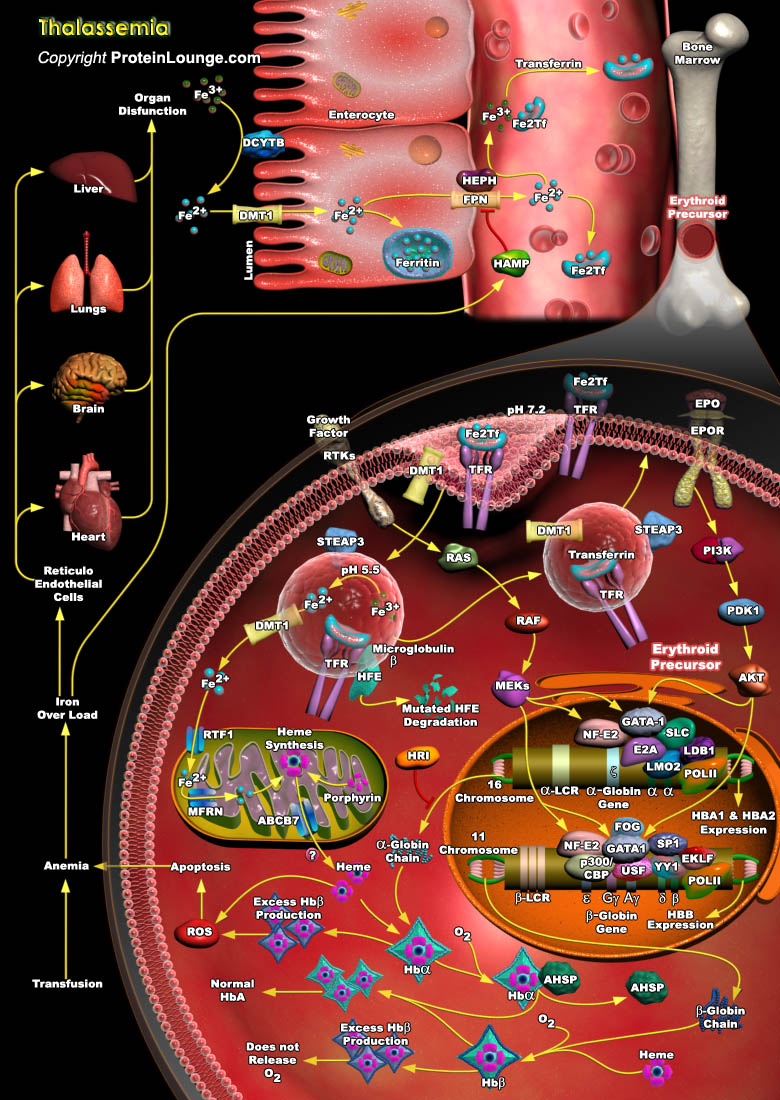
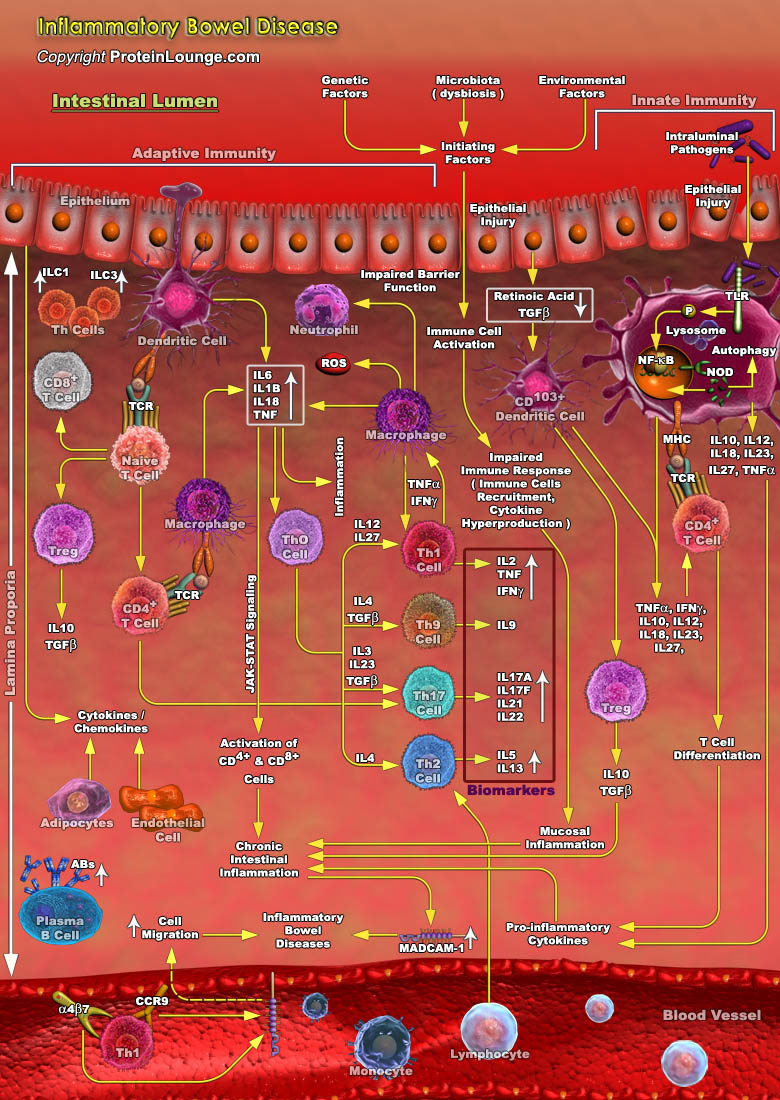
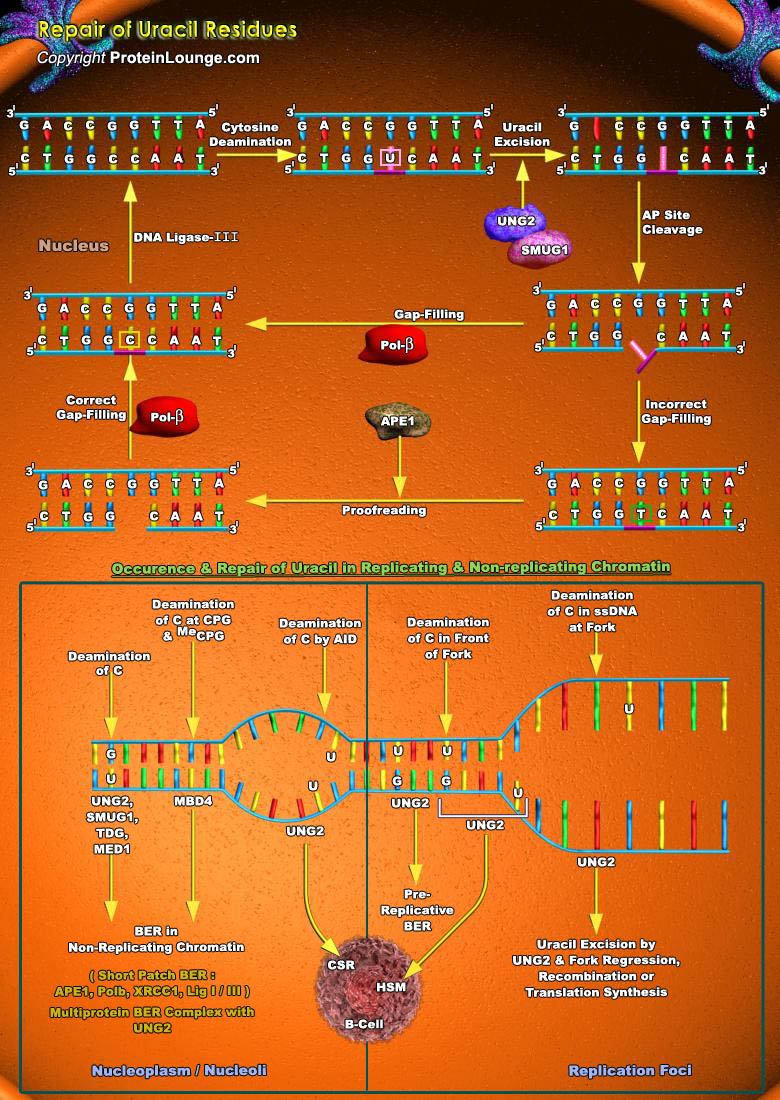
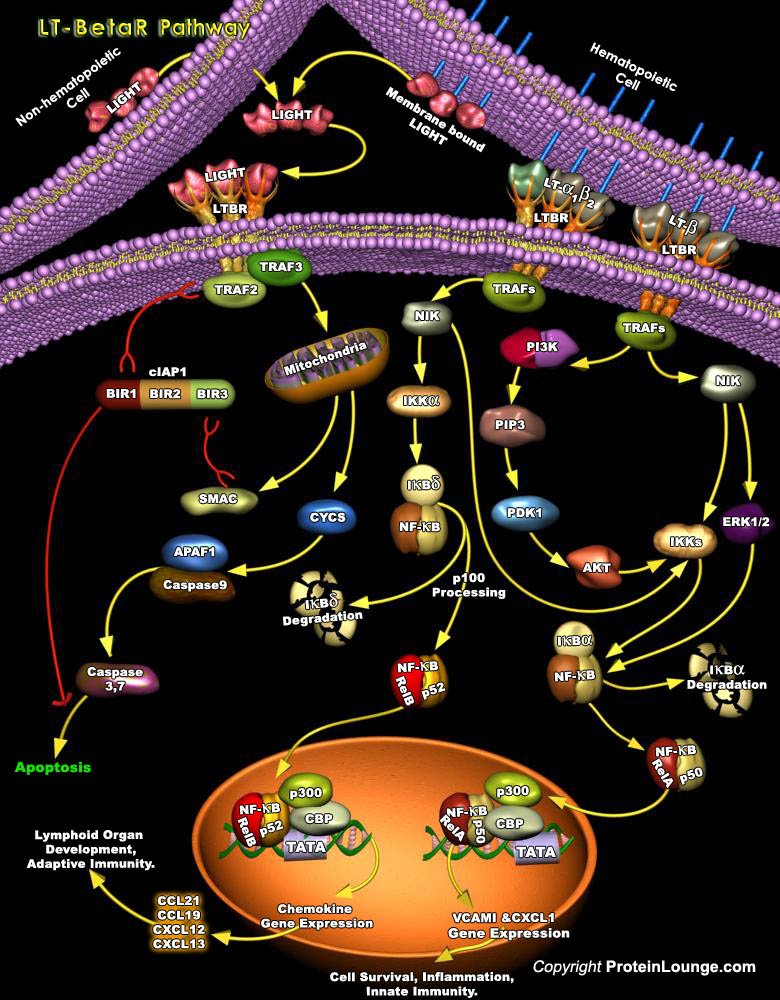
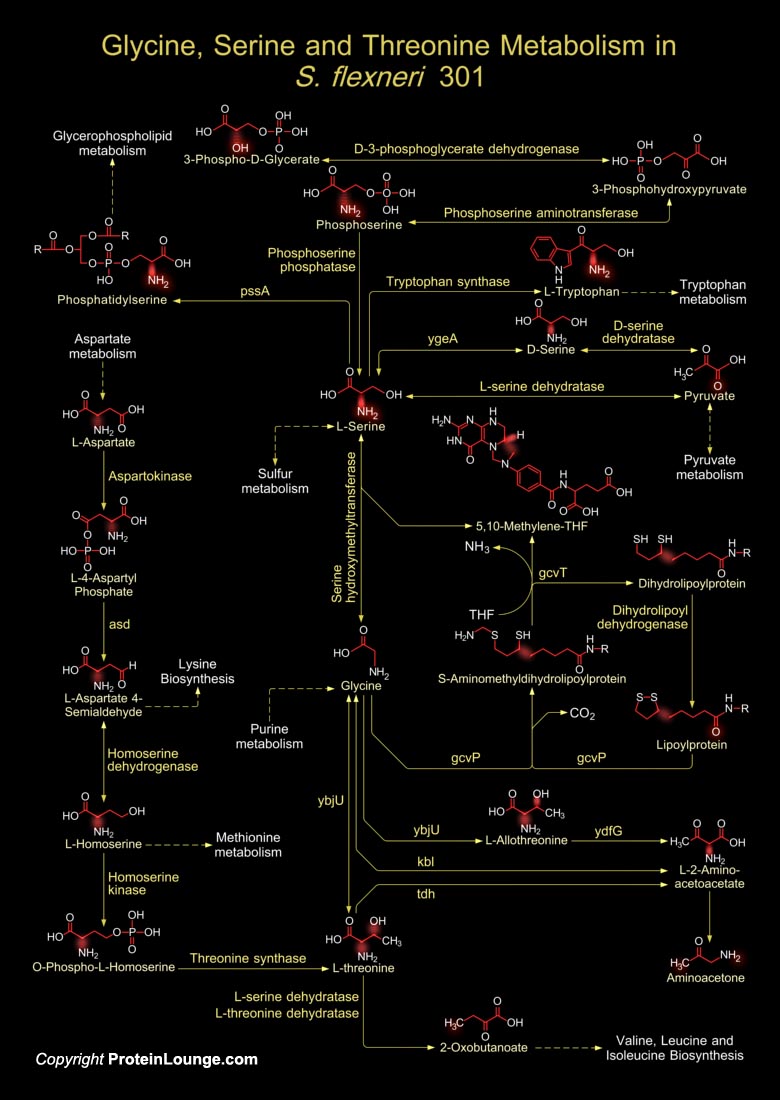
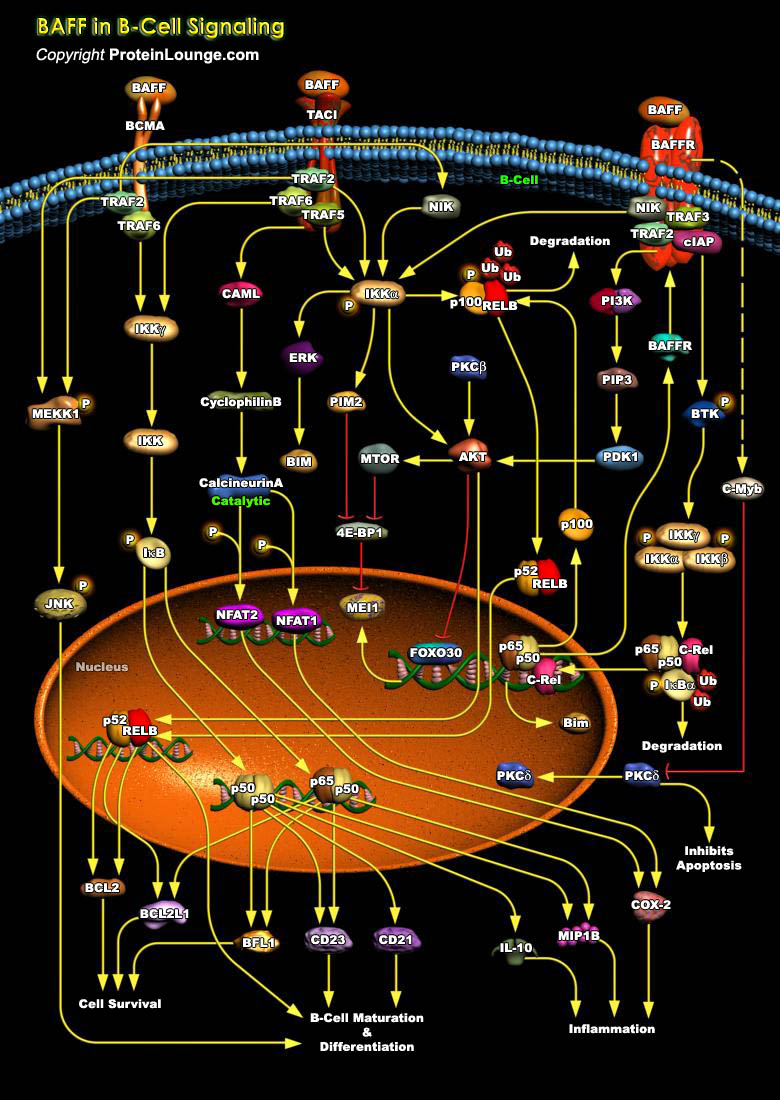
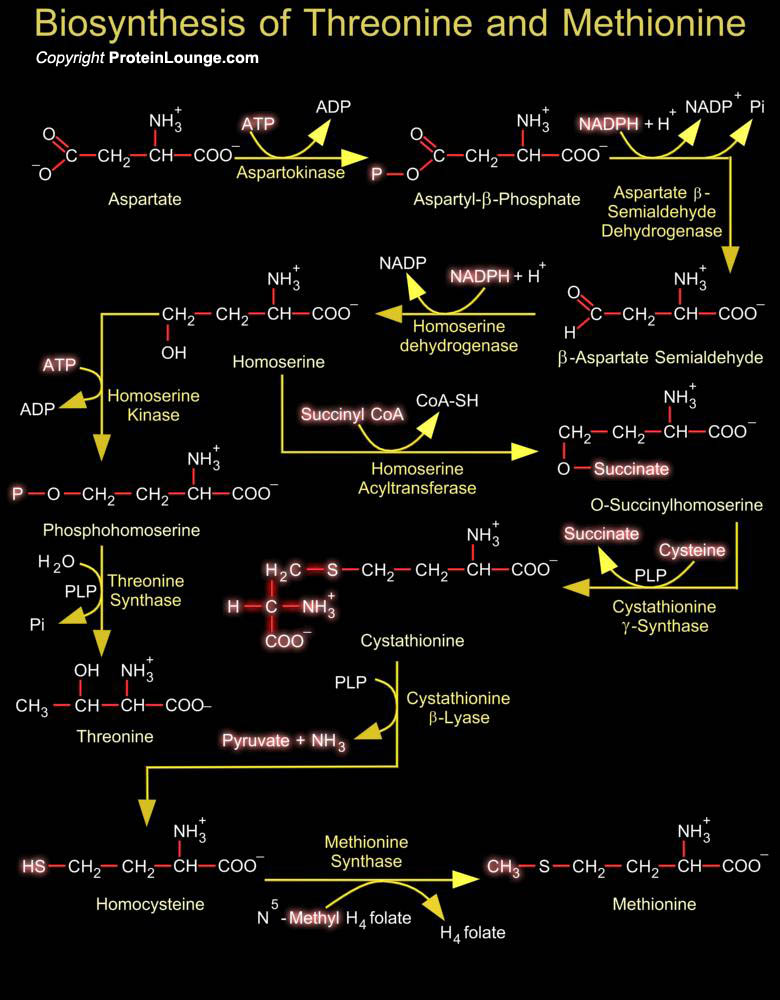
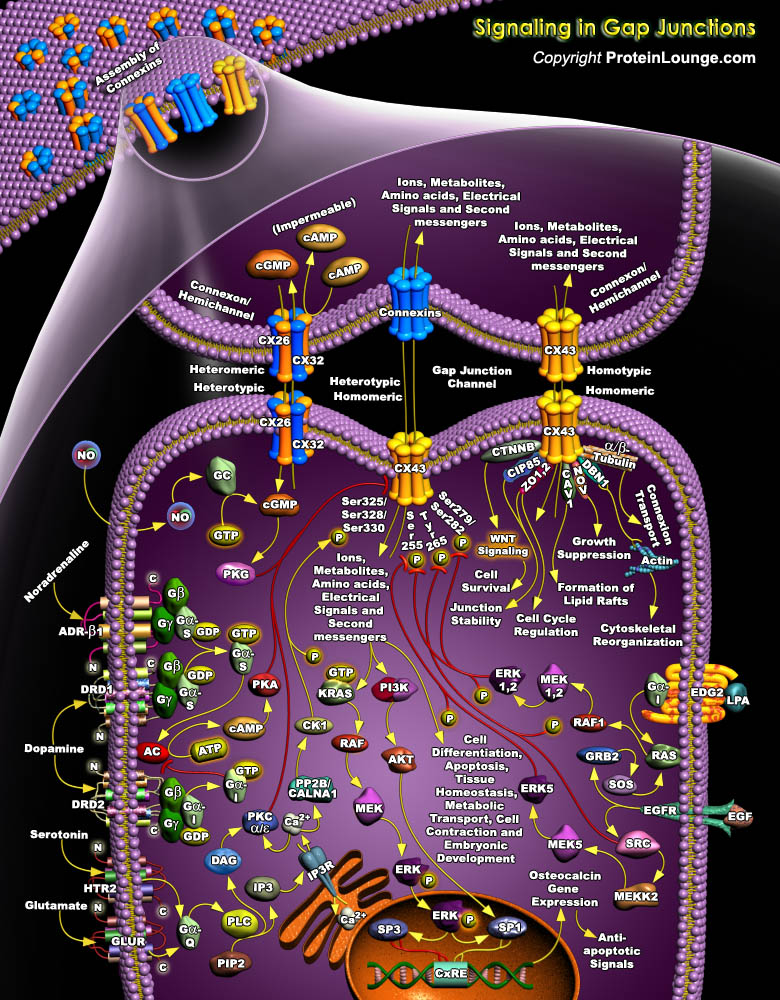
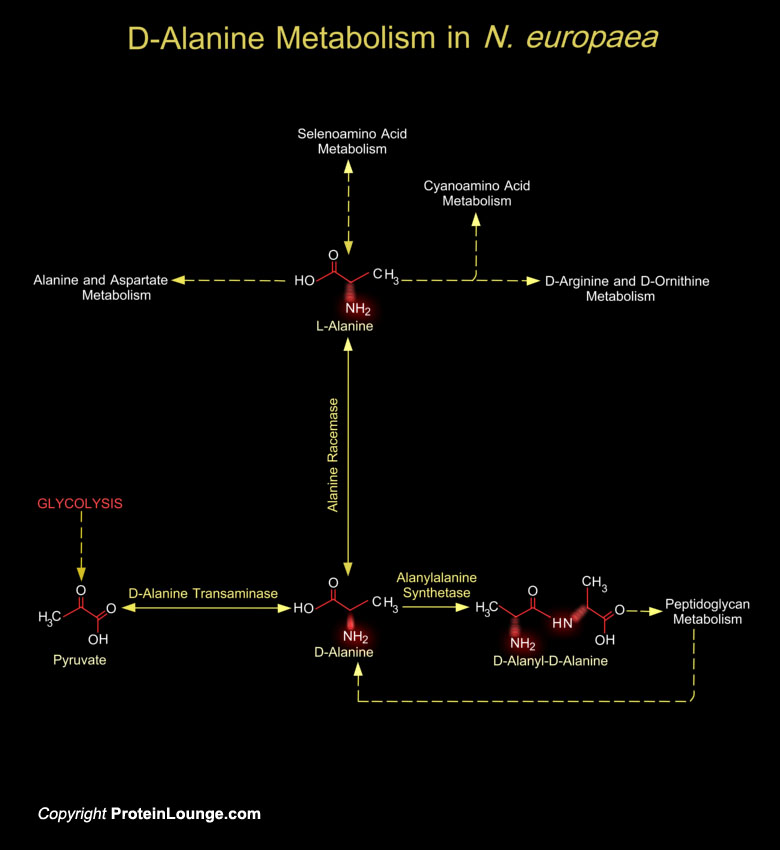
