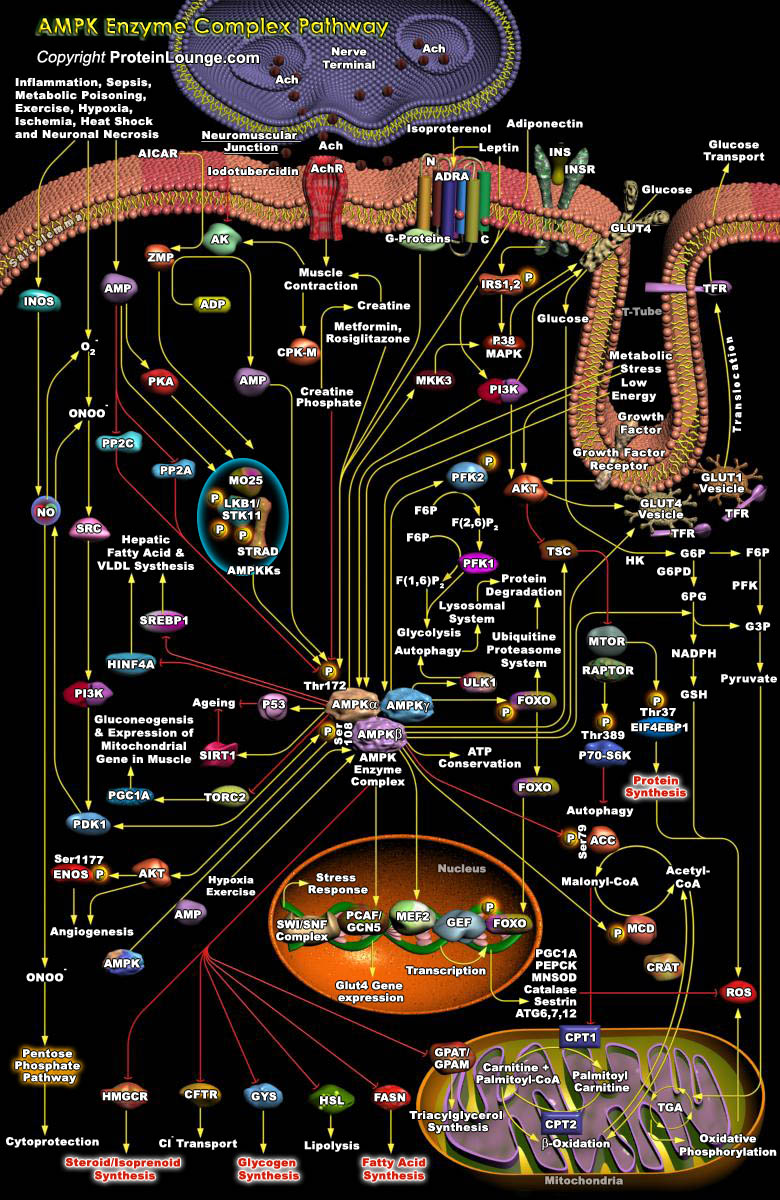
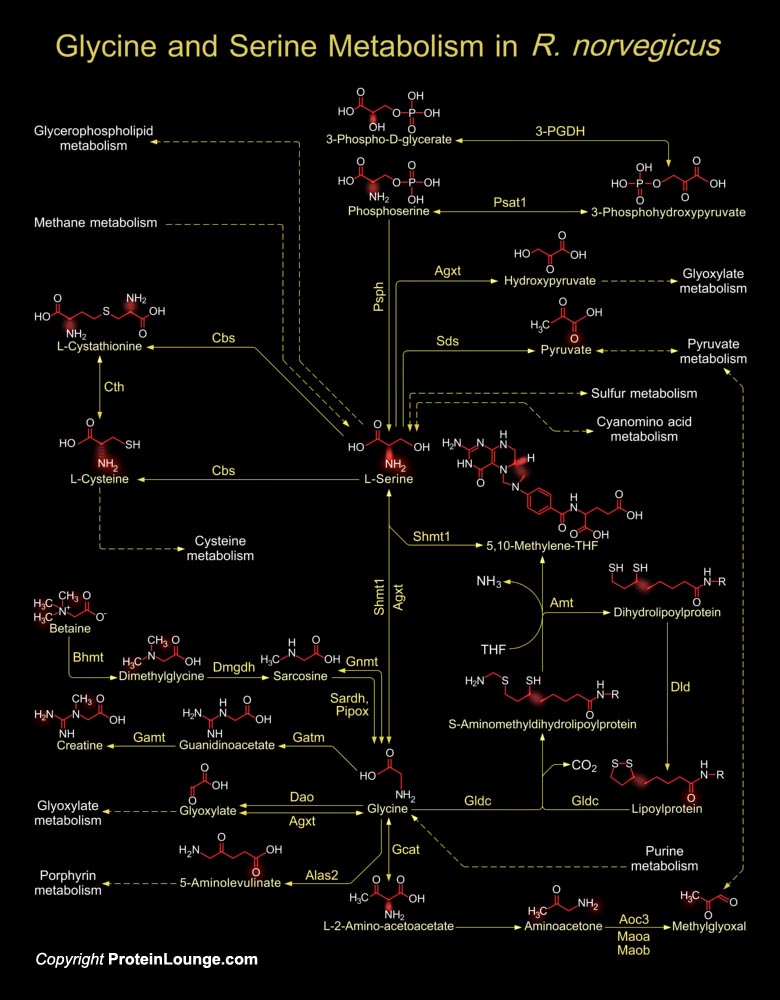
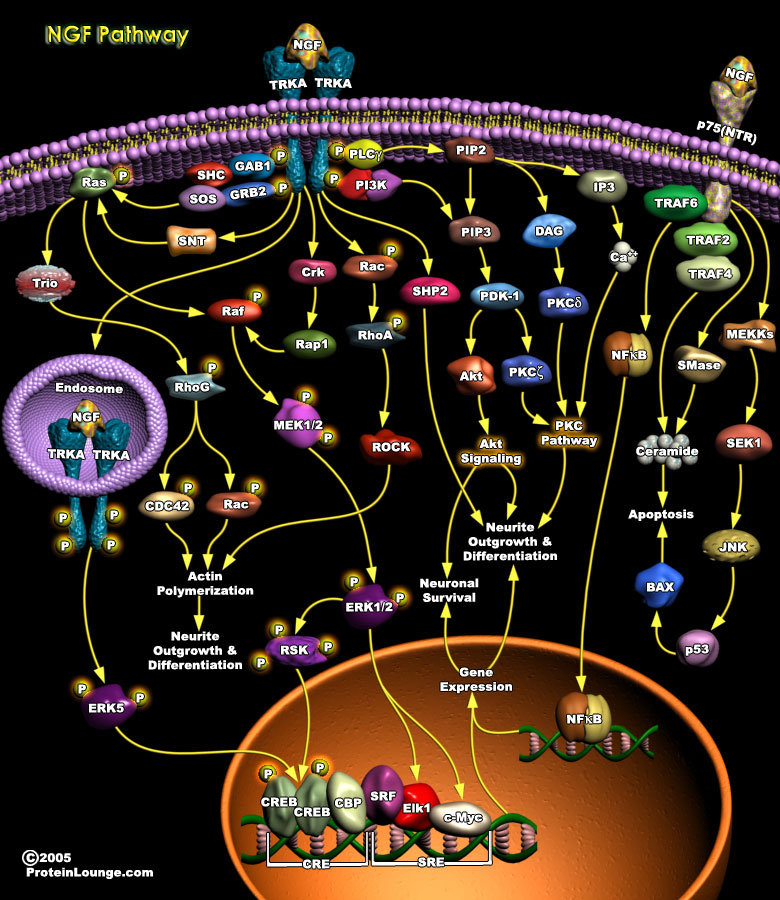
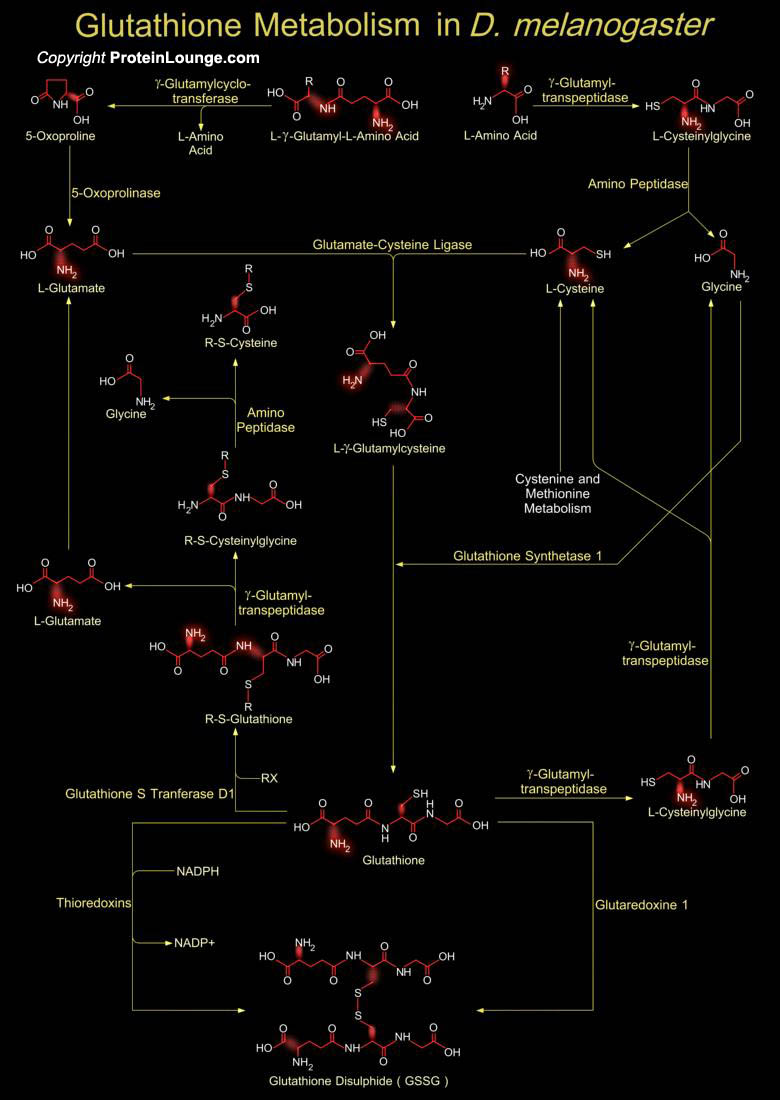
Featured Pathways
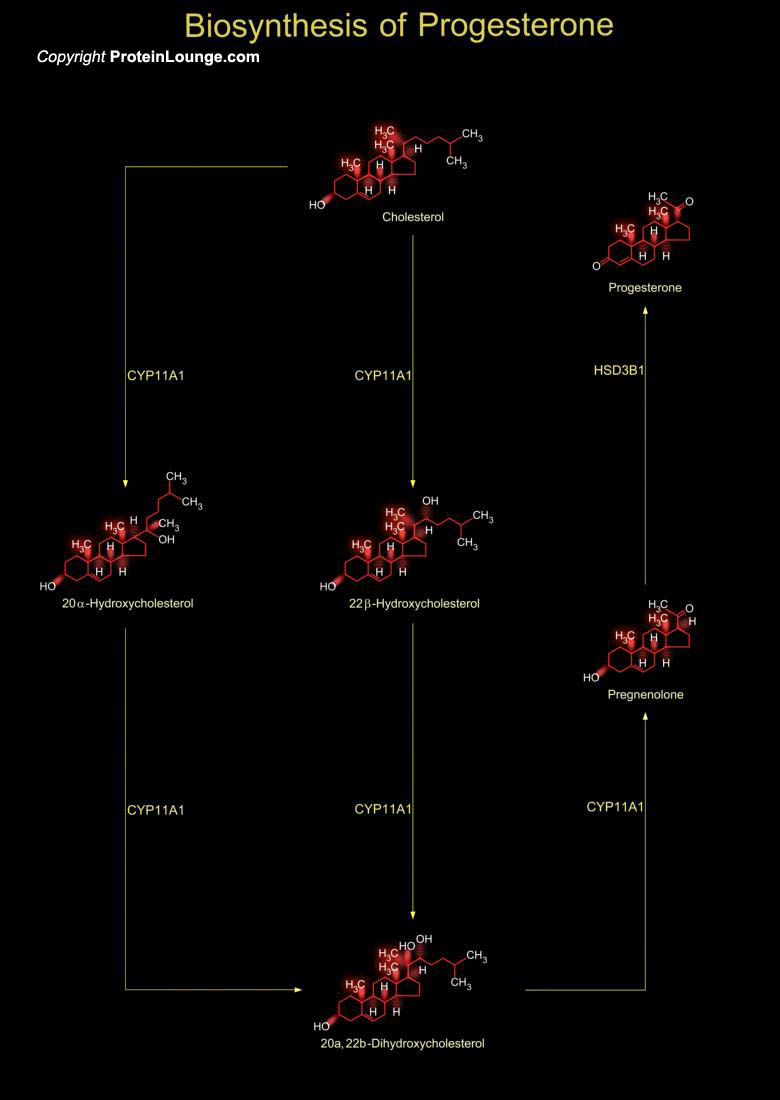
Cholesterol is the common precursor of all steroid hormones and is biosynthesized in many tissues. Steroid hormones are characterized by a common basic structure of cyclopentane-perhydro-phenantrene, a polycyclic complex of 17 carbon atoms forming a four-ring system. Altering a side chain or subsistent group of a cholesterol molecule produces various steroids molecules. Pregnenolone and[..]
