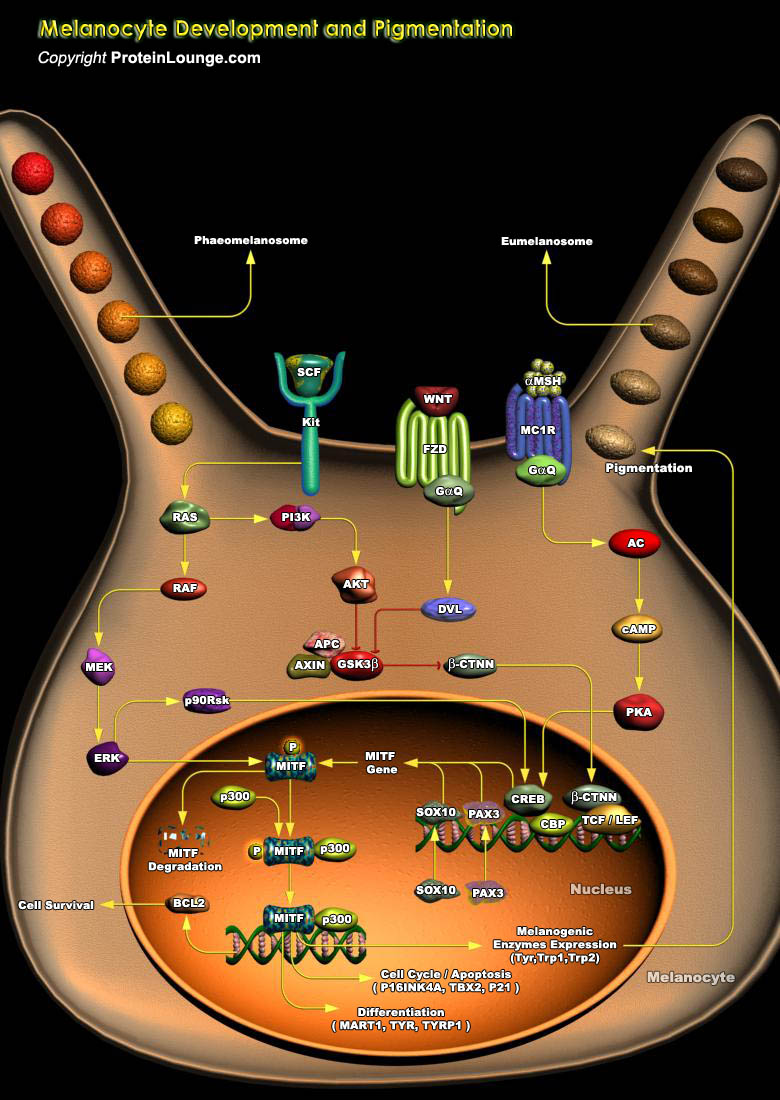
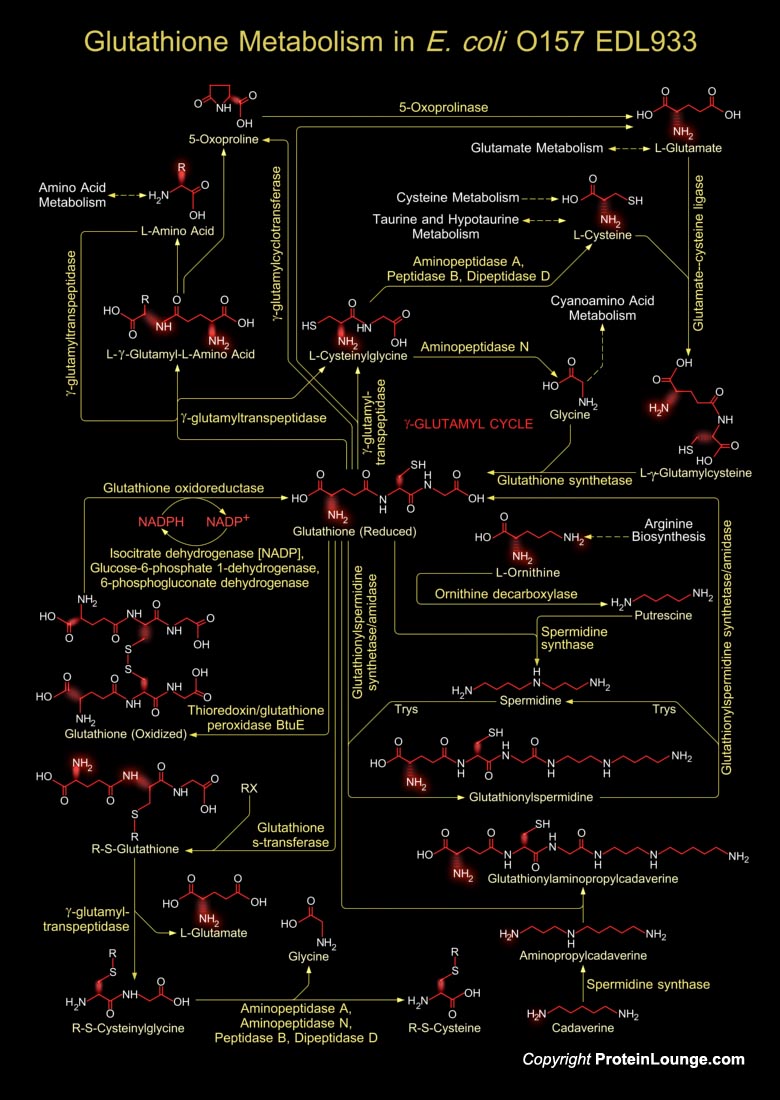
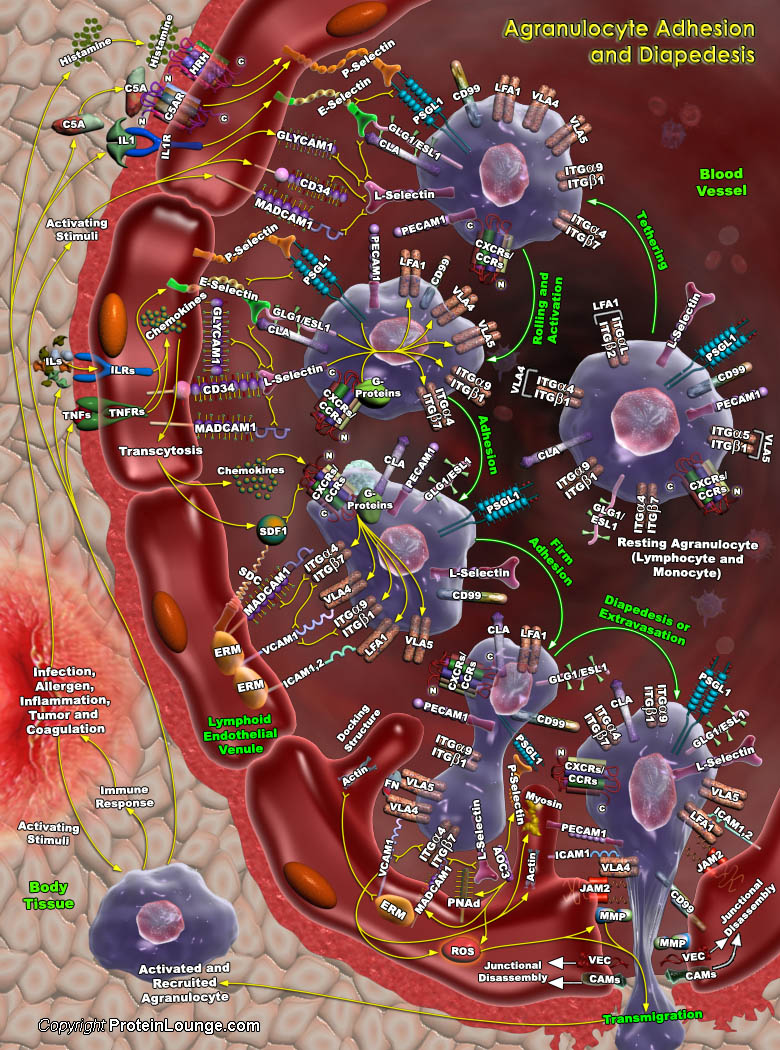
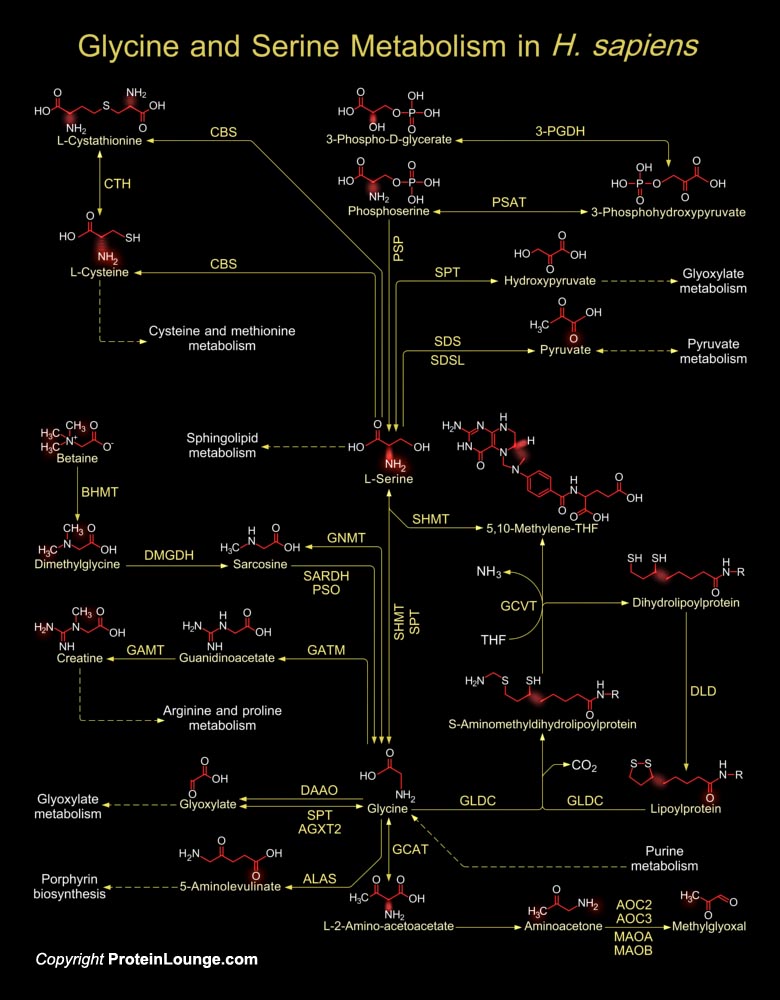
Featured Pathways
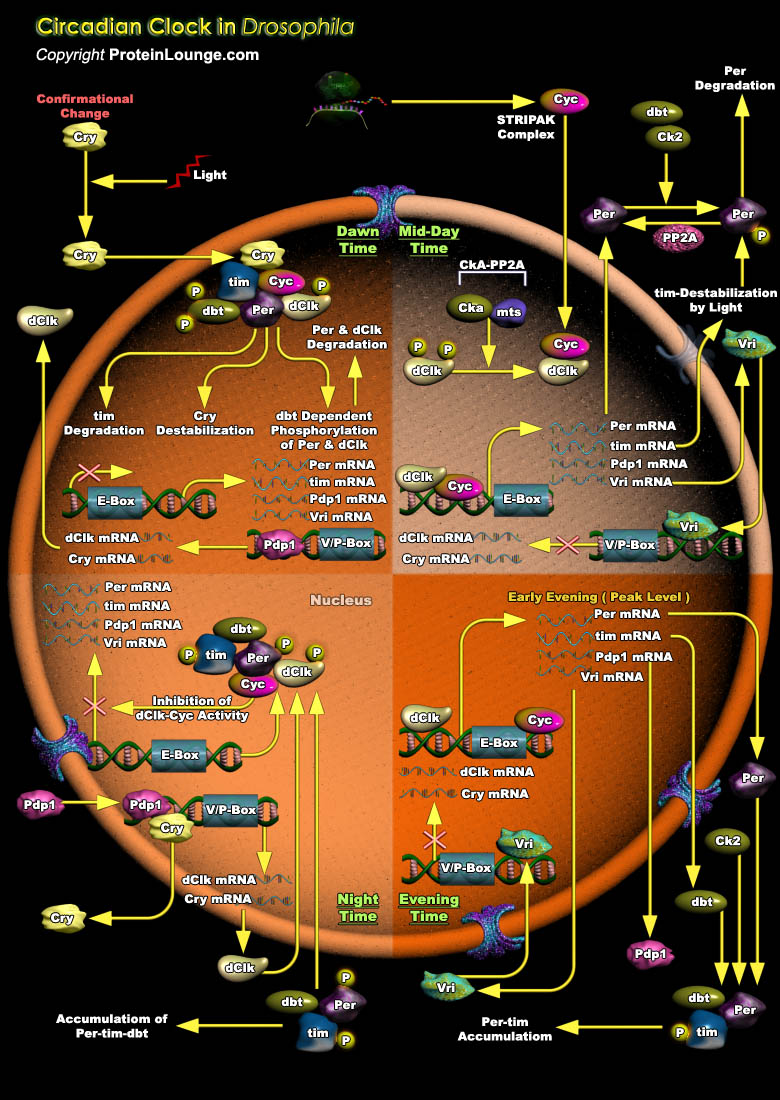
Circadian rhythms are daily rhythms of biological processes in behavior or physiology that reoccur approximately every 24 