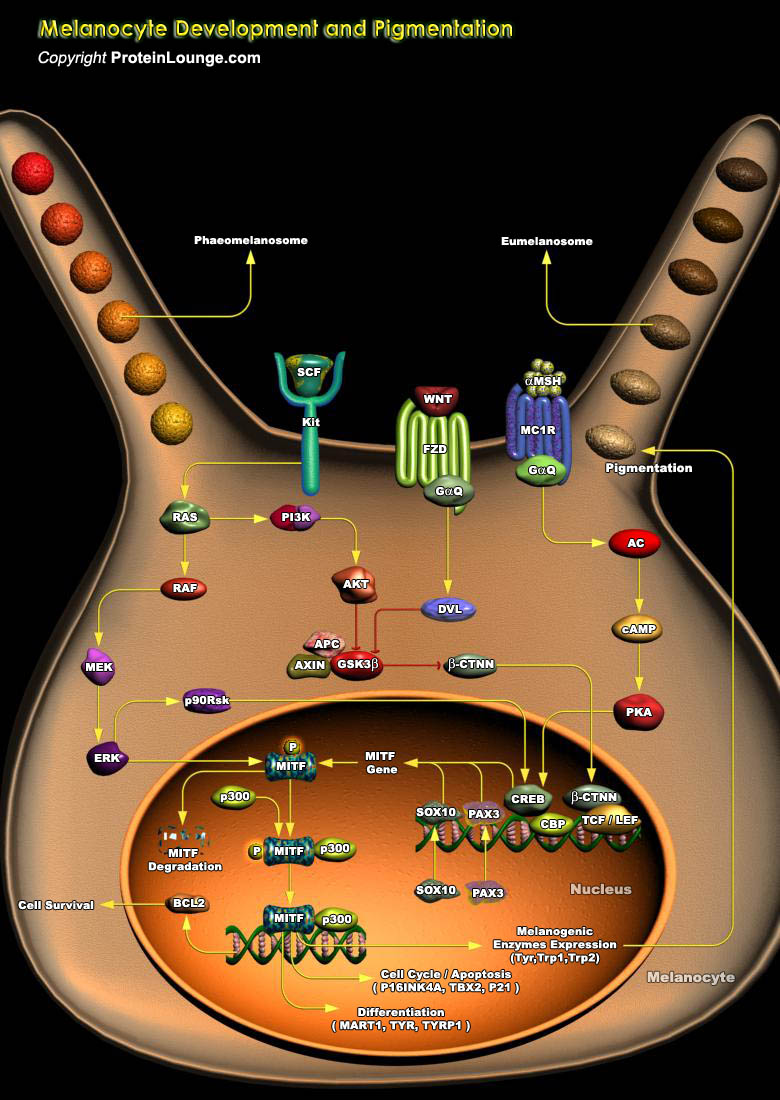
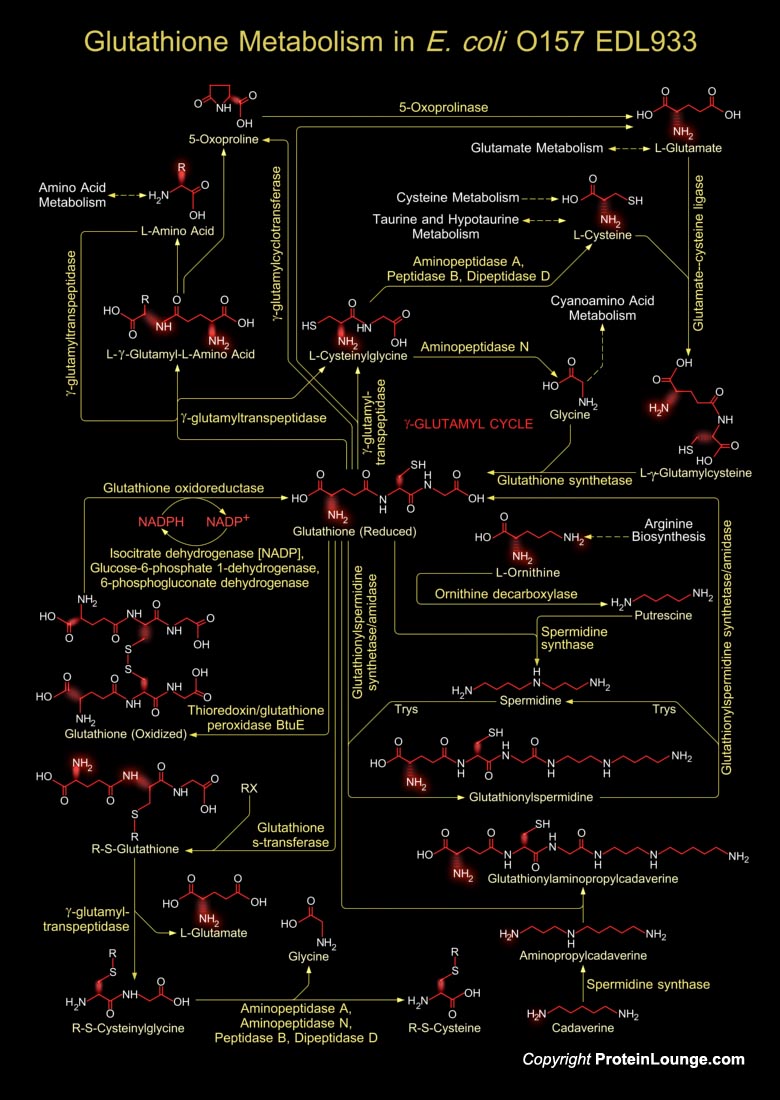
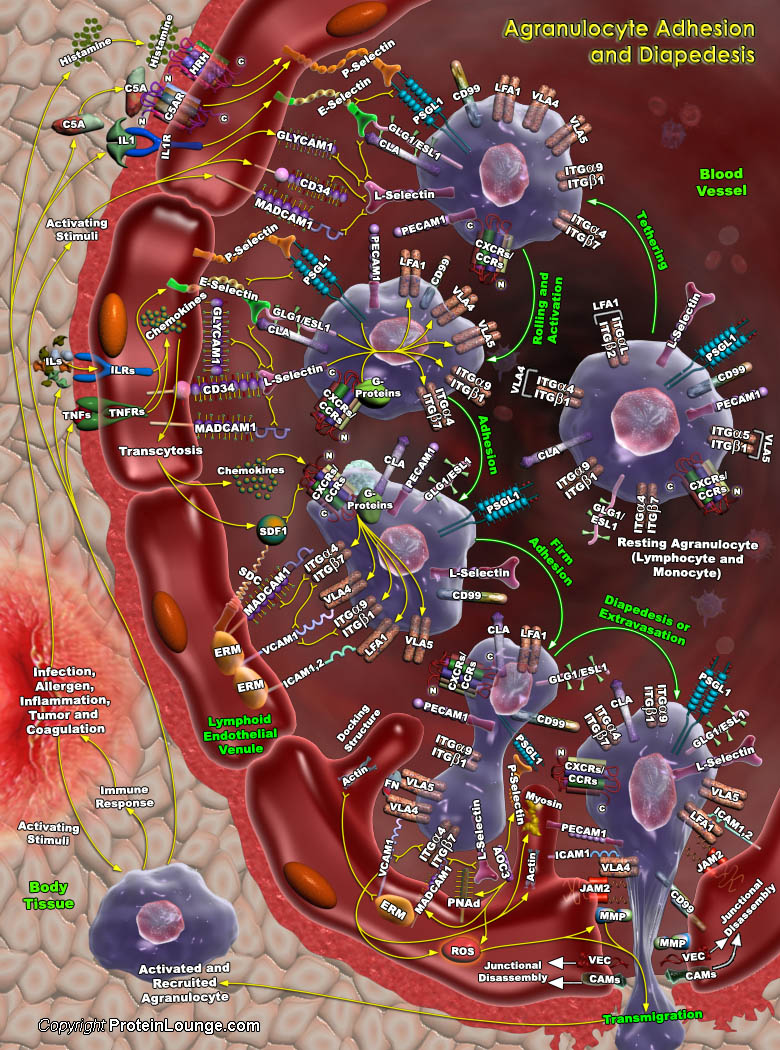
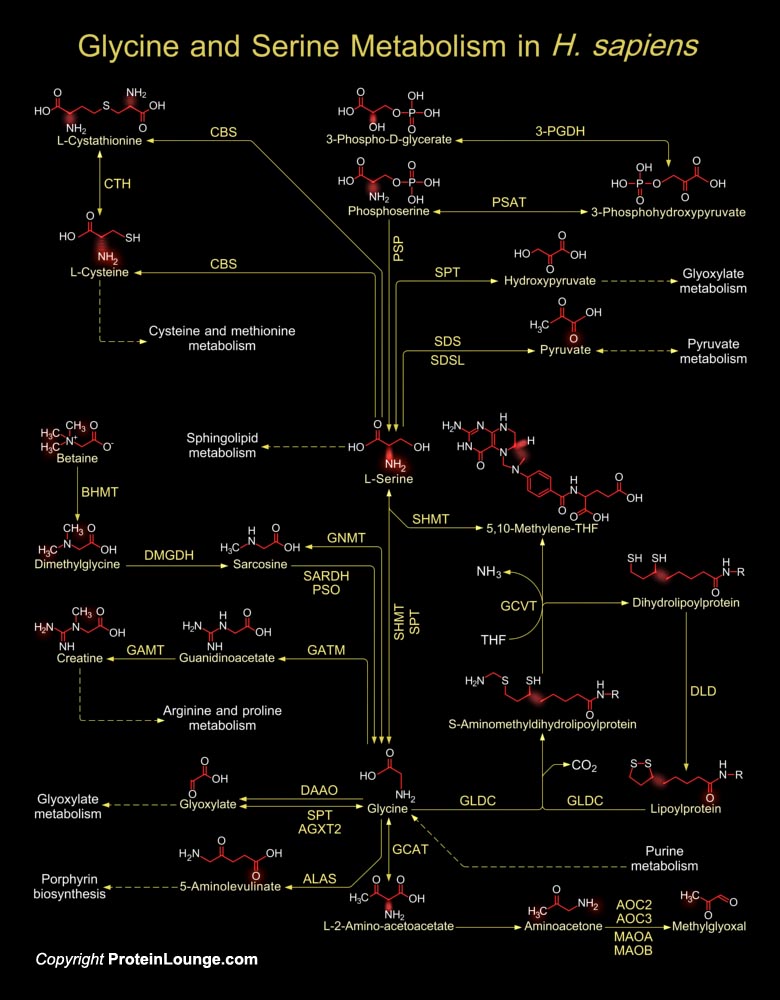
Featured Pathways
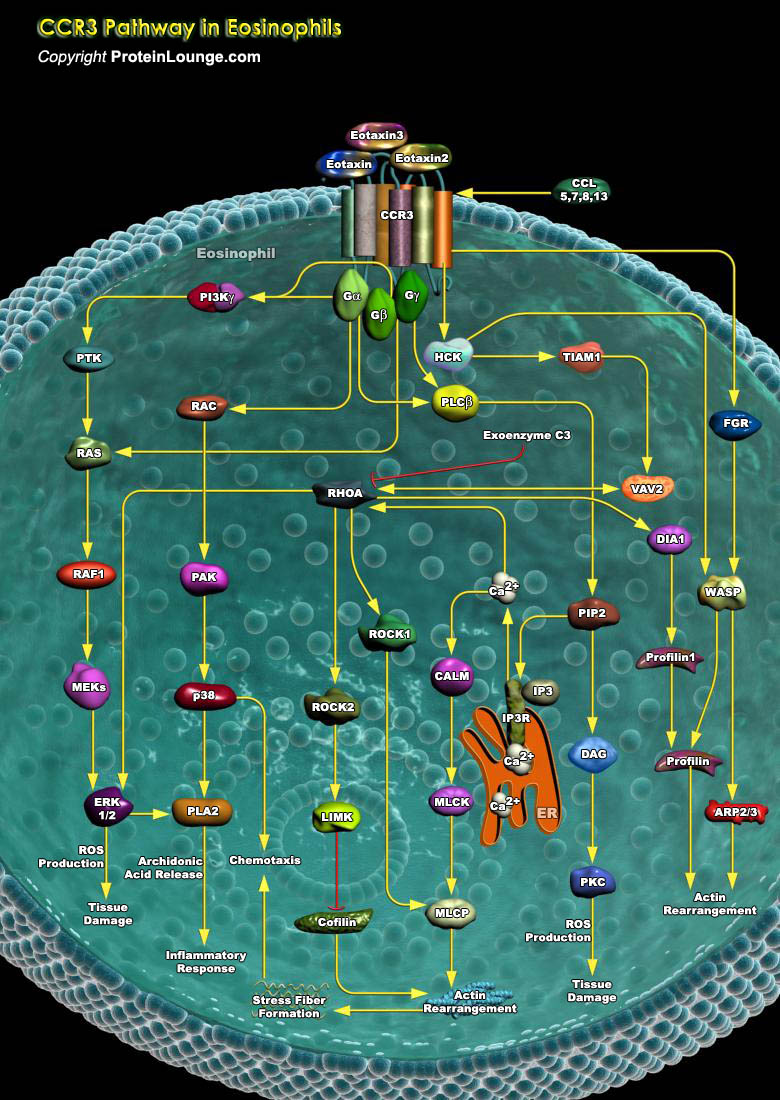
Human eosinophils are crucial effector cells implicated in a number of chronic inflammatory reactions, associated with bronchial asthma, allergic-inflammatory diseases, and parasitic infections.The chemotactic response of eosinophils is mostly mediated by CCR3 (CC Chemokine Receptor-3), a member of the G protein-coupled, seven-transmembrane receptor family, linked to heterotrimeric G-Proteins.[..]
