Featured Pathways
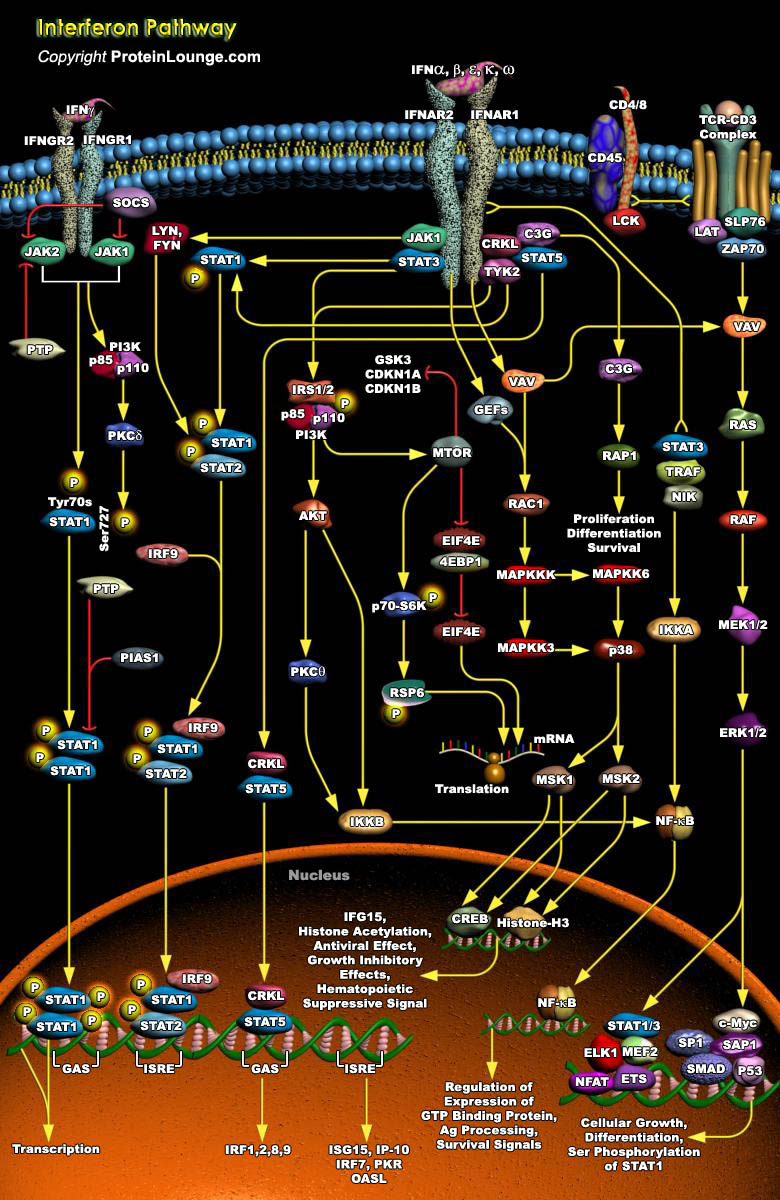
To thwart viral infection, our cells have developed a formidable and integrated defense network that comprise of innate and adaptive immune responses. In an attempt to prevent viral replication, viral dissemination or persistent viral infection of the cell, many of these protective measures actually involve the induction of programmed cell death, or apoptosis. Once the virus has invaded the cell,[..]
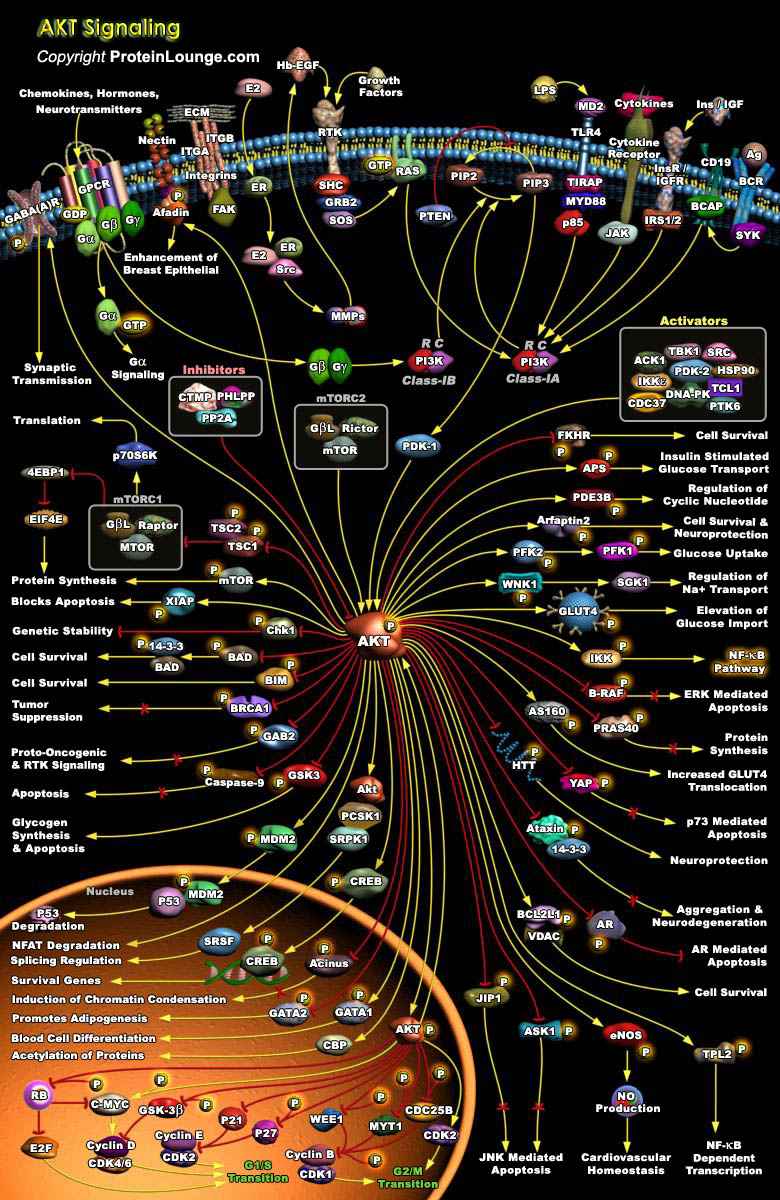
AKT/PKB Pathway is an evolutionarily conserved serine/threonine kinase Pathway involved in a wide variety of cellular functions, including proliferation, cell survival, differentiation, glucose