hr. They are determined and modified by environmental cues like light and temperature, but can also persist in the absence of these cues. Although circadian rhythms are present in nearly all living organisms, Drosophila melanogaster is used as model[..]
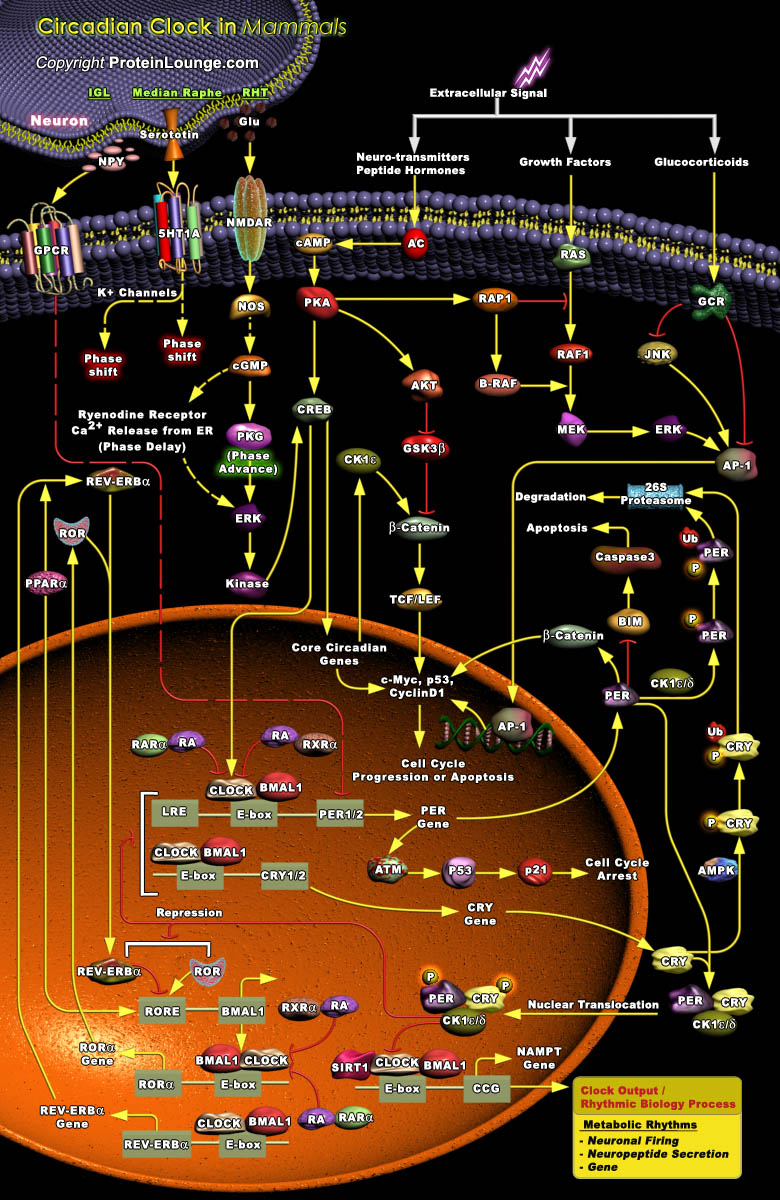
Circadian clocks are molecular time-keeping mechanisms that reside in a diverse range of cell types in a variety of organisms. The primary role of these cell-autonomous clocks is to maintain their own 24-hour molecular rhythm and to drive the rhythmic expression of genes involved in physiology, metabolism and behavior. The ability of the clock to persist in the absence of environmental cues[..]
