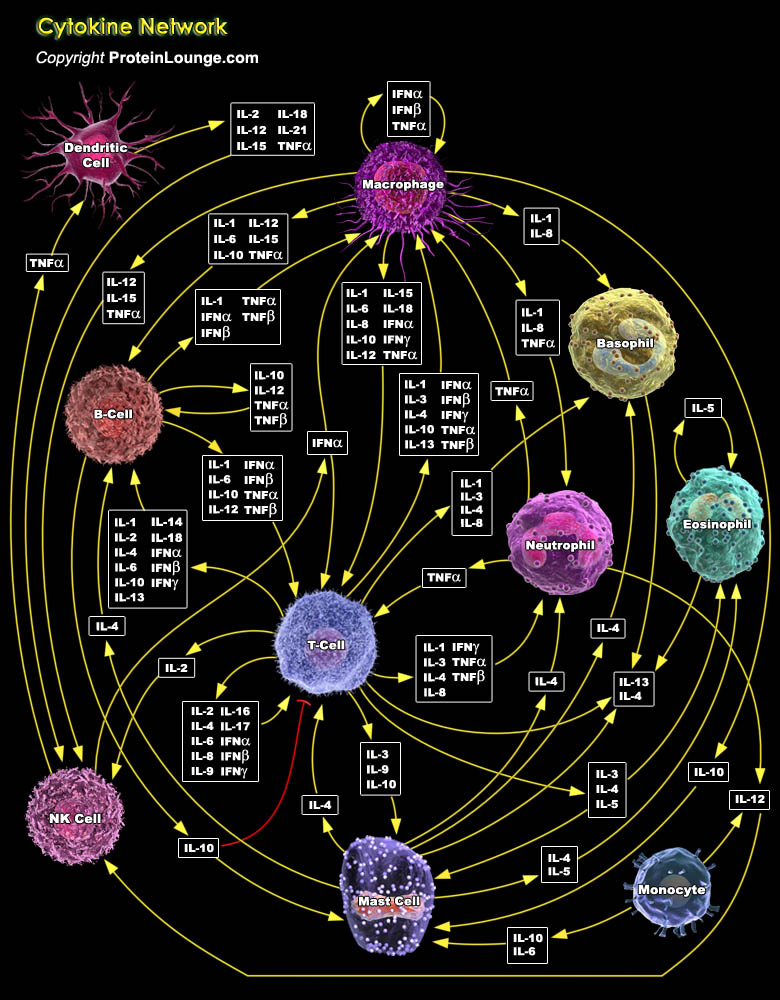
Featured Pathways
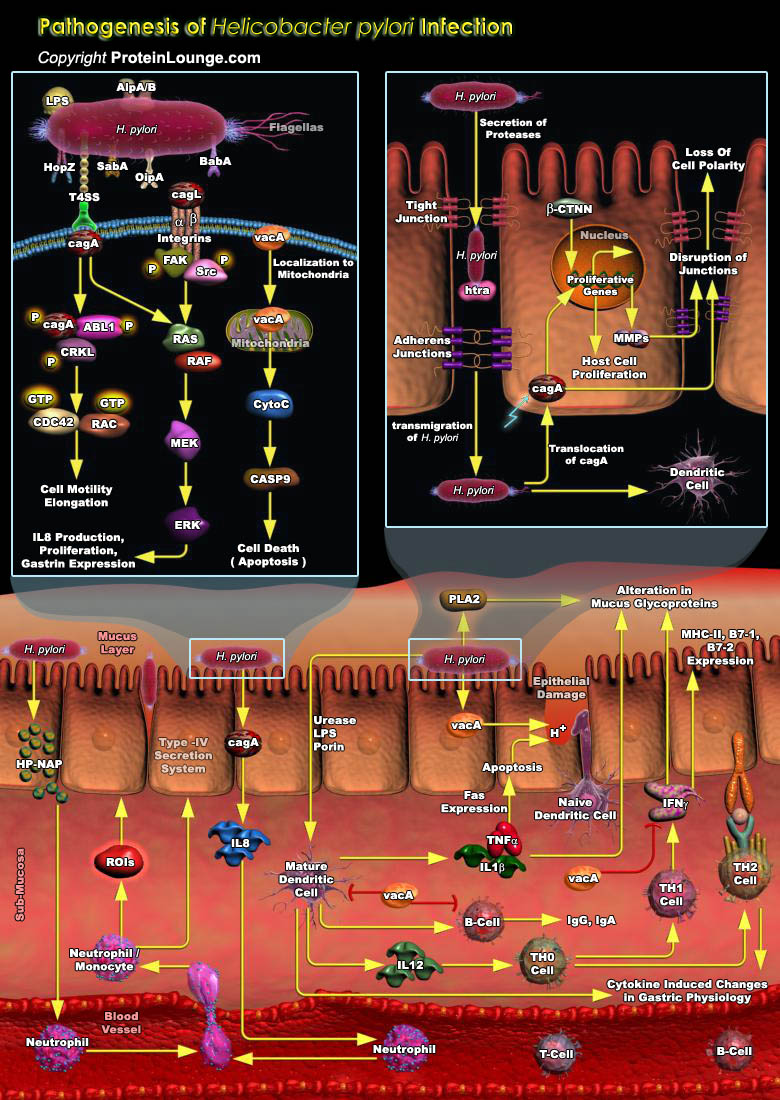
The gastrointestinal tract represents an important barrier between human hosts and microbial populations. One potential consequence of host-microbial interactions is the development of mucosal inflammation. A paradigm for such chronic host-microbial relationships is carriage of Helicobacter pylori, Gram-negative bacteria that colonize the stomachs of humans and primates. H. pylori colonization[..]
