Featured Pathways
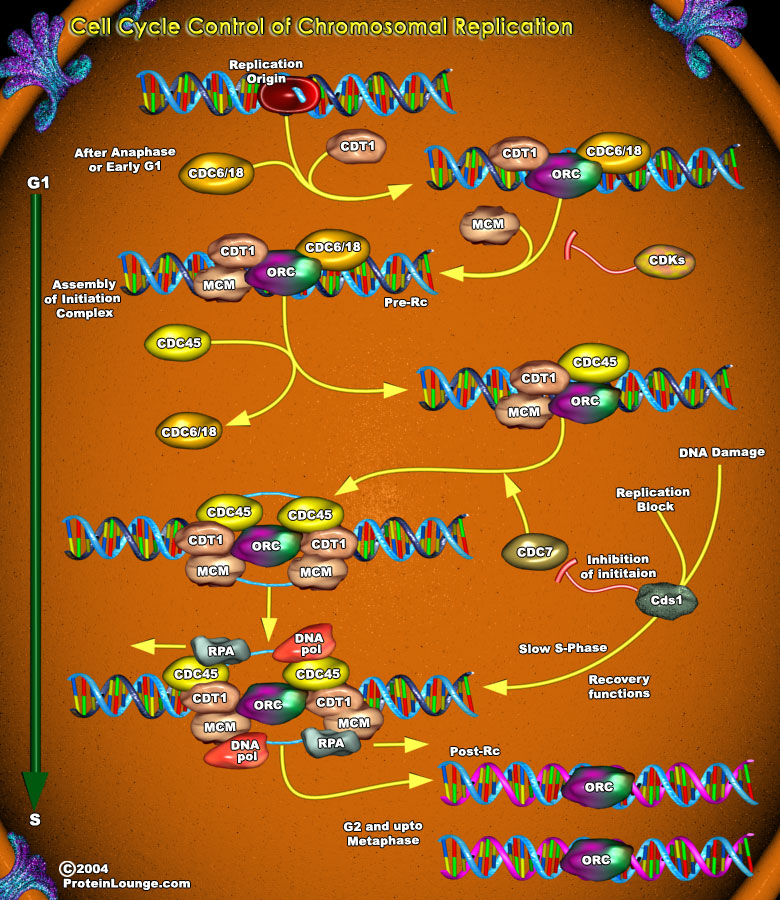
The stable propagation of genetic information requires that the entire genome of an organism be faithfully replicated only once in each cell cycle. In eukaryotes, this replication is initiated at hundreds to thousands of replication origins distributed over the genome, each of which must be prohibited from re-initiating DNA replication within every cell cycle (Ref.1). Initiation of DNA[..]
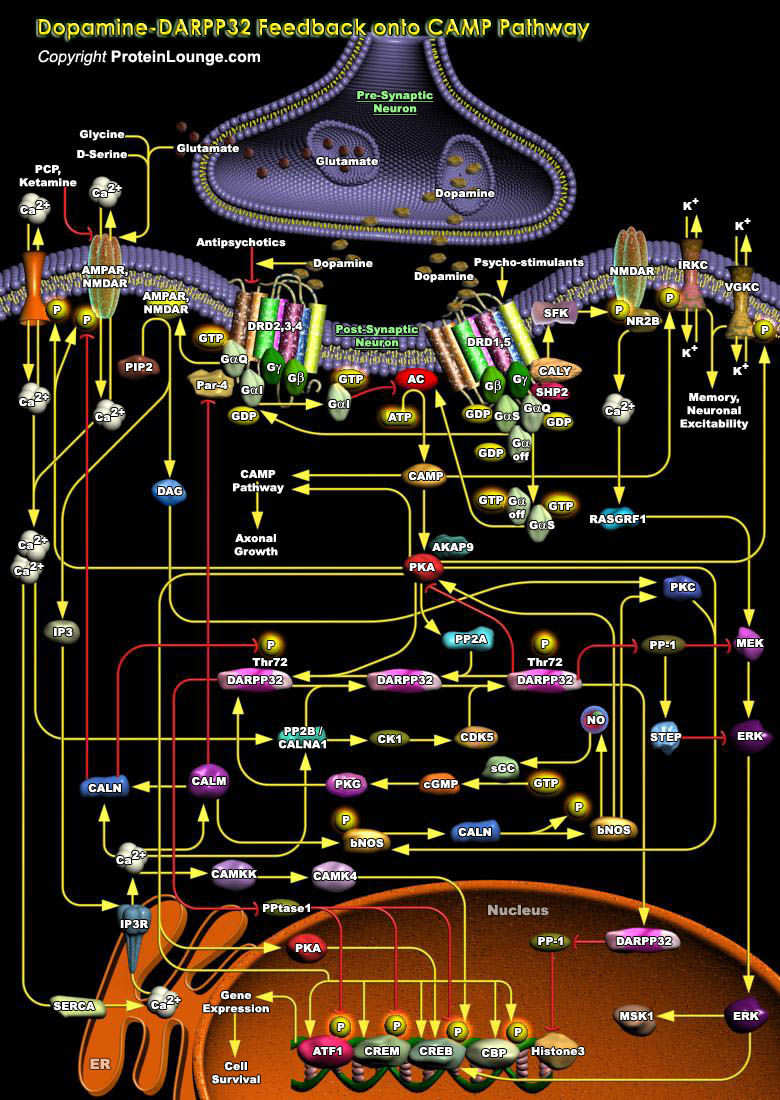
One of the ultimate frontiers for mankind is the elucidation of the function of the mind. Dopaminergic and Glutamergic are two primary neurotransmitter systems in