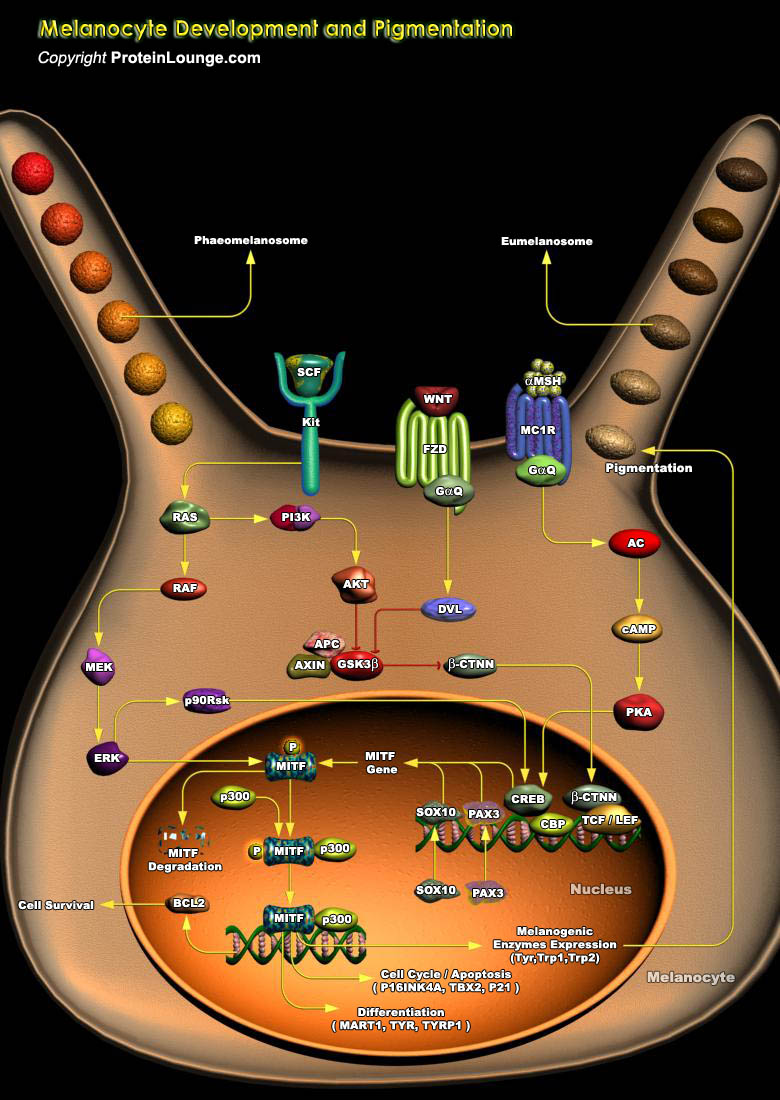
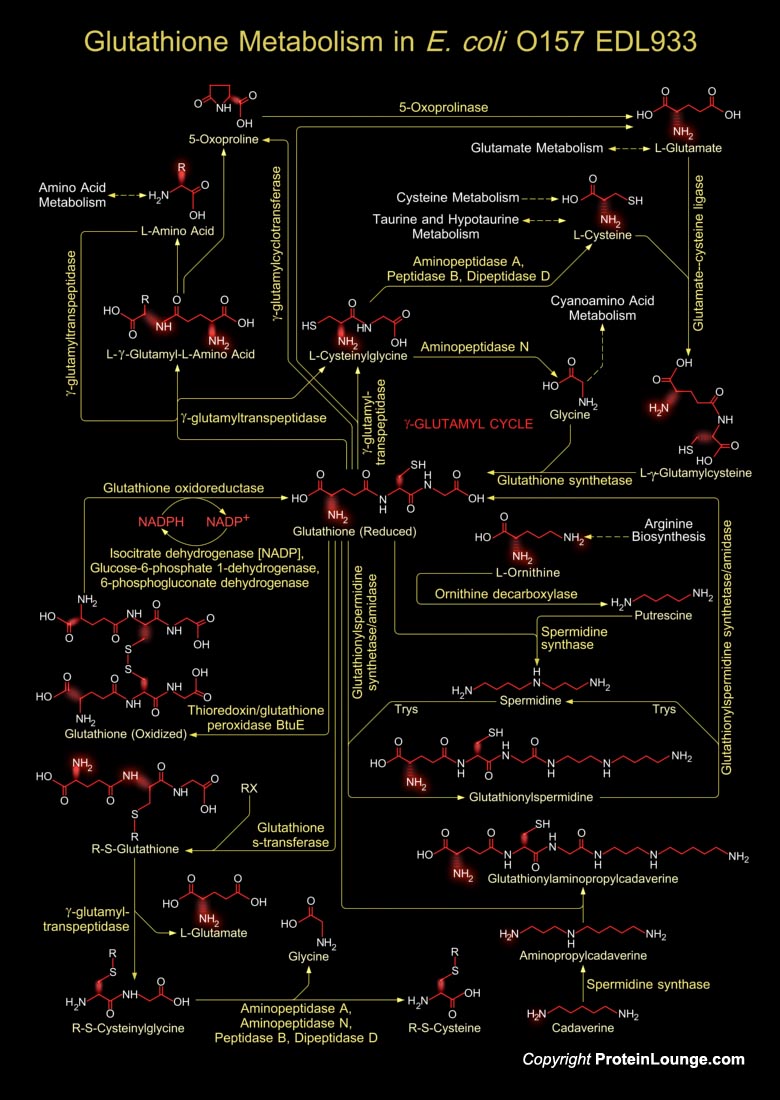
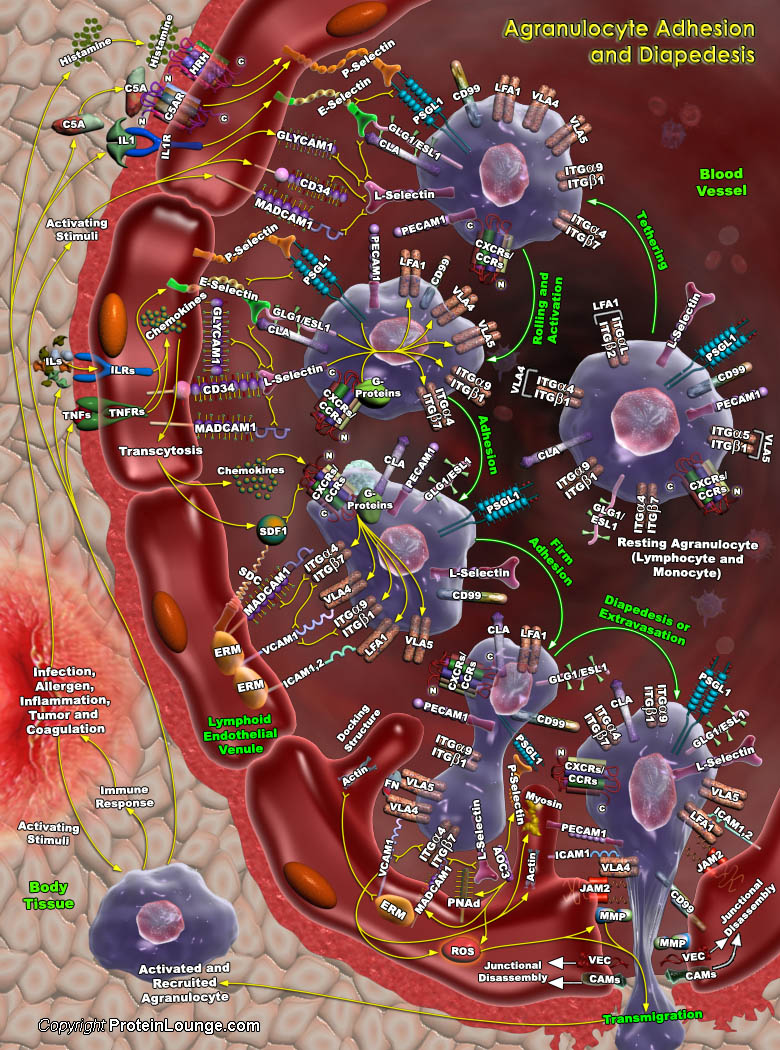
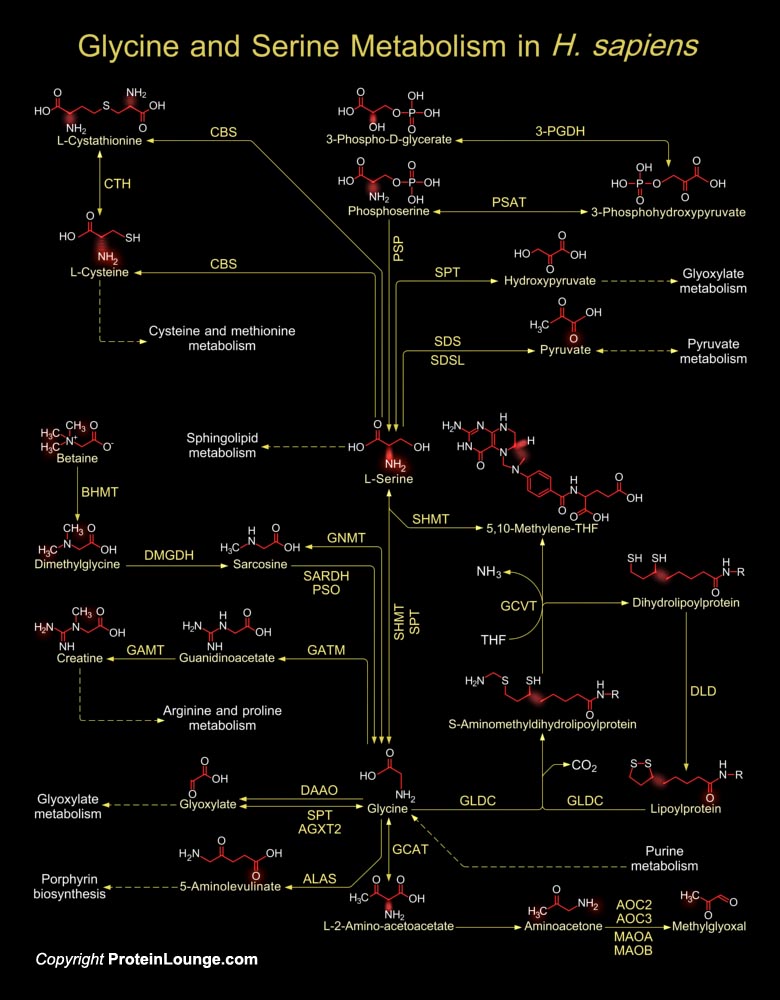
Featured Pathways
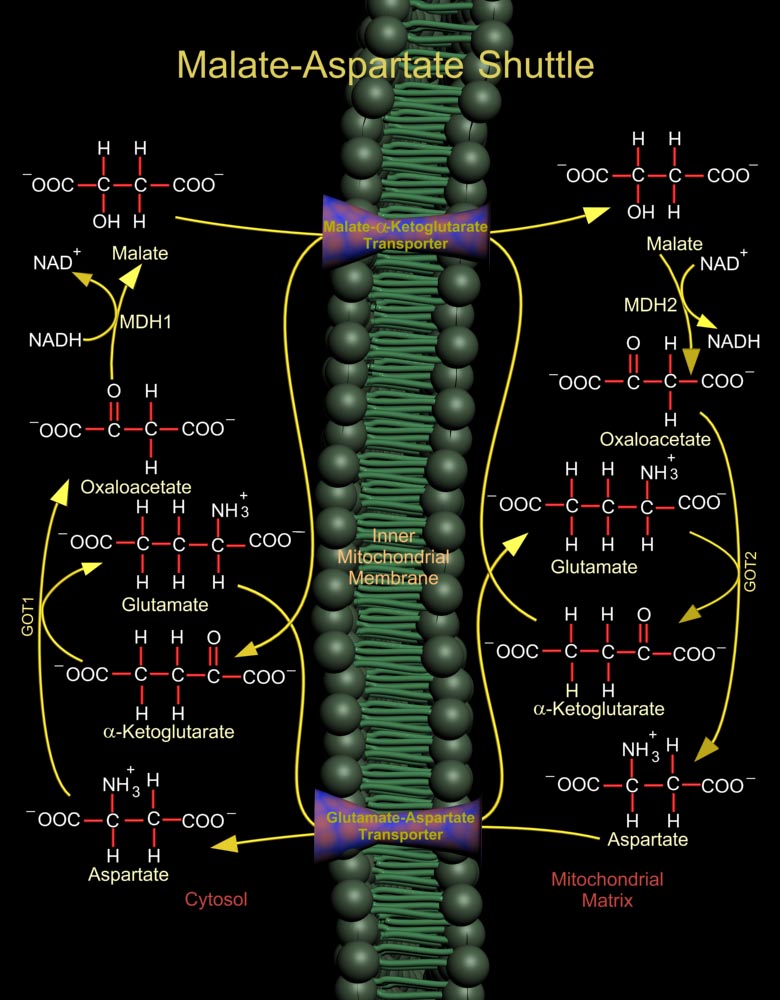
The Malate (L-Malic Acid)-Asp (Aspartate or L-Aspartate or Aspartic Acid) Shuttle of mammalian systems is more complex but more energy efficient. Mitochondrial NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is reduced by cytosolic NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, Reduced) through the intermediate reduction and subsequent regeneration of OAA (Oxaloacetate) (Ref.1). In the cytosol, the shuttle[..]
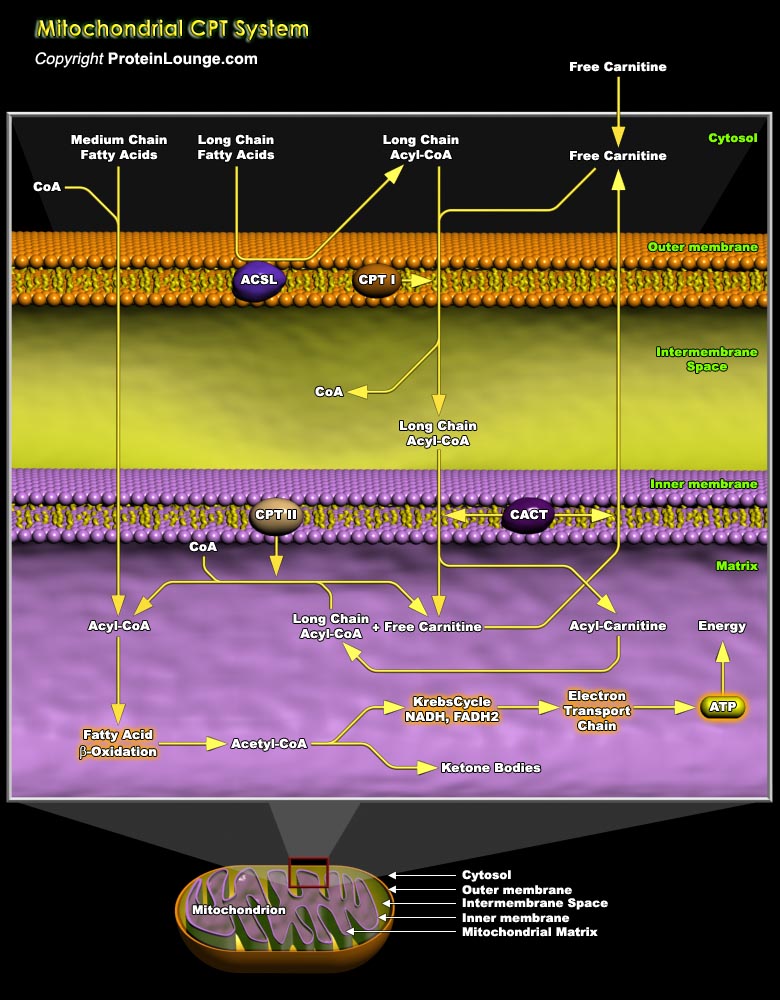
Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (FAO) and its key rate-limiting enzyme, the carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT) system, are important for energy homeostasis in situations like fasting or during exercise. They also regulate host immune responses and the deficiency or over-activation of CPT may cause energy metabolism disorder that may lead to many diseases starting from inflammatory[..]