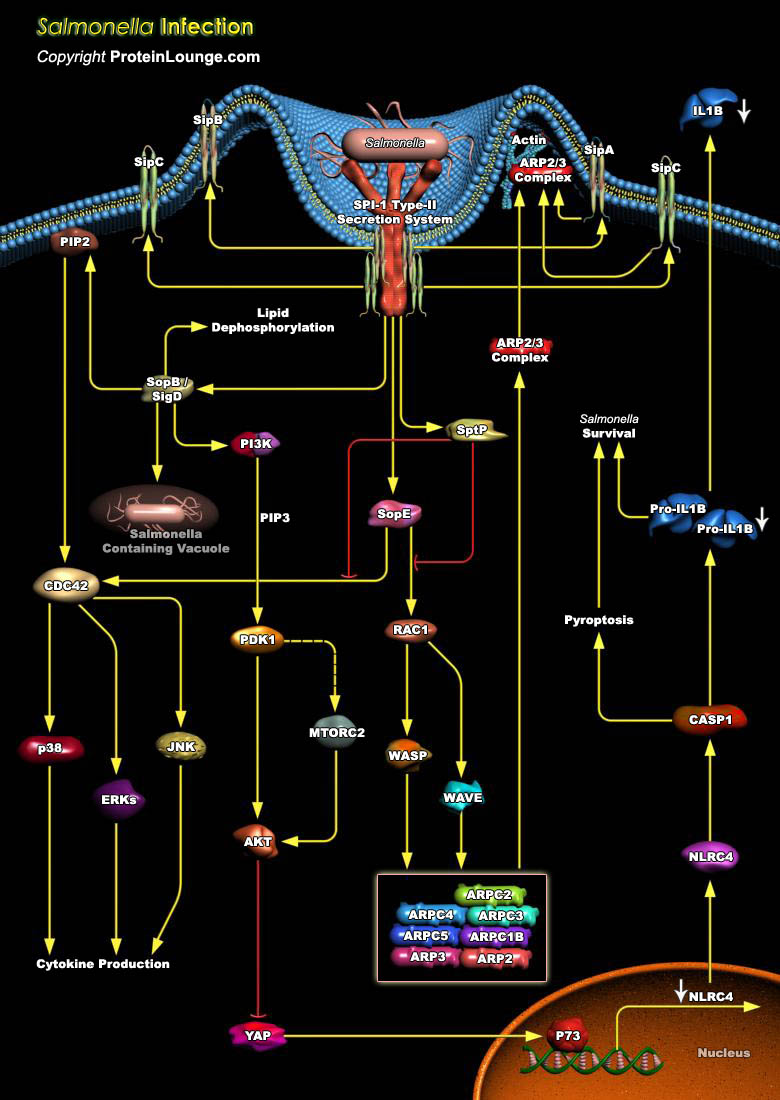
Phagocytic cells are a critical line of defense against infection. The ability of a pathogen to survive and even replicate within phagocytic cells is a potent method of evading the defense mechanisms of the host. A number of pathogens survive within macrophages after phagocytosis and this contributes to their virulence. Salmonella is one of these pathogens. Salmonella spp are Gram-negative[..]