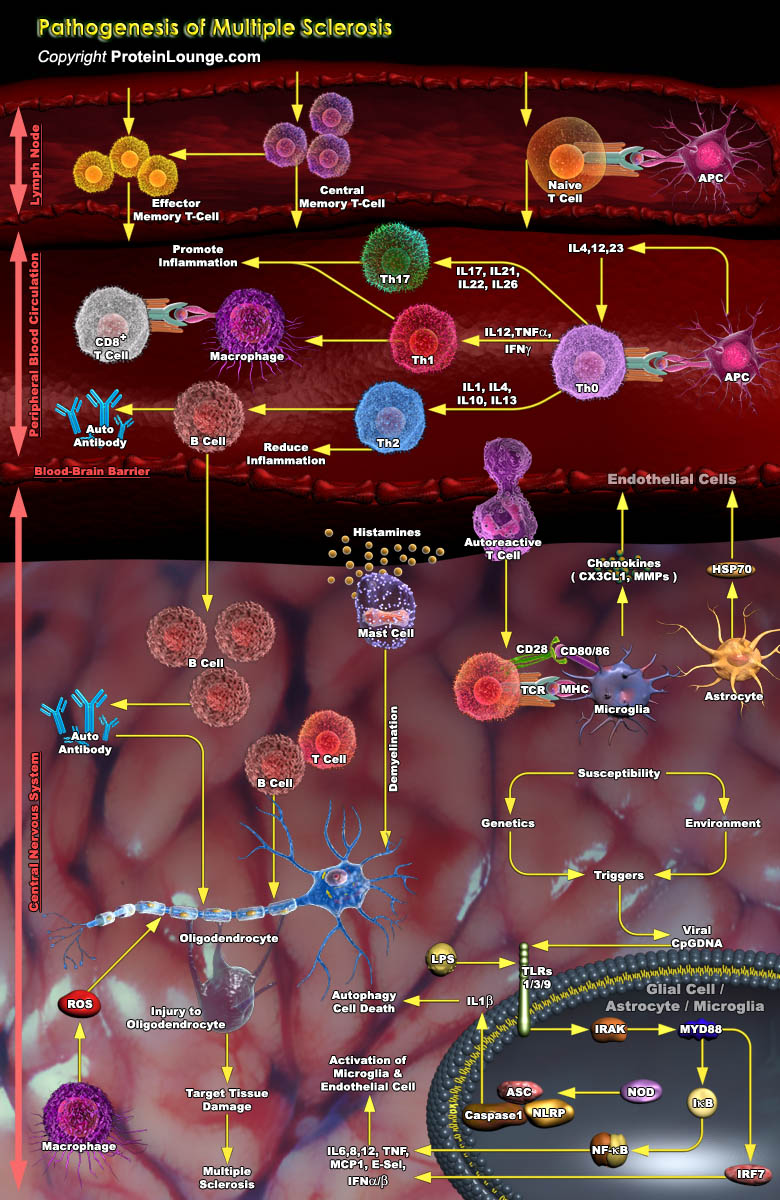
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory, demyelinating, and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system that affects both adults and children. MS is characterized by the formation of multiple lesions along the nerve fibers in the brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. Inflammation of the white and gray matter tissues in the CNS due to focal immune cell infiltration and their[..]
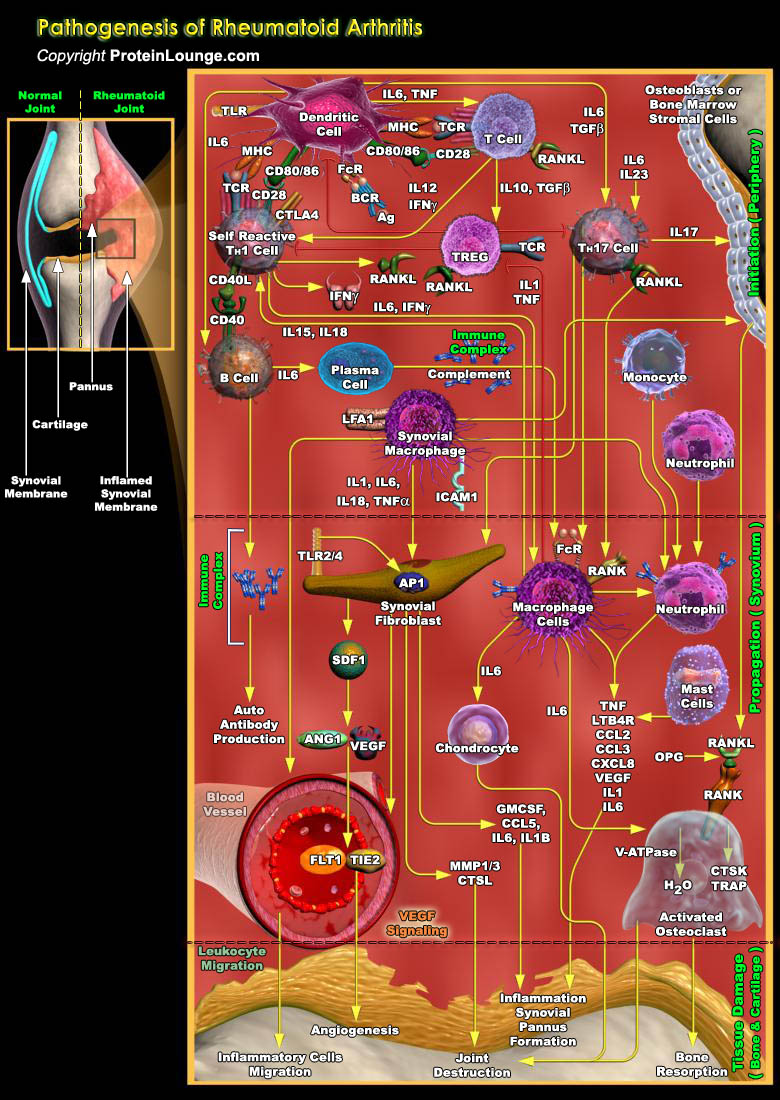
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic symmetric polyarticular joint disease that primarily affects the small joints of the hands and feet. The inflammatory process is characterized by infiltration of inflammatory cells into the joints, leading to proliferation of synoviocytes and destruction of cartilage and bone.This is a chronic debilitating autoimmune disease of unknown etiology affecting[..]
