Featured Pathways
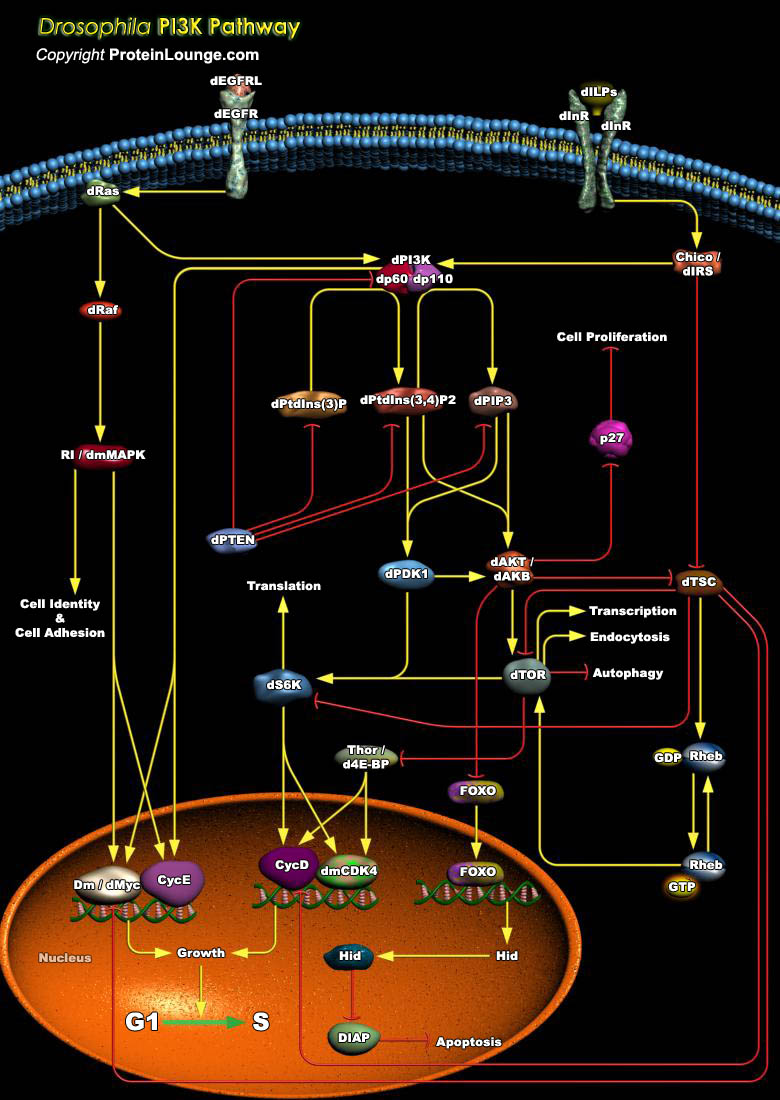
The (Phosphatidylinositde-3-Kinase) family of enzymes regulate diverse biological functions in every cell type by generating lipid second messengers that ultimately results in the mediation of cellular activities such as proliferation, differentiation, chemotaxis, survival, trafficking and Glucose homeostasis. On the basis of structural similarities, the members are sub-divided into three[..]
