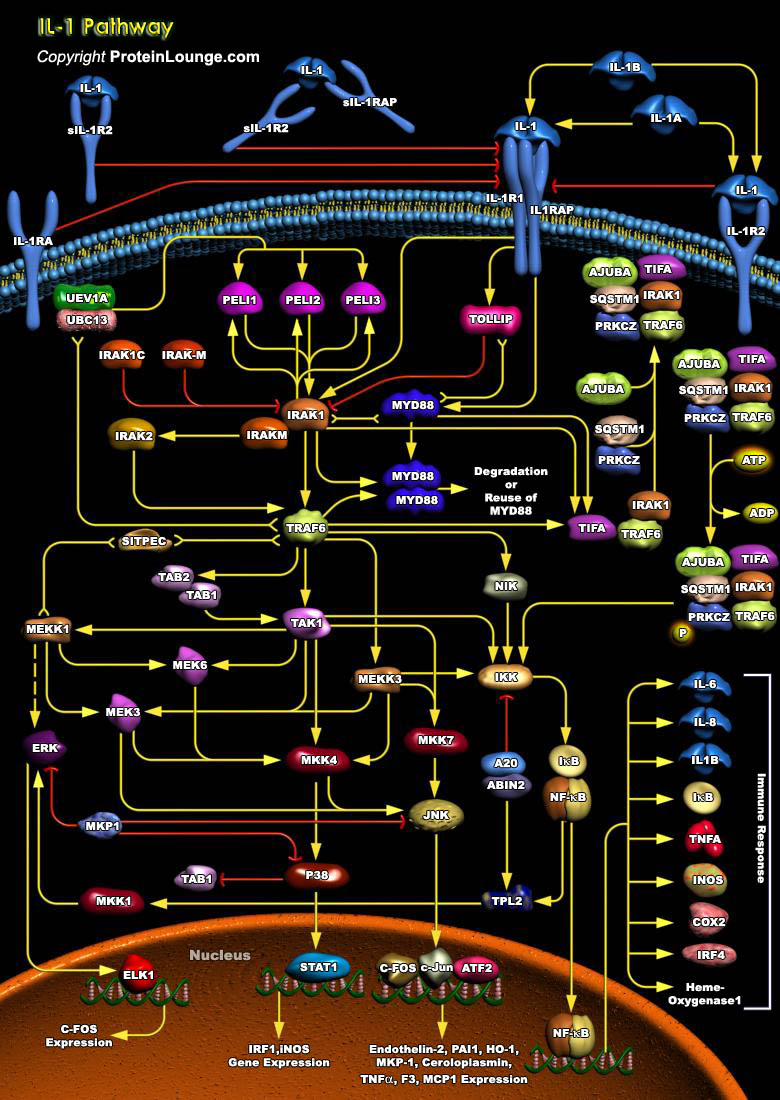
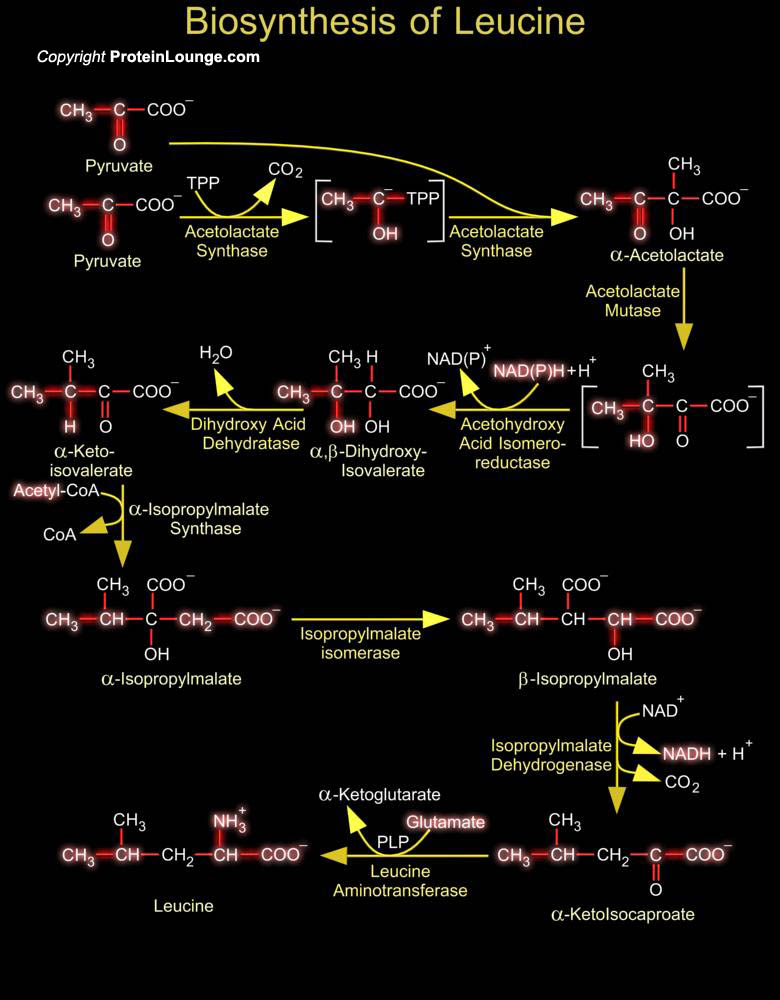
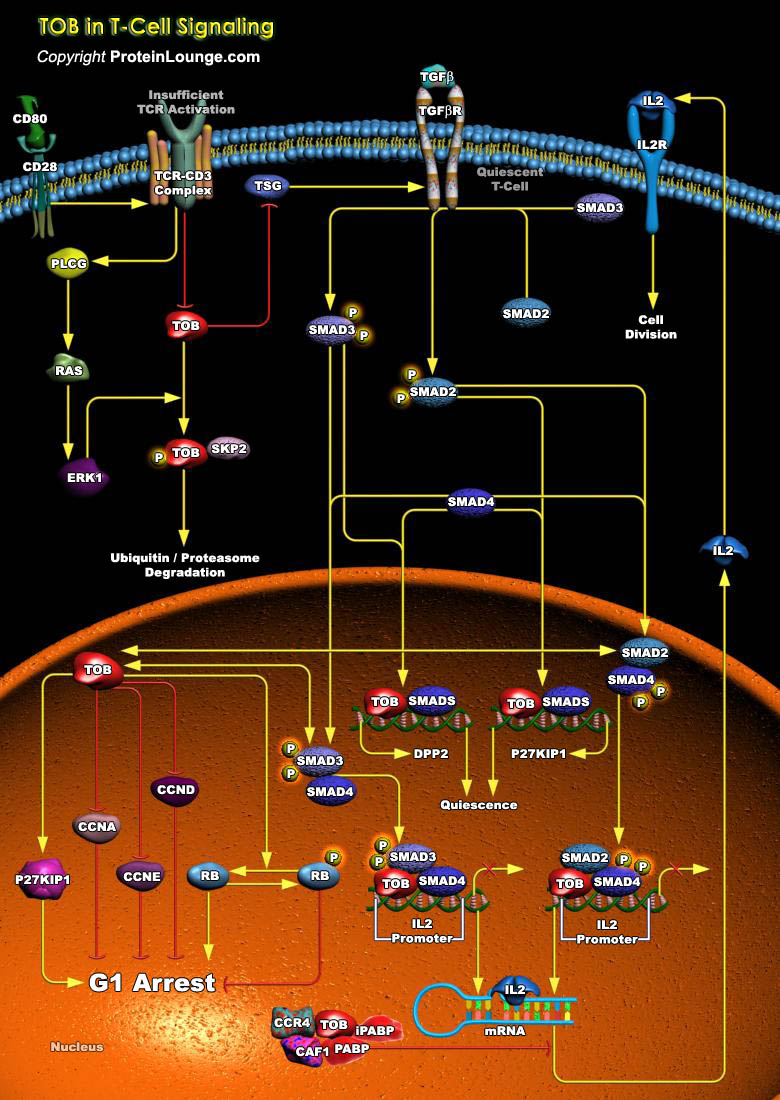
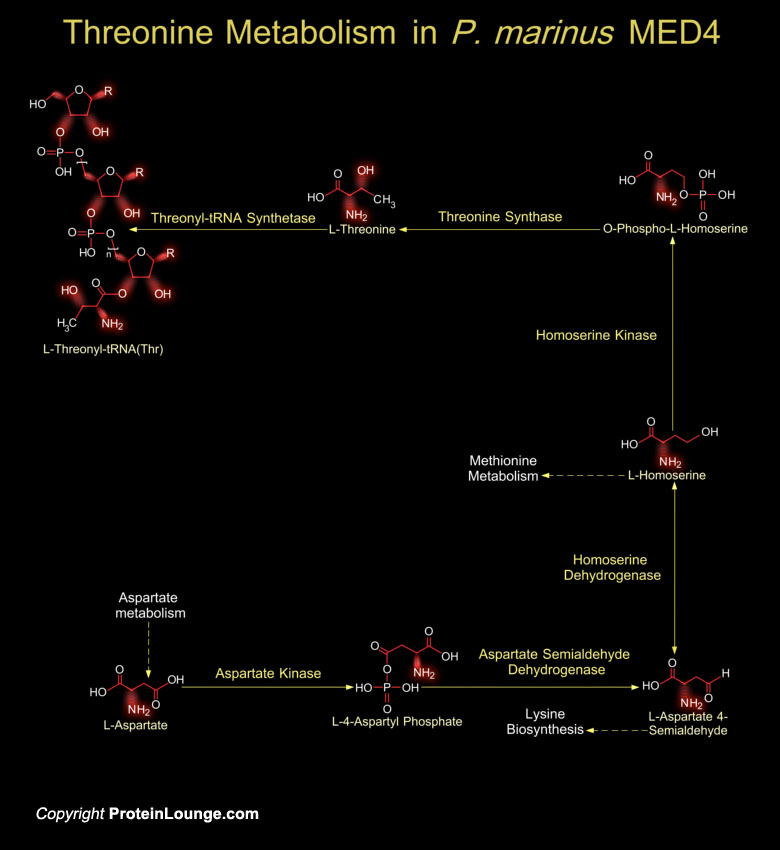
Featured Pathways
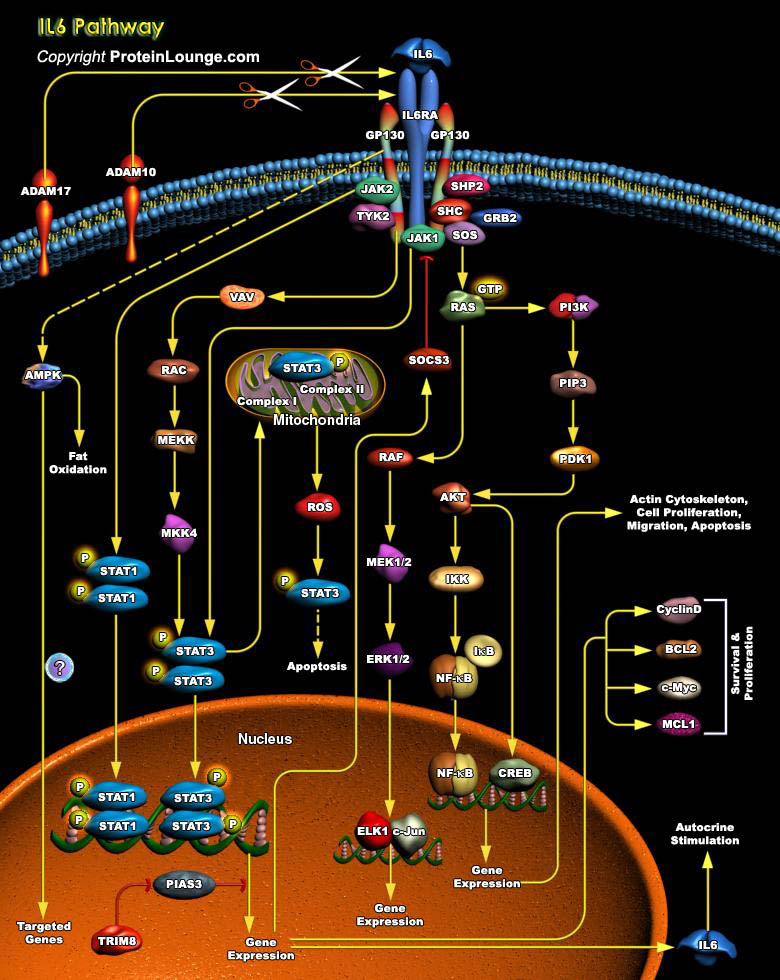
IL6 (Interleukin-6) is a pleiotropic cytokine