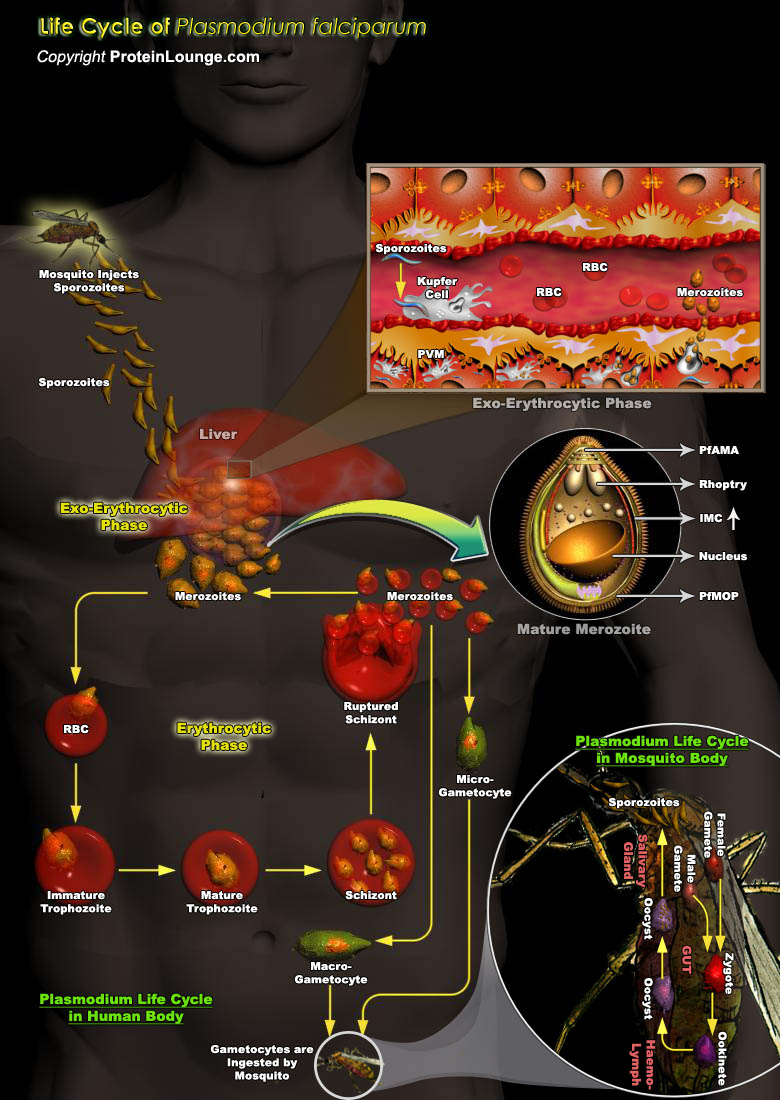
Malaria is the world's largest parasitic disease, killing more people than any other communicable disease except Tuberculosis. Malaria is a major public health problem in more than 100 countries, inhabited by a total of some 2.4 billion people, or close to half of the world's population. Each year, 300–500 million people contract malaria and about 3 million die, most of which are[..]