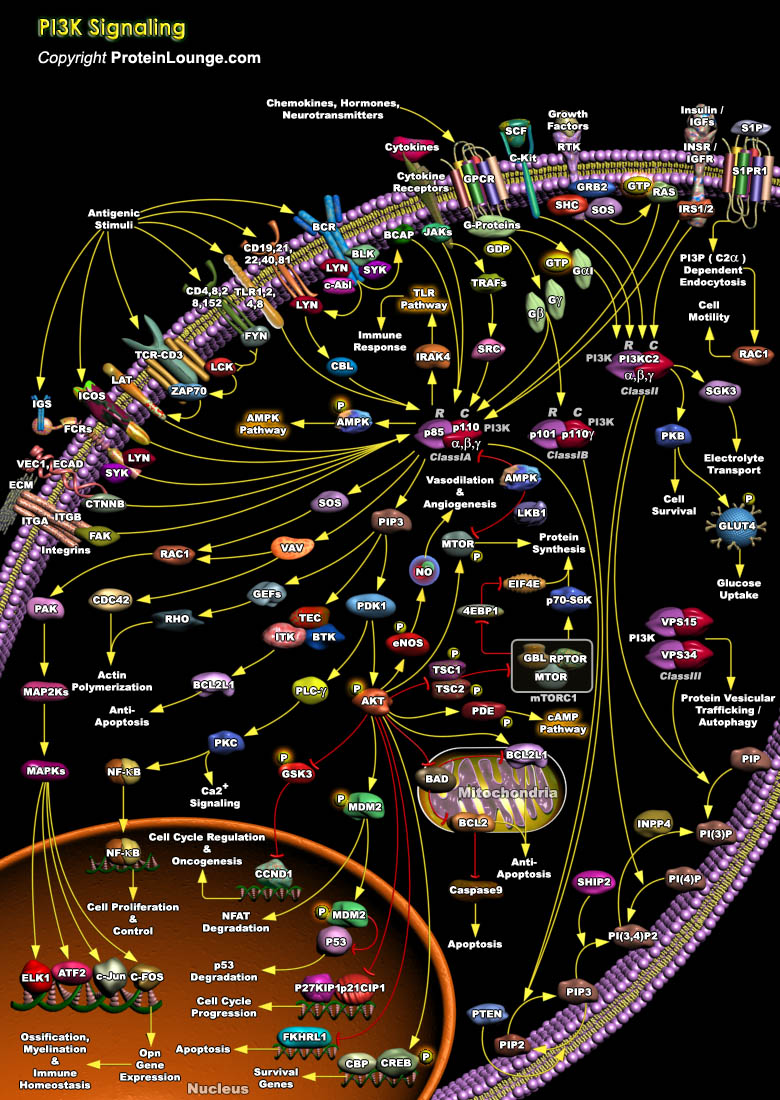
The PI3K (Phosphatidylinositde-3 Kinase) family of enzymes is recruited upon growth factor receptor activation and produces 3' phosphoinositide lipids. The lipid products of PI3K act as second messengers by binding to and activating diverse cellular target proteins. Therefore, PI3Ks play a central role in many cellular functions. In mammals, the PI3Ks have a p110 catalytic subunit[..]
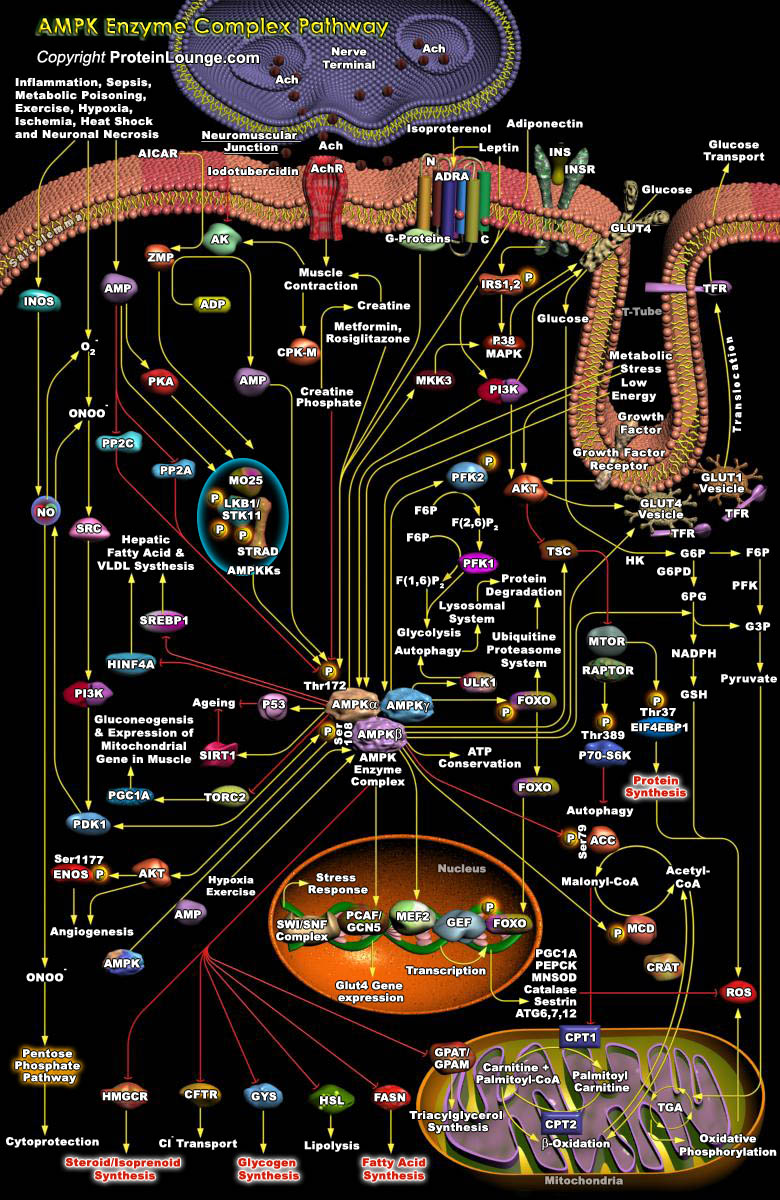
One of the key functions of catabolic metabolism is to maintain high levels of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and cells rapidly respond to any stress that threatens to lower ATP levels by arresting non-essential ATP-utilizing functions and stimulating available ATP-generating pathways. A central player in this system is the AMPK (AMP (Adenosine 5'-Monophosphate)-Activated Protein Kinase). AMPK is a[..]