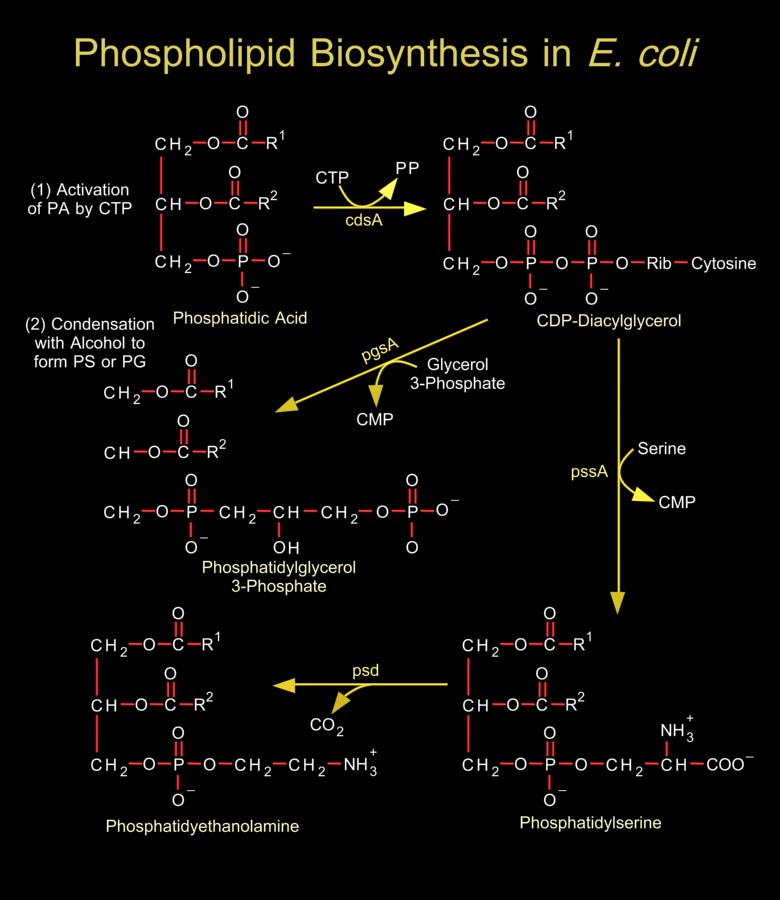
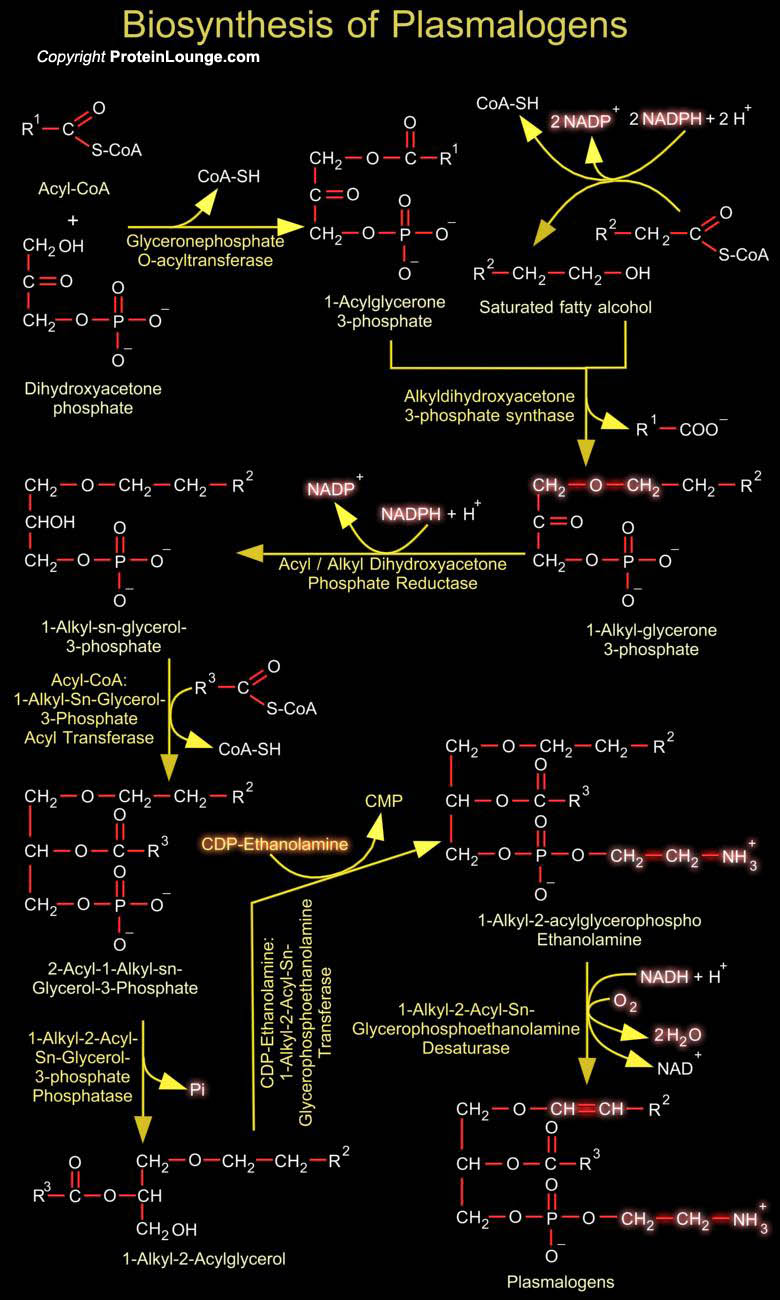
Biological membranes are composed of hundreds of distinct proteins and phospholipids. Phospholipids are diacylglycerol derivatives with a hydrophilic, zwitter ionic, often charged headgroup at position C3 of the glycerol backbone. The properties of phospholipids give lipid bilayer membranes their self-organizing structure. Phospholipids are usually composed of two fatty acid[..]