the brain, which are crucially important for the control of the body musculature and the Dopamine-induced signaling pathways. Dopamine, a derivative of the amino acid Tyrosine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter that serves as a[..]
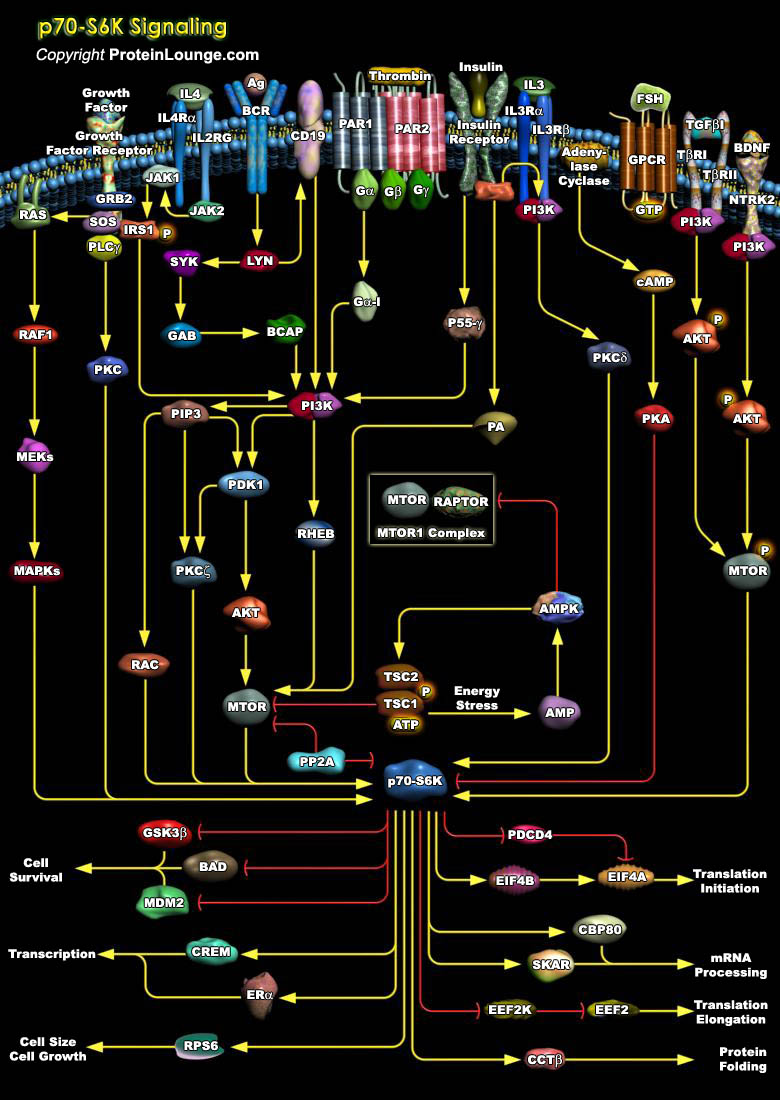
p70S6K is a protein Ser-Thr kinase that phosphorylates the ribosomal S6 subunit, a component of the 40S subunit of eukaryotic ribosomes. It plays a role in protein synthesis and in cell growth control during G1 phase in vivo to enhance translation of certain mRNA species (Ref.1). In the living cell, ribosomal p70S6K is activated through a complex network of[..]