mobilization, homeostasis, cell migration, and apoptosis. Three isoforms, AKT1,AKT2, and AKT3, are expressed in mammals (Ref.1 & 2). Akt is a central node in cell signaling downstream of growth factors,[..]
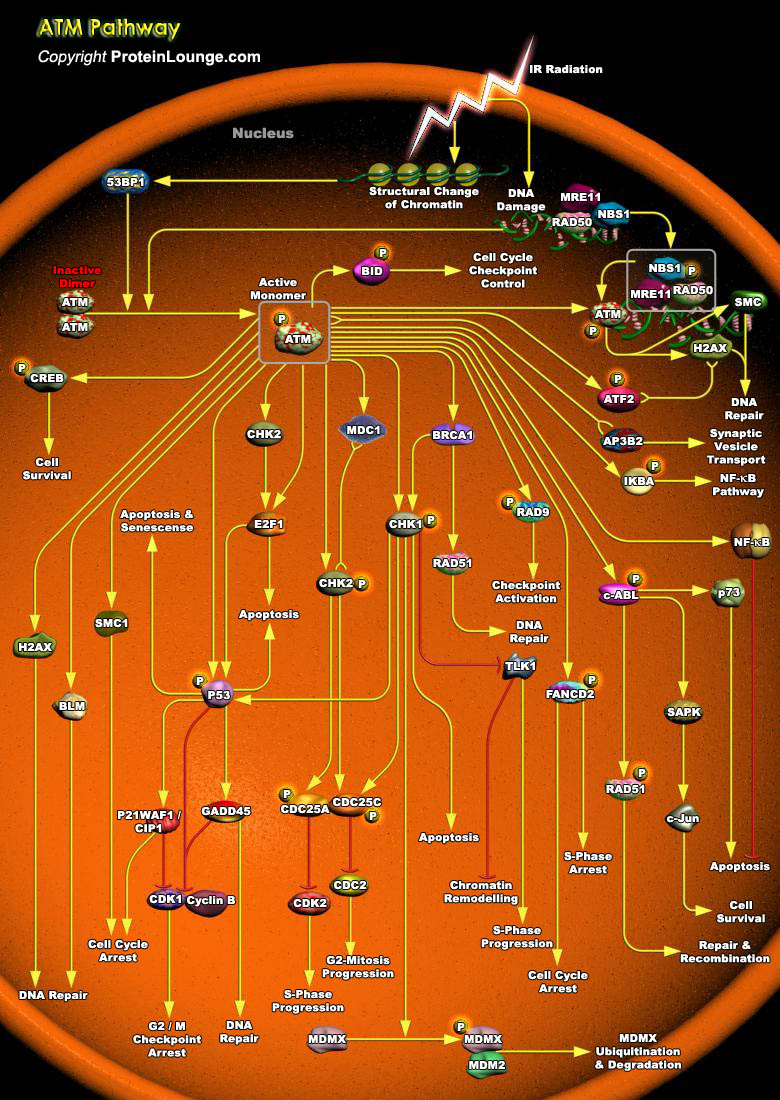
ATM (Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated Protein) belongs to a family of Kinases that have sequence homology to PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase).ATM is a key regulator of multiple signaling cascades which respond to DNA strand breaks induced by damaging agents IR (Ionizing Radiation), radiometric agents or by normal processes. These responses involve the activation of cell cycle CHK factors[..]