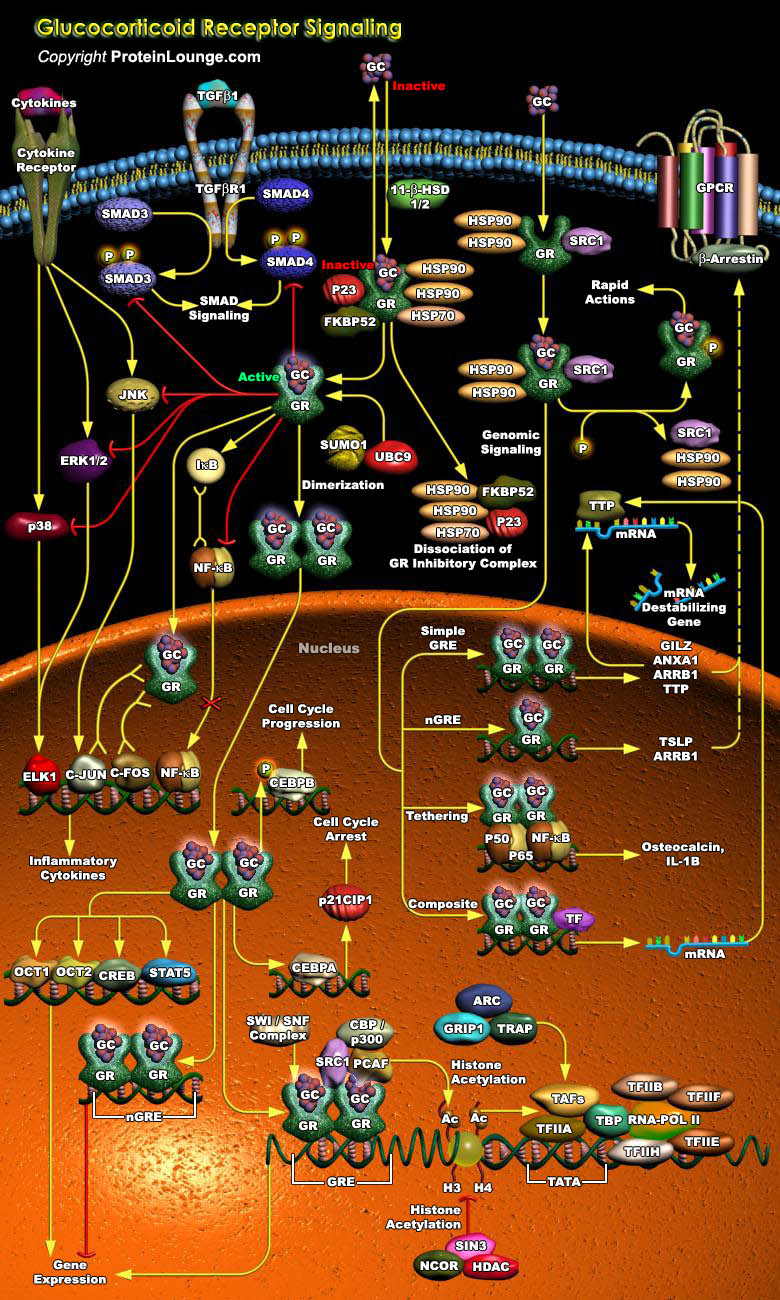
Our bones get more brittle with increasing age, and to add insult to injury, the most effective therapy for another problem that is associated with getting older, rheumatoid arthritis, often adds to the problem by causing bone resorption. The Glucocorticoid steroids, are the best available anti-inflammatories, and are used widely in the treatment of arthritis, as well as other inflammatory[..]

Apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis are the three major ways of PCD(programed cell death) following virus infection. Among them, apoptosis is the most extensively investigated PCD during viral infection. Apoptosis elicited by virus infection has both negative and positive influence on viral replication.Apoptosis is triggered by two distinct signaling pathways, namely the intrinsic and[..]
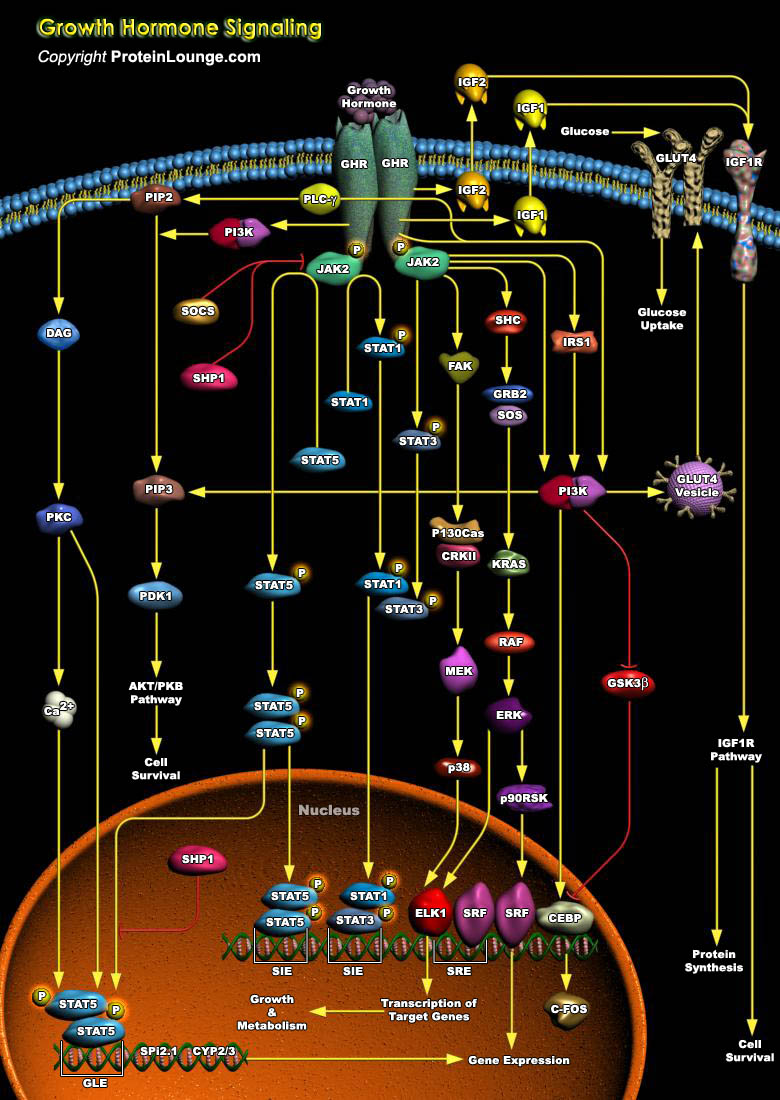
Most aging individuals die from atherosclerosis, cancer, or dementia; but in the oldest old, loss of muscle strength resulting in frailty is the limiting factor for an individual's chances of living an independent life until death. Three hormonal systems show decreasing circulating hormone concentrations during normal aging: (i) estrogen (in menopause) and testosterone (in andropause), (ii)[..]