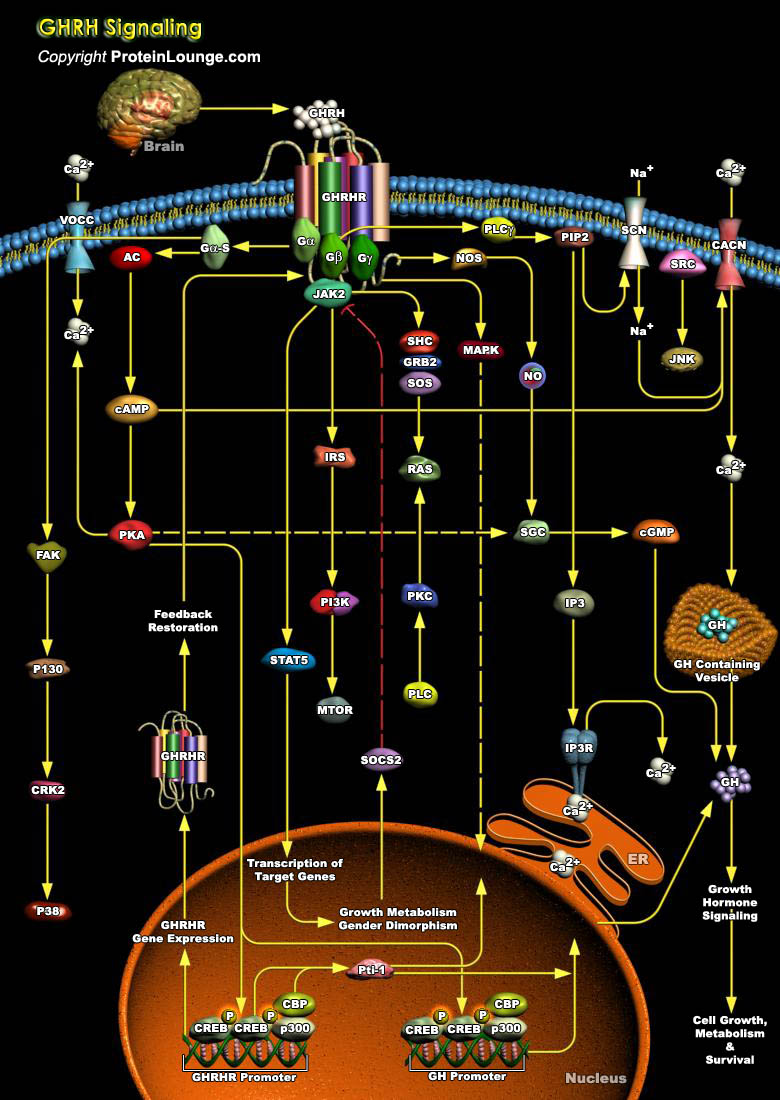
GHRH (Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone) is a hypothalamic hormone that is essential for normal expansion of the somatotrope lineage during pituitary development. GHRH is produced by GHRH cells in the hypothalamus and reaches the adenohypophysis via the portal system. It stimulates the release of GH (Growth Hormone)/Somatotropin from the adenohypophysis. GH is required for normal postnatal growth,[..]

Relaxin is a polypeptide hormone that is secreted by the corpus luteum, into the circulation during the menstrual cycle and throughout pregnancy. During the cycle, it stimulates blood vessel growth in the endometrial lining of the uterus during the midluteal phase; coincident with the temporal window during which embryonic implantation occurs. If conception occurs,[..]
