Featured Pathways
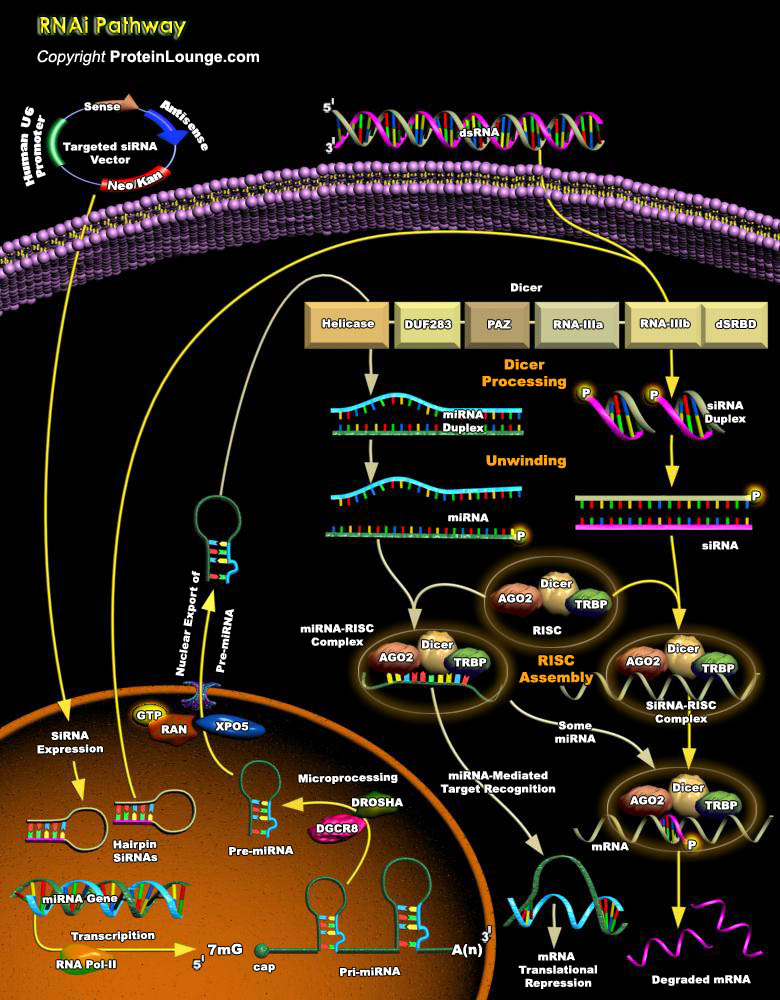
RNAi (RNA interference) is broadly defined as a gene silencing pathway that is triggered by dsRNA (double-stranded RNA). The dsRNA trigger can be supplied exogenously, as an experimental tool, or can derive from the genome. RNAi involves a number of steps from biogenesis of the trigger RNA, processing of dsRNA to small RNAs and formation of an effector complex containing the small RNA which[..]