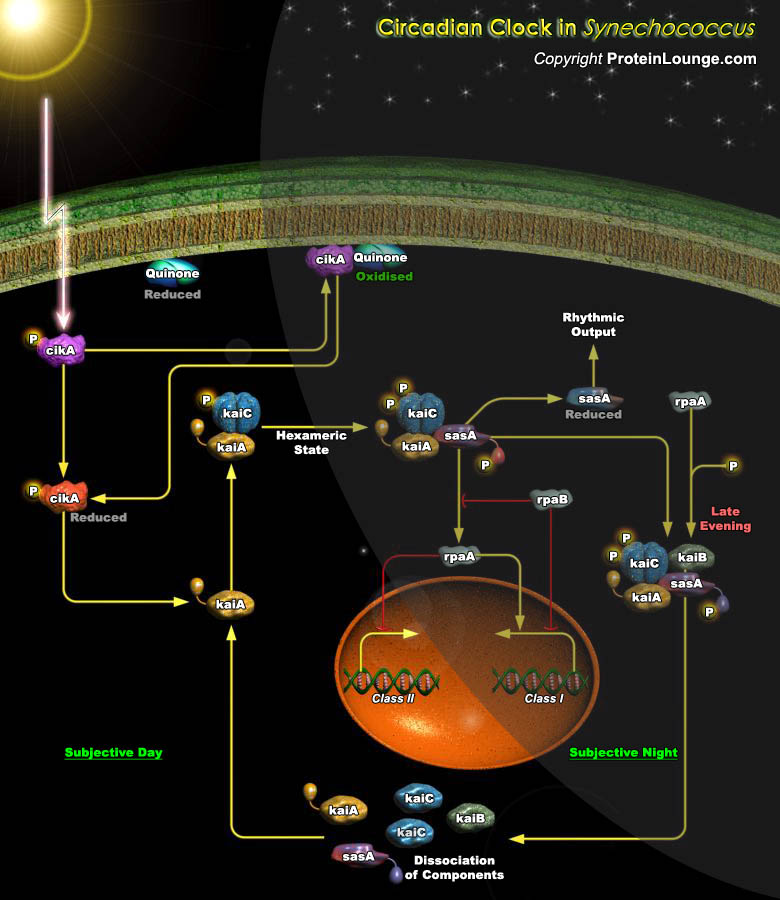
The unicellular cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus is an obligate photoautotroph and the simplest model organism in circadian biology. Circadian rhythms, regulated by a 24-h biological clock, enable the coordination of biological activity over the course of the day and facilitate adaptation to daily environmental changes in diverse organisms. Unlike the circadian[..]