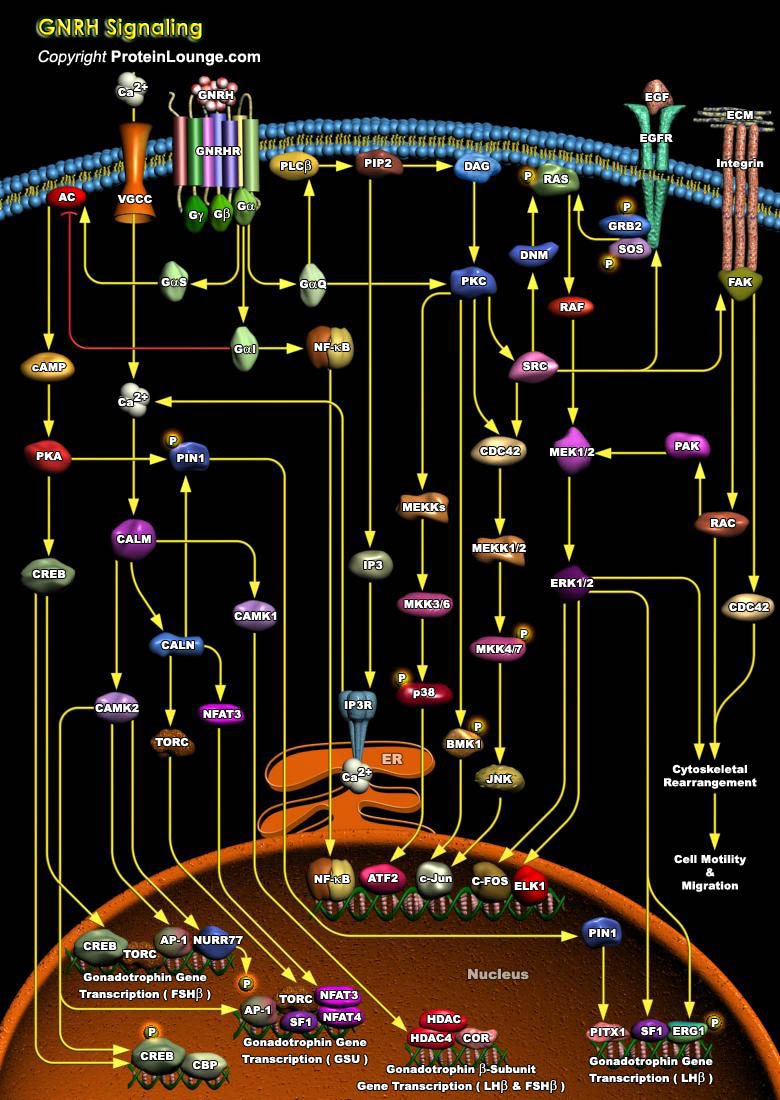
Normal mammalian sexual maturation and reproductive functions require the integration and precise coordination of hormones at the hypothalamic, pituitary, and gonadal levels. The hypothalamic GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone), also called LHRH (Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone), is a key regulator in this system (the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis), that plays a decisive role[..]
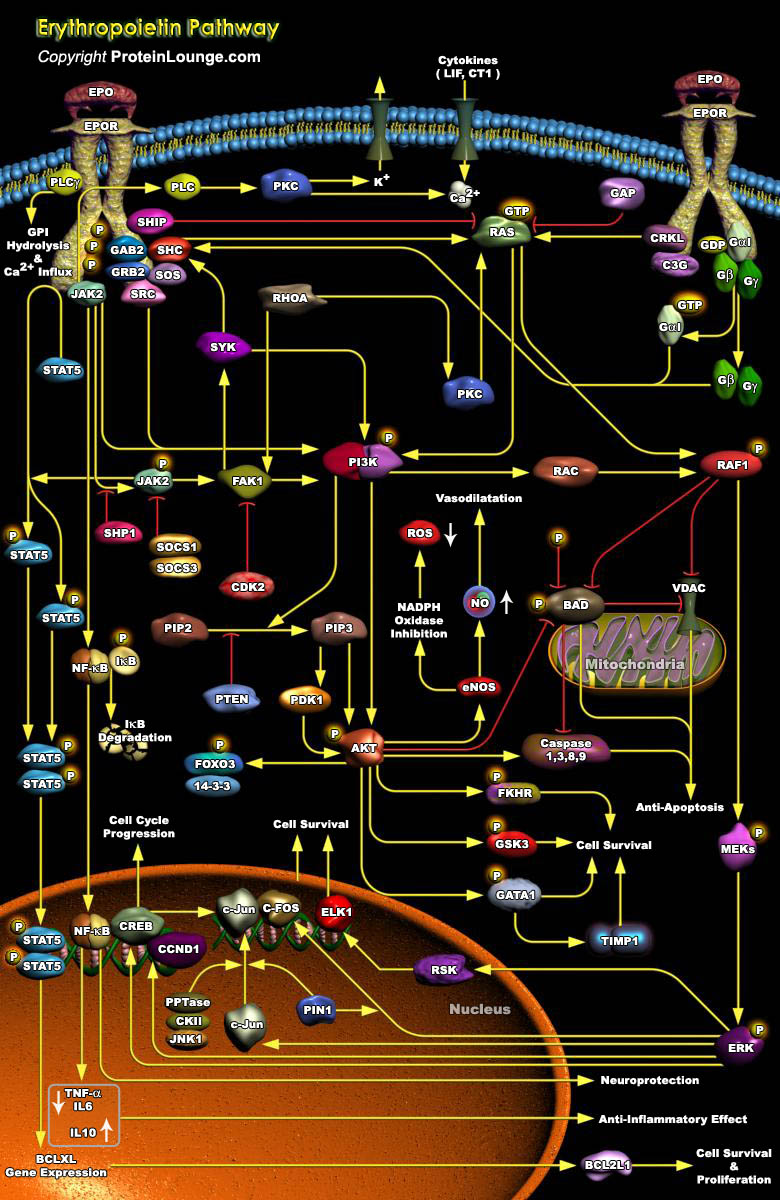
Erythropoiesis is a major pathway for Erythrocyte production, by which pluripotent Hematopoietic Stem Cells give rise to mature end stage cells via a series of differentiations. Epo (Erythropoietin), a glycoprotein hormone and a multifunctional Hematopoietic Cytokine ligand, is the master regulator of Erythropoiesis. As a major function, it monitors the safe passage of the committed[..]