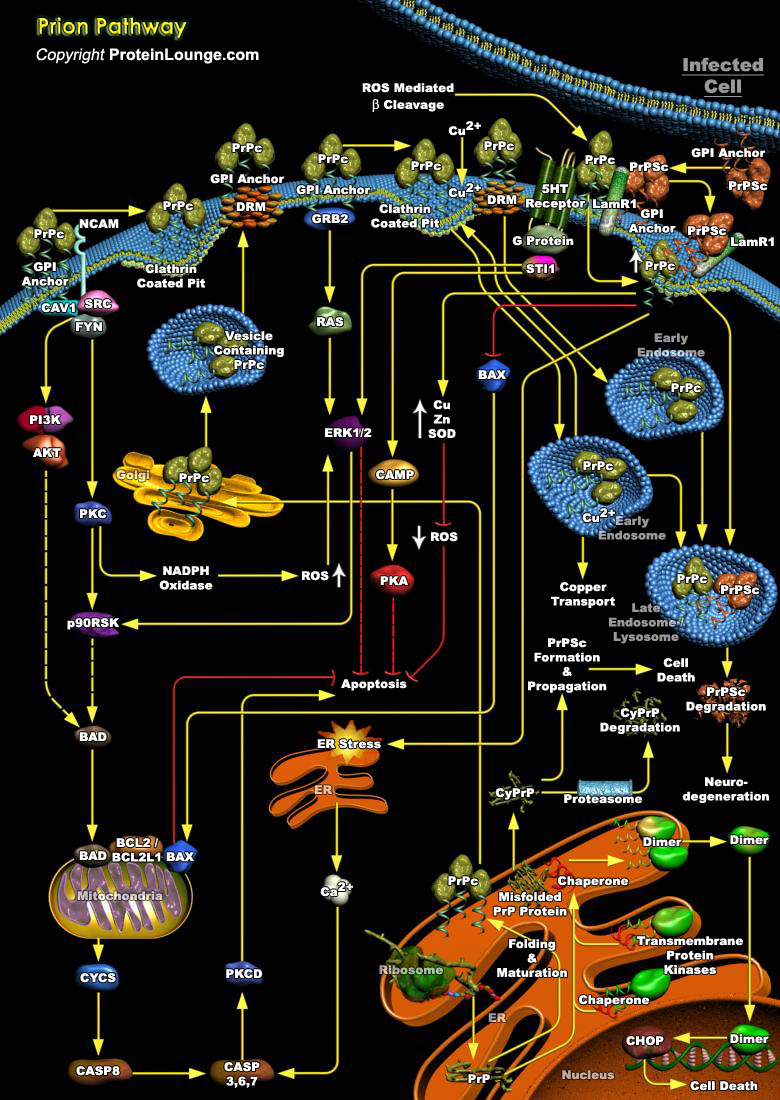
Prion diseases or transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) are fatal neurodegenerative disorders affecting humans and animals. Human TSEs are often categorized with other protein misfolding neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, fronto-temporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The[..]
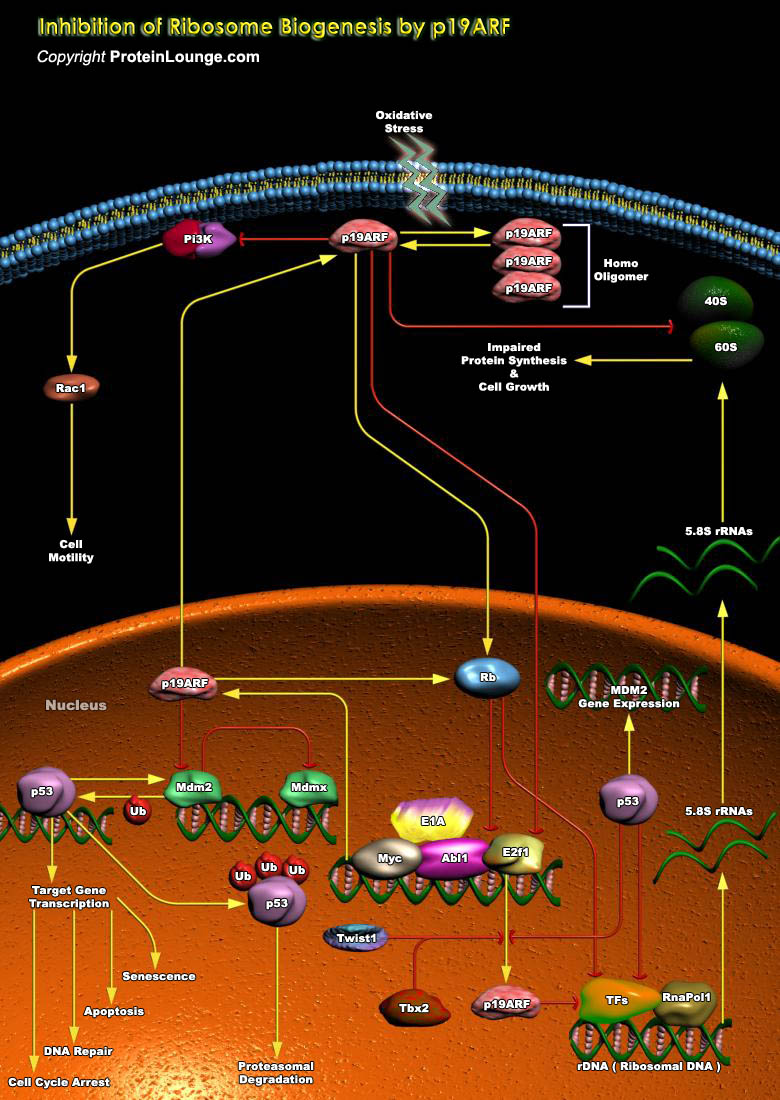
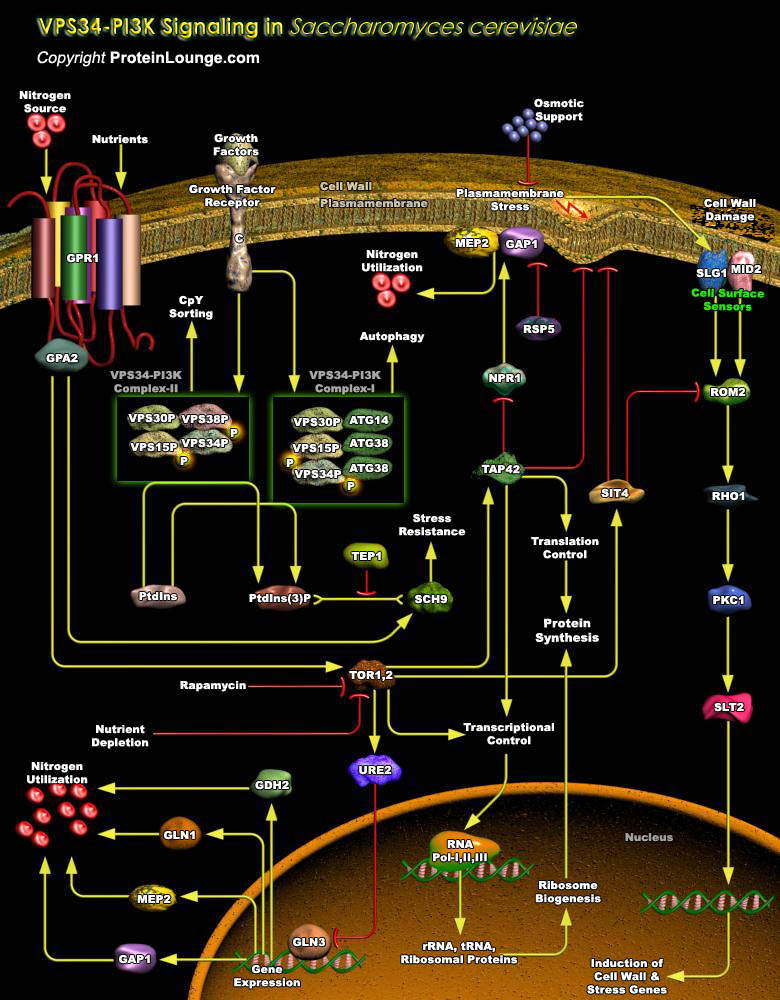
PI3Ks (Phosphoinositide-3 Kinases) are heterodimeric lipid kinases that are composed of a regulatory and catalytic subunit that are encoded by different genes. The phosphorylated lipid phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns3P) is an important signaling molecule and has been found to localize to endosomes, multivesicular bodies, phagosomes, midbodies, peroxisomes and omegasomes. The generated[..]

cAMP (Cyclic Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate) is the first identified second messenger, which has a fundamental role in the cellular response to many extracellular stimuli. The cAMP signaling pathway controls a diverse range of cellular processes. Indeed, not only did cAMP provide the paradigm for the second messenger concept, but also provided the paradigm for signaling[..]