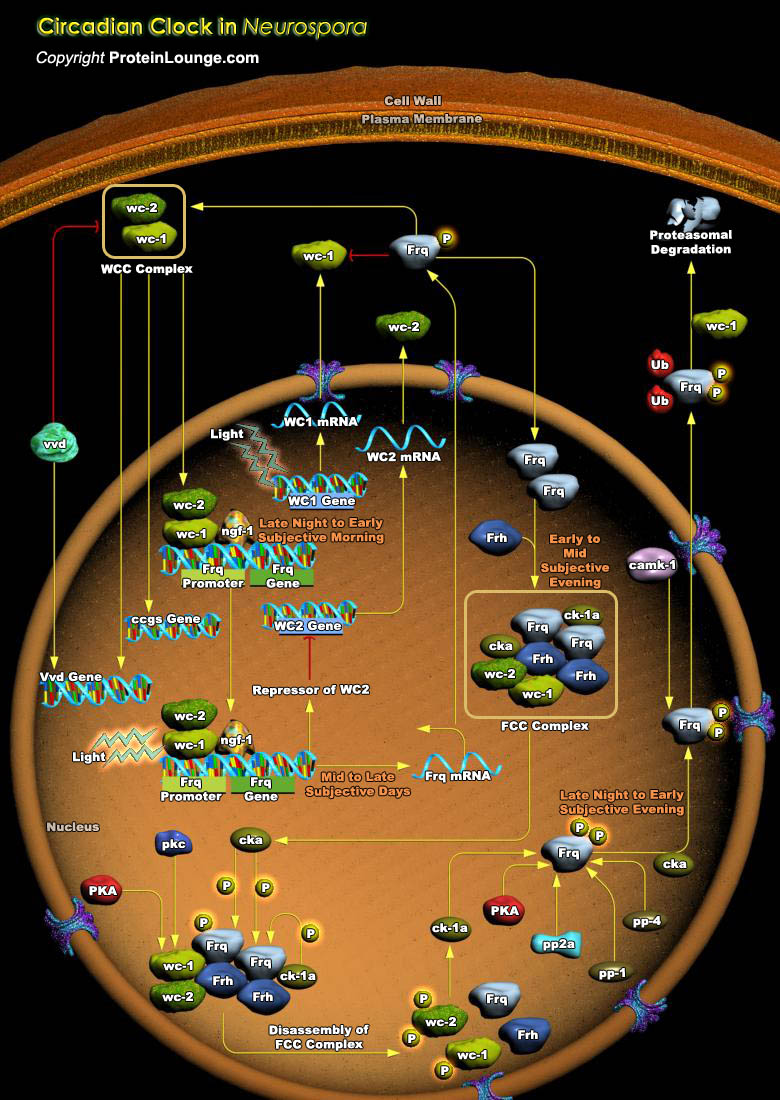
Circadian clocks are internal timekeepers that utilize environmental signals to induce cellular events to occur at the most favourable time of day. Circadian clocks in animals, plants, fungi and bacteria have similar characteristic properties and molecular architecture. They have a periodicity of approximately 24 hours, persist in constant conditions and can be reset by environmental time cues[..]
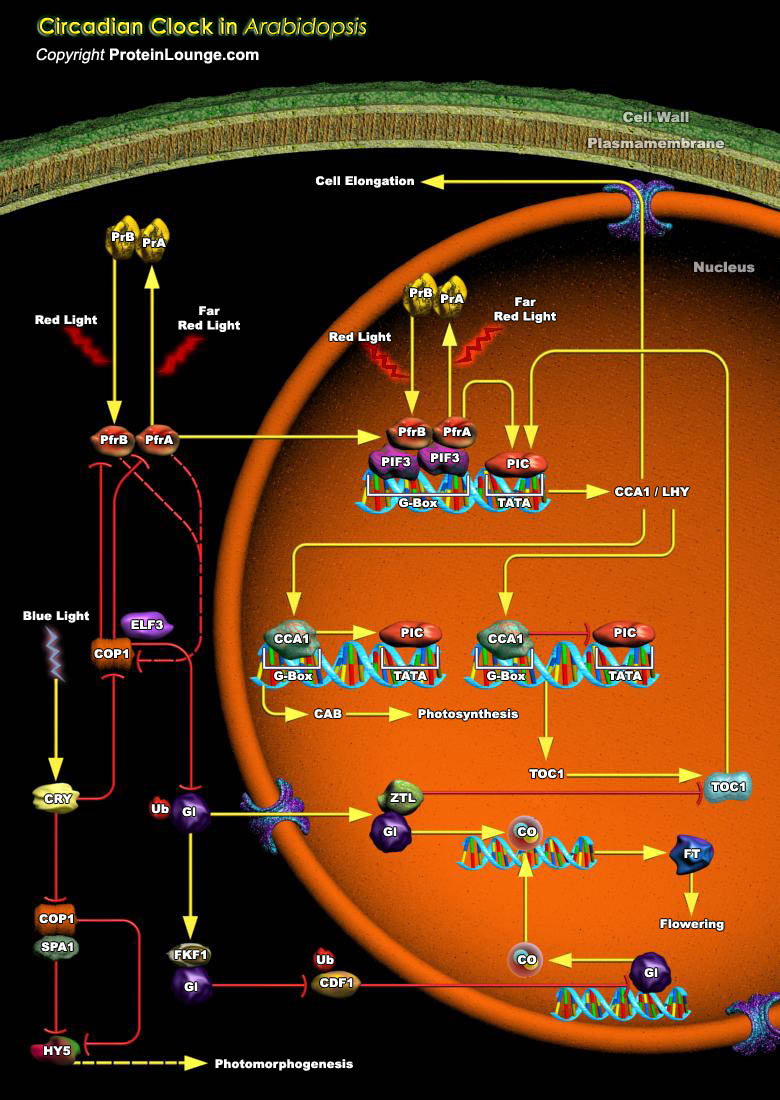
Photoreceptors and circadian clocks are univesal mechanisms for sensing and responding to the light environment. In addition to regulating daily activities, photoreceptors and circadian clocks are also involved in the seasonal regulation of processes such as flowering. Circadian rhythms govern many plant processes, including movements of organs such as leaves and petals, stomata opening, stem[..]