Programmed cell death, a form of altruistic suicide is a genetically controlled means of cellular self-destruction that leads to dismantling and packaging of cell material for removal by phagocytosis. All cells possess the ability to undergo programmed cell death (otherwise known as apoptosis), and the process is essential for normal development to shape organs and tissues as well as to remove[..]
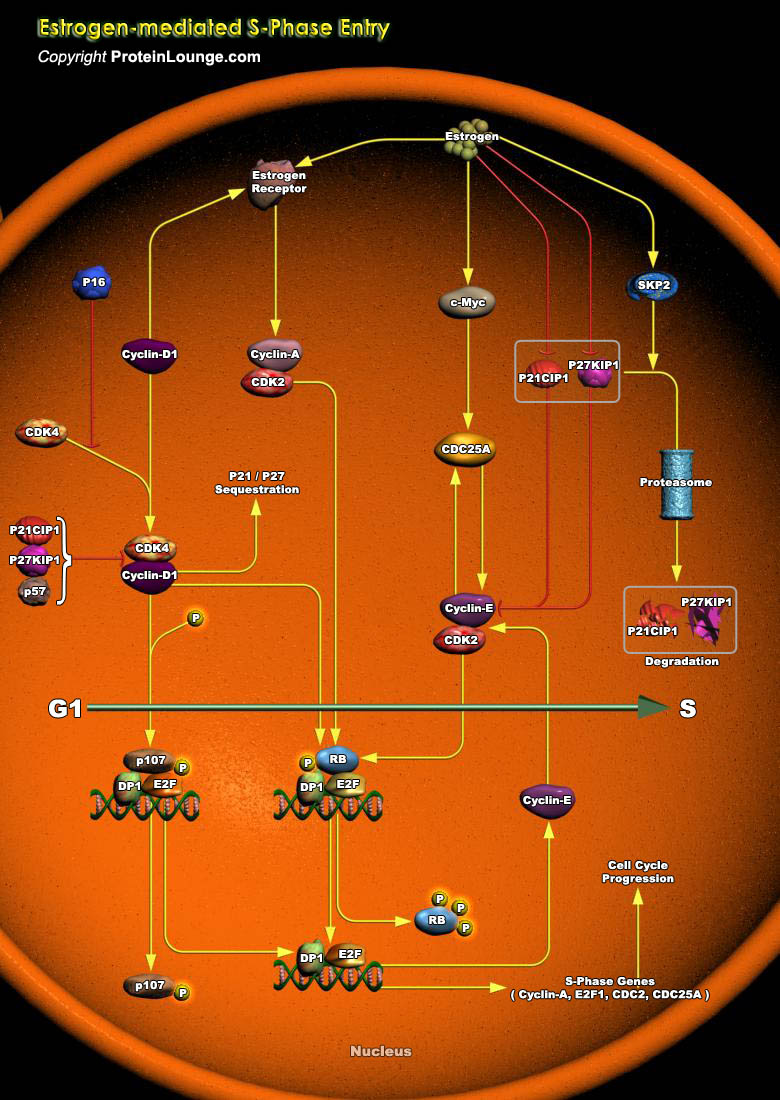
Estrogens are a class of steroid hormones that play a central role in reproduction, and are regarded as the powerful female hormones that make a girl develop into a woman capable of reproduction. Estrogenic steroids, that include: E1 (Estrone), E2 (Estradiol/17-beta Estradiol) and E3 (Estriol), regulate cellular functions in a wide variety of tissues and influence proliferation in the female[..]