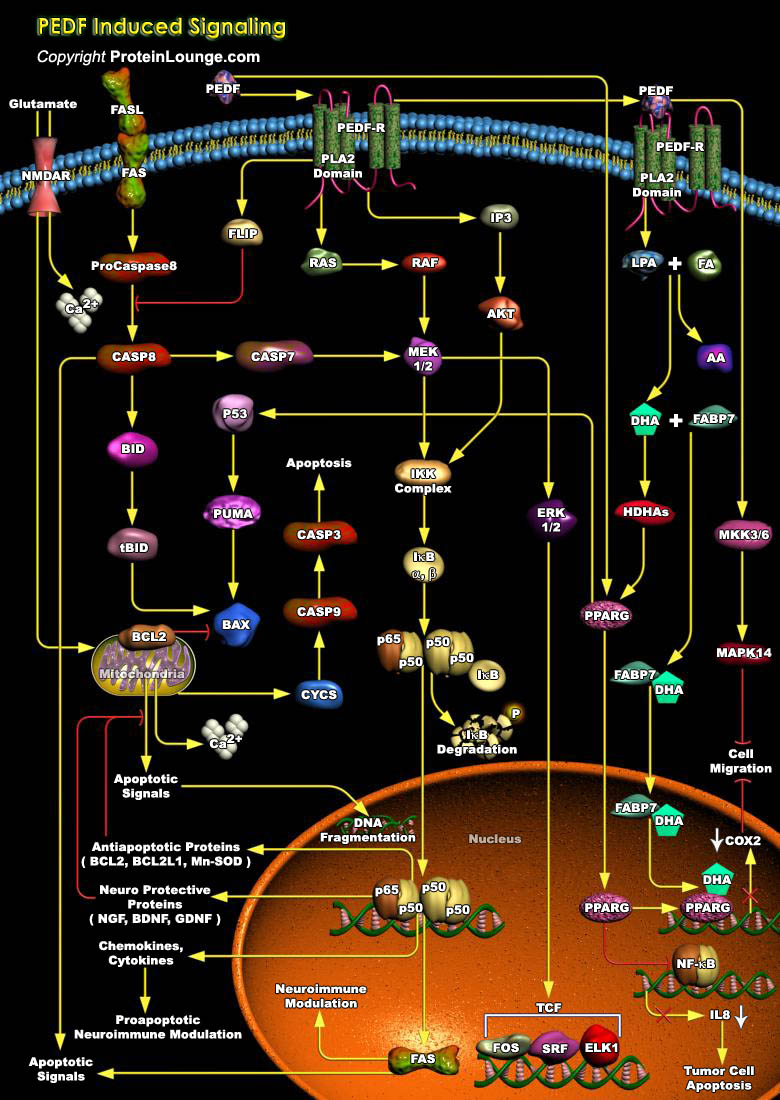
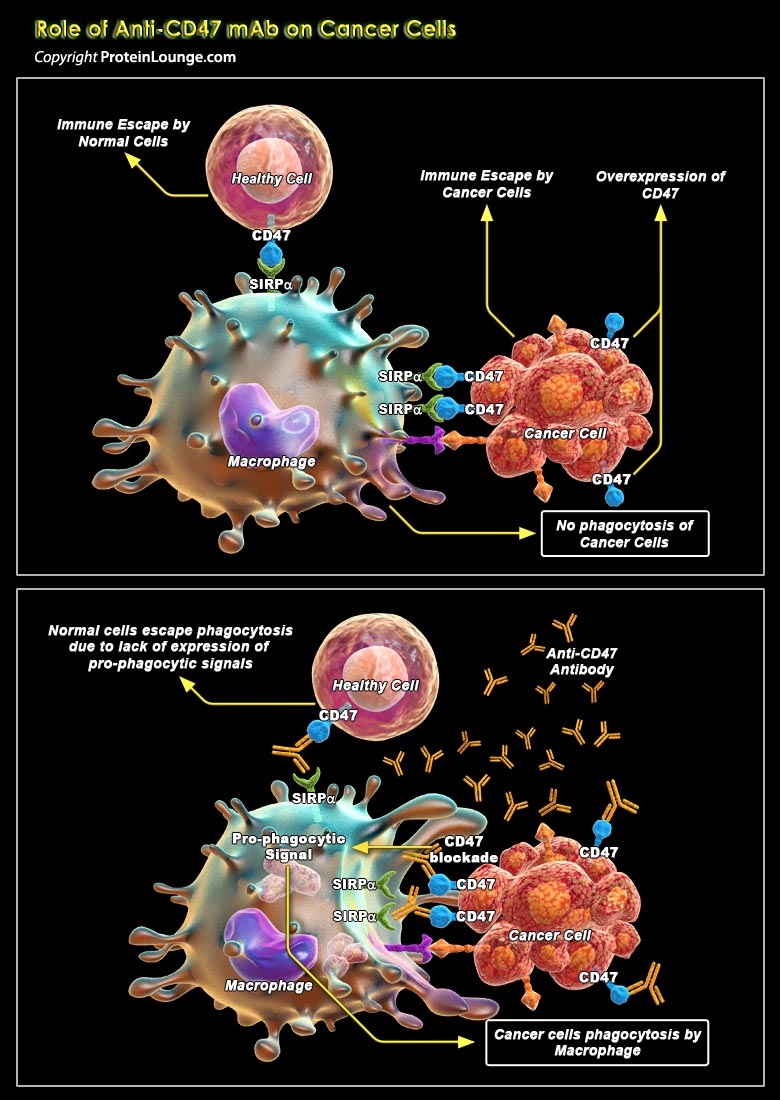
Blood vessel growth and stability are under the exquisite control of a network of pro- and anti-angiogenic factors. Disruption of the balance between these factors is a characteristic of tumor growth and many vascular diseases. Endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors, particularly those that act broadly at the earliest stages, are excellent pharmacological tools in combating pathogenic vessel[..]