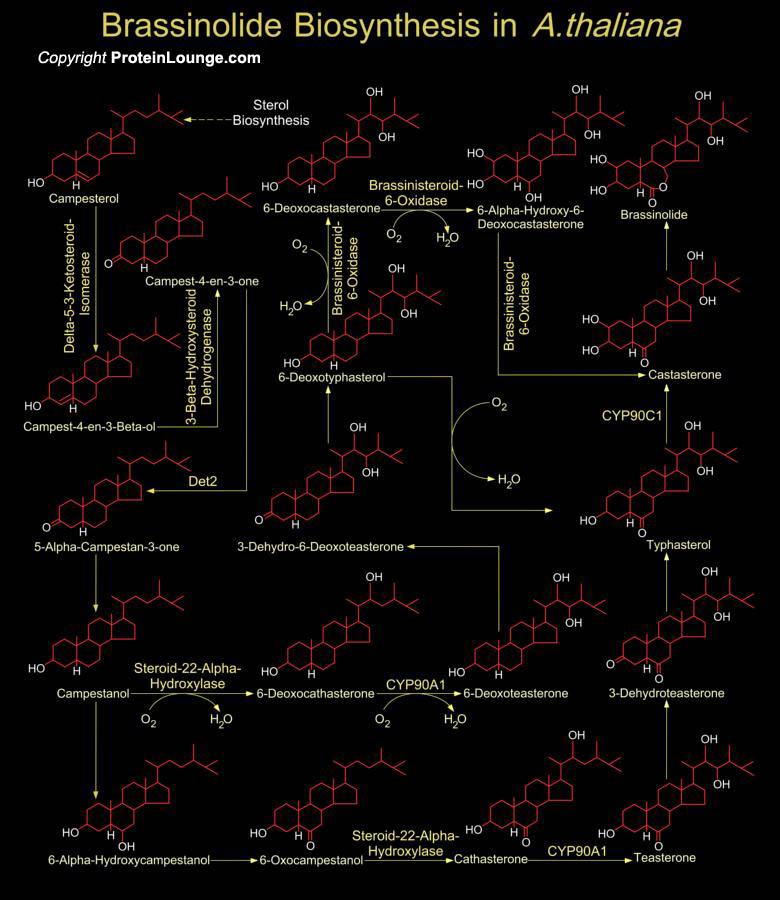
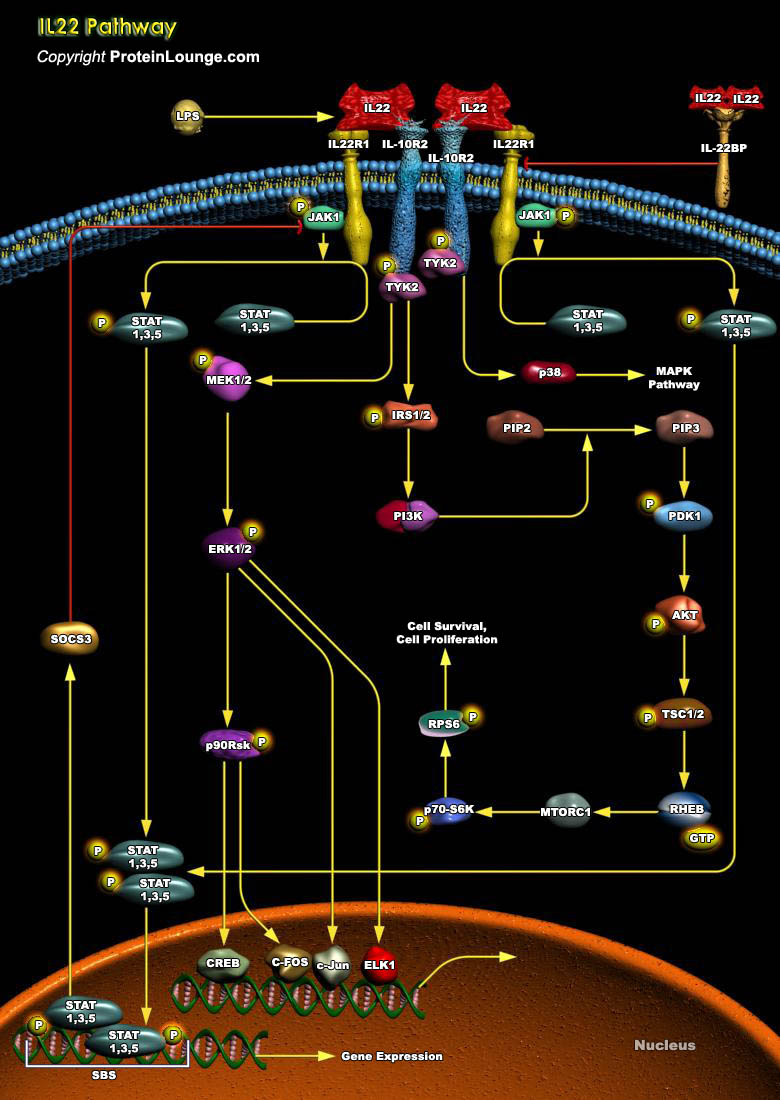
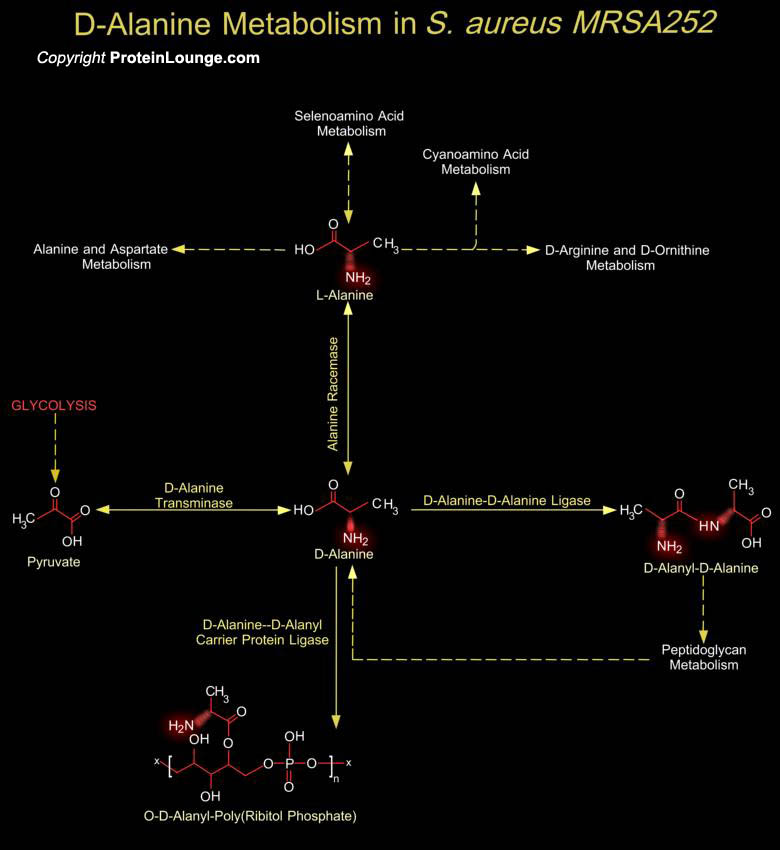
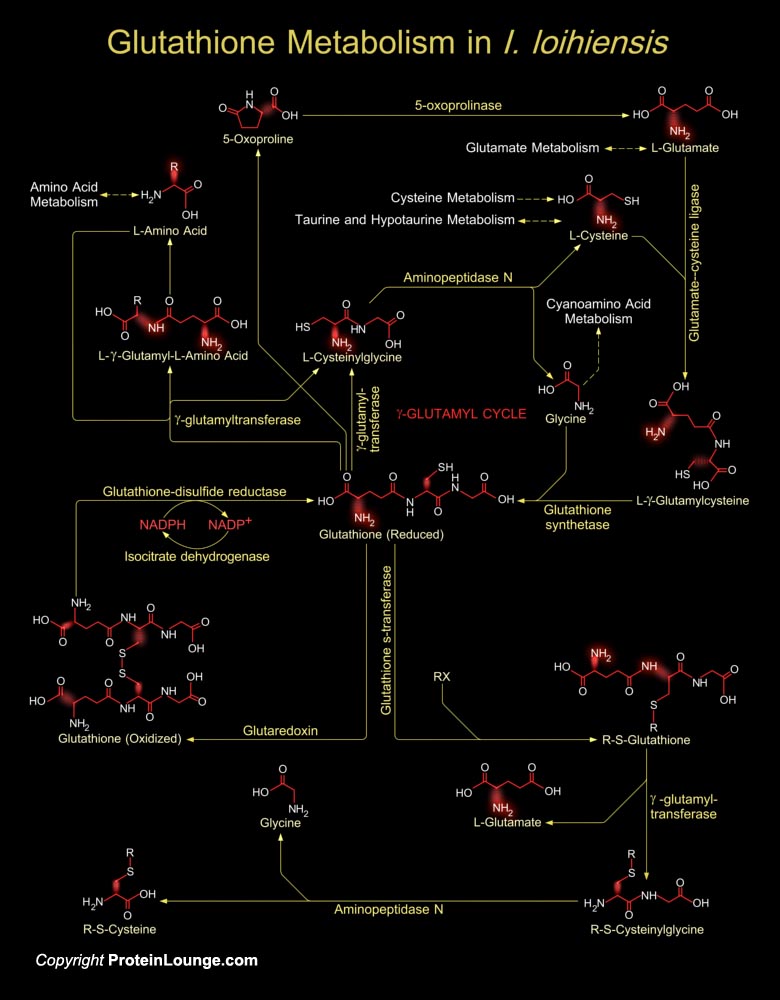
Featured Pathways
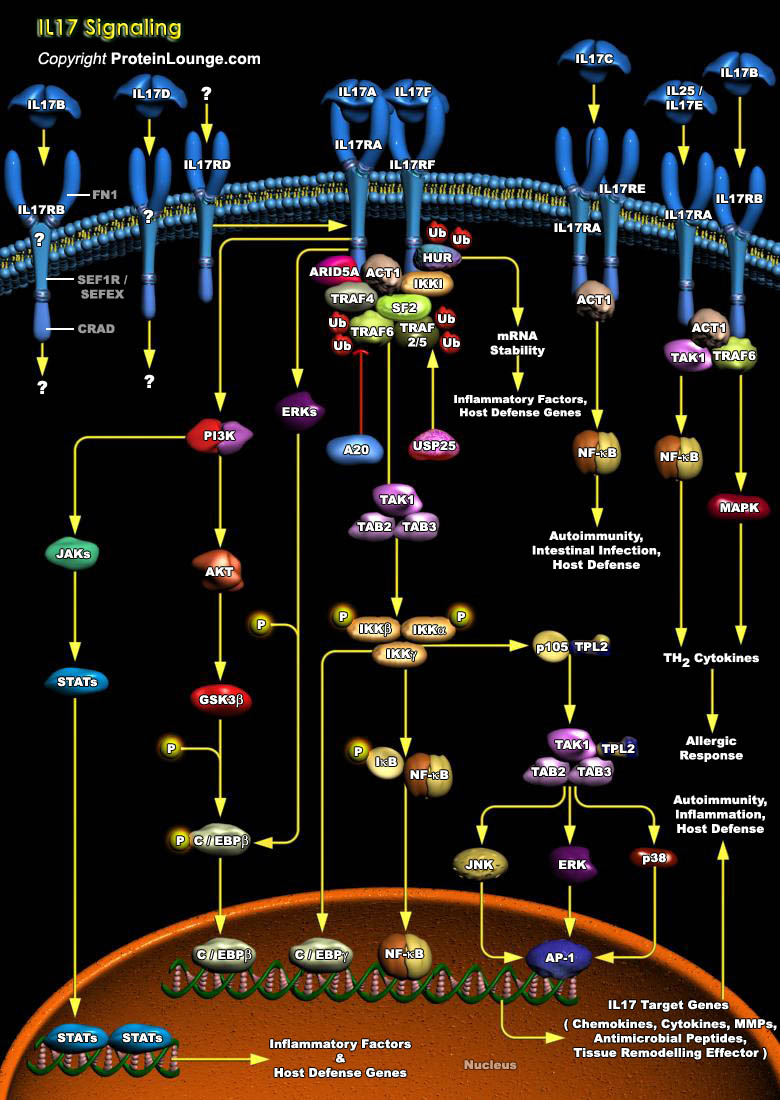
Cytokines are key messenger molecules in cell-to-cell communication and are involved in various aspects of the immune system such as maintaining homeostasis and mediating and resolving