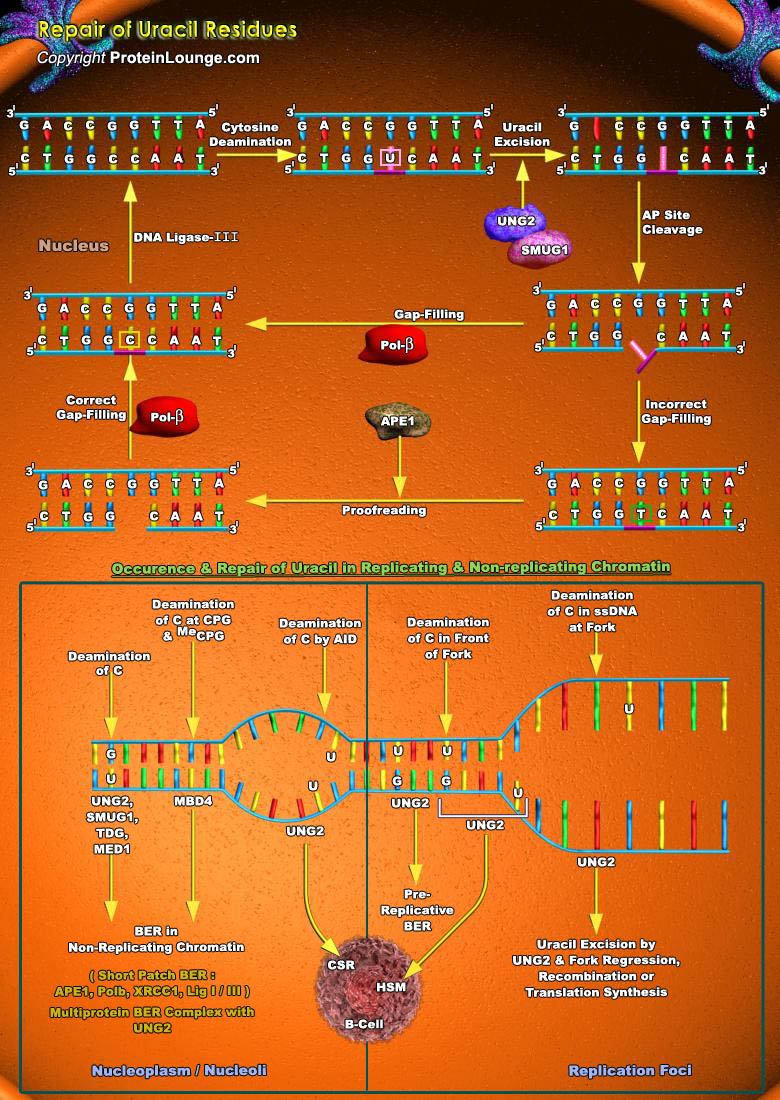
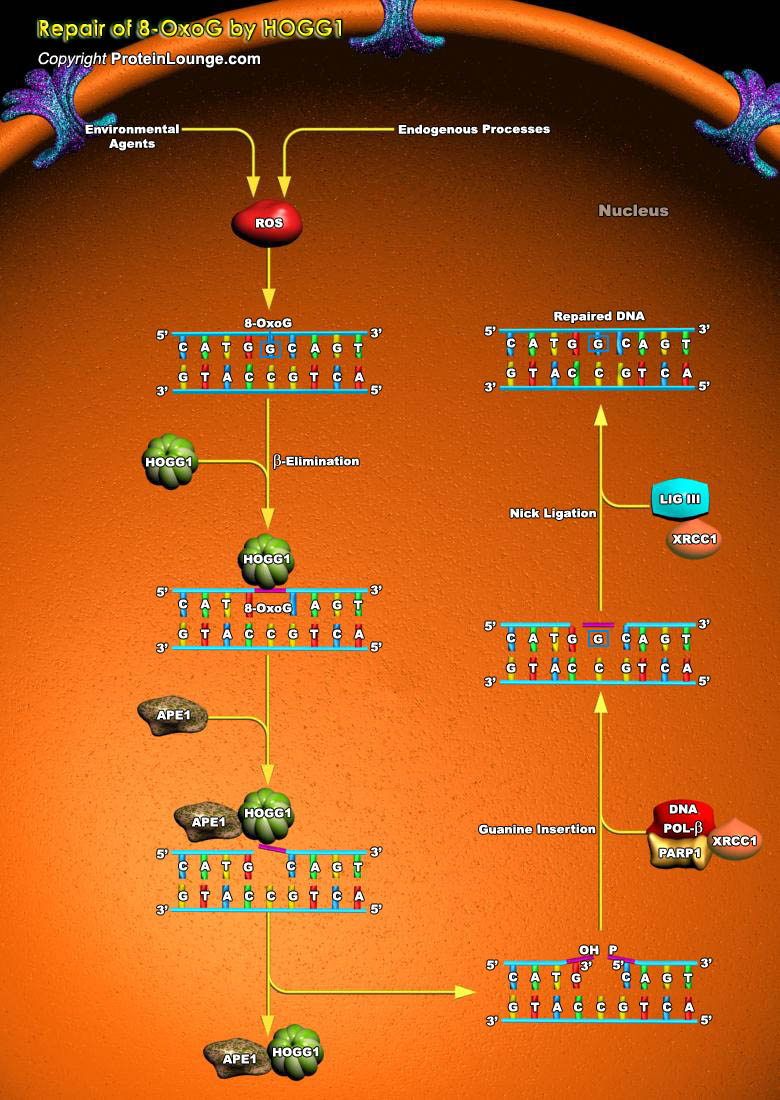
Hydrolytic deamination of cytosine to uracil is a major source of genome instability in human cells. This mutagenic process is mostly enhanced in single stranded DNA . Single stranded DNA can be found in transcribed genes, near forks, in mitochondrial DNA as well as in breathing DNA. It is believed to be much higher in replicating cells as compared to non-replicating cells. The cytosine[..]