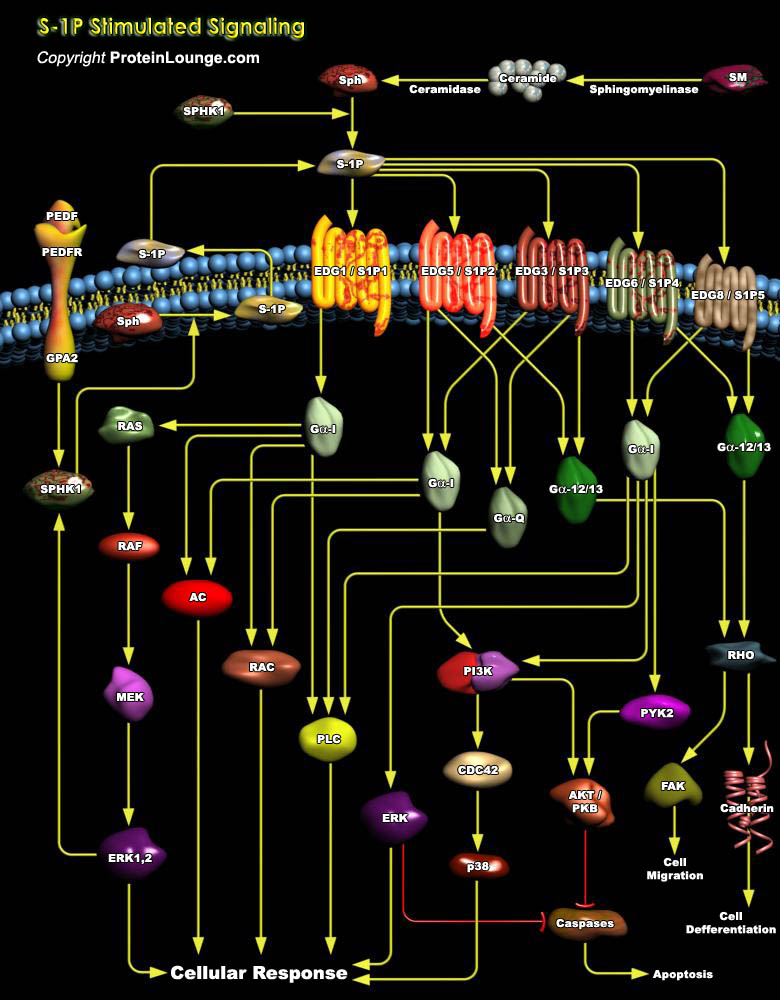
Various lipid molecules serve as second messengers for transducing signals from the cell surface to the cell interior and trigger specific cellular responses. Sphingolipids represent a complex group of lipids that have recently emerged as new transducers in eukaryotic cells. Sphingolipids are found in all mammalian cells and are mostly located in the plasma membrane. They all contain as a[..]
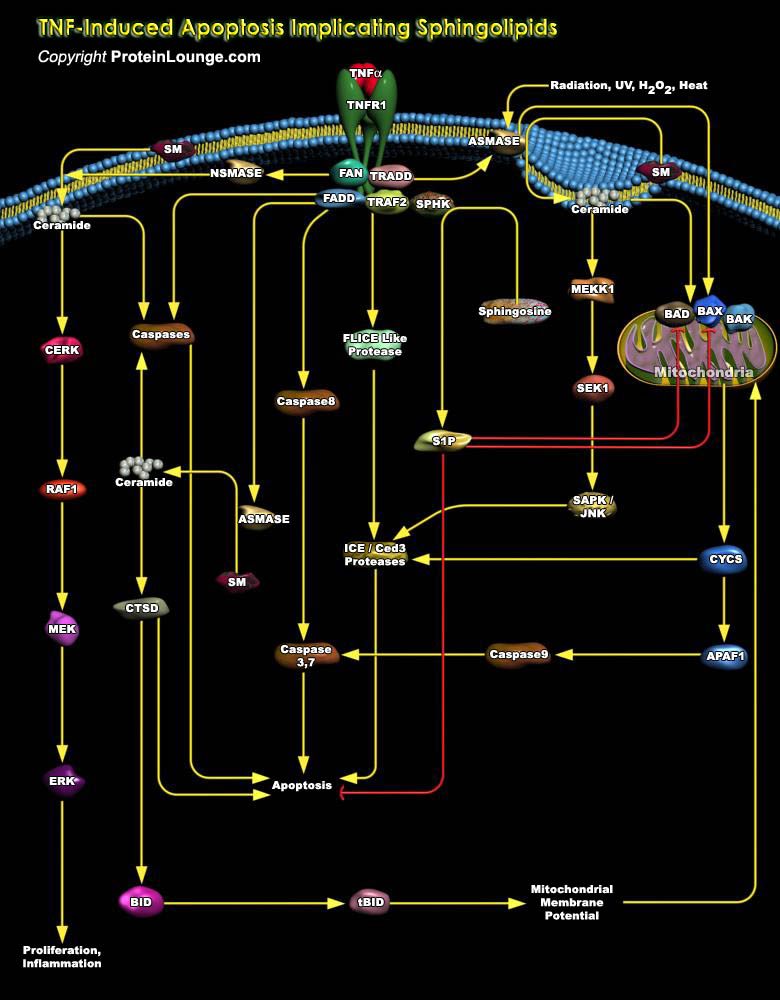
Various lipid molecules serve as second messengers for transducing signals from the cell surface to the cell interior and trigger specific cellular responses. Recently, several sphingolipids have emerged as cellular constituents that are able to promote, mediate or counterbalance apoptosis. Sphingolipids are a family of membrane lipids whose structure is made up of a long-chain sphingoid base[..]