pathologic conditions. IL-17 (Interleukin-17) family is a group of cytokines sharing homology in amino acid sequences with highly conserved cysteine residues critical to their 3-dimensional shape. IL-17, the[..]
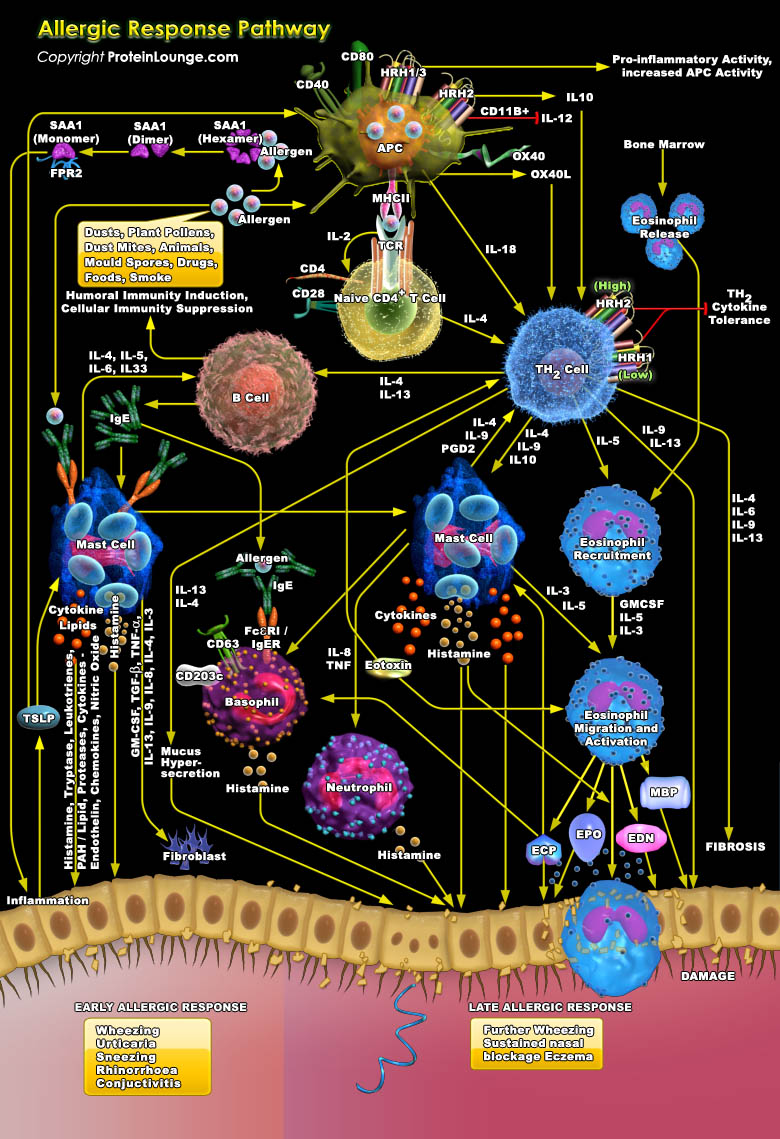
Atopy or Allergic disease is a complex familial disorder with multiple manifestations, including allergic