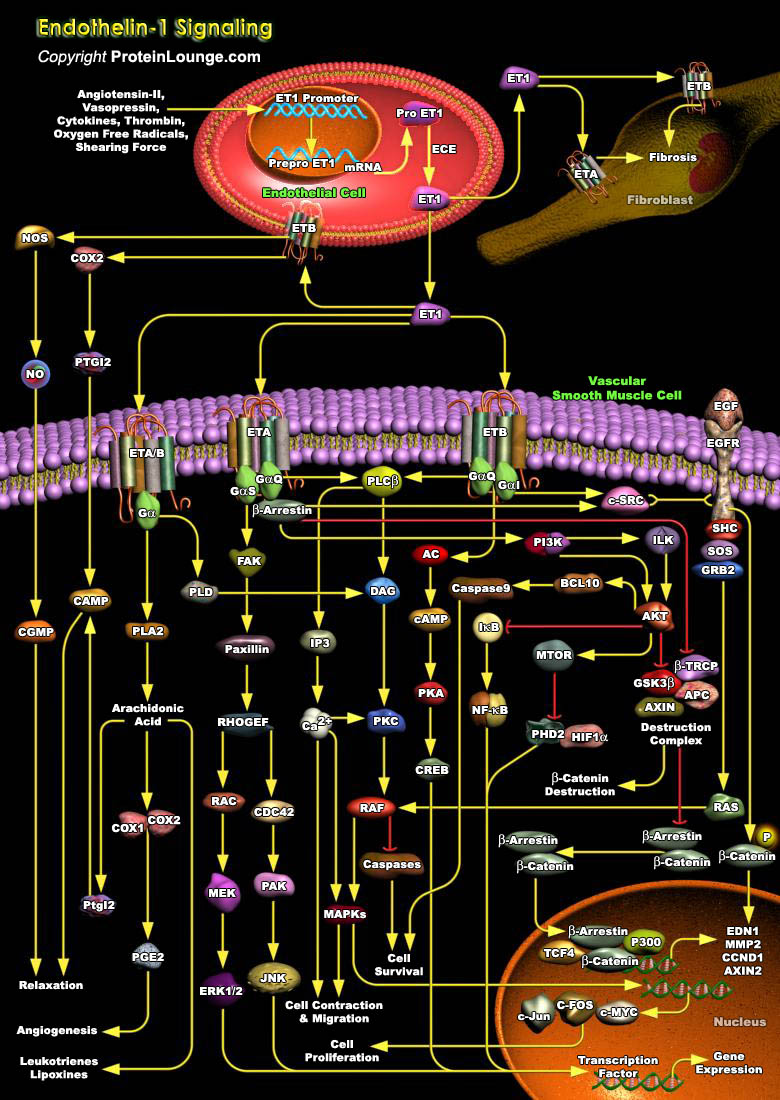
Cardiac hypertrophy describes an abnormal condition where the heart becomes enlarged. Several factors, such as increased mechanical loading and neuro-hormonal chemicals can induce hypertrophy. ET1 (Endothelin-1) is a 21-amino acid vasoconstrictor peptide, which is able to induce cardiac hypertrophy. In mammals this peptide family also includes ET2 and ET3. ET1 is the principal isoform in the[..]