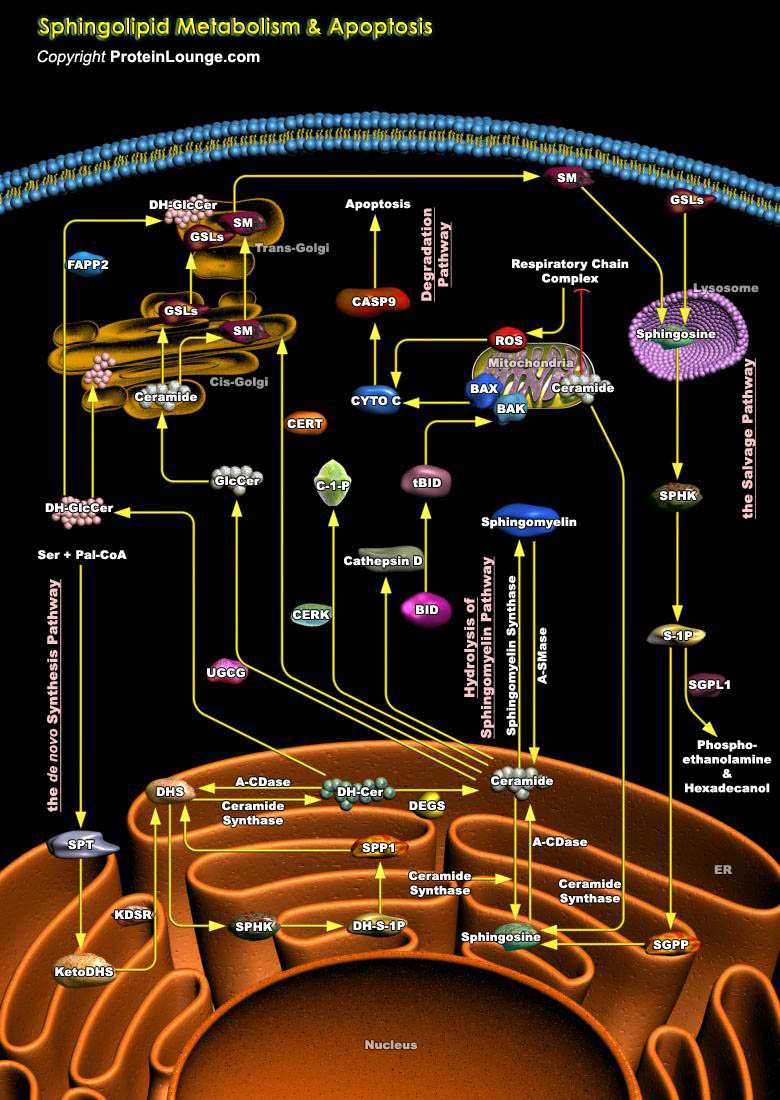
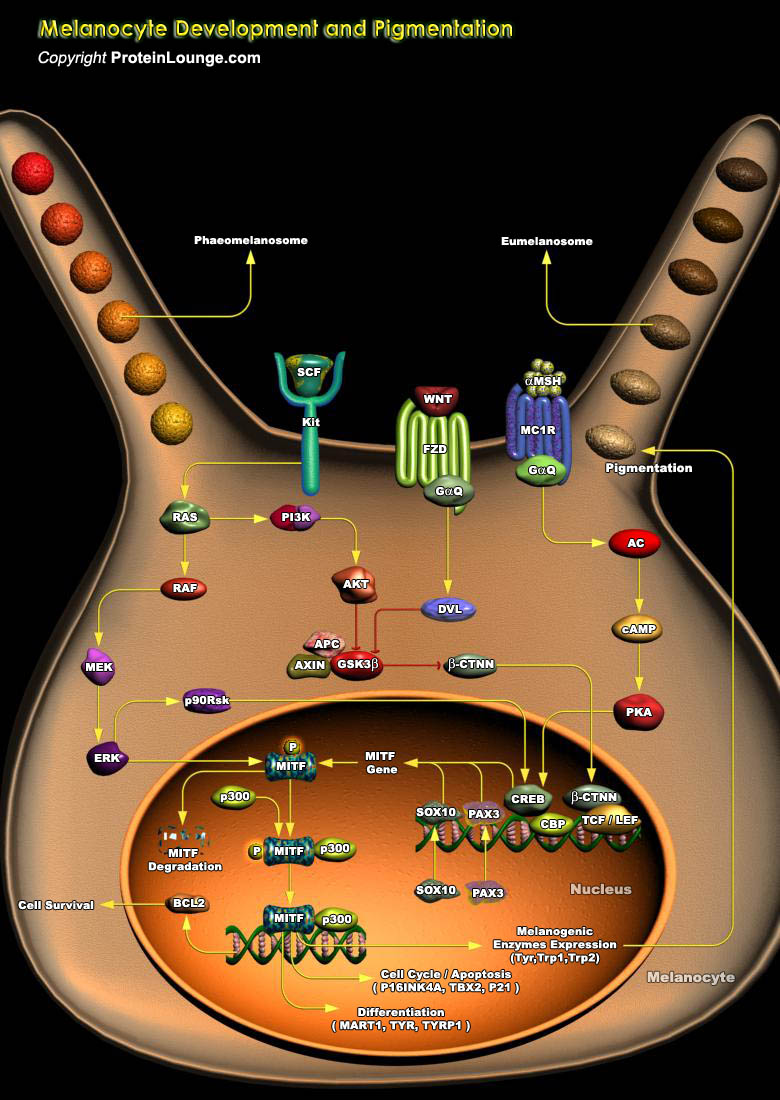
The sphingolipids are primarily situated in the noncytoplasmic leaflet of cellular membranes contribute to the structural integrity and fluidity characteristics of cell membranes and signal transduction complexes. Ceramide sits at the hub of sphingolipid metabolism as the neutral, lipid building block for complex sphingolipids and glycosphingolipids, serving as a[..]