asthma, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, and dermatitis. Allergens are derived from different sources such as cockroaches, ragweed pollens, and house dust mites. The primary immune cell lineages involved in the initiation and progression of allergic inflammation include DCs (Dendritic Cells),[..]
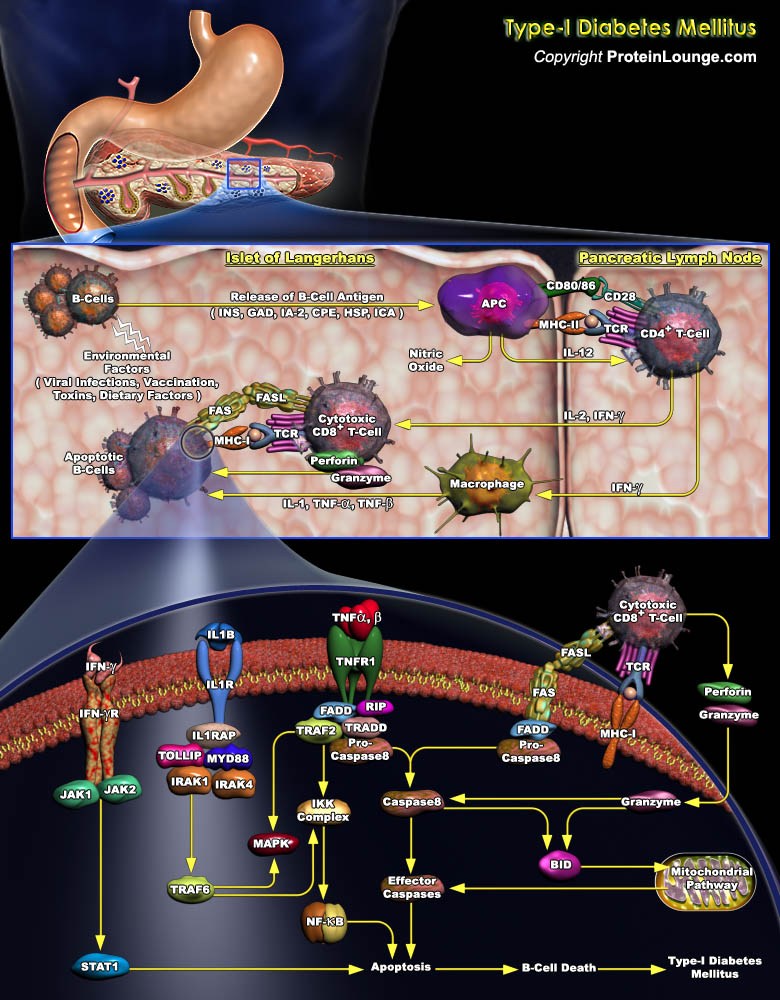
Type 1 diabetes, formerly termed IDDM (Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus), is a chronic organ-specific autoimmune disorder caused by proinflammatory autoreactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, which mediate progressive and selective damage of insulin producing pancreatic beta-cells. The reduction of beta-cell mass leads to a lack of insulin and thereby loss of blood glucose control. To date, it has[..]