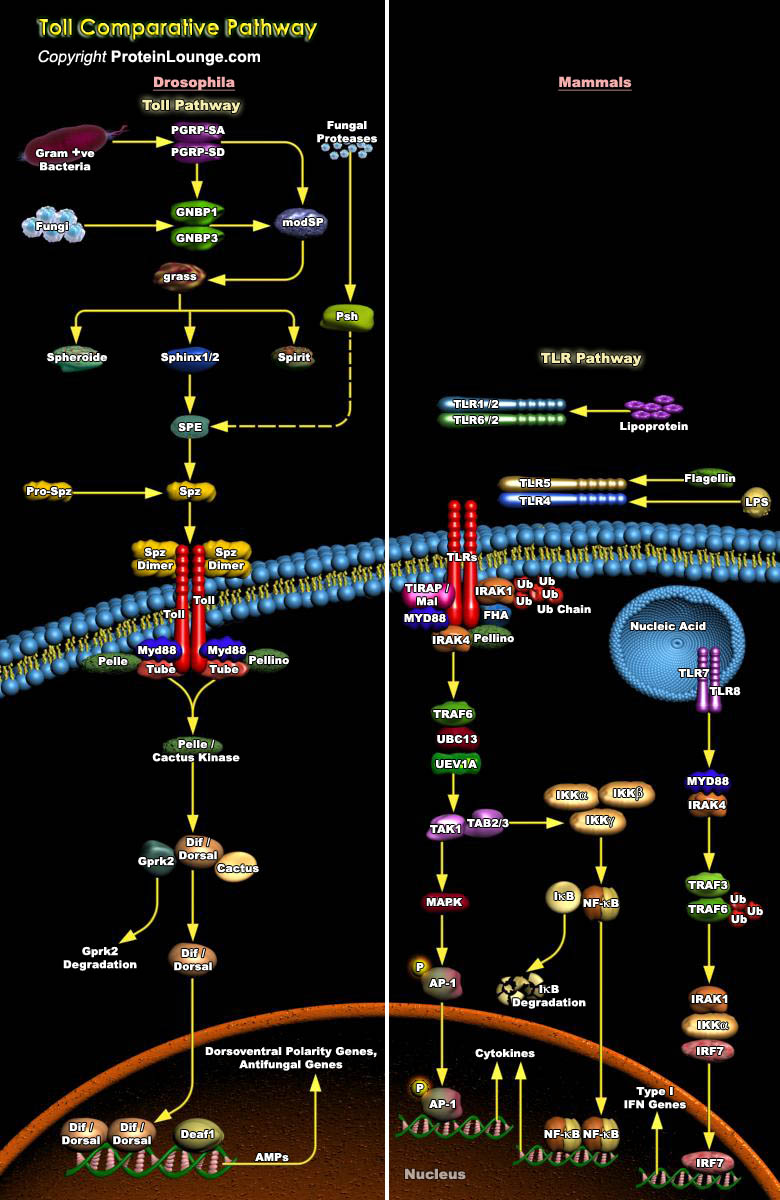
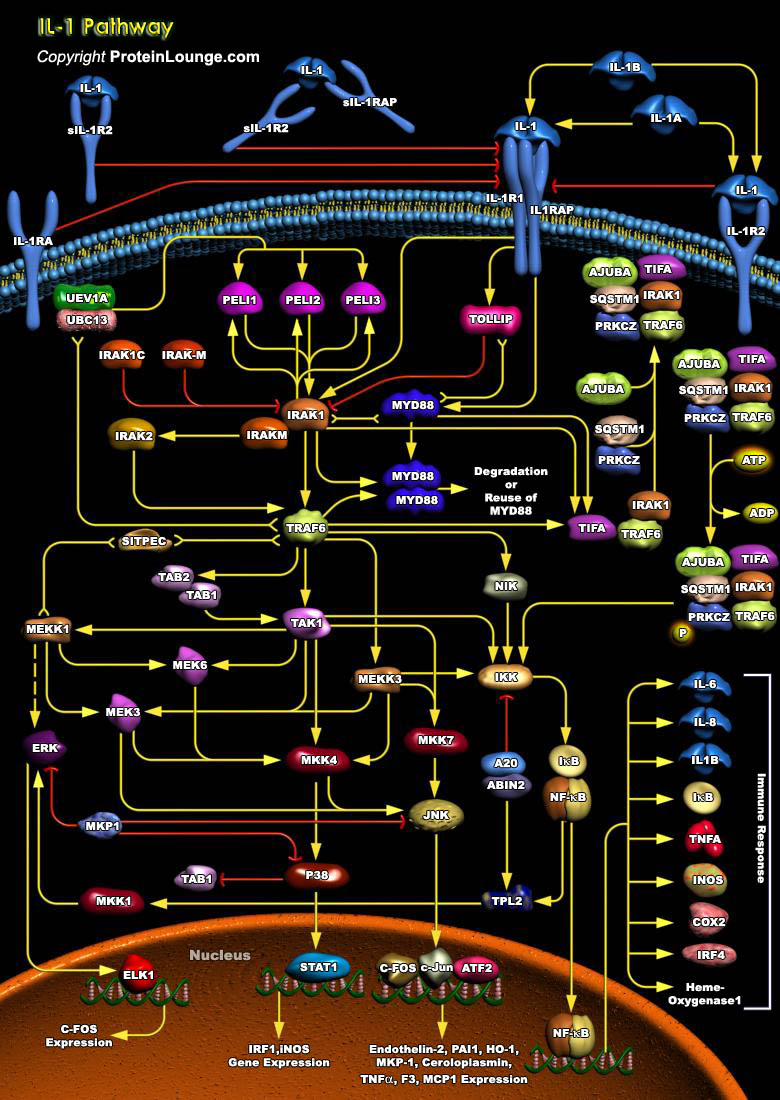
Innate immune system plays an important role in immune responses against pathogen invasion in vertebrates and invertebrates. In mammalian systems, it provides the first line of defense against multiple pathogens, whereas in insects, the entire immune system is innate. The Toll pathway plays important functions in innate immunity against infectious pathogens in vertebrates and invertebrates.[..]