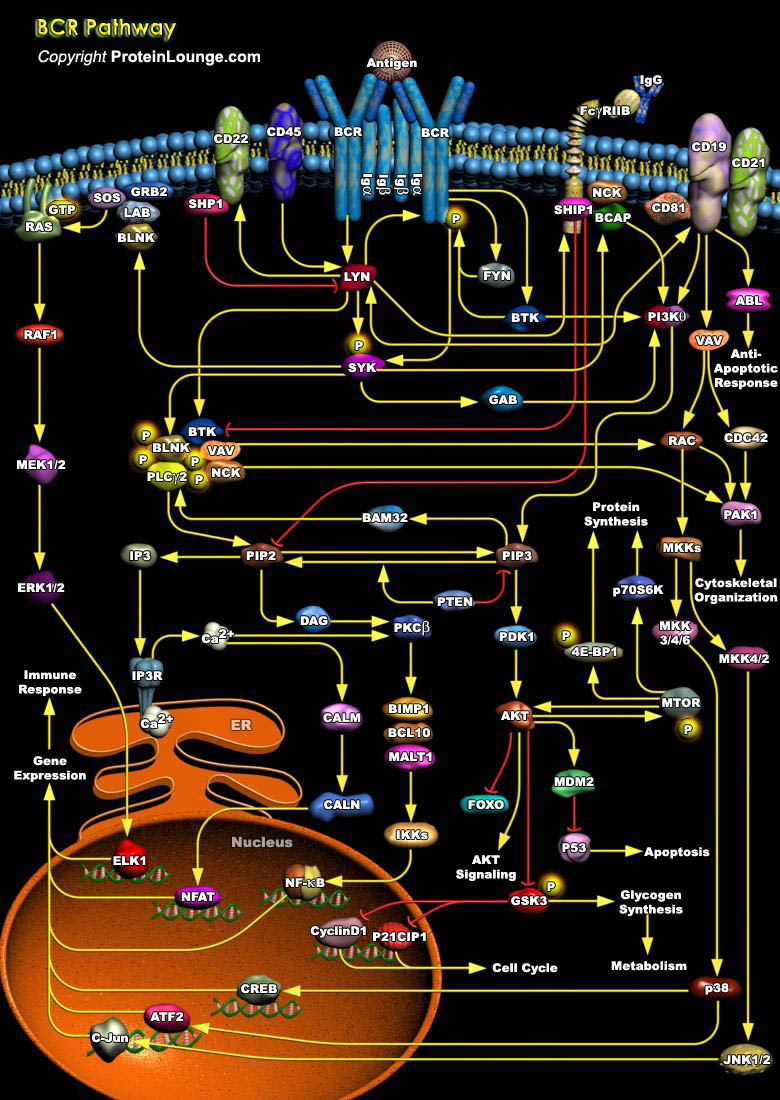
The BCR (B-Cell antigen Receptor) plays a critical role in development, survival, and activation of B cells. The BCR is composed of mIg molecules (Membrane Immunoglobulin) and associated Ig-Alpha/Ig-Beta heterodimer [Ref.1]. The mIg subunits bind antigen and cause receptor aggregation, while the Alpha/Beta subunits transduce signals to the cell interior. Engagement of receptor activates three[..]