that not only affects the immune system, but also acts in other biological systems and many physiological events in various organs including the inflammation, hematopoiesis, and oncogenesis by regulating cell growth, gene activation, proliferation, survival, and differentiation. This protein signals through a receptor composed of two different[..]
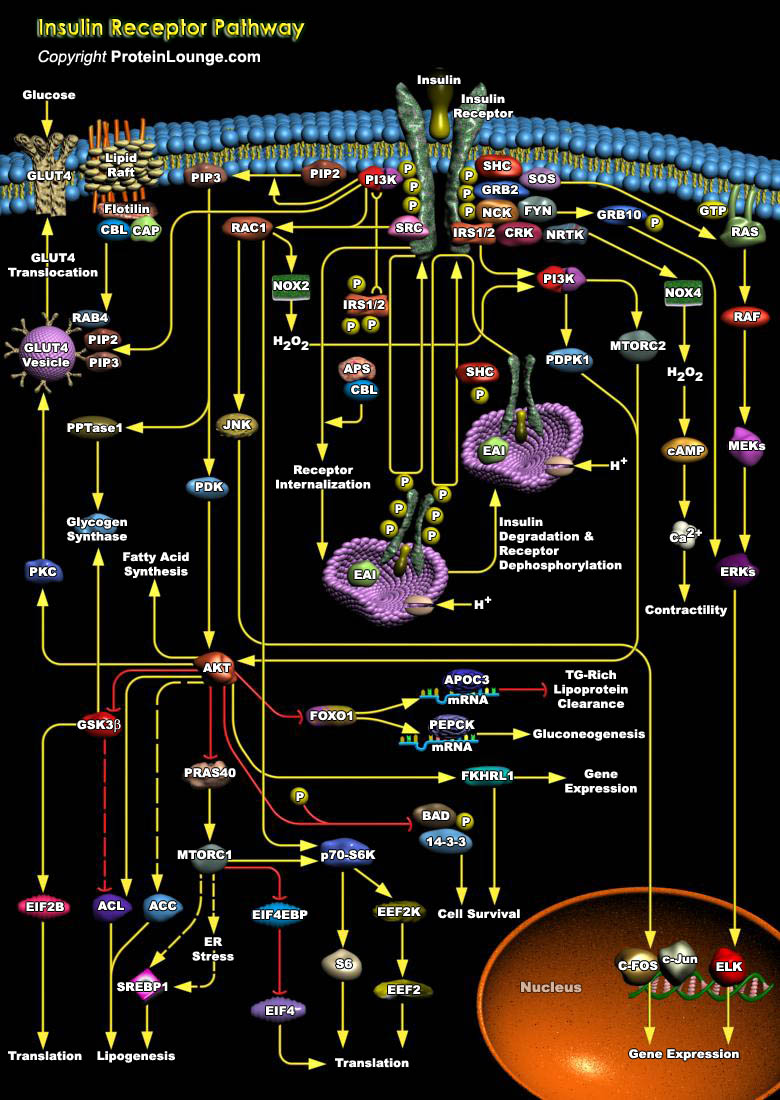
Insulin is the major hormone controlling critical energy functions such as glucose and lipid metabolism. Insulin elicits a diverse array of biological responses by binding to its specific receptor. The insulin receptor belongs to a subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases that includes the IGF (Insulin-like Growth Factor) receptor and the IRR (Insulin Receptor-Related Receptor). These receptors[..]