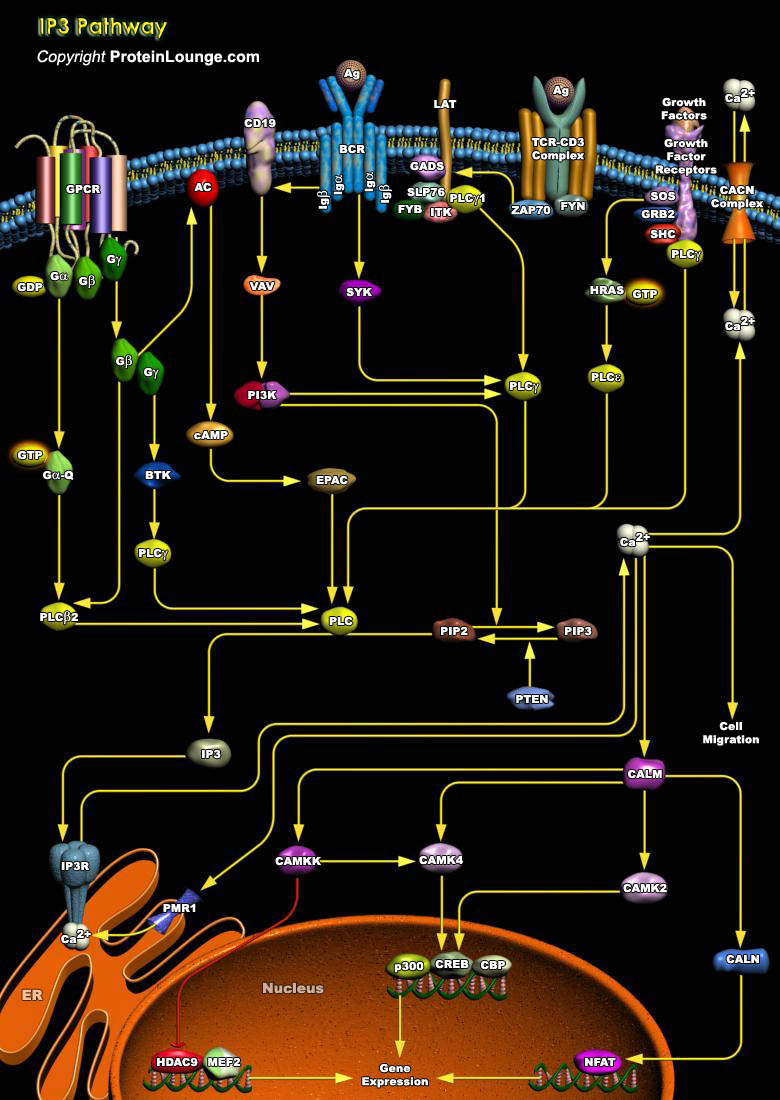
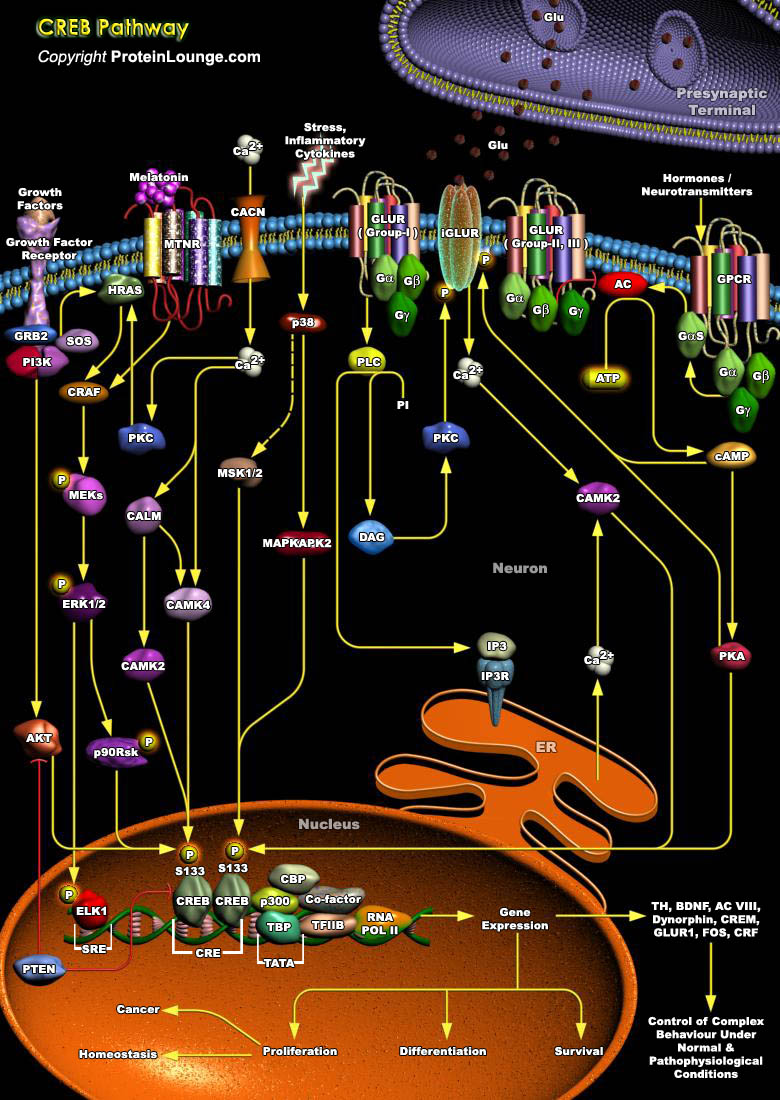
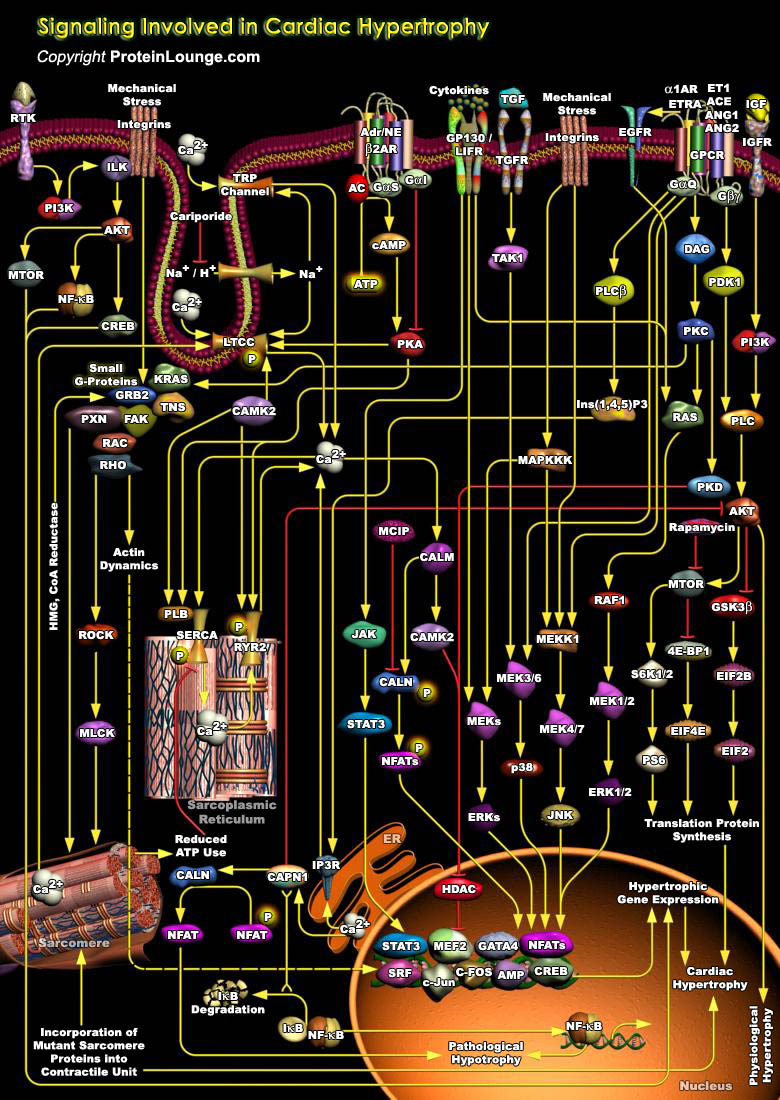
IP3 (Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate), also known as a second messenger, is a molecule that functions to transfer a chemical signal received by the cell, such as from a hormone, neurotransmitters, growth factors and hypertrophic stimuli such as AngII (Angiotensin-II), Beta-adrenergic receptor agonists, and ET1 (Endothelin-1) to various signaling networks within the cell. IP3 is known to play a[..]