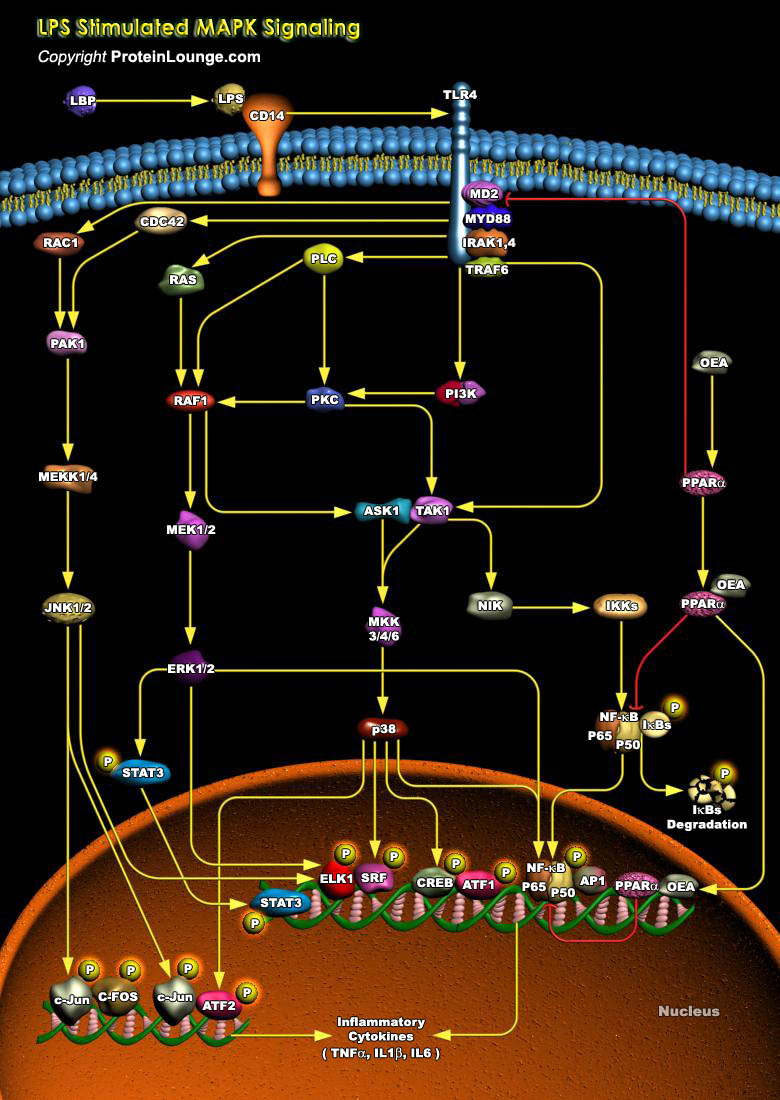
Endotoxin LPS (Lipopolysaccharide) is a component of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria that potently promotes the activation of macrophages and microglia cells, which are important sensors of infection by bacteria, fungi, and viruses, in both the periphery and the CNS (Central Nervous System). There are several known LBP (LPS-Binding Proteins) present on macrophage membranes, including[..]