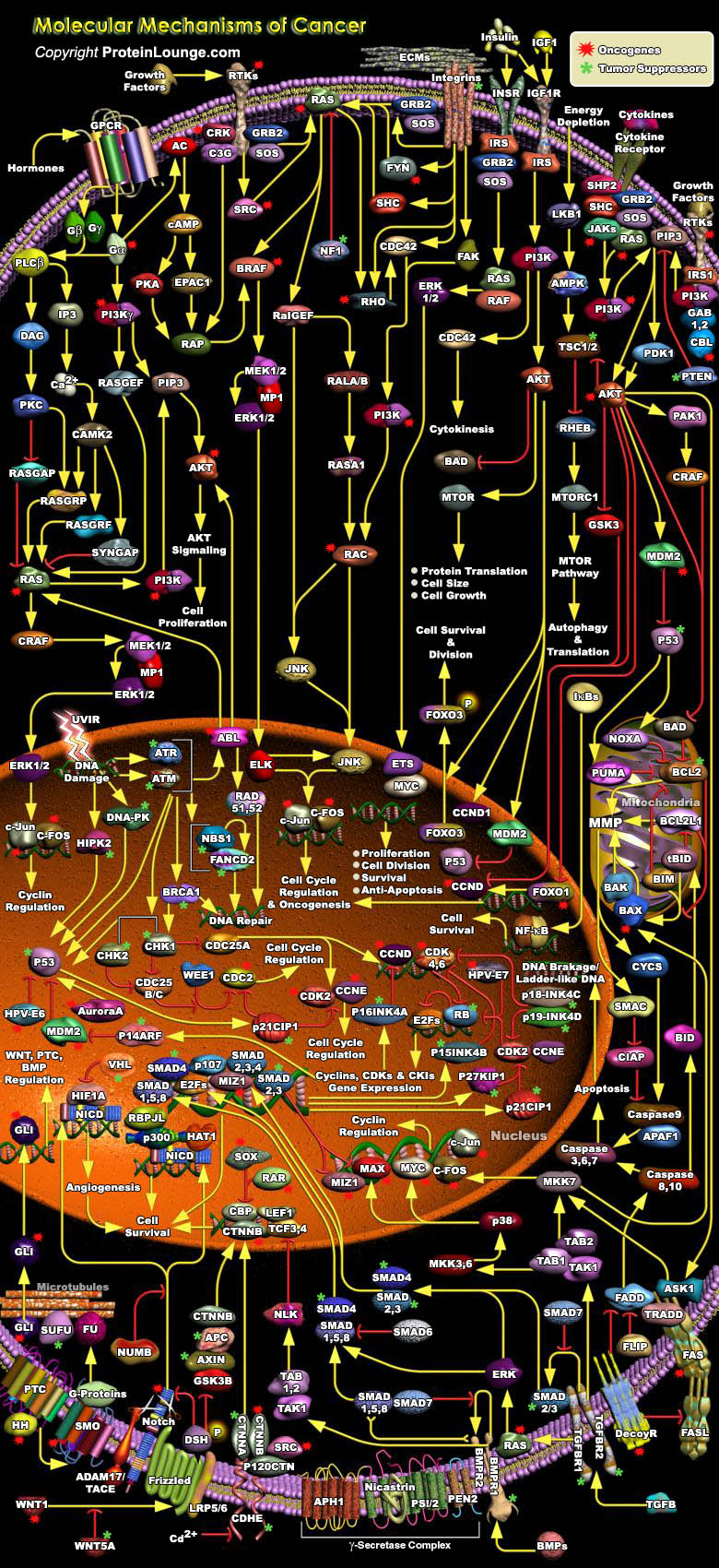
Cancer cell genotypes are a manifestation of six essential alterations in cell physiology that collectively dictate malignant growth; self-sufficiency in growth signals, insensitivity to growth-inhibitory (anti-growth) signals, evasion of programmed cell death (apoptosis), limitless replicative potential, sustained angiogenesis and tissue invasion and metastasis. Environmental and endogenous[..]