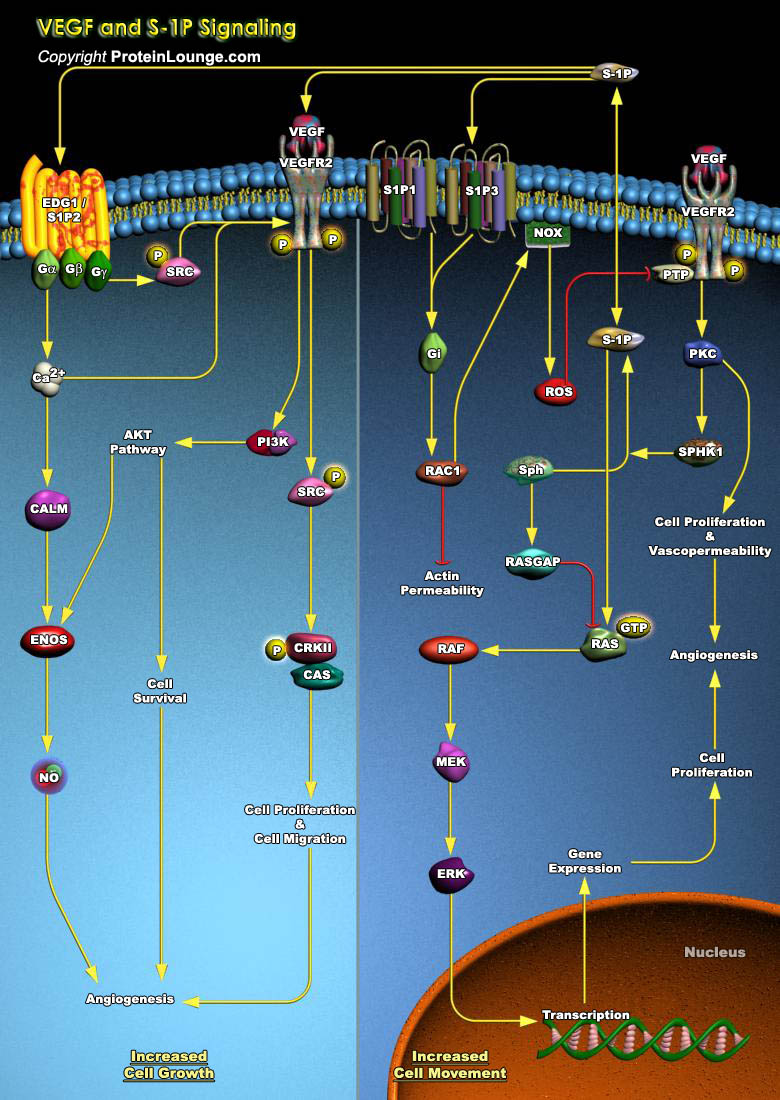
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a bioactive sphingomyelin derivative that is present in plasma and serum at high nanomolar concentrations. S1P acts via the specific cell surface G-protein-coupled receptors, S1P1-5. S1P1 and S1P2 were originally identified from vascular endothelial cells (ECs) and smooth muscle cells, respectively. S1P receptors modulate multiple intracellular pathways and[..]
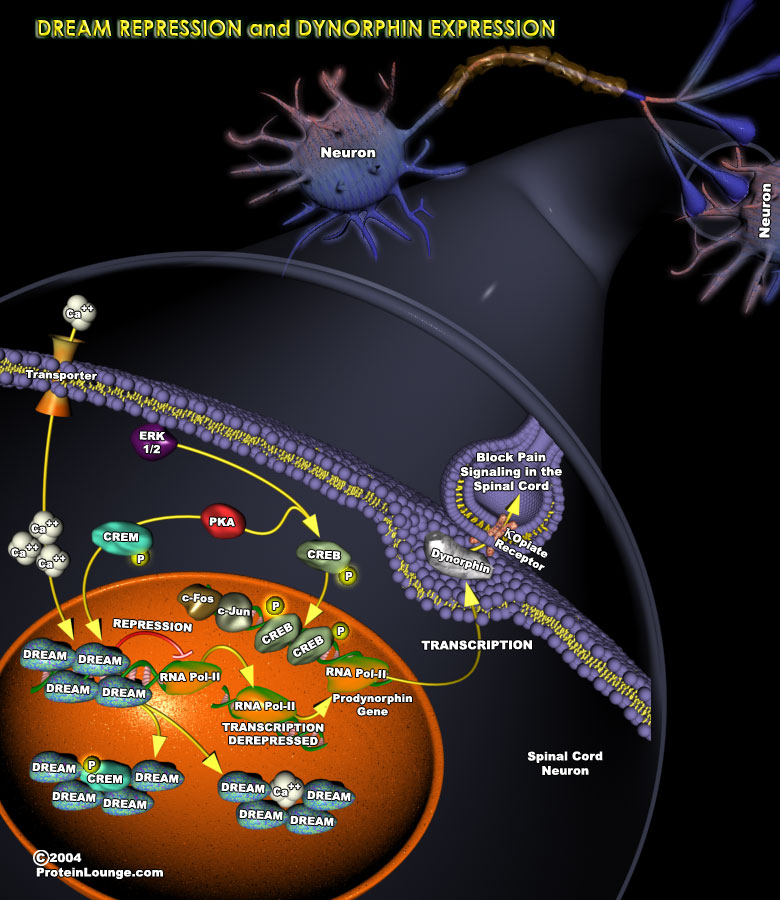