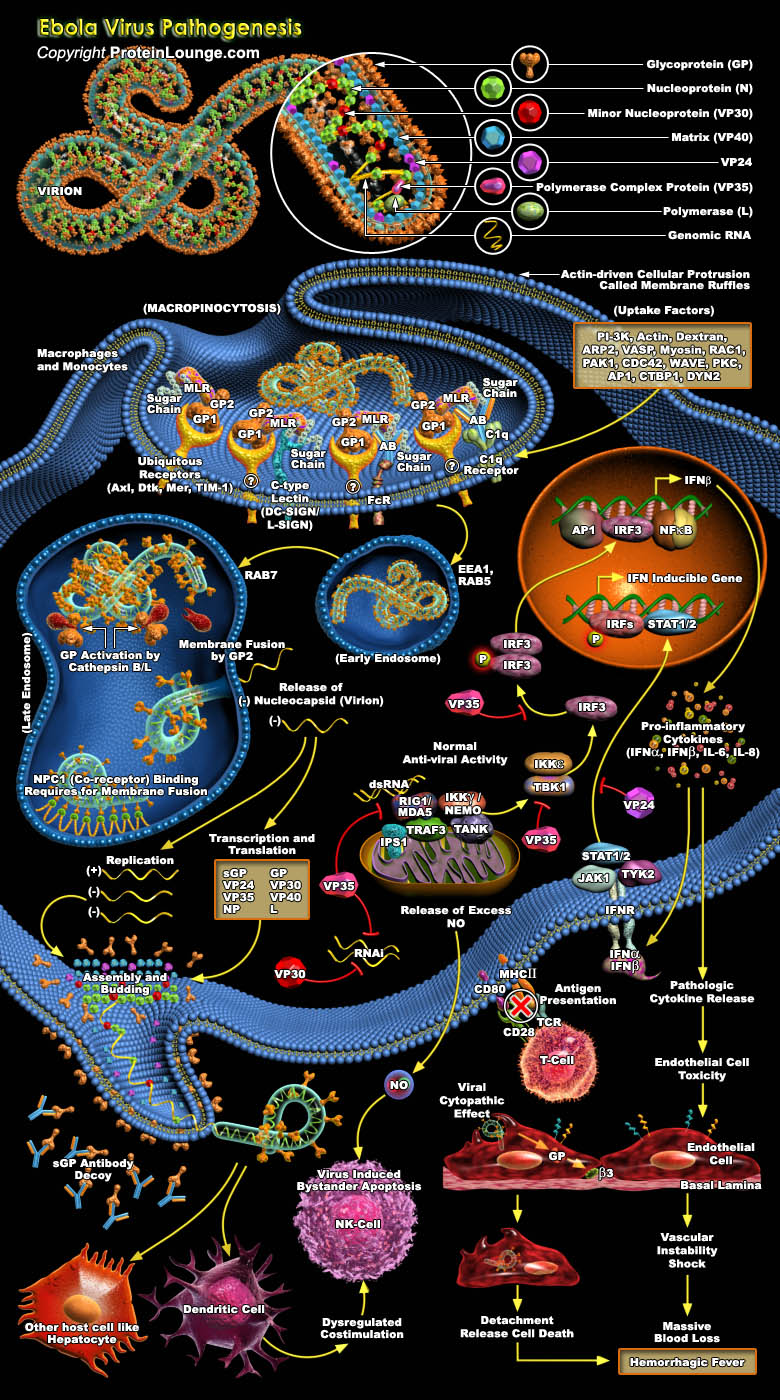
Ebola virus is an aggressive pathogen that causes a highly lethal hemorrhagic fever syndrome in humans and nonhuman primates. Typically, Ebola virus infection runs its course within 14 to 21 days. Infection initially presents with nonspecific flu-like symptoms such as fever, myalgia, and malaise. As the infection progresses, patients exhibit severe bleeding and coagulation abnormalities,[..]
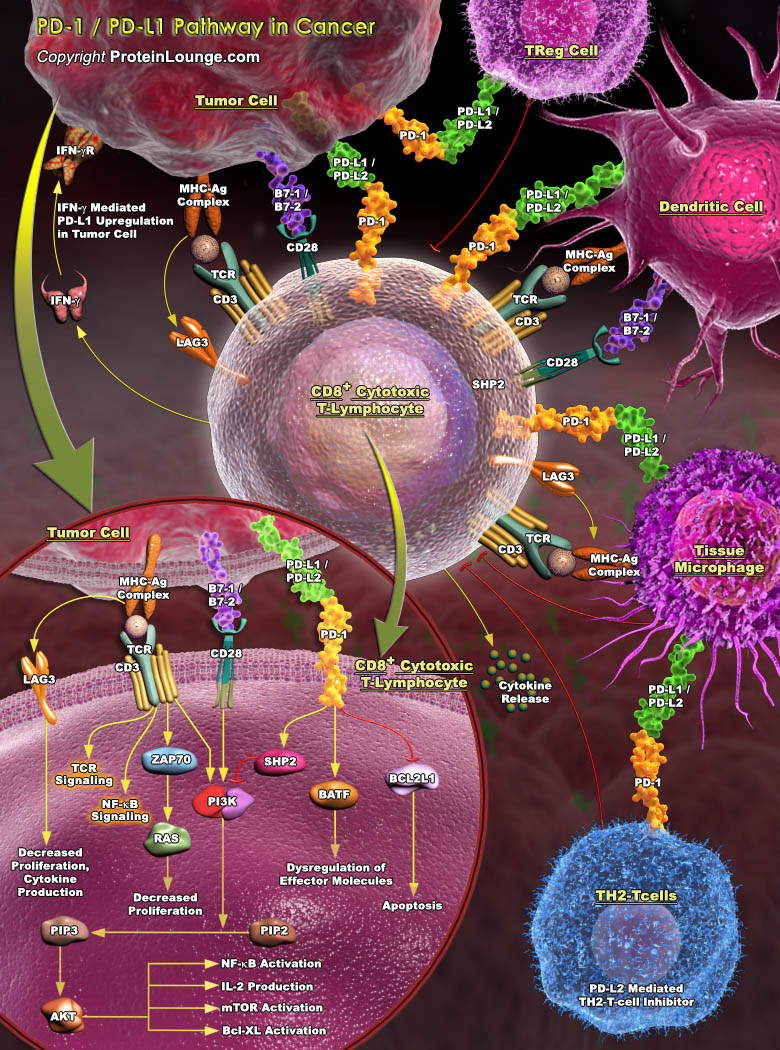
Immune checkpoints refer to a plethora of inhibitory pathways hardwired into the immune system that are crucial for maintaining self-tolerance and limiting collateral tissue damage during anti-microbial immune responses. Checkpoint molecules include Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Antigen-4 (CTLA-4), Programmed Death-1 (PD-1), Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3 (LAG-3), and T-cell immunoglobulin and Mucin[..]