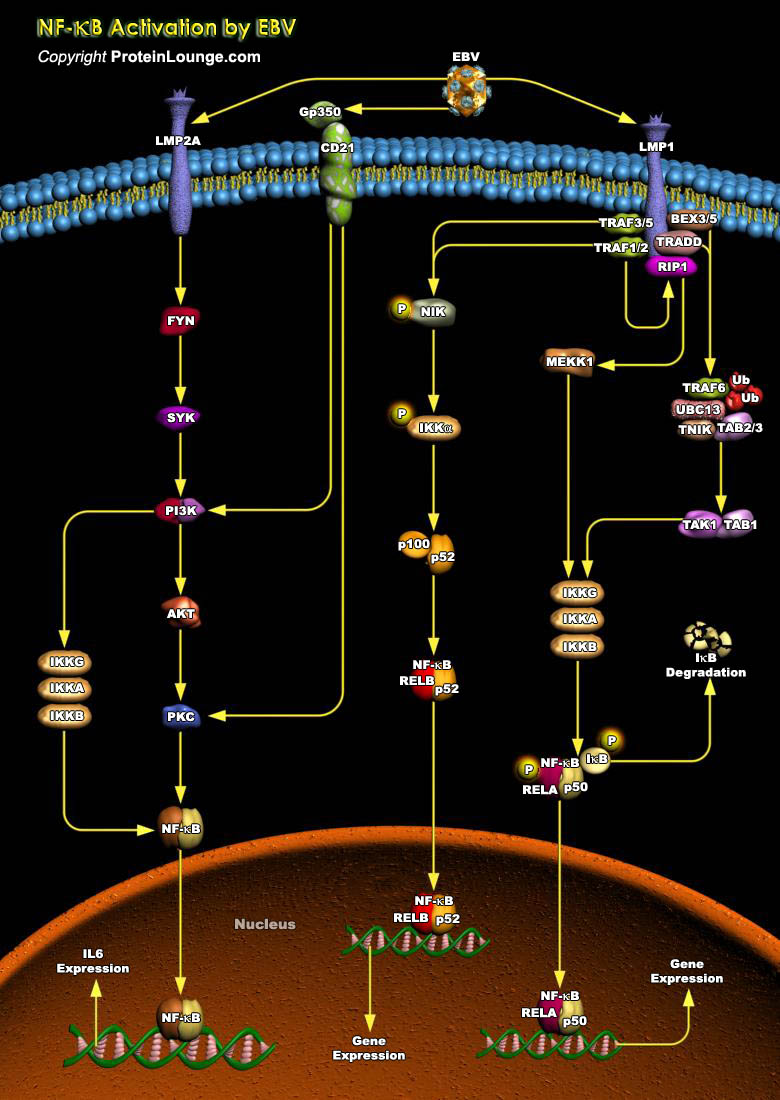
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a gamma-herpesvirus that infects more than 90% of people worldwide, is the etiologic agent of infectious mononucleosis, and is associated with multiple human malignancies, primarily of lymphoid and epithelial cell origin, including Burkitt’s lymphoma, post-transplant lymphoma, AIDS-associated lymphomas, Hodgkin’s disease, T-Cell lymphoma, NPC (Nasopharyngeal[..]