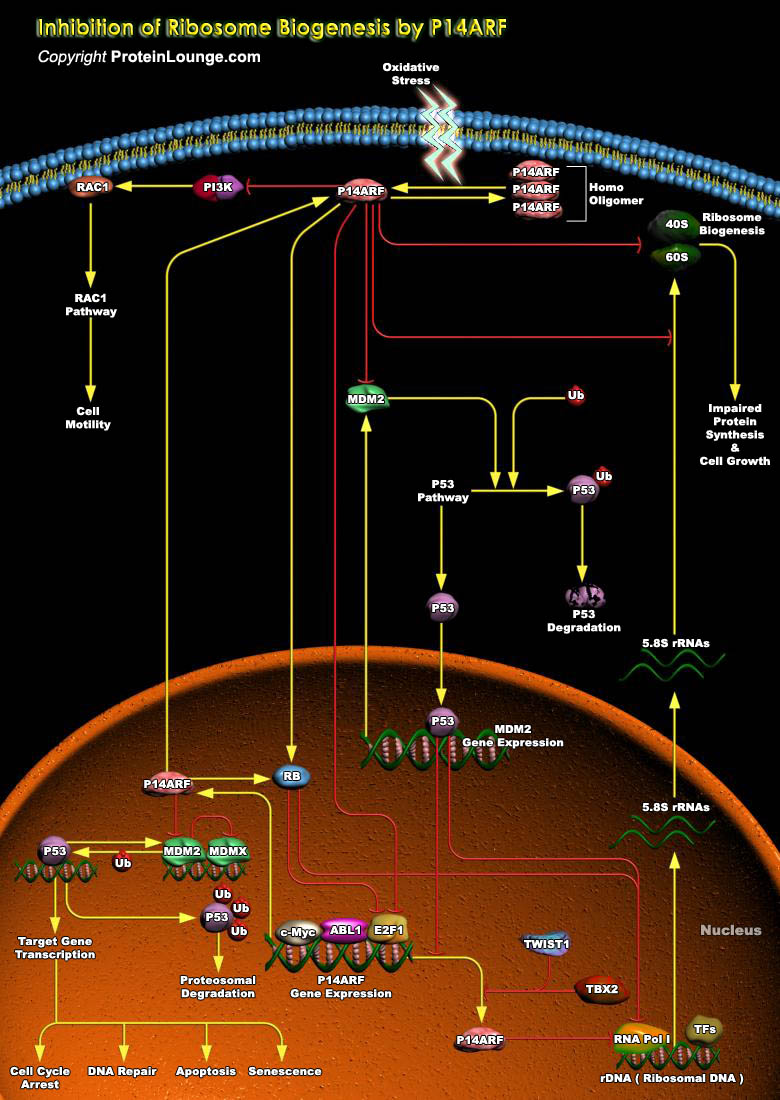
p14(ARF) is a key component of a major human tumor suppressor pathway that is responsible for arresting cell-cycle progression and inducing cell death in response to DNA damage and oncogenic stress. It plays an important role as an inhibitor of the MDM2-mediated degradation of p53. p14(ARF) activity is linked to its oligomerization and is sensitive to the redox status of the cell. Oxidative[..]
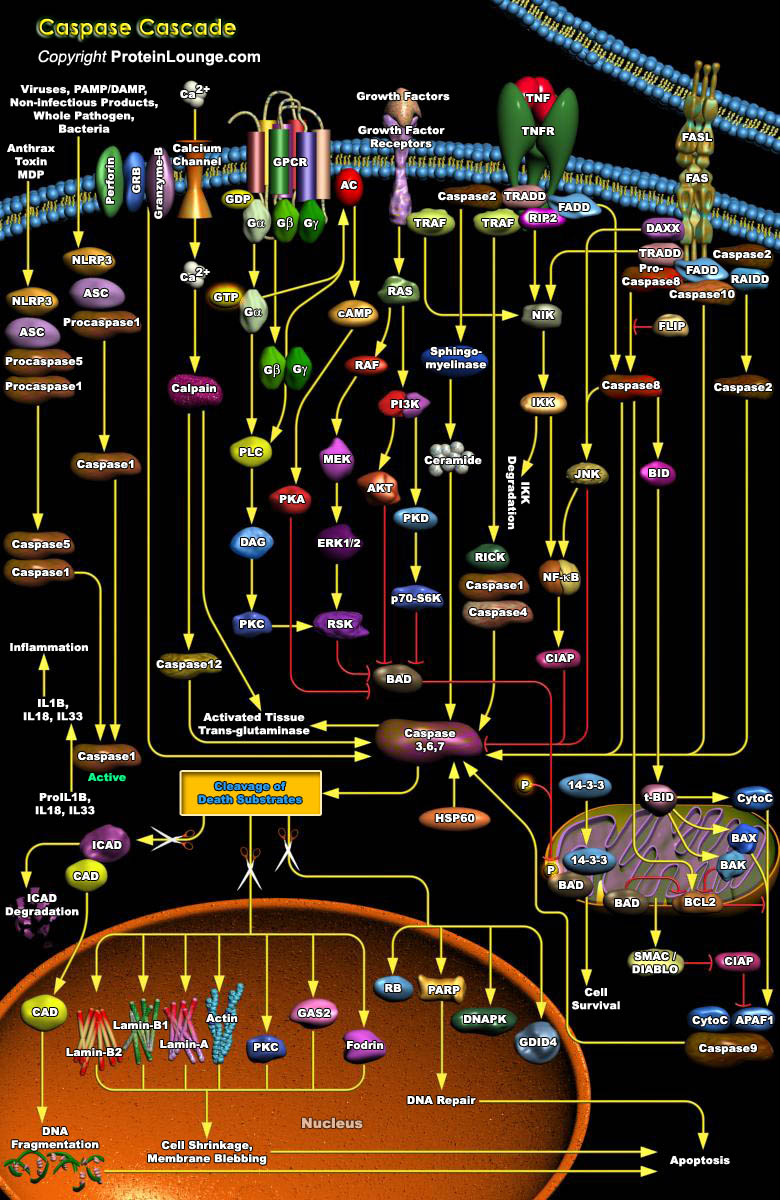
Caspases are a family of evolutionary conserved cysteine dependent aspartate-specific proteases that play crucial roles in maintaining organismal homoeostasis throughout life.Mammalian caspases are broadly classified as being inflammatory/pyroptotic (human caspase-1, 4, 5 and 12, murine caspase-1, 11 and 12), or as initiators (human and murine caspase-2, 8, 9 and human caspase-10) and[..]