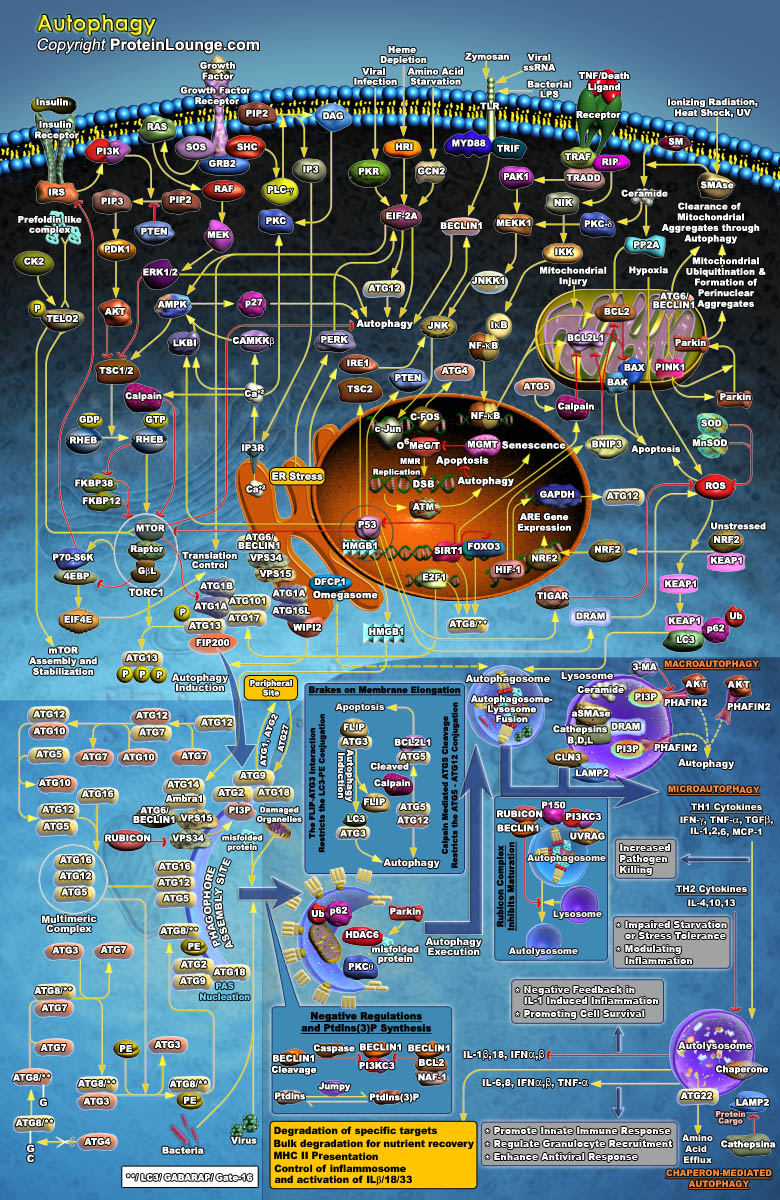
Autophagy is a process of self-degradation of cellular components in which double-membrane autophagosomes sequester organelles or portions of cytosol and fuse with lysosomes or vacuoles for breakdown by resident hydrolases. It also plays a housekeeping role in removing misfolded or aggregated proteins, clearing damaged organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum and peroxisomes, as[..]
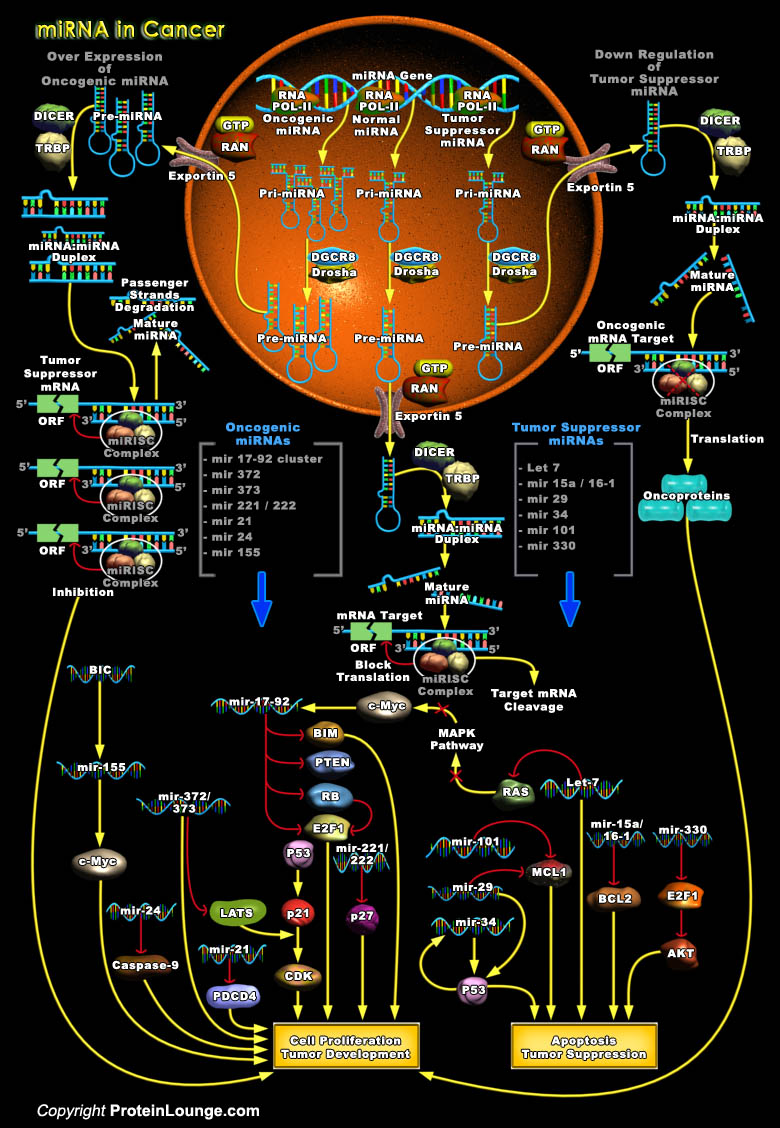
Over the last decade, a growing number of non-coding transcripts have been found to have roles in gene regulation and RNA processing. The most well known small non-coding RNAs are the miRNAs/miRs (microRNAs), which have been found to be involved in human tumorigenesis, revealing a new layer in the molecular architecture of cancer. Gene expression studies have shown that hundreds of miRNAs are[..]
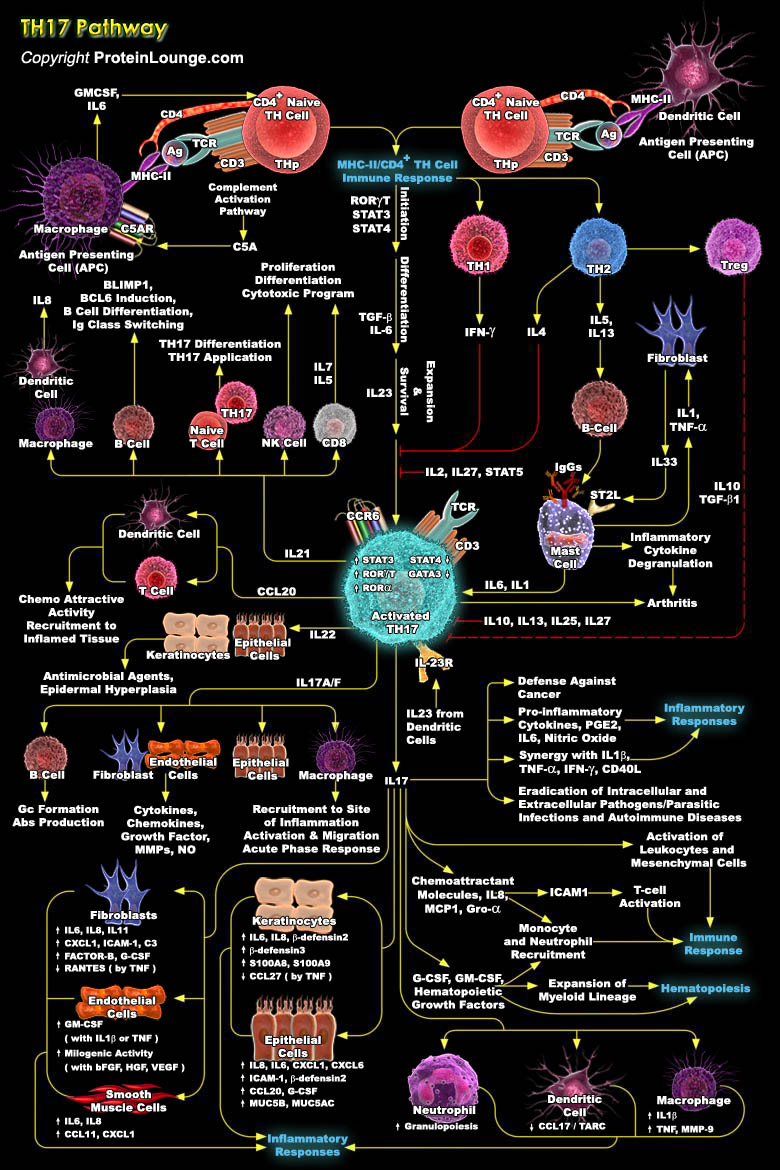
T cells acts as a workhorse for the adaptive immune system, with the job of orchestrating defences against microbial invasion. A subcategory of T cells, T helper cells, defends against microbes, also causes trouble by inducing inflammation in immune-mediated diseases. T helper cells become further specialized, or differentiated, and a type known as TH17 has recently stepped into the limelight.[..]