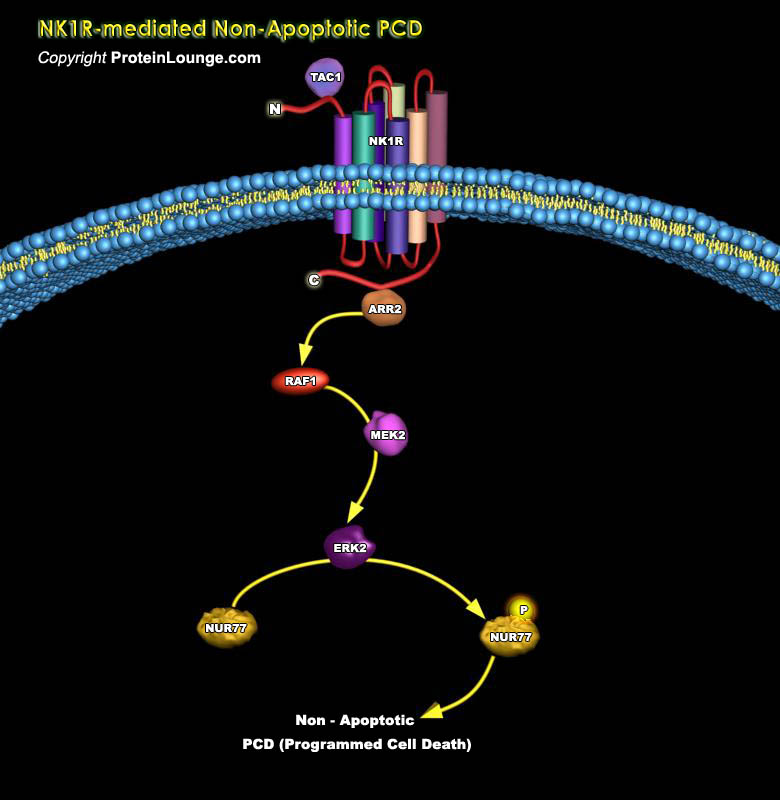
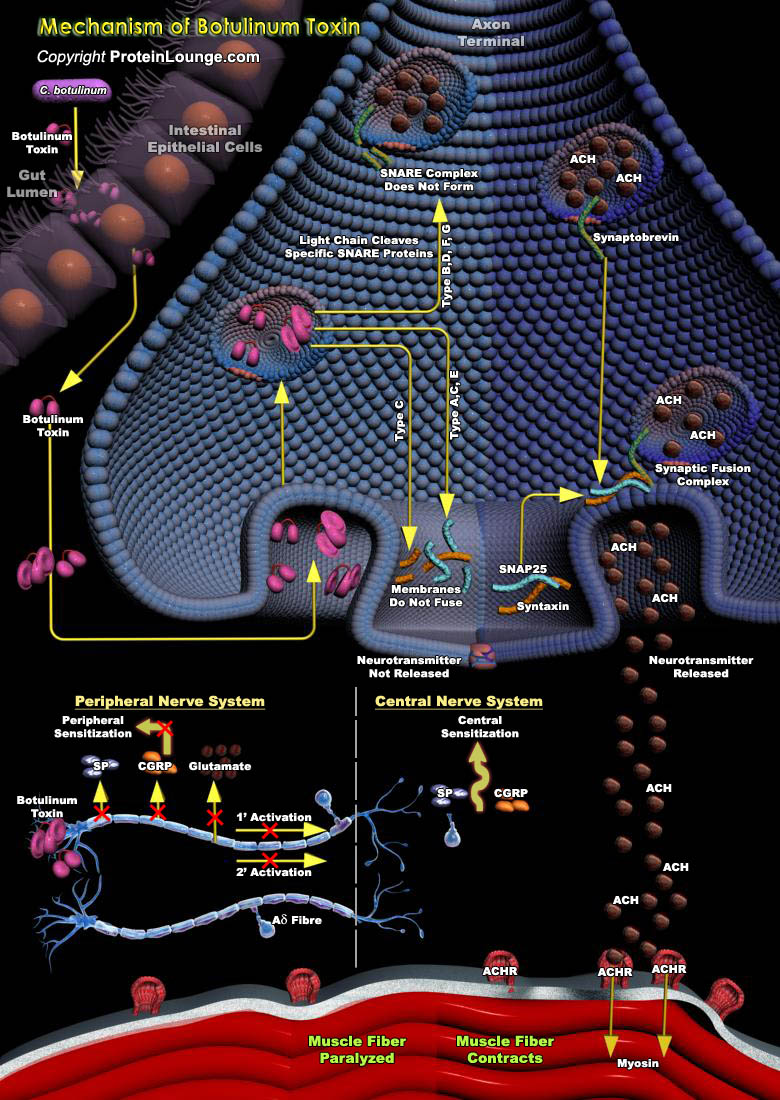
The experience of pain in response to noxious stimuli serves a crucial biological purpose: it alerts a living organism to environmental dangers, inducing behavioral responses that protect the organism from further damage. In contrast, chronic pain arising from disease states and/or pathological functioning of the nervous system offers no advantage and may be debilitating to those afflicted.[..]