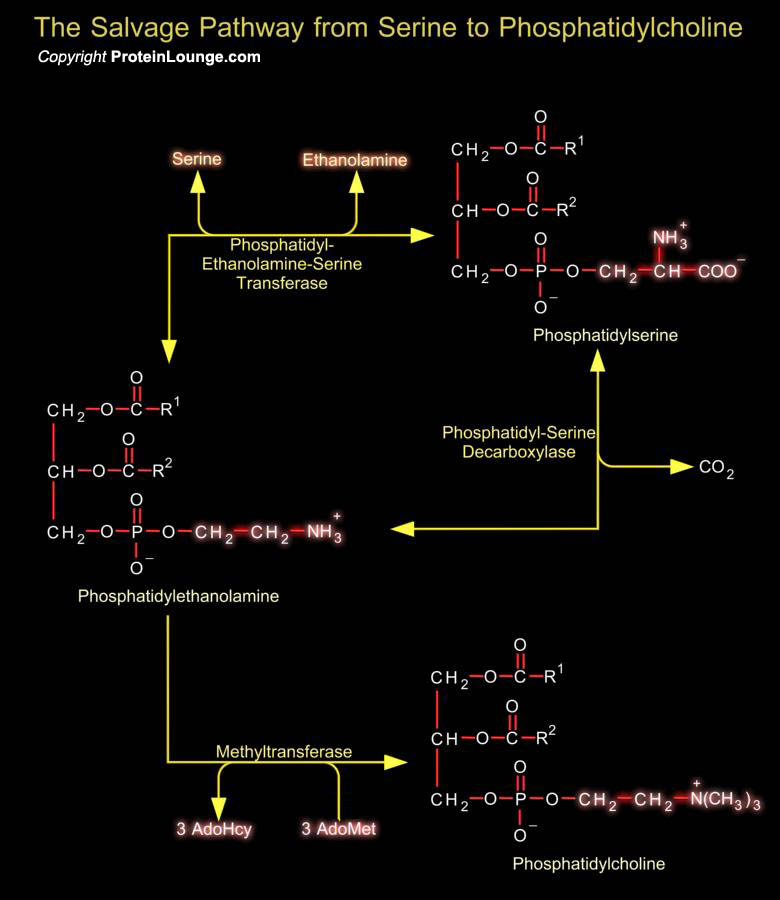
Phosphatidylserine (or 1, 2-Diacyl-sn-Glycero-3-Phospho-L-Serine) is the only amino acid-containing glycerophospholipid in animal cells. Although it is distributed widely among animals, plants and microorganisms, it is usually less than 10% of the total phospholipids, the greatest concentration being in myelin from brain tissue. It is an acidic (anionic) phospholipid with three ionizable[..]
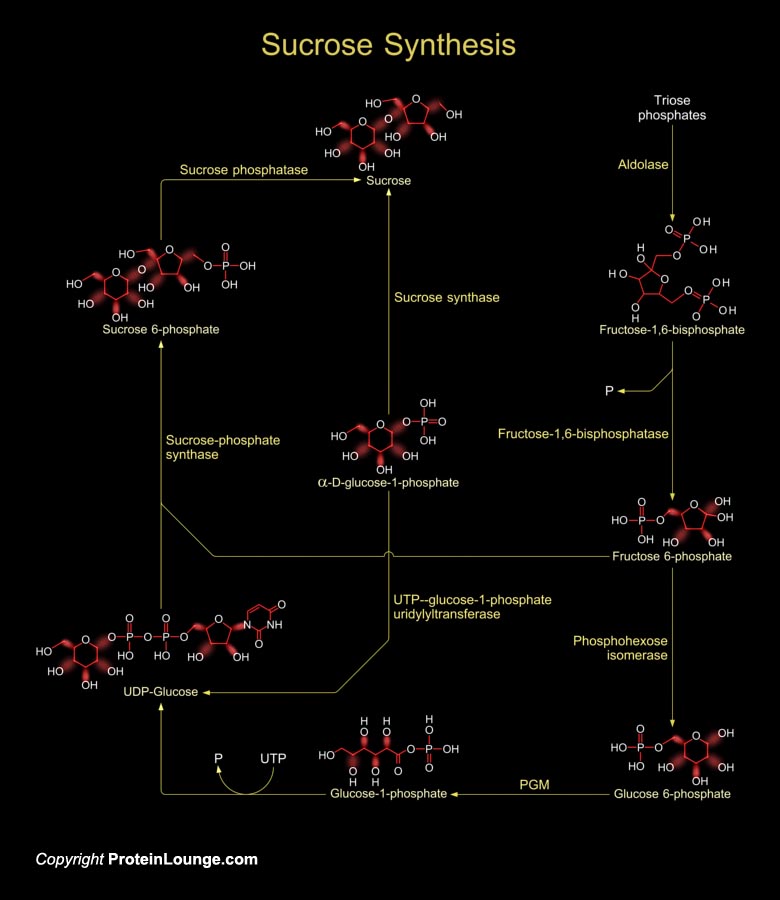
Sucrose is produced by plants, algae and cyanobacteria as an end product of photosynthesis. It is the primary sugar transported from the source tissues to sink tissues by the phloem in most plants. In other non-photosynthetic tissues, sucrose serve as raw material for many metabolic pathways (Ref.1).
Sucrose synthesis starts in the cytosol where two triose-phosphates[..]