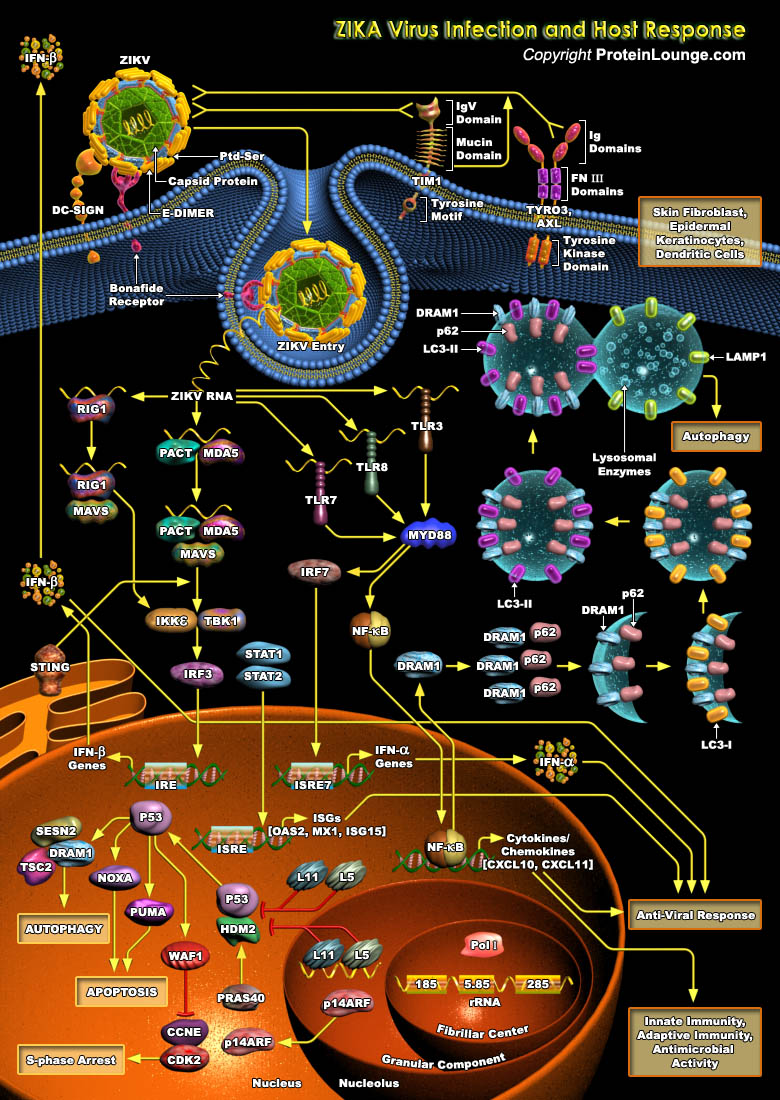
Zika virus (ZIKV) is an emerging arbovirus of the Flaviviridae family, which can cause microcephaly, a birth defect where a baby's head is smaller than usual. Additionally, it is associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome, a neurological disorder that could lead to paralysis and even death. Zika virus illness has been described as self-limited and moderate in severity with the common findings of[..]
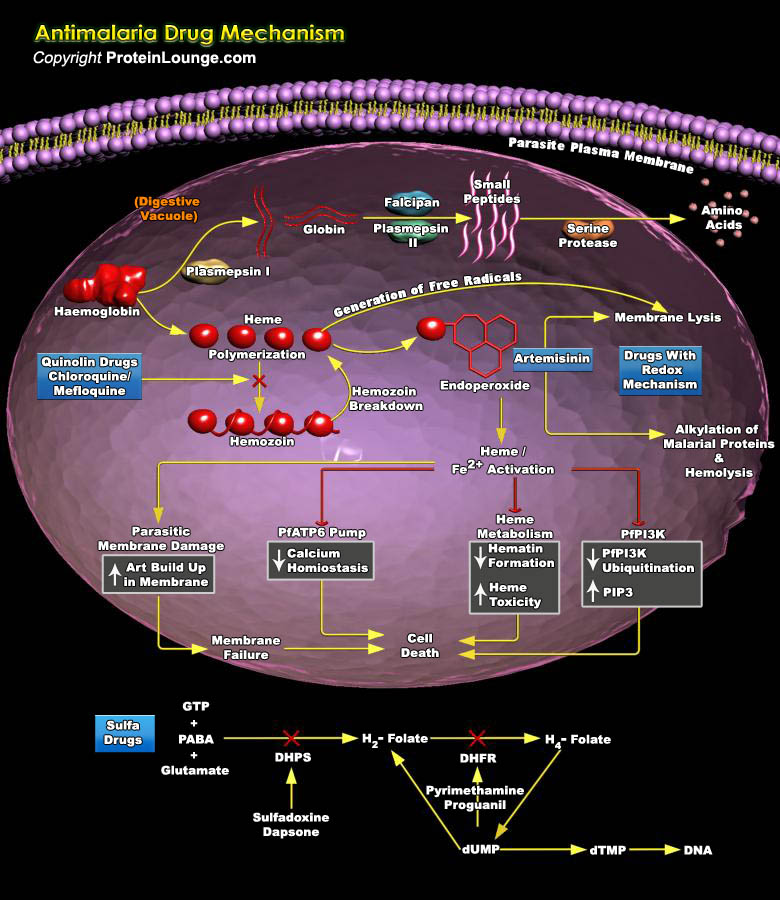
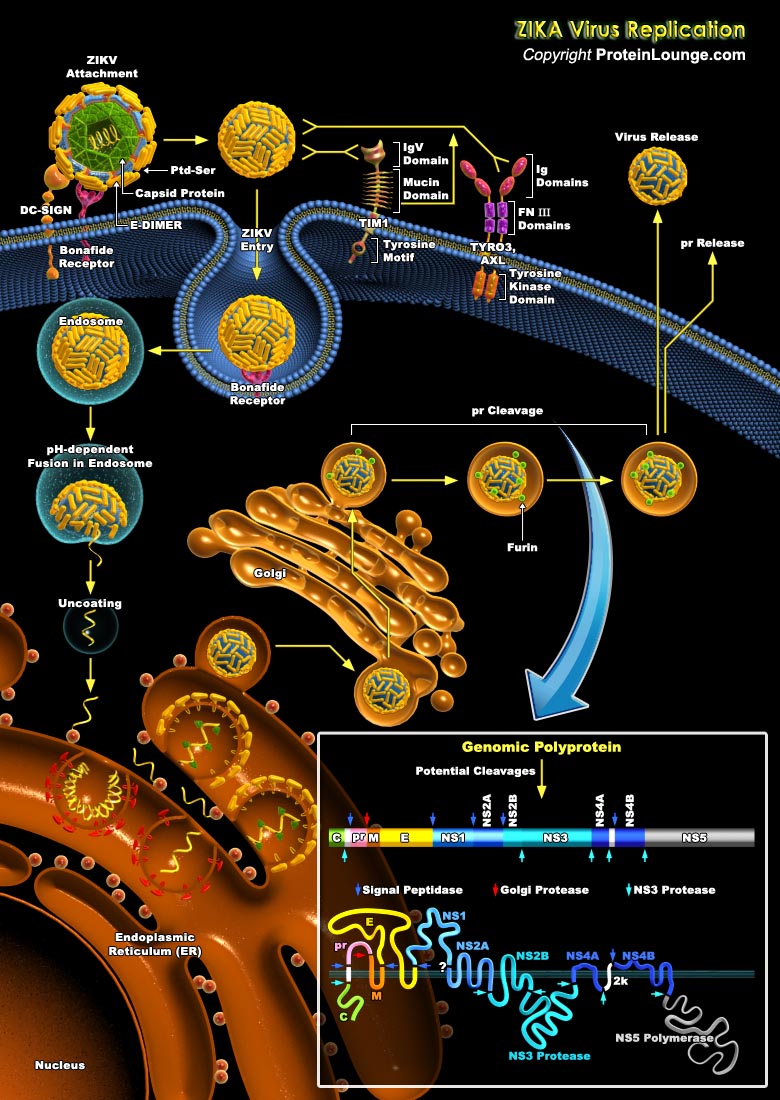
Zika virus (ZIKV) is an arbovirus of the Flaviviridae family, which includes dengue, West Nile, yellow fever, and Japanese encephalitis viruses, that causes a mosquito-borne disease transmitted by the Aedes genus. Zika virus has emerged as a severe health threat by virtue of its fast paced global spread and its associated morbidities, including microcephaly and Guillain-Barre syndrome (Ref.1).[..]