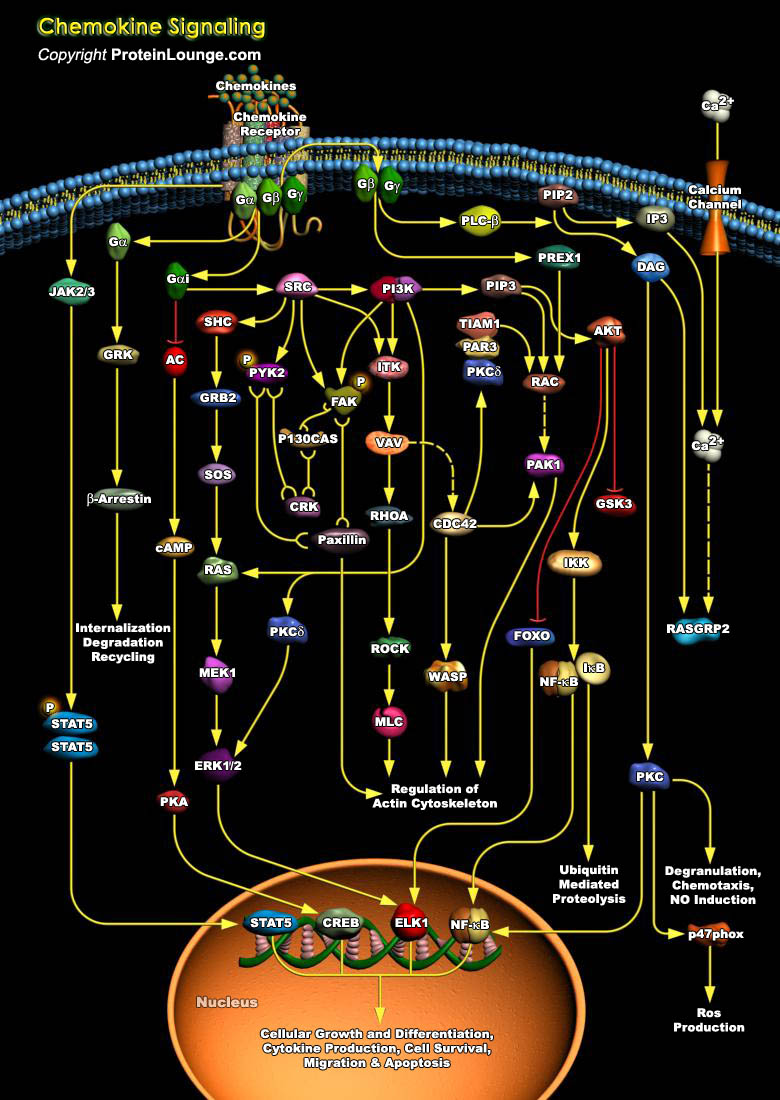
Chemokines are a group of small, secreted molecules that signal through G protein-coupled receptors to promote cell survival and proliferation and to provide directional guidance to migrating cells. Initially chemokines were divided into groups based on having chemotactic or homeostatic function, but several dual-function chemokines have since been described. To date, 44 chemokines and 23[..]