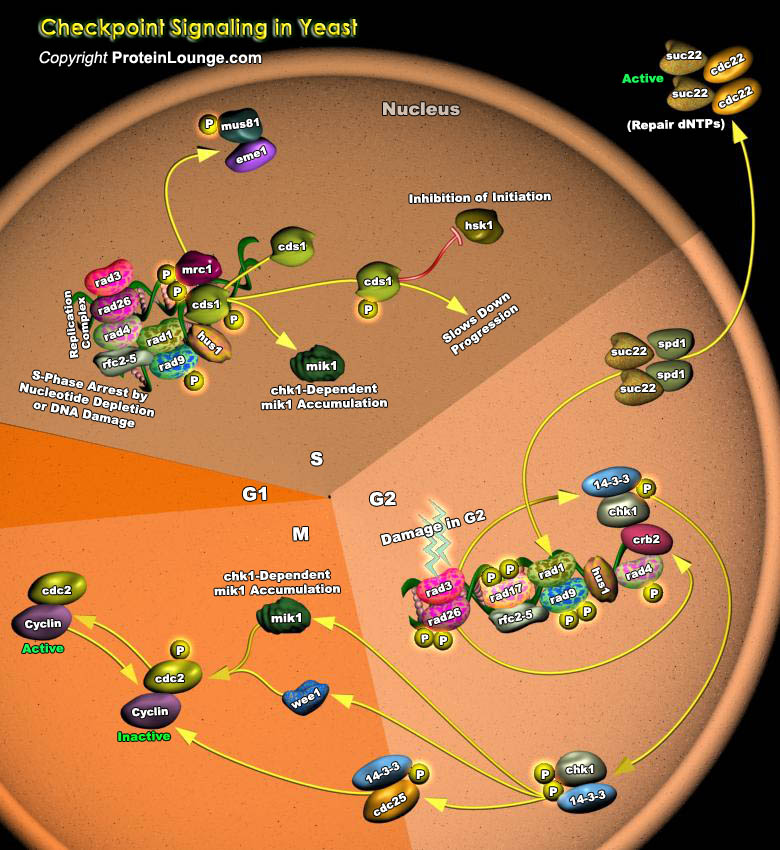
The maintenance of genomic integrity is important for the survival of eukaryotic cells. Checkpoint mechanisms prevent cell cycle transitions until previous events have been completed or damaged DNA has been repaired. Various forms of DNA damage and various treatments that block replication trigger these checkpoints. Checkpoint pathways and proteins are evolutionarily conserved from yeast to[..]
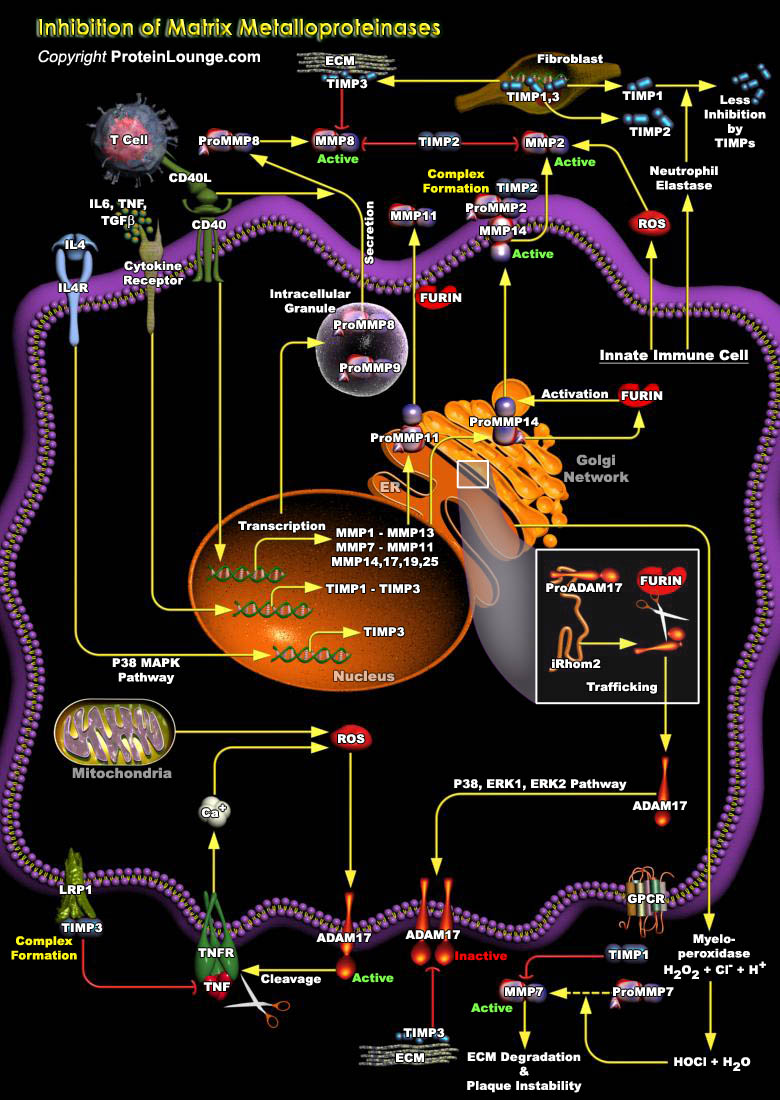
MPs (Metalloproteinases) play a key role in the responses of cells to their microenvironment. By effecting proteolytic degradation or activation of cell surface and ECM (Extracellular Matrix) proteins they can modulate both cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions, which influence cell differentiation, migration, proliferation and survival. Both secreted and membrane bound forms of[..]