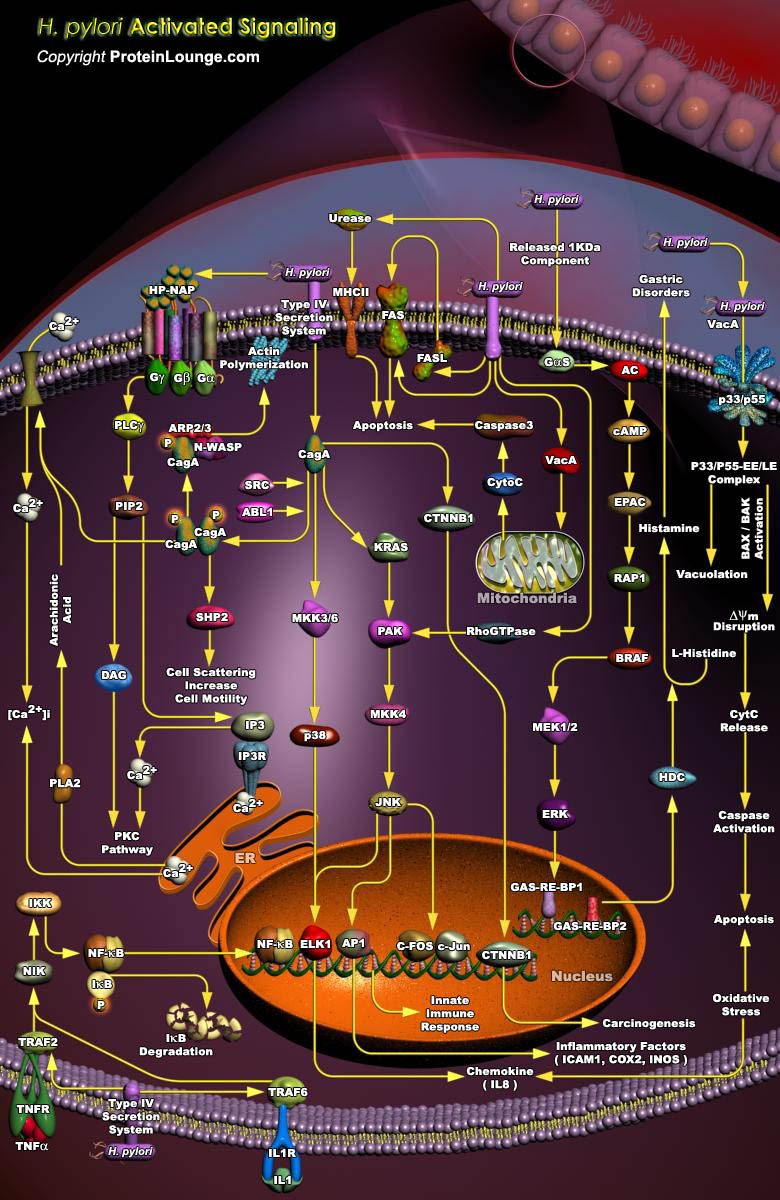
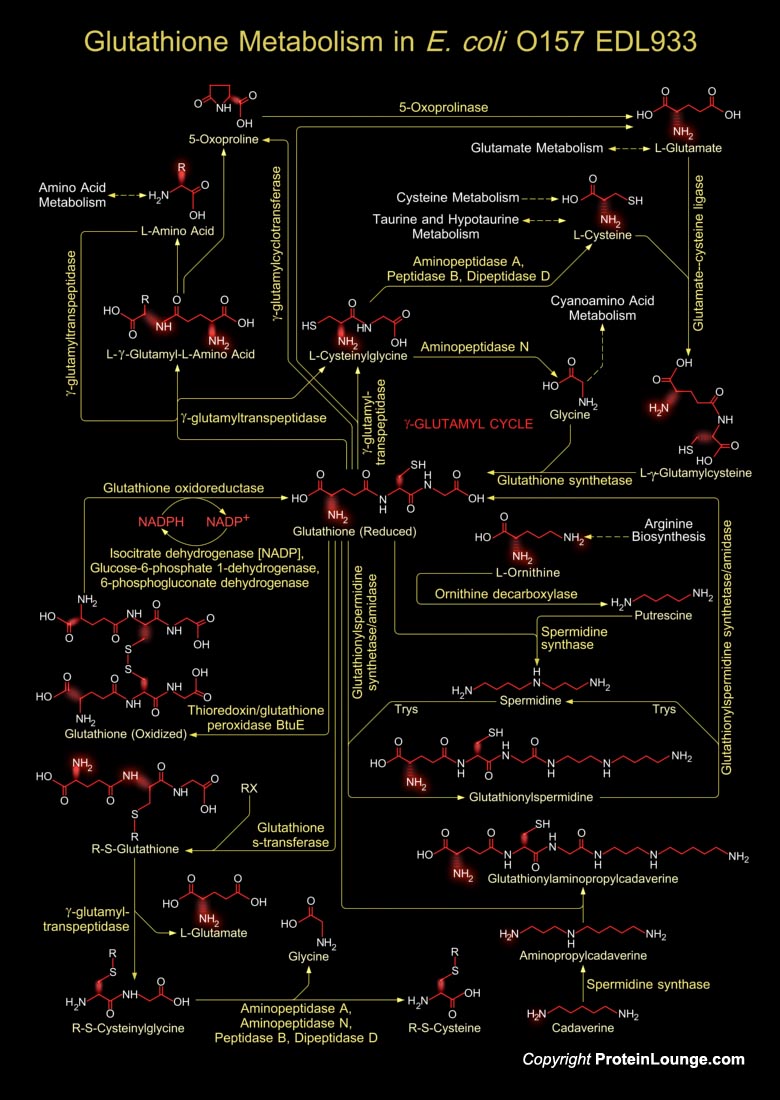
Helicobacter pylori is a gram negative bacterium that causes chronic inflammation in essentially all hosts, a process that increases the risk of developing peptic ulceration, distal gastric adenocarcinoma, and gastric mucosal lymphoproliferative disease. This bacterium also is the most common cause of ulcers worldwide. H. pylori infection is most likely acquired by ingesting contaminated food[..]