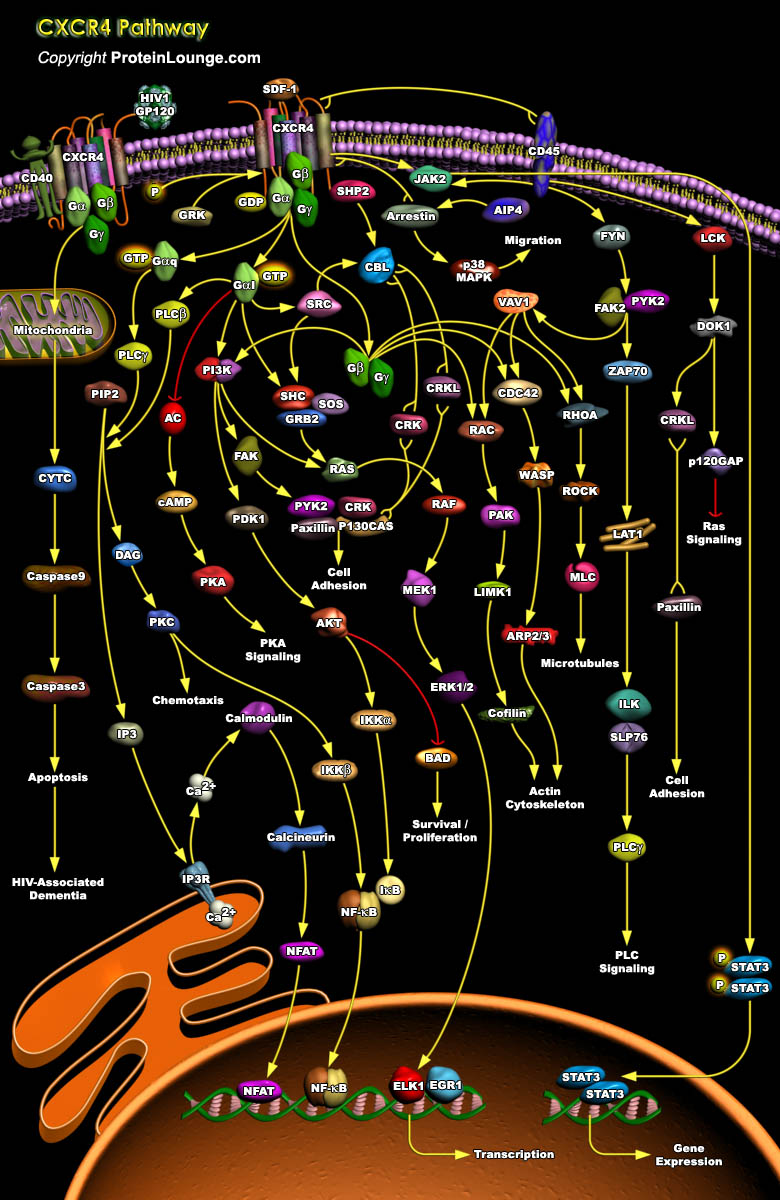
The Chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a 352 amino acid rhodopsin-like GPCR and selectively binds the CXC chemokine Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 (SDF1) also known as CXCL12. Classically, two alternatively spliced isoforms of SDF have been identified. SDF1Alpha is an 89 amino acid protein that is the predominantly expressed form of SDF1 while SDF1Beta contains a four amino acid extension at the[..]
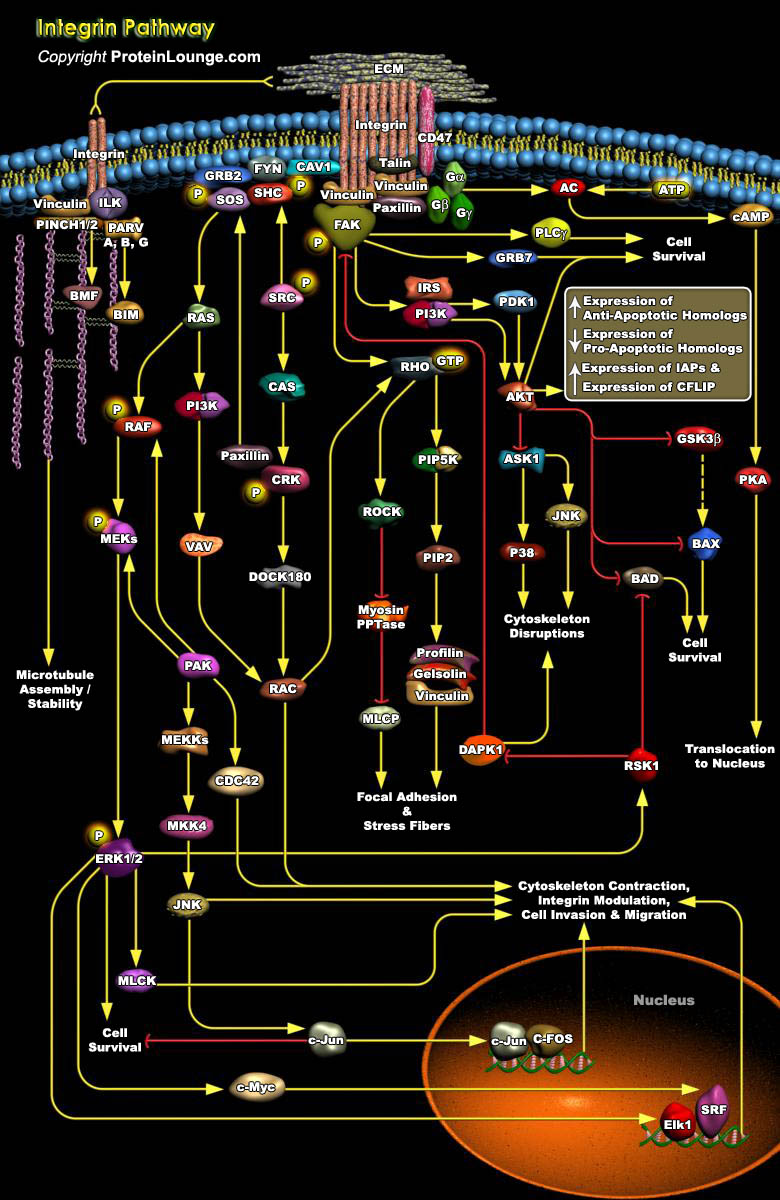
Adhesive interactions between cells and ECM (Extracellular Matrix) proteins play a vital role in biological processes, including cell survival, growth, differentiation, migration, inflammatory responses, platelet aggregation, tissue repair and tumor invasion and perturbing this coordination can lead to events such as malignant transformation. The major groups of proteins mediating these[..]