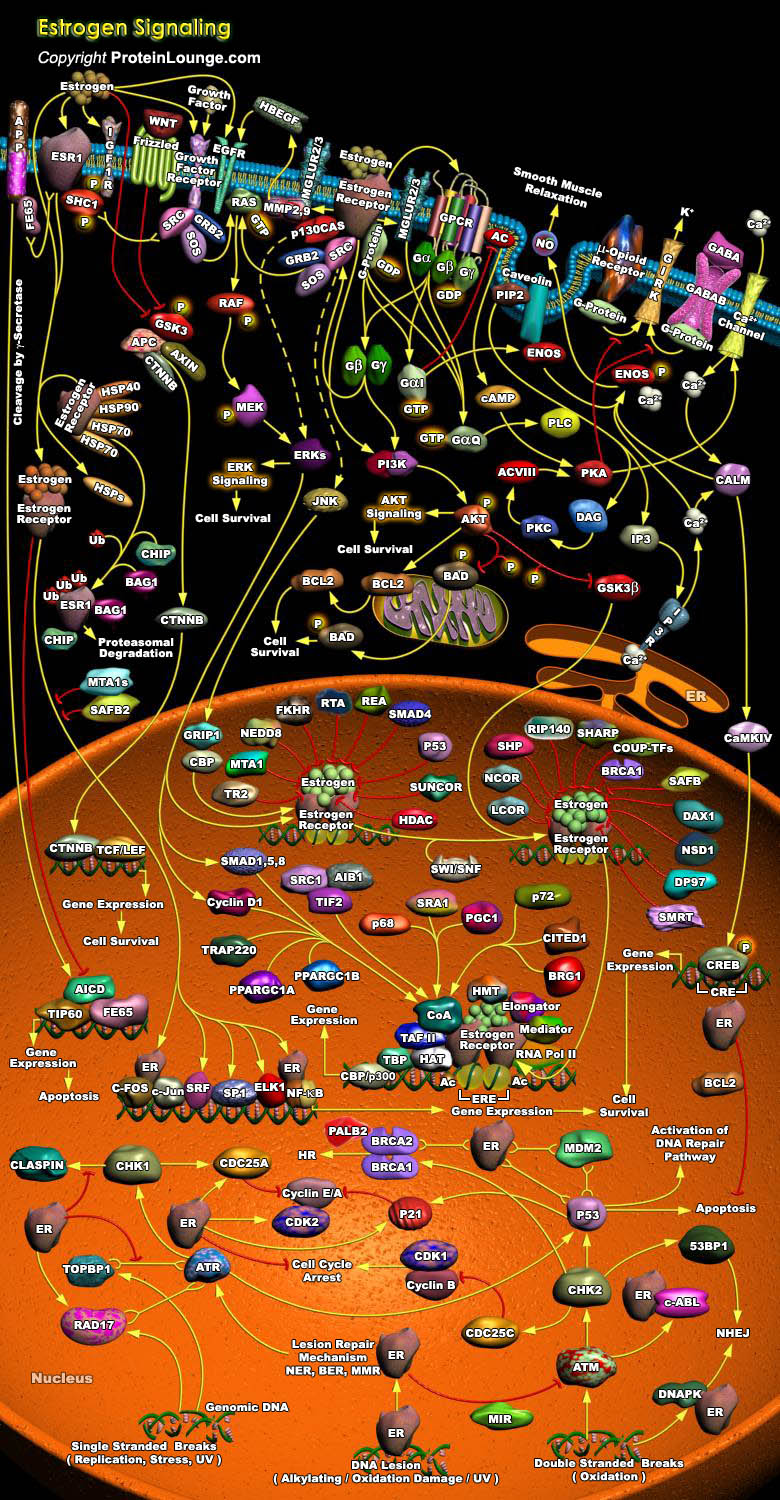
Estrogens play important roles in growth, development, reproduction, and maintenance of a diverse range of mammalian tissues. The physiological effects of estrogens are mediated by the intracellular ERs (Estrogen Receptors), which regulate transcription of target genes through binding to specific DNA target sequences. The ERs orchestrate both transcriptional and non-genomic functions in response[..]