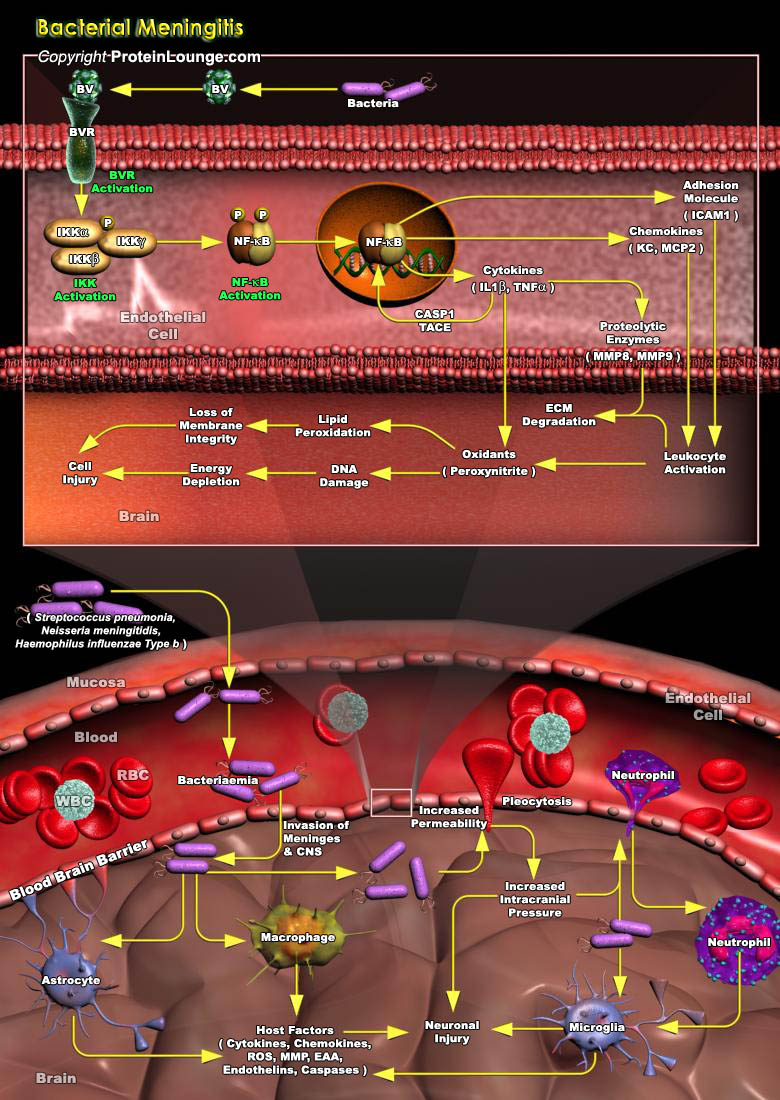
Bacterial meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges, in particular the arachnoid and the pia mater, associated with the invasion of bacteria into the subarachnoid space.The pathogens take advantage of the specific features of the immune system in the CNS, replicate and induce inflammation. A hallmark of bacterial meningitis is the recruitment of highly activated leukocytes into the CSF.The[..]