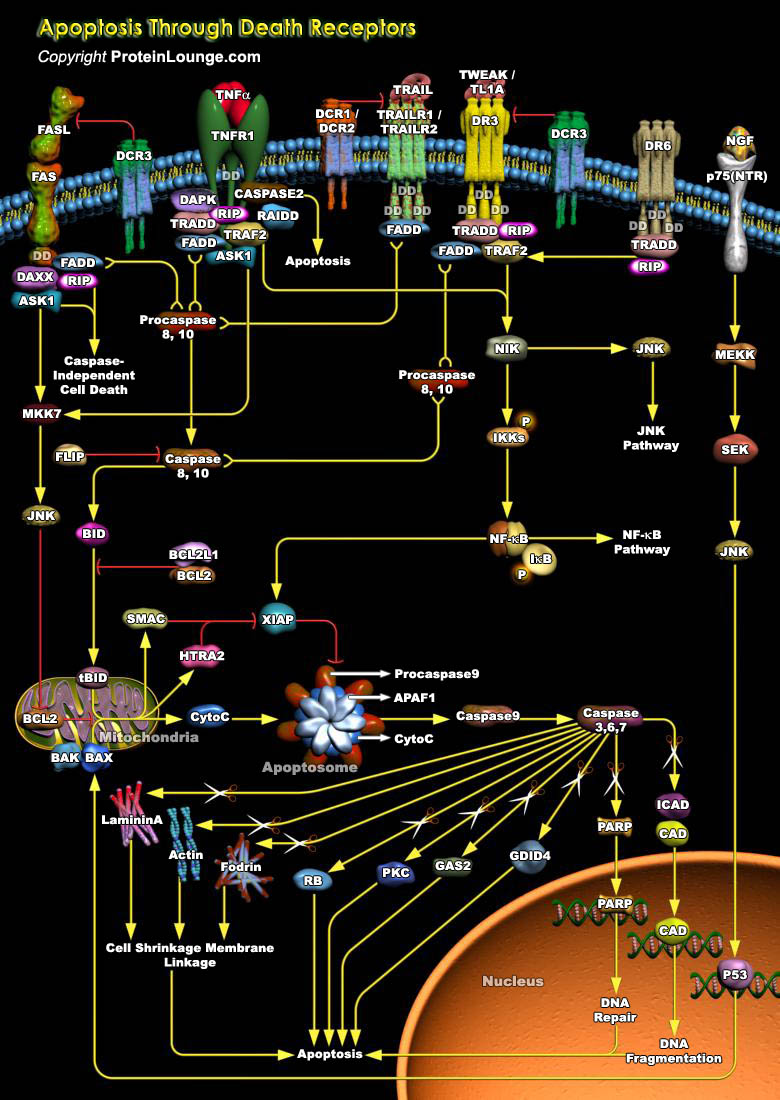
Apoptosis is a cell suicide mechanism that enables metazoans to control cell number in tissues and to eliminate individual cells that threaten the animal's survival. Certain cells have unique sensors, termed DR (Death Receptors), on their surface, which detect the presence of extracellular death signals and, in response; they rapidly ignite the cell's intrinsic apoptosis machinery. Death[..]