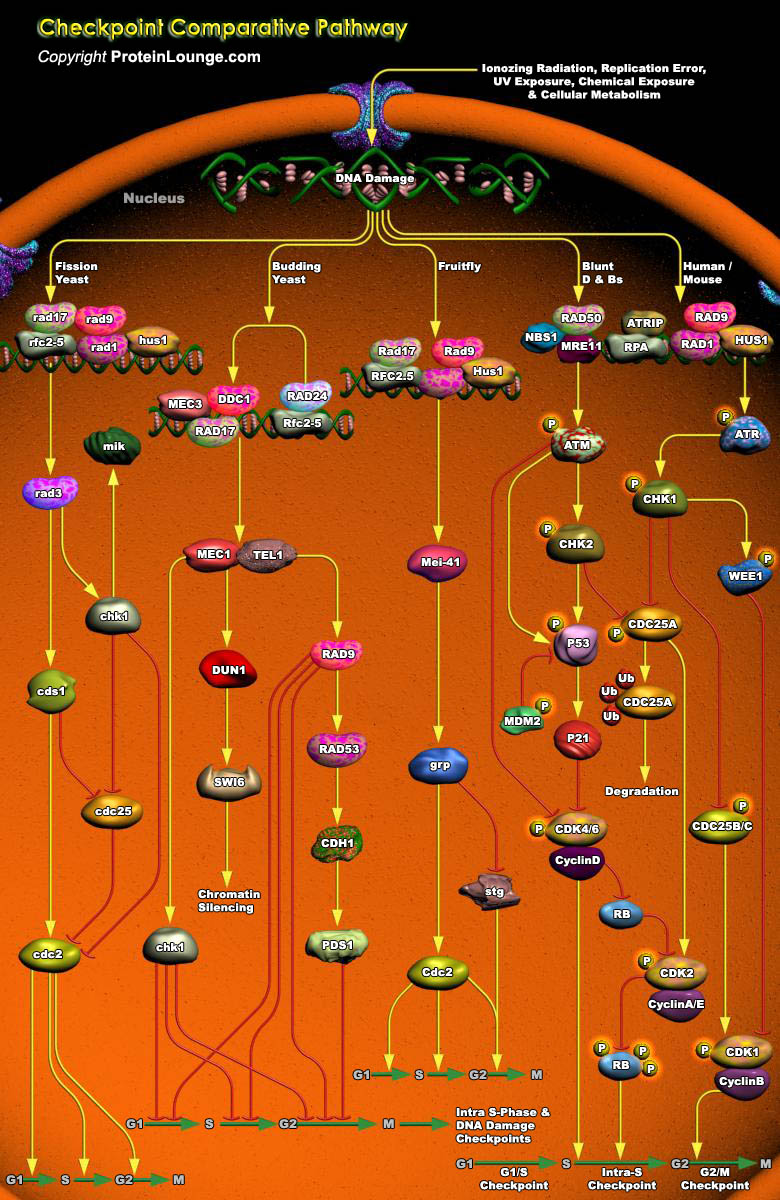
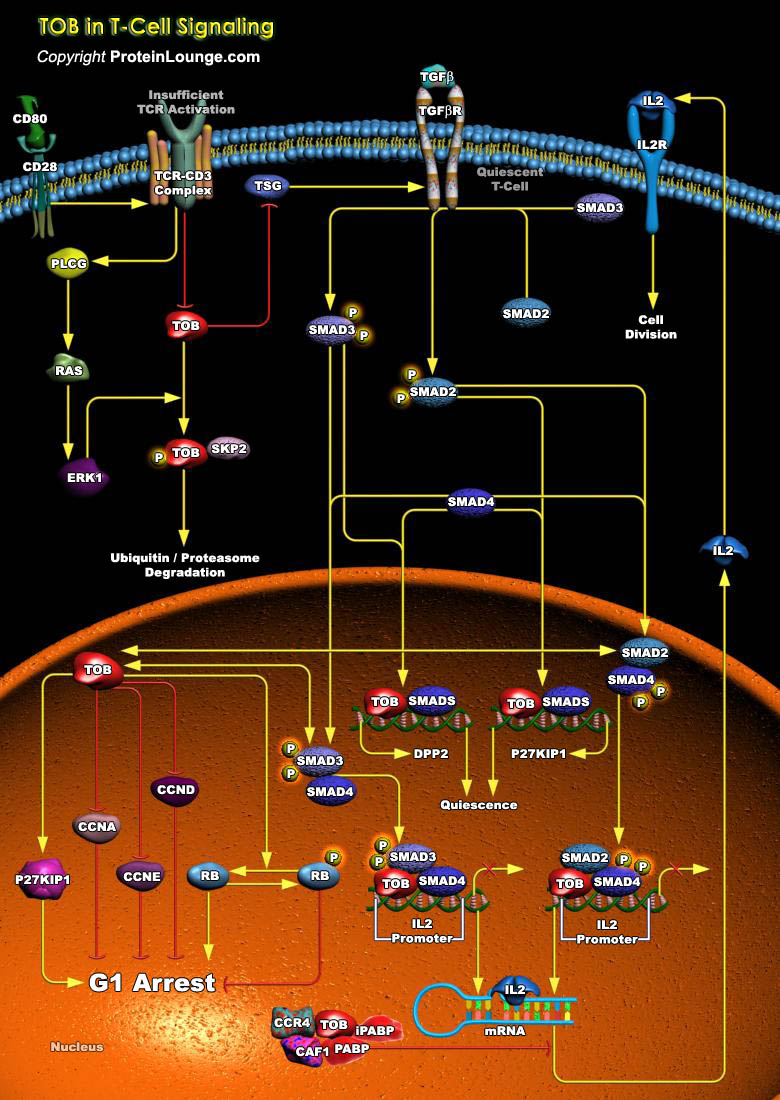
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. These include growth to the appropriate cell size, the replication and integrity of the chromosomes, and their accurate segregation at mitosis. Many of these mechanisms are ancient in origin and highly conserved, and hence have been heavily informed by studies[..]