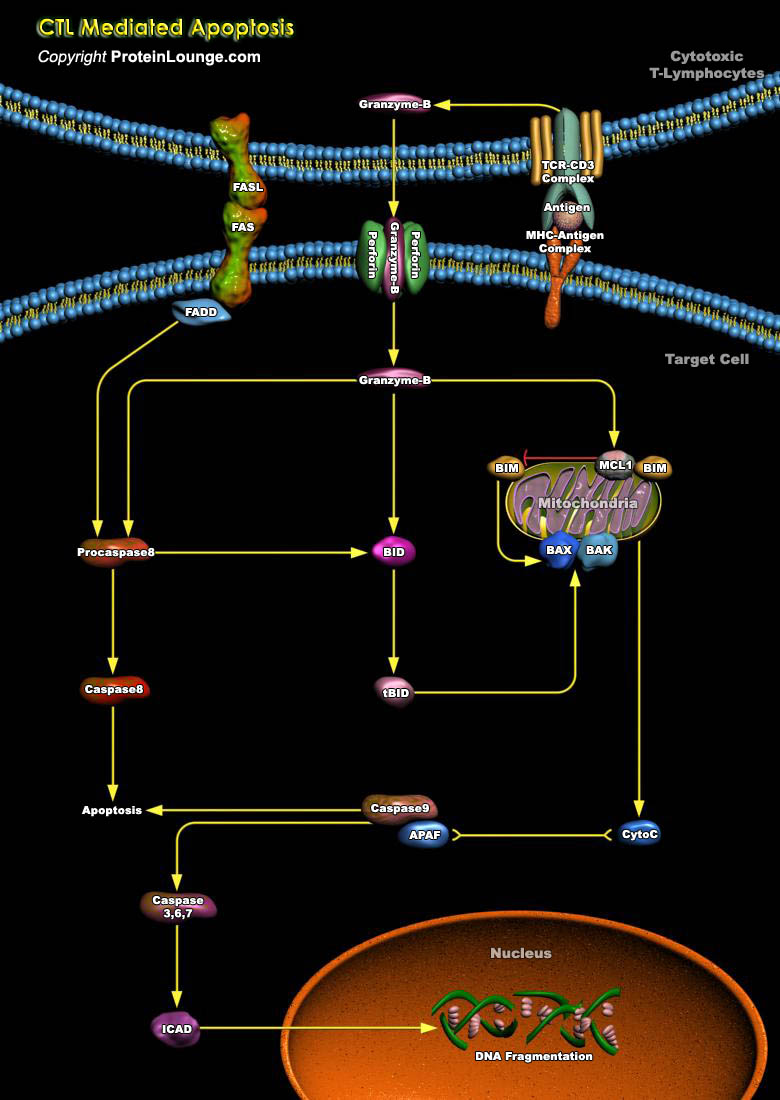
The CTLs (Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes), also known as killer T-Cells are produced during cell-mediated immunity designed to remove body cells displaying "foreign" epitope, such as virus-infected cells, cells containing intracellular bacteria, and cancer cells with mutant surface proteins. The CTLs are able to kill these cells by inducing a programmed cell death known as apoptosis (Ref.1).
CTLs[..]