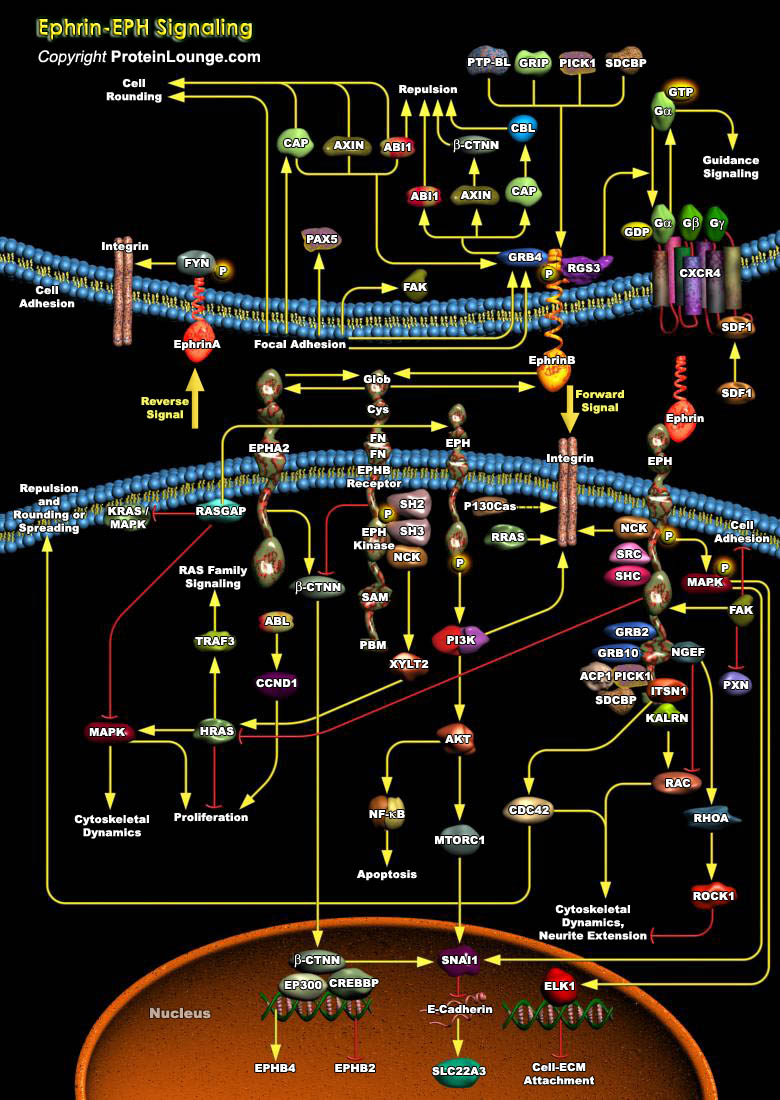
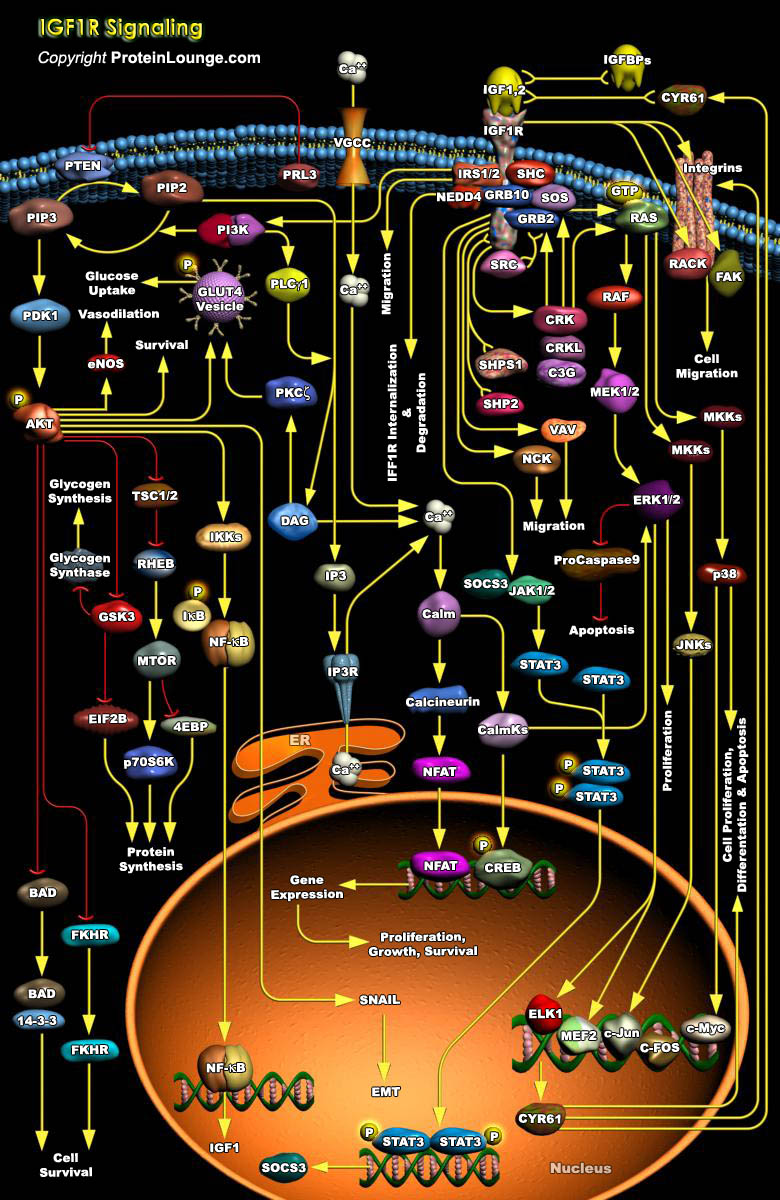
In numerous processes that are vital for the development and maintenance of organism function, cells must communicate crucial information to respond appropriately to the changing environment. As such, RTKs (Receptor Tyrosine Kinases) are transmembrane proteins, which, on receiving an external stimulus, respond by transmitting a signal to the inside of the cell. Of all the RTKs that are found[..]