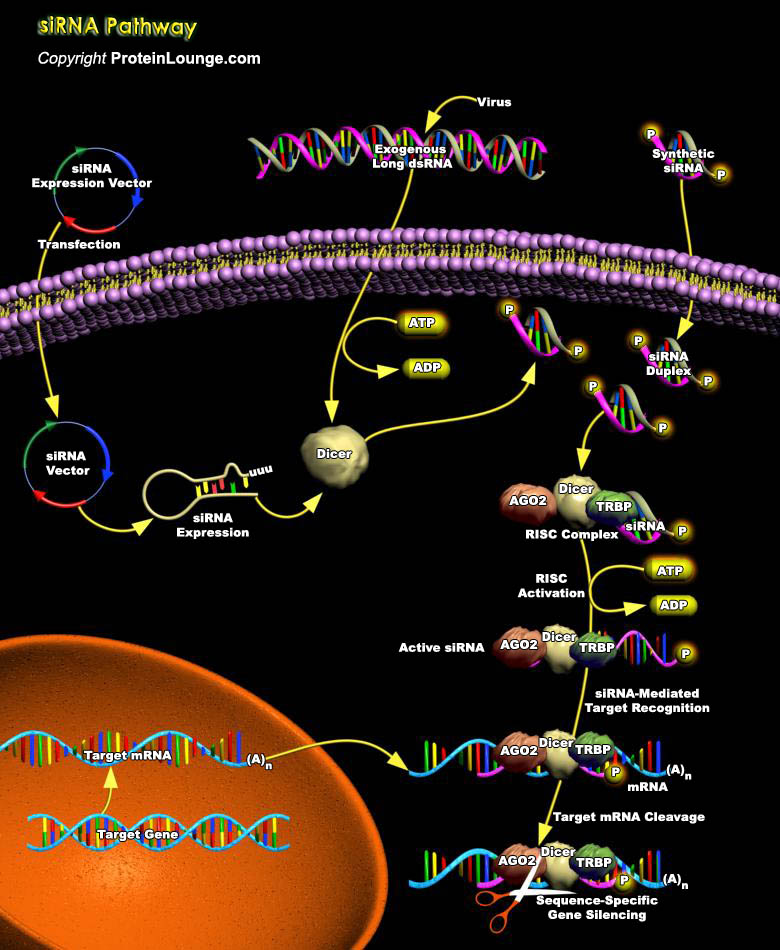
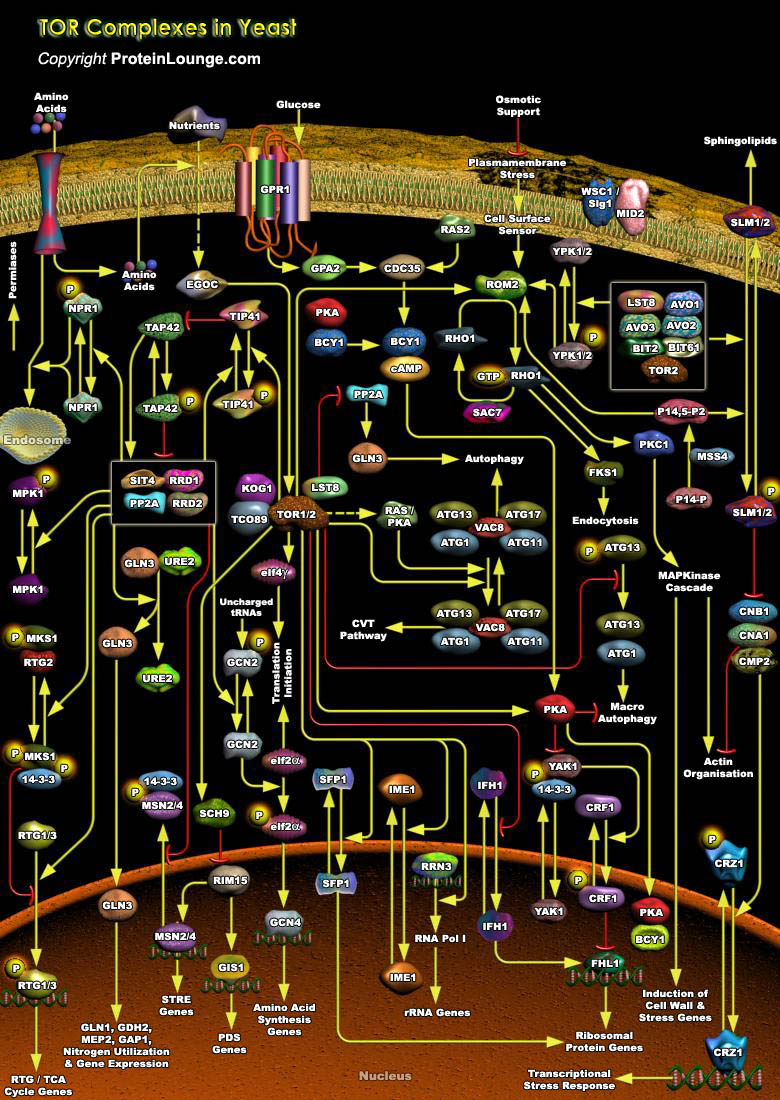
TOR (Target of Rapamycin) is a PIKK (Phosphatidylinositol Kinase-related protein Kinase) that controls cell growth and proliferation. In all eukaryotic cells expressing the protein, TOR function is controlled by nutrient availability, which ensures that protein synthesis is repressed when the supply of precursor amino acids is insufficient. In mammalian cells, one branch of this pathway[..]