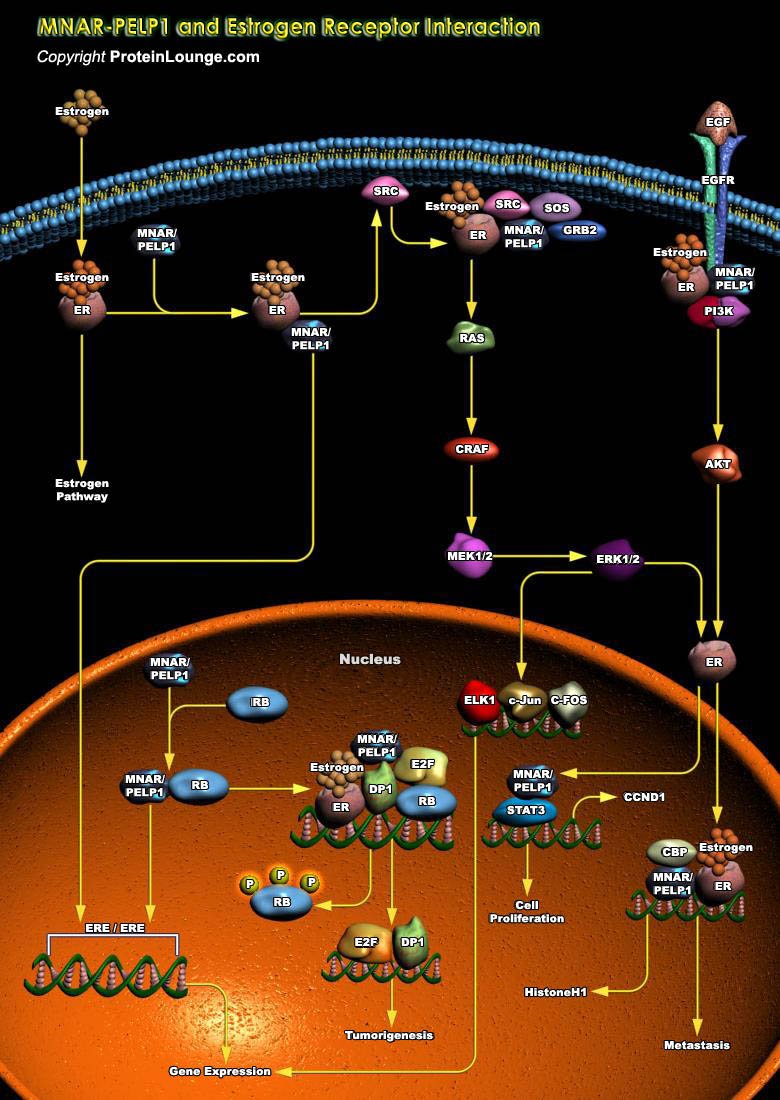
.jpg)
NF-KappaB (Nuclear factor-KappaB)/Rel proteins are dimeric, sequence-specific transcription factors involved in the activation of an exceptionally large number of genes in response to inflammation, viral and bacterial infections, and other stressful situations requiring rapid reprogramming of gene expression. NF-kappB pathway is crucial for the regulation of immune responses, inflammation, and[..]
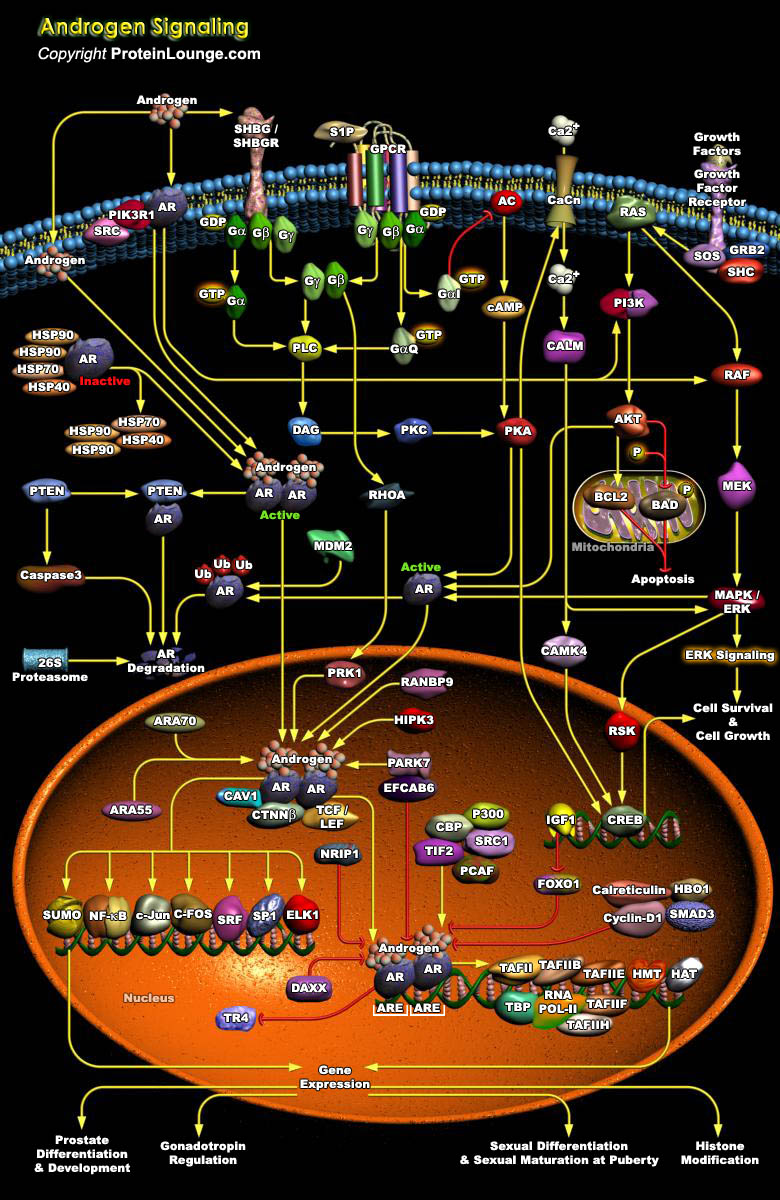
Androgens are recognized as genotropic inducers of a number of physiological functions mainly associated with the development of sexual characteristics. Androgens promote the growth and differentiation of prostate cells through ligand activation of the AR (Androgen Receptor) (Ref.1&2). The AR, upon activation by Androgens, mediates transcription of target genes that modulate growth and[..]