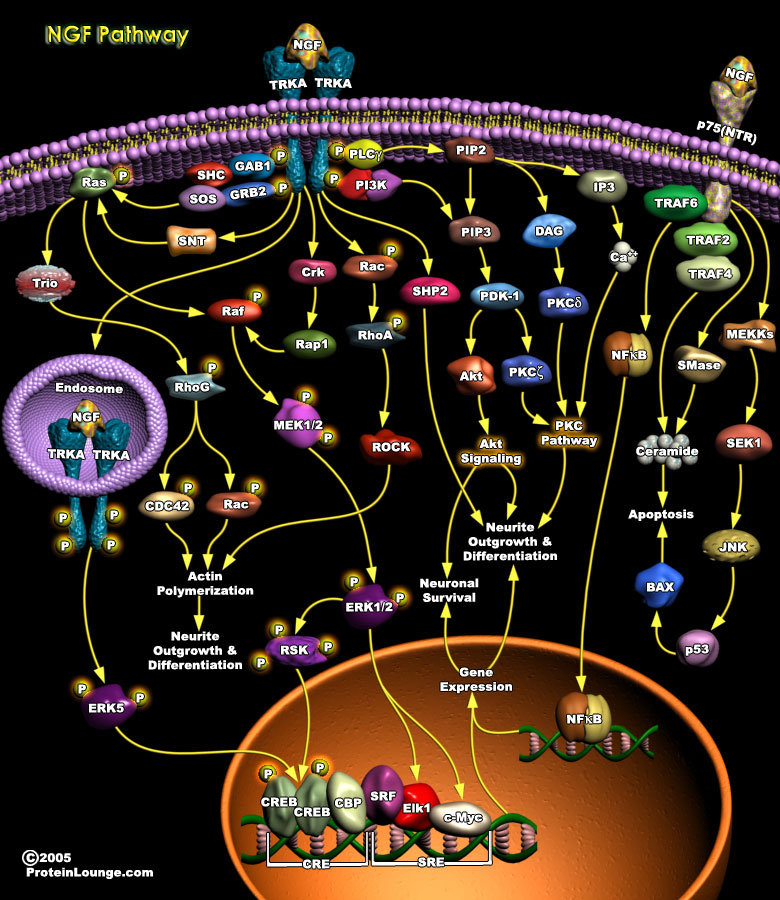
One of the most fundamental issues in current biology is how to maintain the critical balance between cell survival and death, both during development and in adulthood. Unrestrained cell division and survival leads to various forms of tumor, while excessive or premature cell death may lead to a variety of diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Multiple Sclerosis. In the nervous[..]
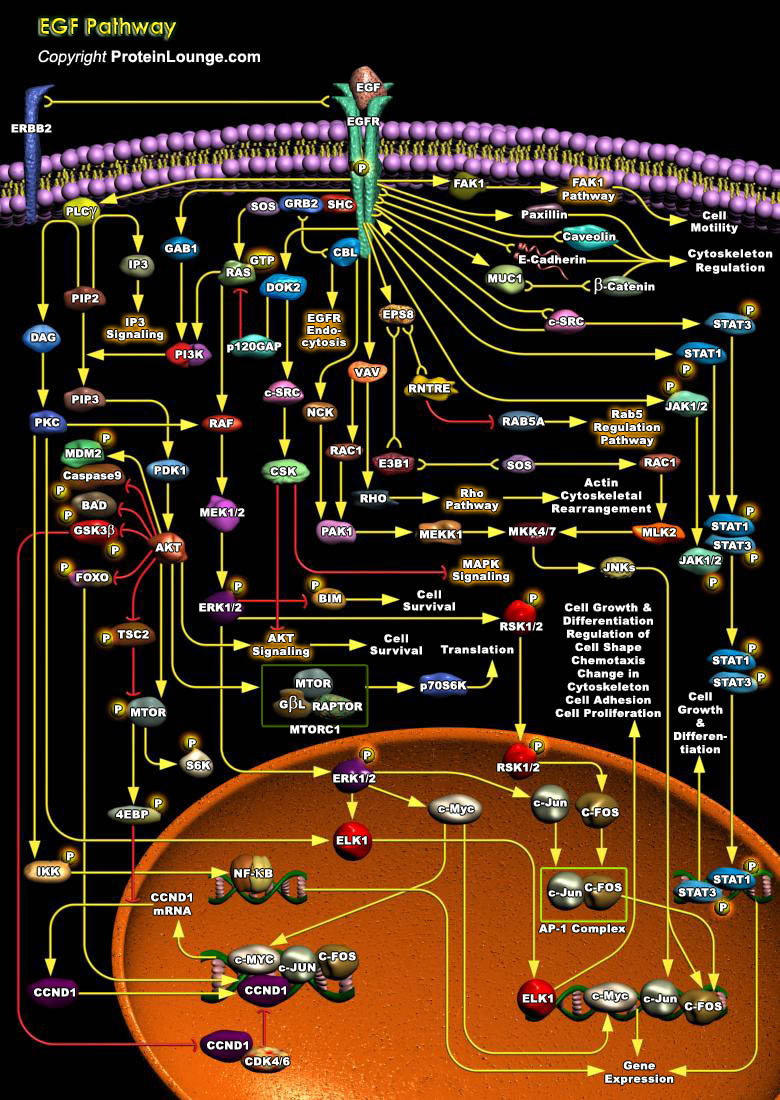
Angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels, plays a key role in many physiological and pathological processes, such as ovulation, embryogenesis, wound repair, inflammation, malignant tumor growth, retinopathies, rheumatoid arthritis, and angiogenesis-dependent diseases. One of the best-characterized modulators of angiogenesis is the heparin-binding FGF (Fibroblast Growth Factor) (Ref.[..]