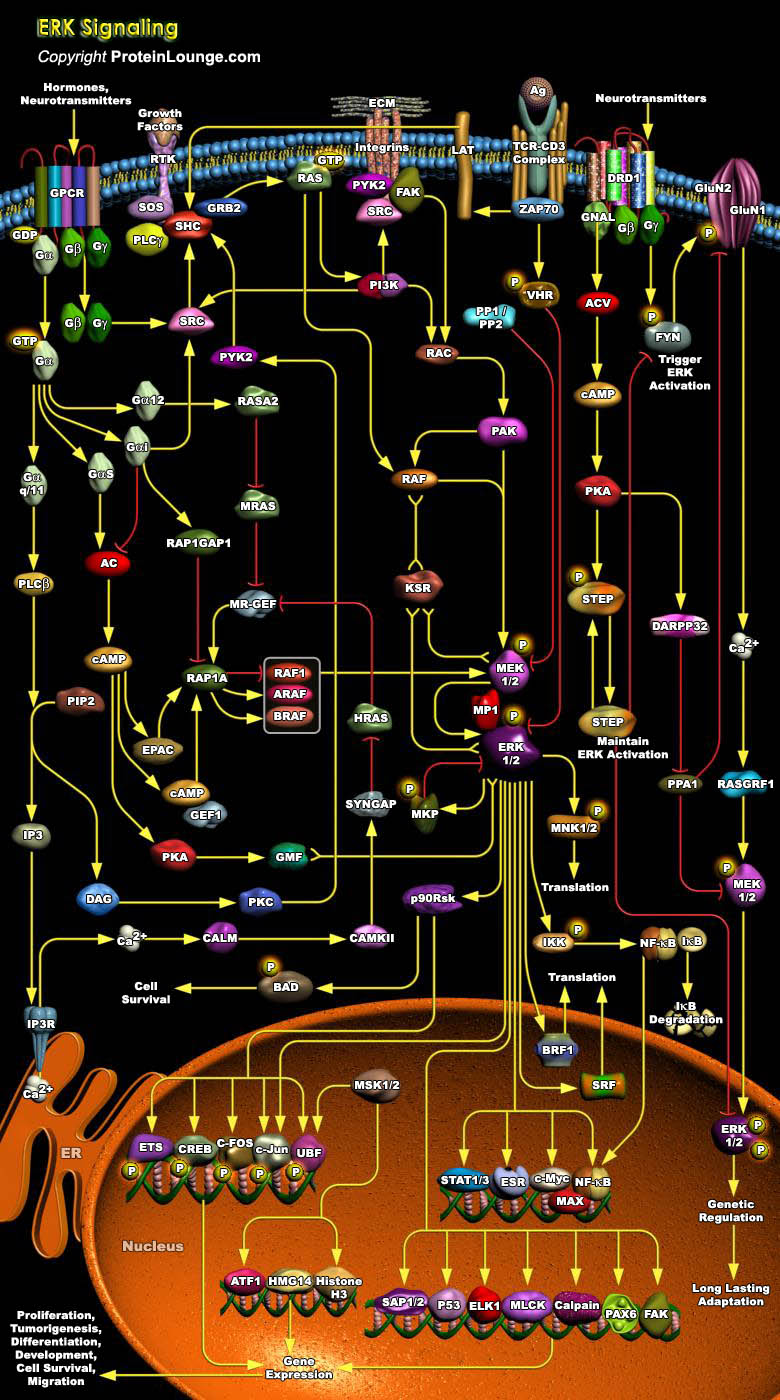
The MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) pathway is one of the primordial signaling systems that nature has used in several permutations to accomplish an amazing variety of tasks. It exists in all eukaryotes, and controls such fundamental cellular processes as Proliferation, Differentiation, Survival and Apoptosis. Mammalian MAPK can be divided into four groups based on their structure and[..]
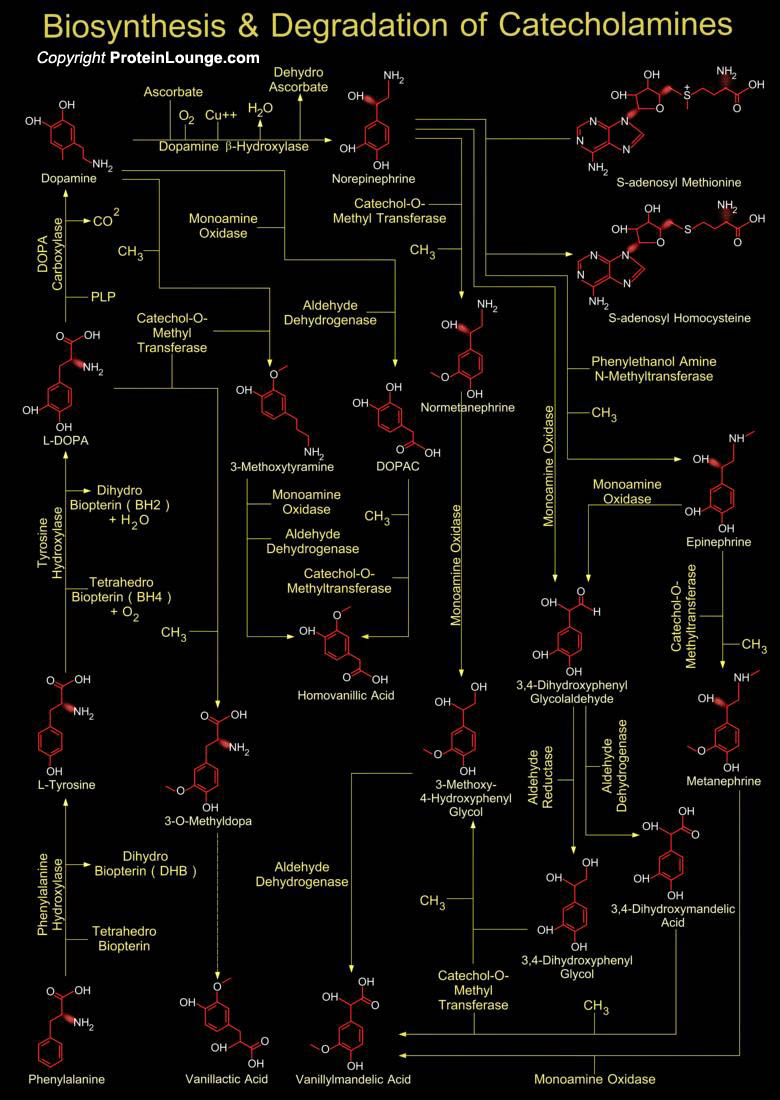
Catecholamine is the common term for the important hormones Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline), Epinephrine (Adrenaline) and Dopamine. Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla are the key site of catecholamine synthesis and collections of these cells are also found in heart, liver, kidney, gonads, adrenergic neurons of the postganglionic sympathetic system, and CNS (Central Nervous System). The[..]
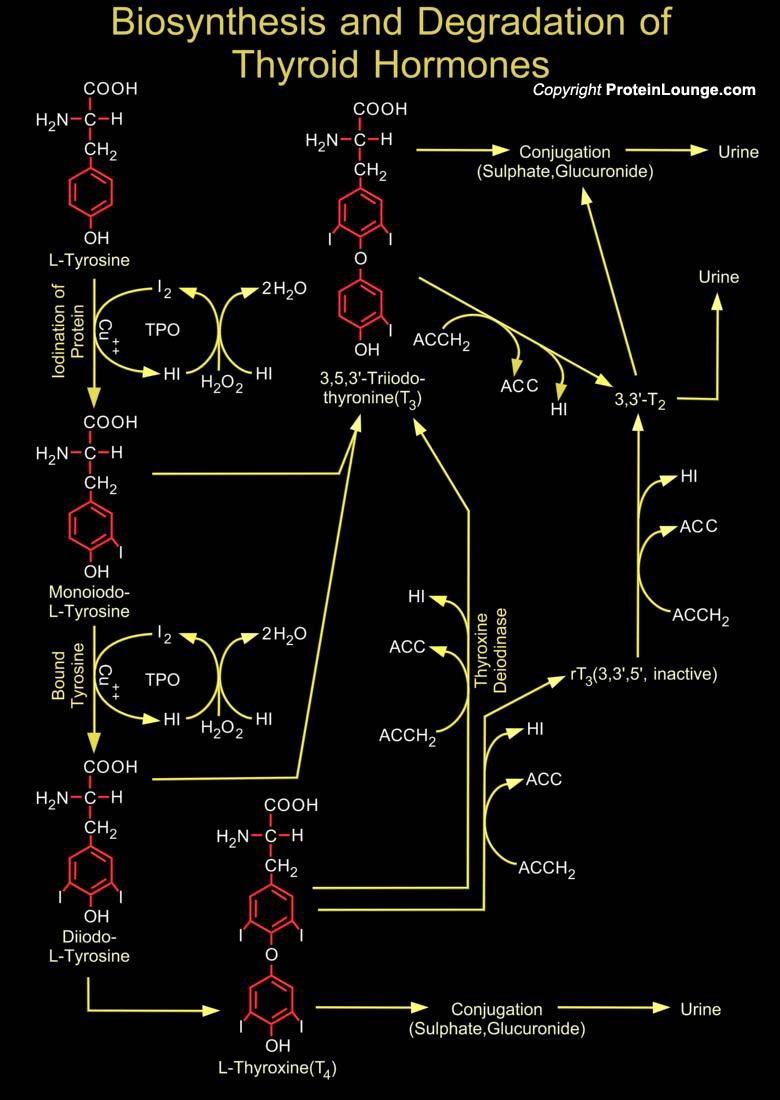
Iodide, which is ingested in food and water, is actively concentrated by the thyroid gland, converted to organic iodine by TPO (Thyroid Peroxidase also known as Iodide Peroxidase), and incorporated into tyrosine in intrafollicular thyroglobulin within the colloid at the basal cell surface of the thyroid follicular cell. The tyrosines are iodinated at one (Monoiodotyrosine) or two[..]