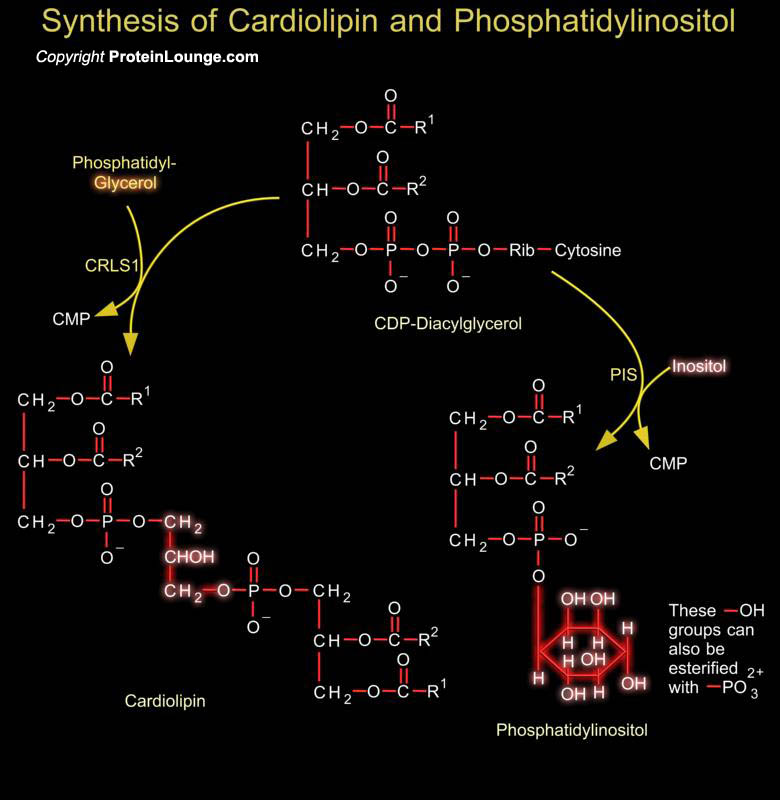
Phosphoglycerides such as phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine are the major component of lipid bilayer membranes in which their detergent-like properties help to provide membranes the quality of self-assembly. Phosphatidylglycerol is a precursor in the synthesis of both cardiolipin and PI (Phosphatidylinositol). Cardiolipin is a unique dimeric phospholipid found in the heart and[..]
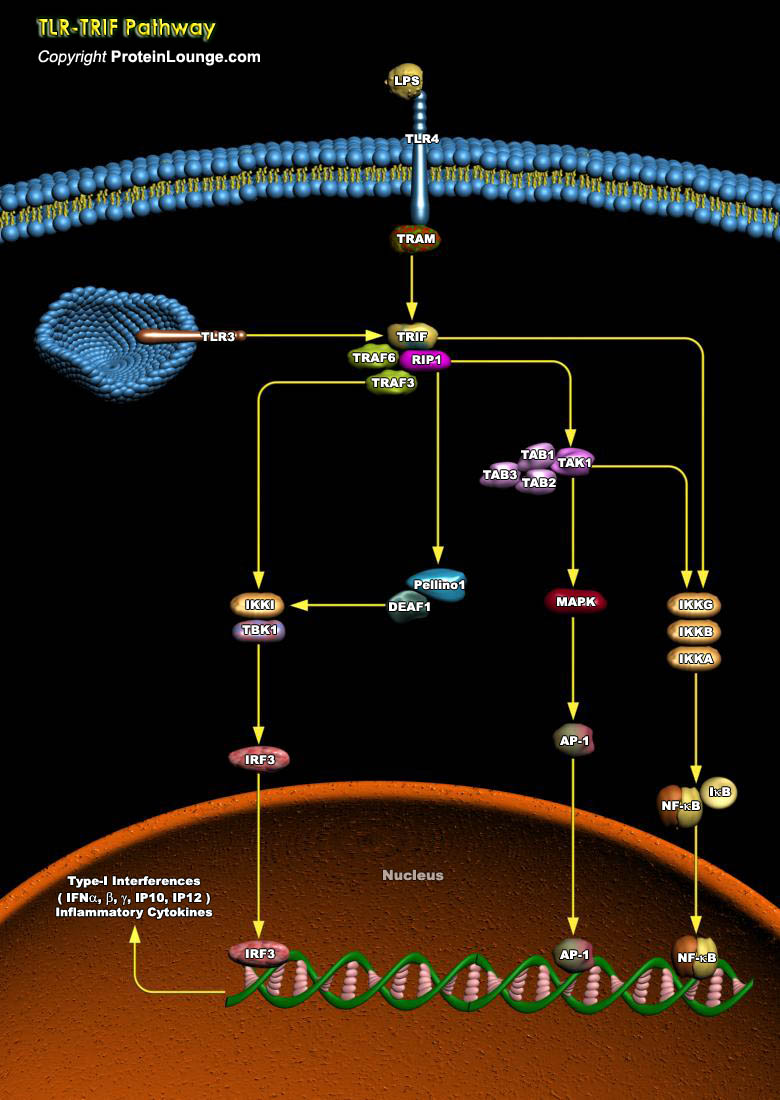
The Toll-like receptors (TLRs), 13 types known to-date, are a group of pattern-recognition receptors that play a crucial role in danger recognition and induction of the innate immune response against bacterial and viral infections. The major adaptors that bind to the intracellular domain of TLR to activate the proinflammatory response are the myeloid differentiation primary response MYD88 and[..]