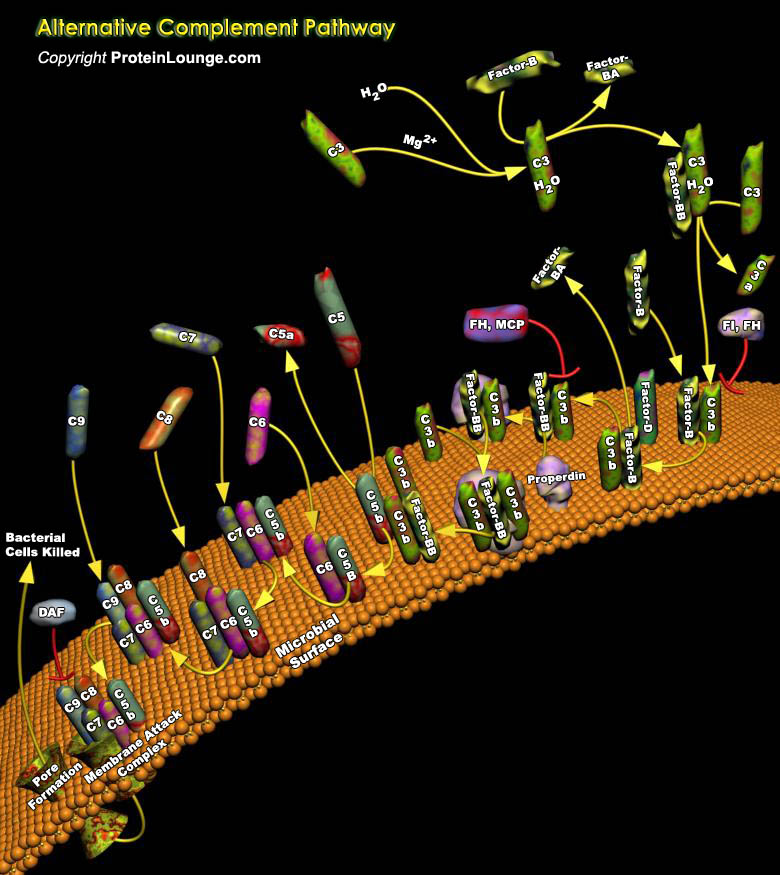
The complement system refers to a series of proteins circulating in the blood and bathing the fluids surrounding tissues. The proteins circulate in an inactive form, but in response to the recognition of molecular components of microorganism, they become sequentially activated, working in a cascade where in the binding of one protein promotes the binding of the next protein in the cascade. There[..]