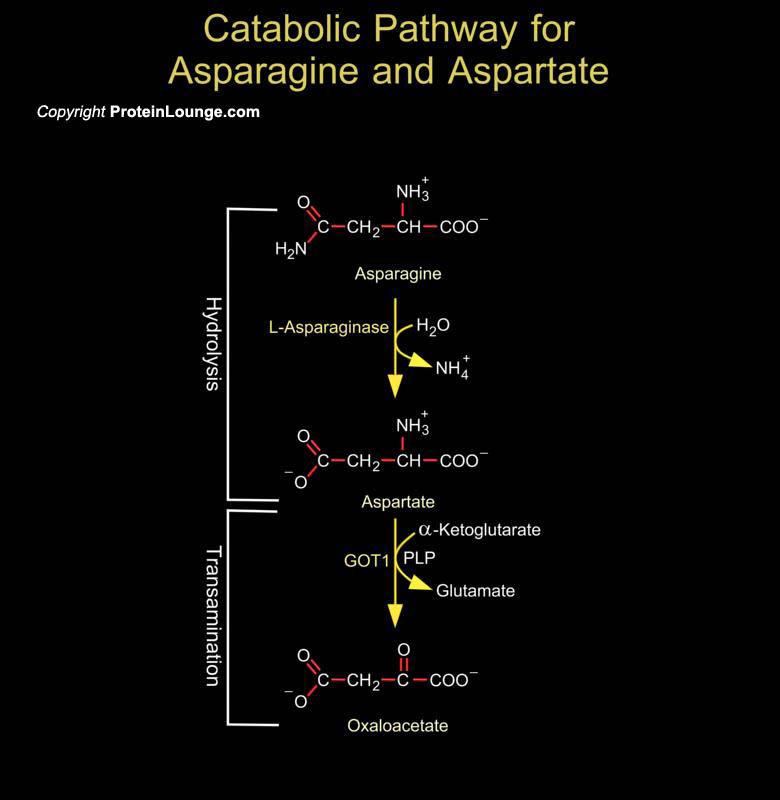
Asparagine, a non essential amino acid, synthesized form oxaloacetic acid. It is an amide of a amino acid Aspartate. The enzymes ASPG (asparaginase) and ASRGL1 (asparaginase and isoaspartyl peptidase 1) catalyze the hydrolysis of Asparagine to Aspartate and Ammonia. The[..]
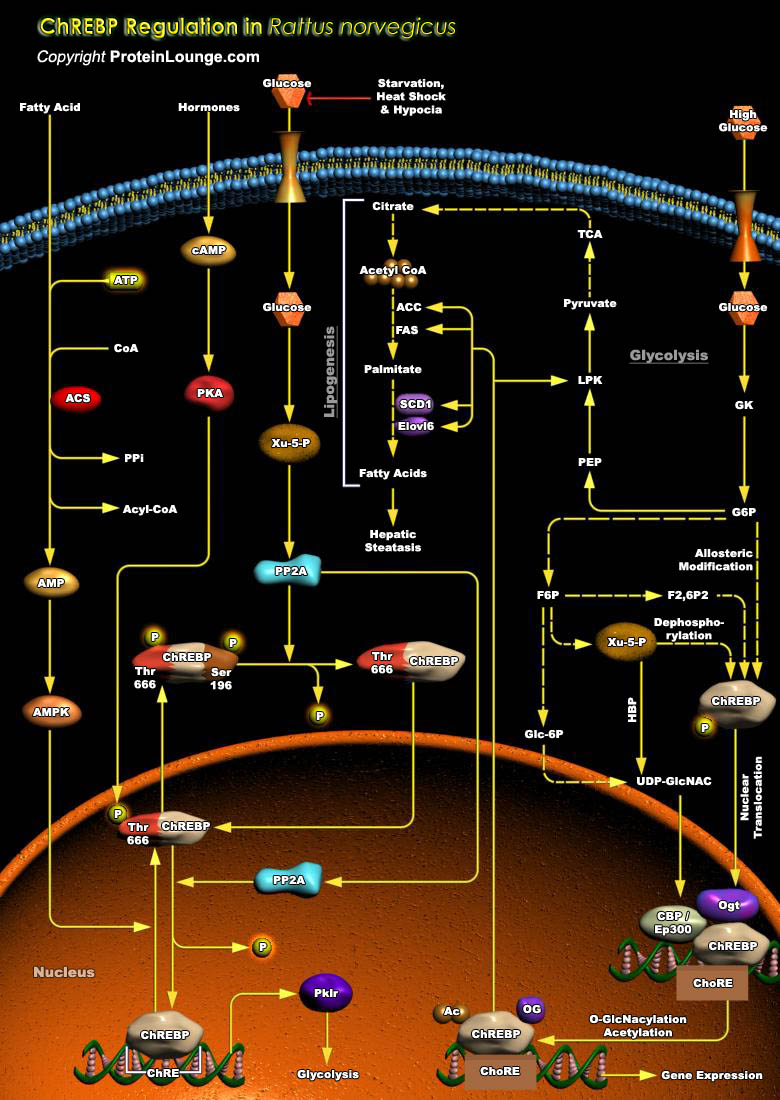
The liver is the major organ responsible for the conversion of excess dietary carbohydrate into triglycerides. Ins (Insulin) and Glucagon (a pancreatic hormone) play critical roles in homeostatsis of Glucose and triglycerides in humans as well as in R. norvegicus (Rattus norvegicus). Glucose serves as a signal independent of hormones in activation of more than 15 enzyme genes in the lipogenic[..]