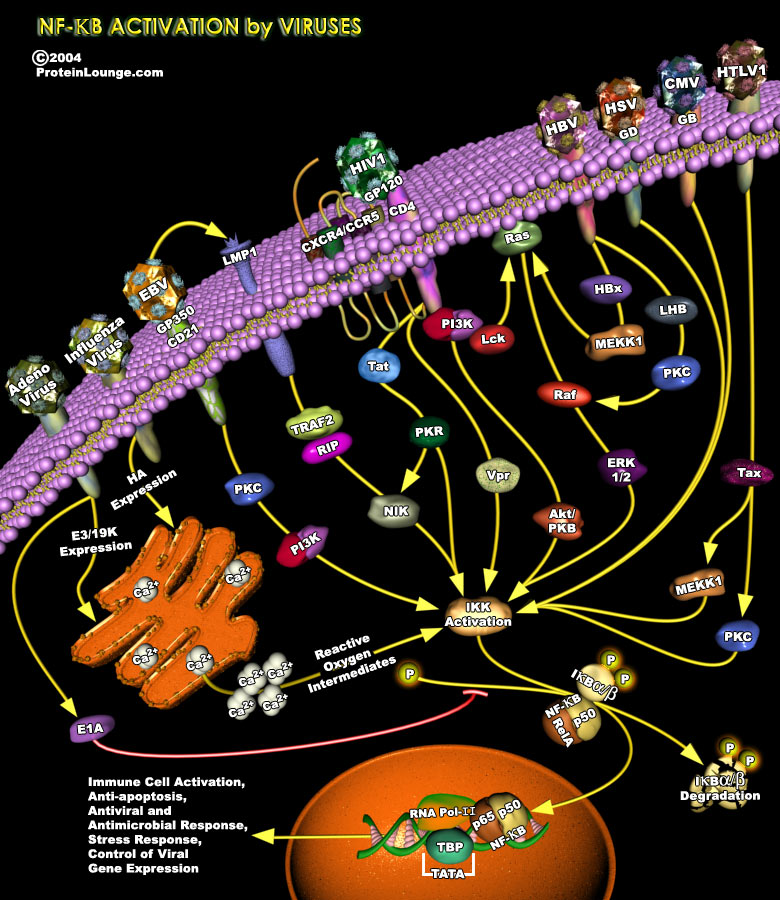
The transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) plays a fundamental role in the innate antiviral response, acting as a hub network in signal transduction that connects cellular sensors of viral invasion with effector mechanisms of antiviral defence (Ref.1). NF-kappaB pathway appears to be an attractive target for common human viral pathogens. Many viruses, including several human[..]
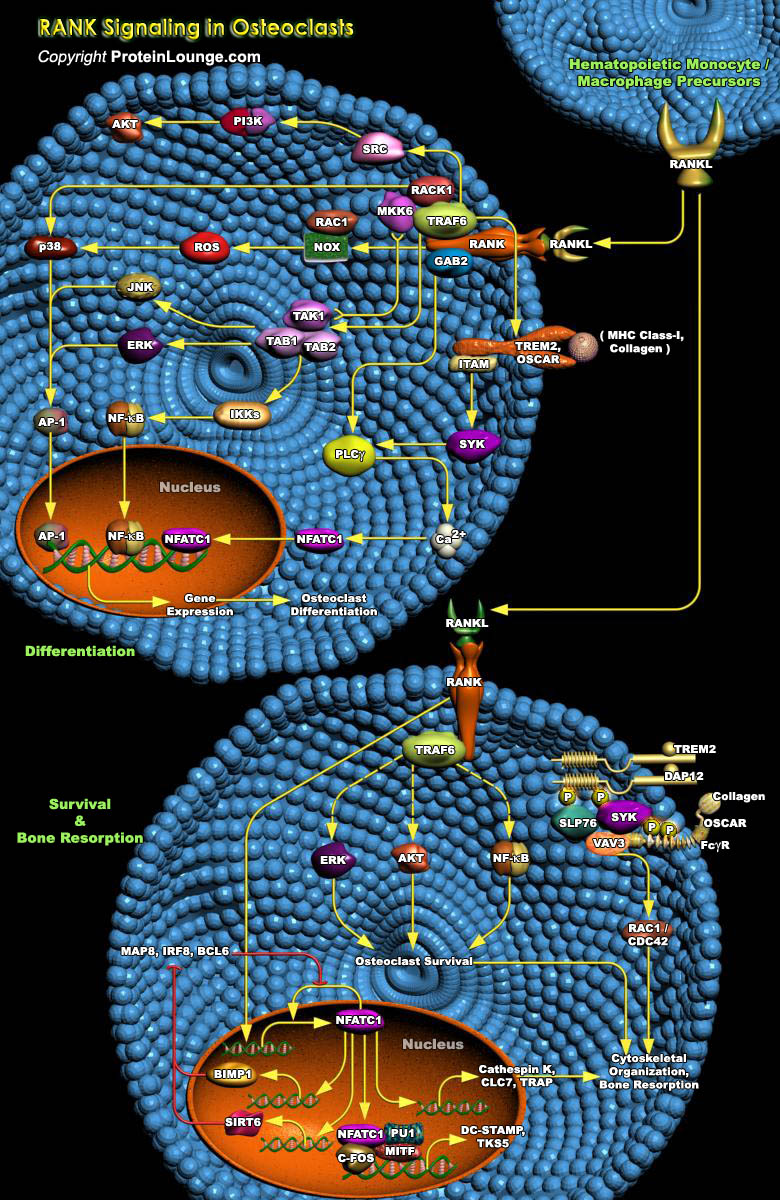
TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) and TNFR (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor) family proteins play important roles in the control of cell death, proliferation, autoimmunity, the function of immune cells, or the organogenesis of lymphoid organs. Recently, novel members of this large family have been identified that have critical functions in immunity and that couple lymphoid cells with other organ systems[..]