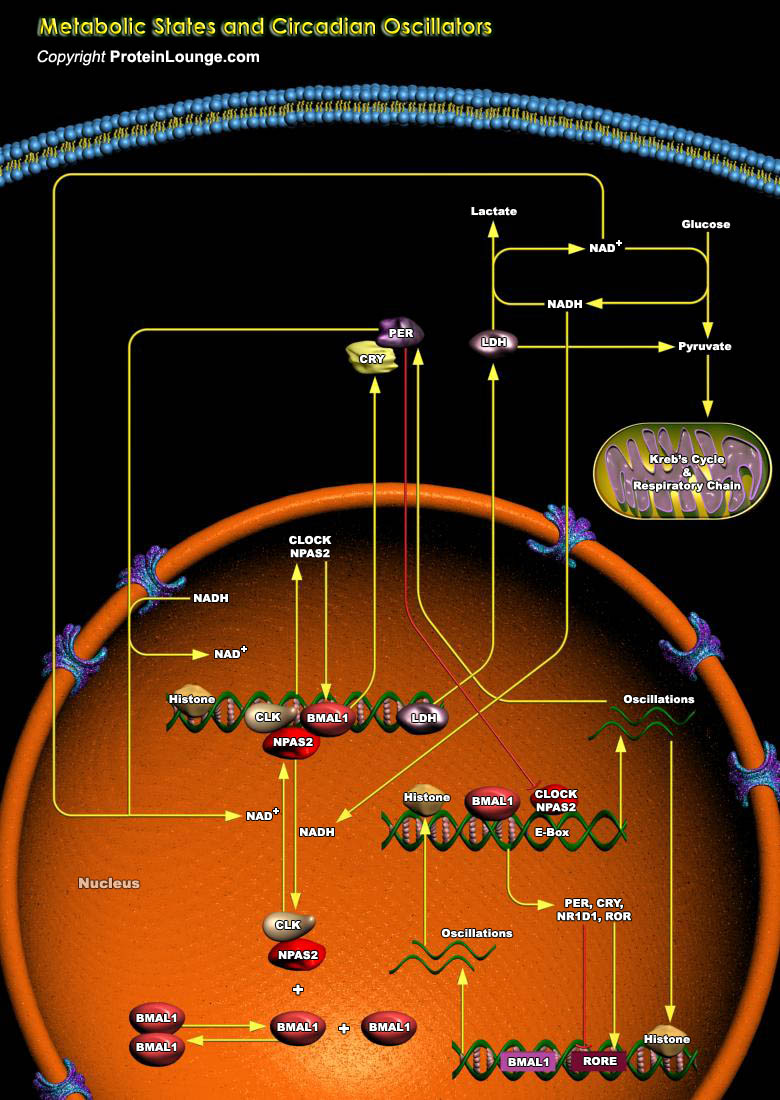
In organisms as diverse as fruit flies and mammals, circadian rhythms are controlled by a transcriptional feedback system whose activity fluctuates as a function of the light-dark cycle. In mammals, the master clock (circadian pacemaker) resides in the SCN (Suprachiasmatic Nucleus) of the brain's hypothalamus and this endogenous clock drives physiology and behavior. In the absence of[..]

The Eph family forms the largest group of RTKs (Receptor Tyrosine Kinases) comprising 14 members in mammals that play critical roles in diverse biological processes during development as well as in the mature animal. They are activated by membrane-bound ligands called Ephrins, which are classified into two subclasses based on their mode of membrane anchorage. The Ephrin-A ligands are GPI[..]