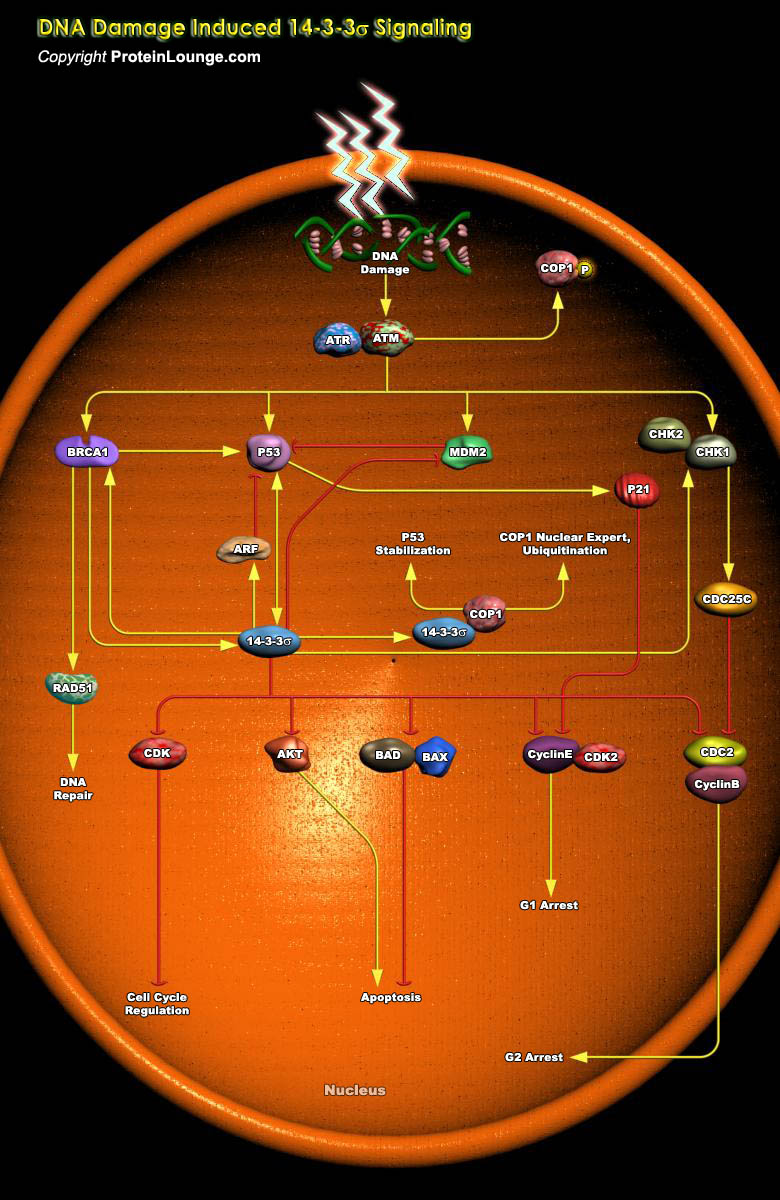
DNA damage checkpoints are critical for preventing tumorigenesis and regulating the response of cells to genotoxic agents. When cells are exposed to DNA damaging agents, they respond by undergoing cell cycle arrest or programmed cell death. 14-3-3 proteins play particularly important roles in coordinating progression of cells through the cell cycle, regulating their response to DNA damage, and[..]