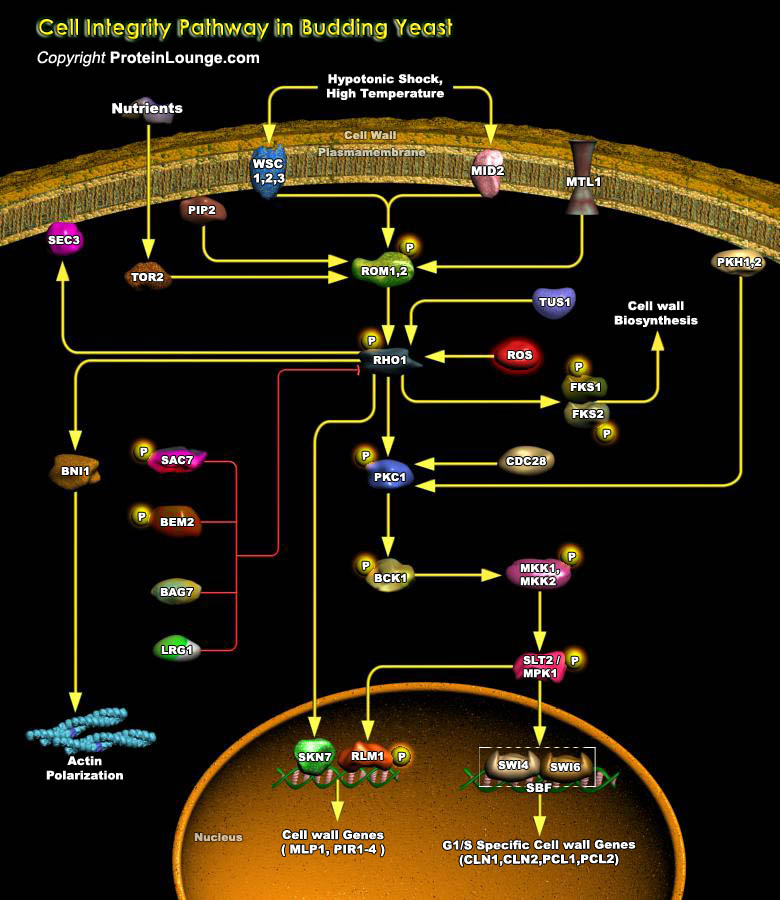
Extracellular environmental changes cause different types of stress in all the organisms and can seriously affect the viability of the cells. All cells have signaling pathways required to transmit the stress signals from outside and to develop the response and gene expression changes required to adapt and survive. Cell Integrity Pathway signaling is activated persistently in response to[..]
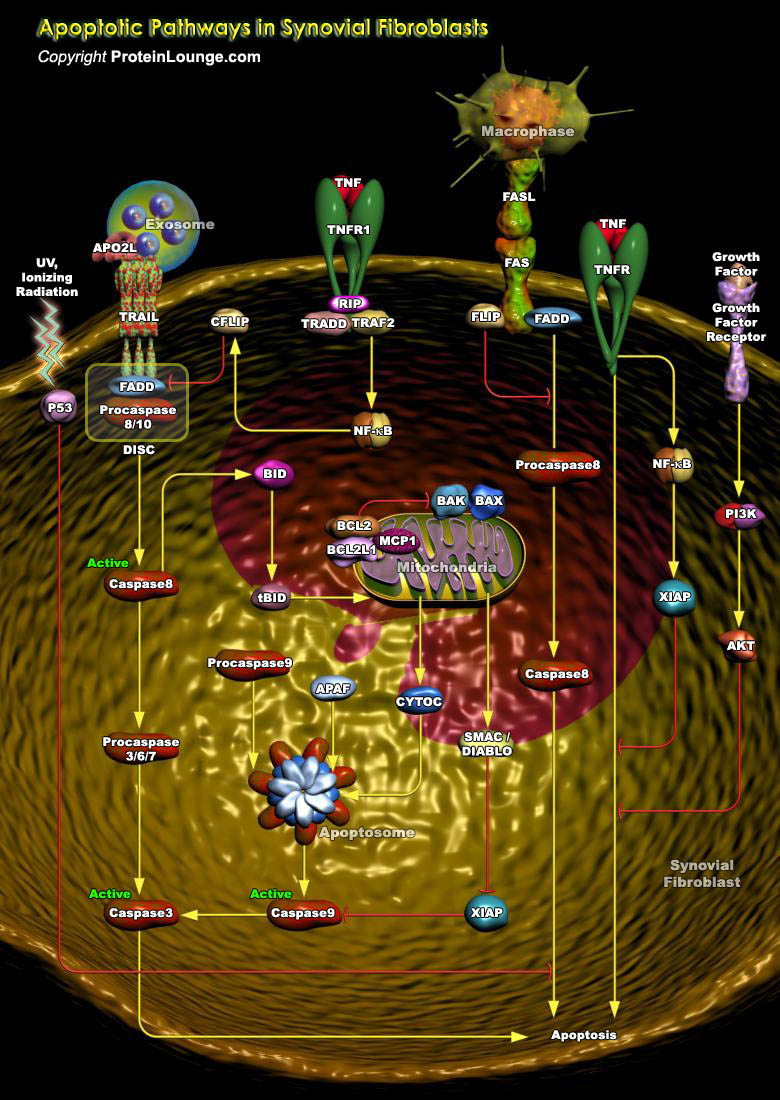
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the lining of the synovial joints and is associated with progressive disability, premature death, and socioeconomic