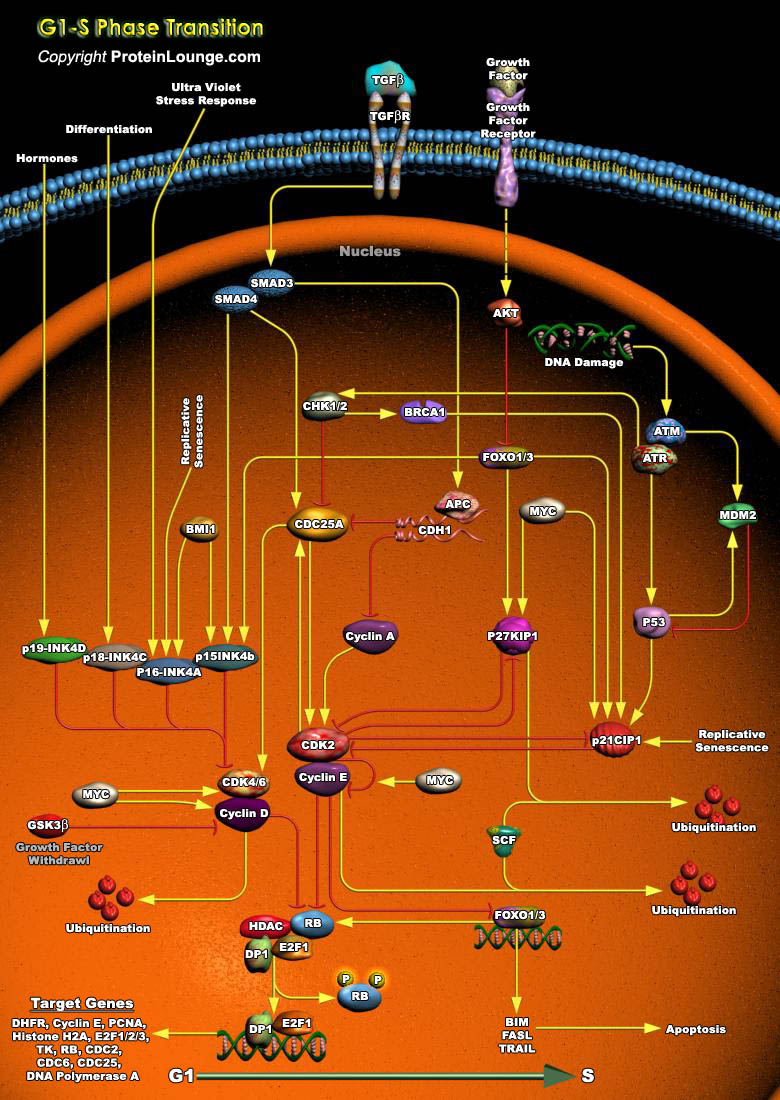
Cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage is an important mechanism for maintaining genomic integrity. This cell cycle arrest provides time for DNA repair to prevent replication or segregation of damaged DNA. Induction of growth arrest by DNA damage occurs mainly through the activation of checkpoint pathways that delay cell cycle progression at G1, S, and G2 (Ref.1 and 2).
In[..]
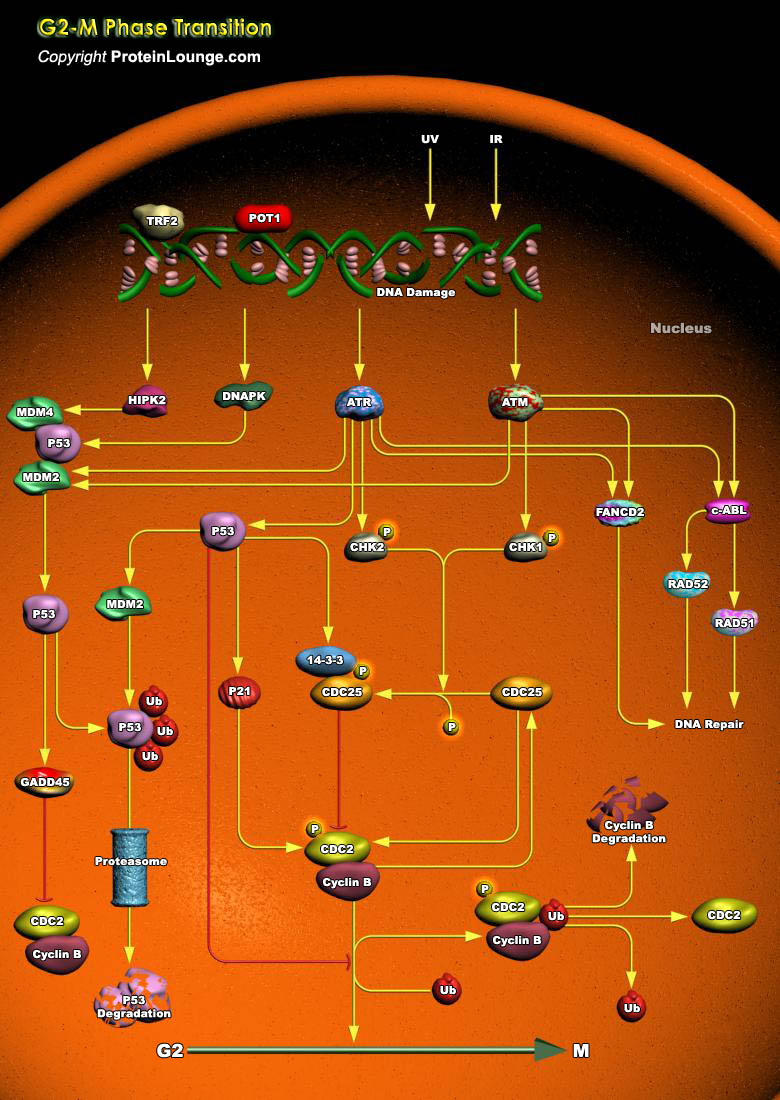
The cellular responses to DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation include activation of cell cycle checkpoints that delay progression of cells through the cell cycle. Ionizing radiation-induced checkpoints are active at the transition from the G1-phase to the S-phase, in the S-phase, and at the transition from the G2-phase to mitosis (G2/M). The surveillance mechanisms responsible for[..]