burdens.It is characterized by chronic inflammation and synovial hyperplasia that eventually lead to cartilage and bone destruction. Synovial fibroblasts are mesenchymal cells recognized as a[..]
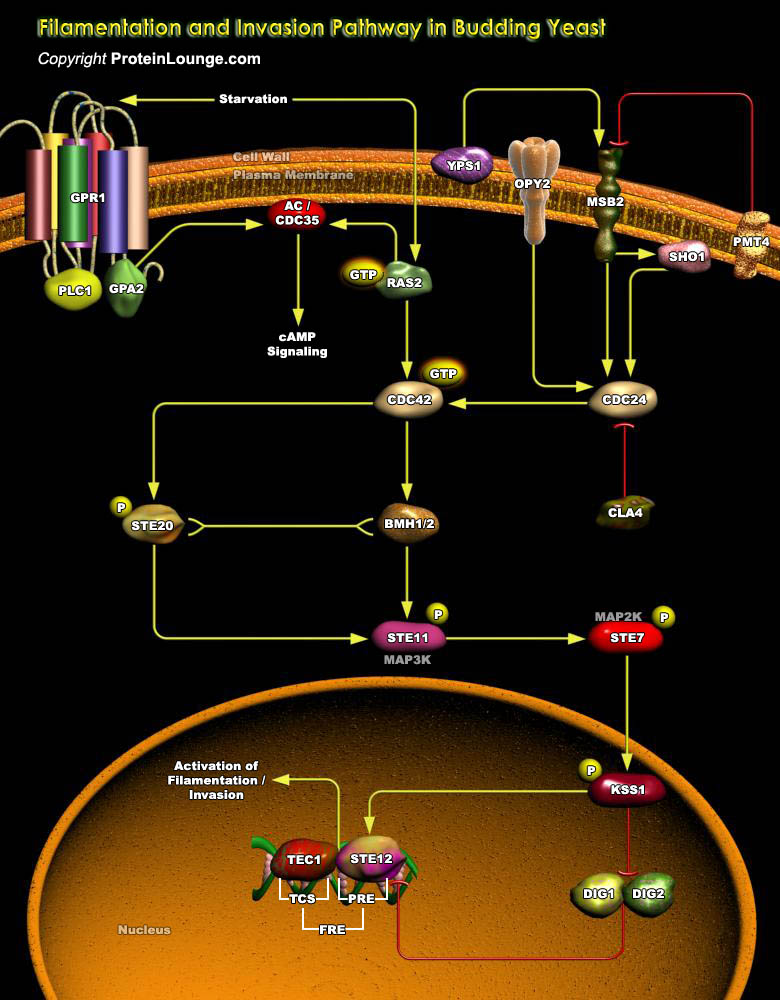
Vegetative yeast cells respond to environmental cues by activating signal transduction pathways that enable them to mount the appropriate physiological response. Each of the cues is dealt with by distinct signaling mechanisms to cause the appropriate response to a given stimulus. In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae, there are at least five MAP kinase (Mitogen-Activated[..]