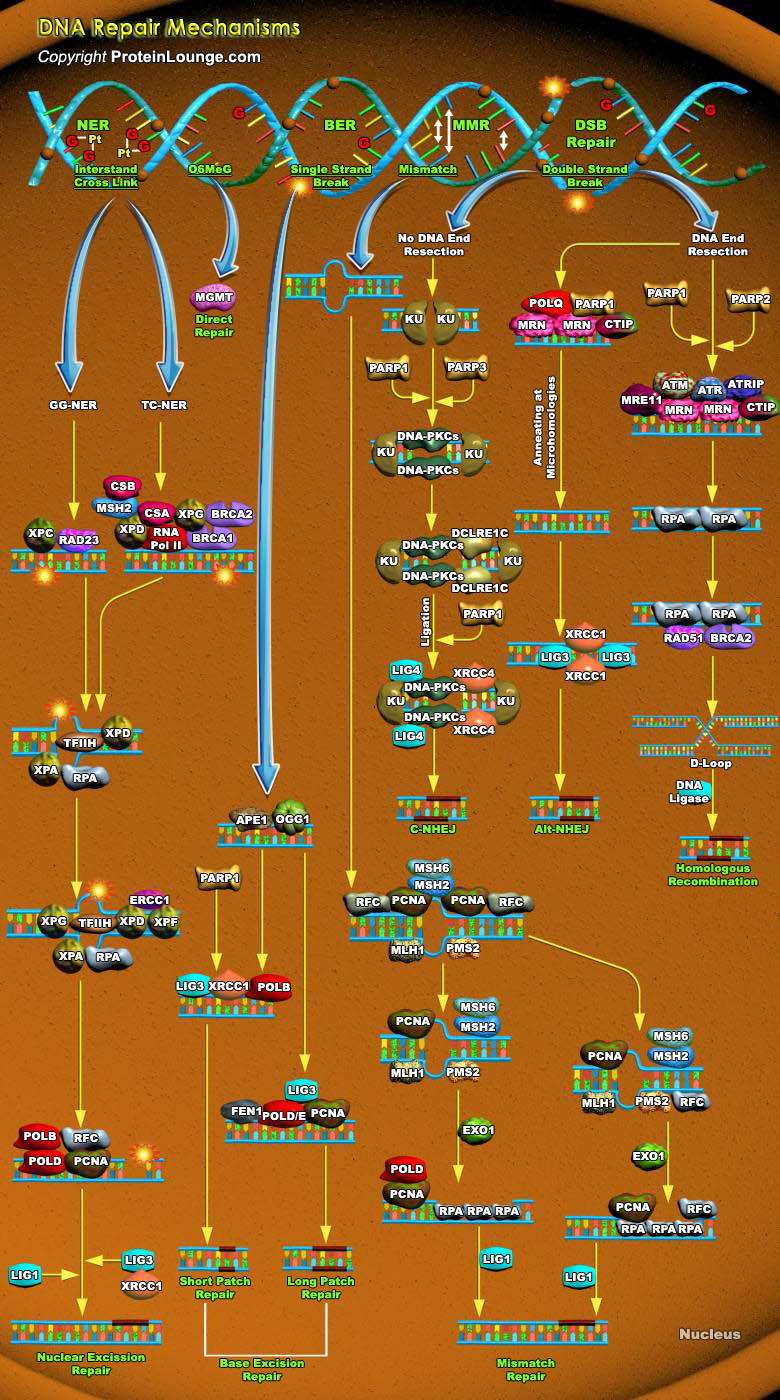
Cells are constantly under threat from the cytotoxic and mutagenic effects of DNA damaging agents that result from either endogenous sources (cellular metabolic processes) or exogenous sources (environmental factors). Endogenous sources of DNA damage include hydrolysis, oxidation, alkylation, and mismatch of DNA bases; sources for exogenous DNA damage include ionizing radiation (IR),[..]
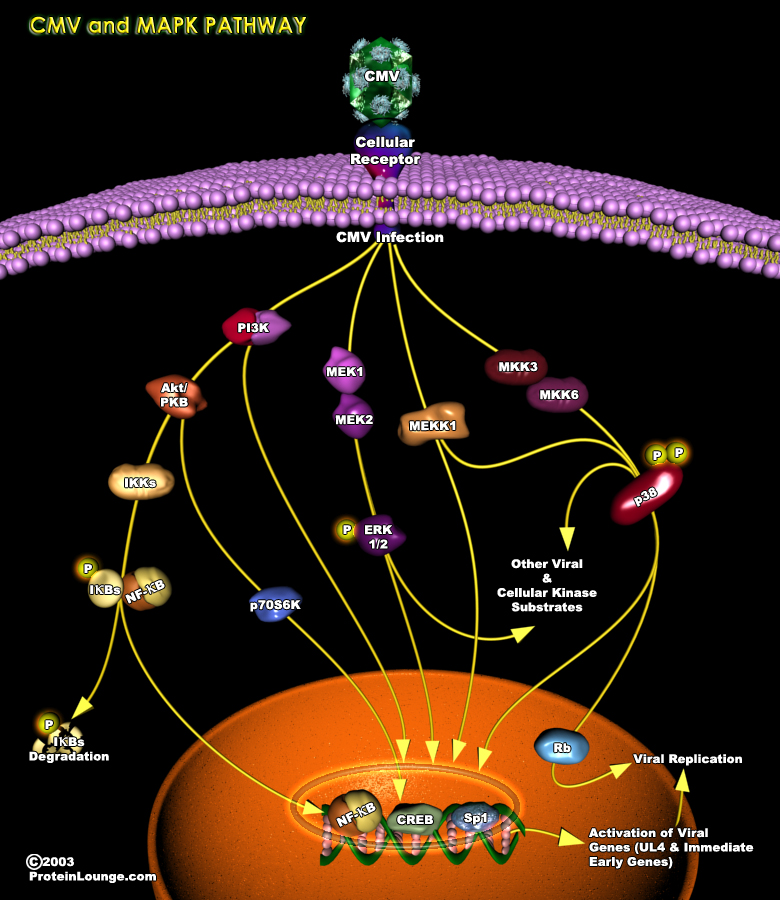
An upregulation of cellular signaling pathways is observed in multiple cell types upon HCMV(human cytomegalovirus) infection, suggesting that a global feature of HCMV infection is the activation of the host cell. HCMV initiates and maintains cellular signaling through a multitiered process that is dependent on a series of events: (1) the viral glycoprotein ligand interacts with its cognate[..]