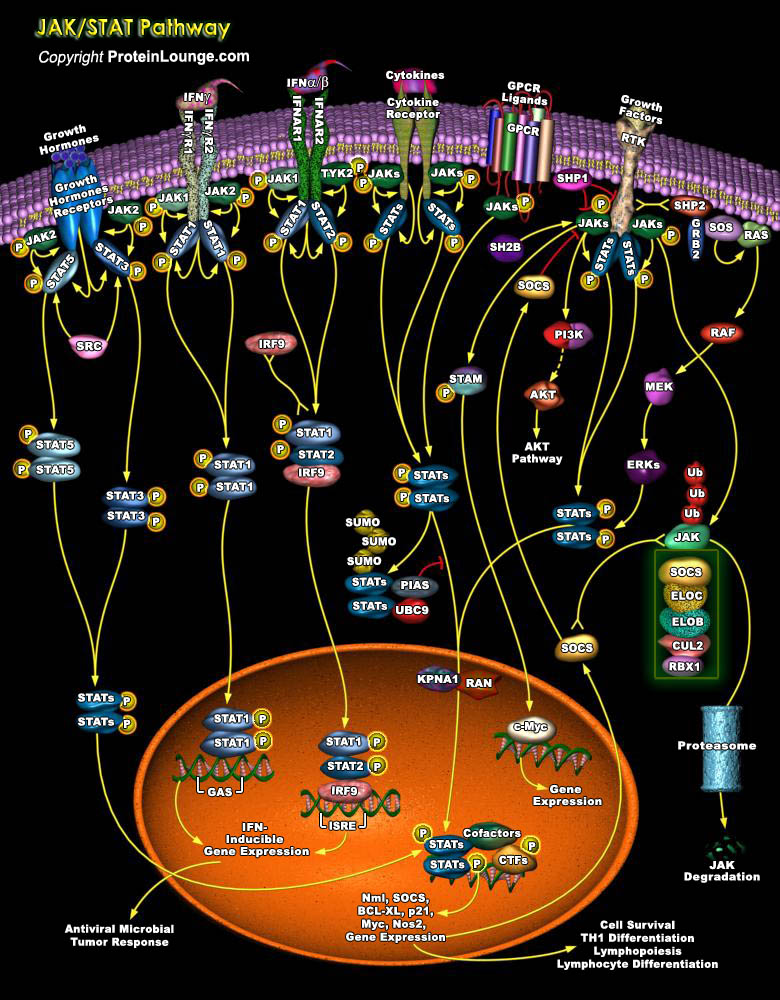
Signaling pathways mediating the transduction of information between cells are essential for development, cellular differentiation and homeostasis. Their dysregulation is also frequently associated with human malignancies. The JAK (Janus tyrosine Kinase)-STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) pathway represents one such signaling cascade whose evolutionarily conserved roles[..]
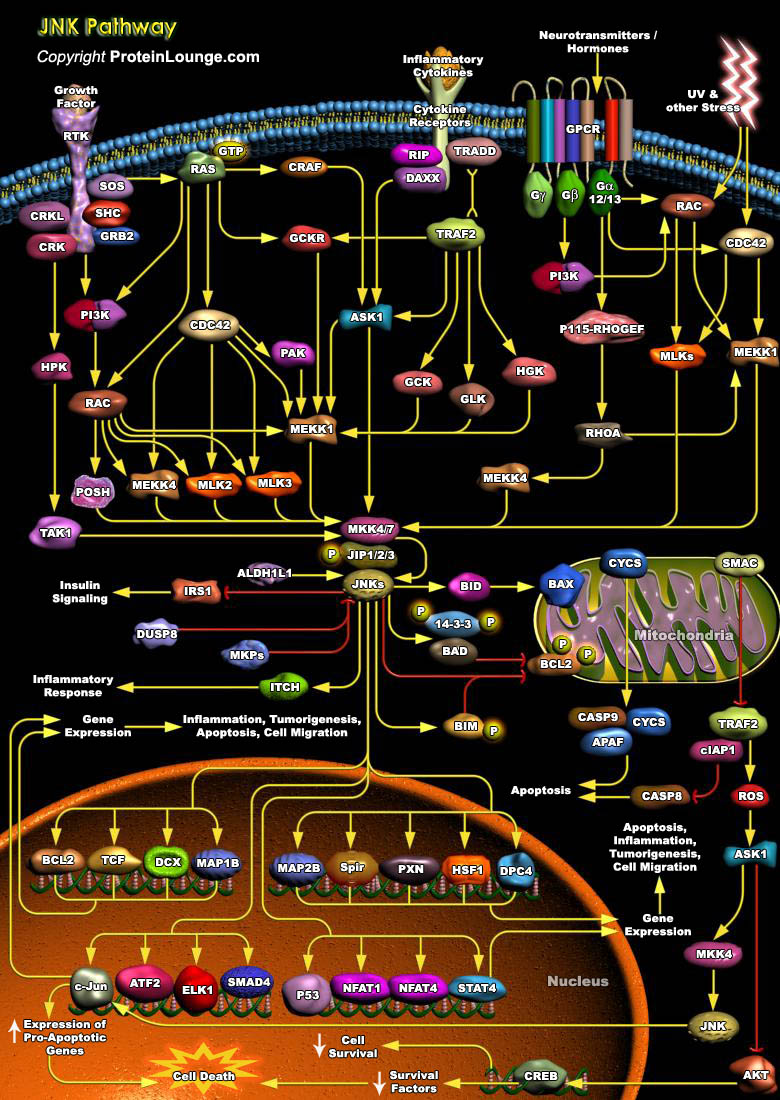
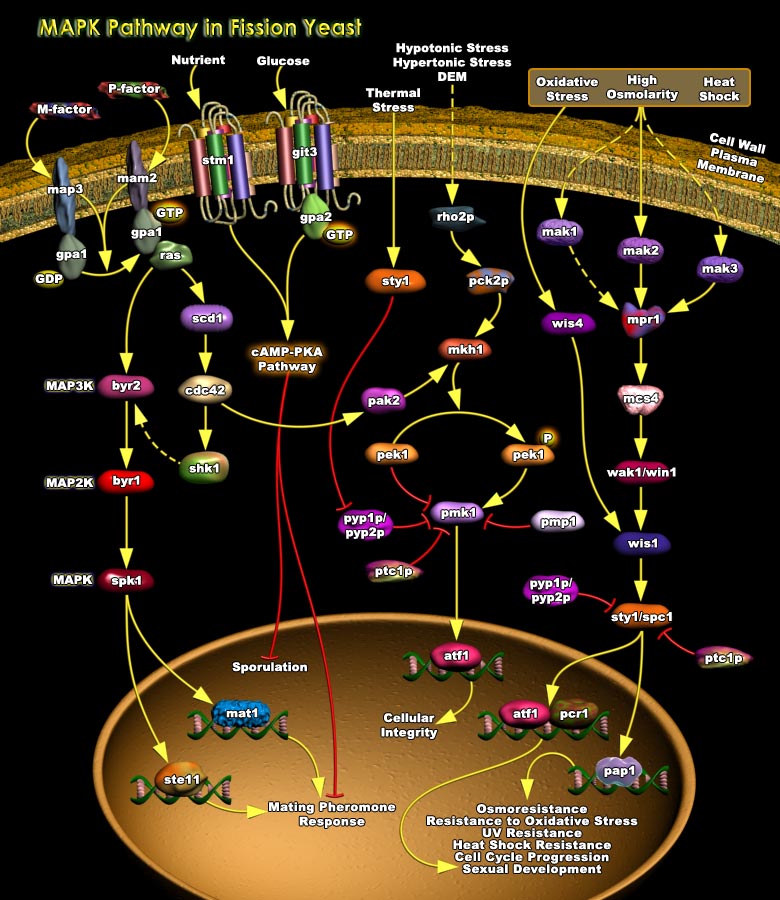
MAPKs (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases) are Serine-threonine protein Kinases that are activated in response to a variety of extracellular stimuli and mediate signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus. MAPKs are expressed in multiple cell types including Cardiomyocytes, Vascular Endothelial cells, and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Three major MAPKs include ERKs[..]

A number of inherited (constitutional/genetic) disorders are characterized by BM (Bone Marrow) failure usually in association with one or more somatic abnormality. The BM failure may involve all or a single lineage; in some cases it may be initially associated with a single peripheral cytopenia and then progress to pancytopenia. Scientifically, they constitute an exciting group of disorders[..]
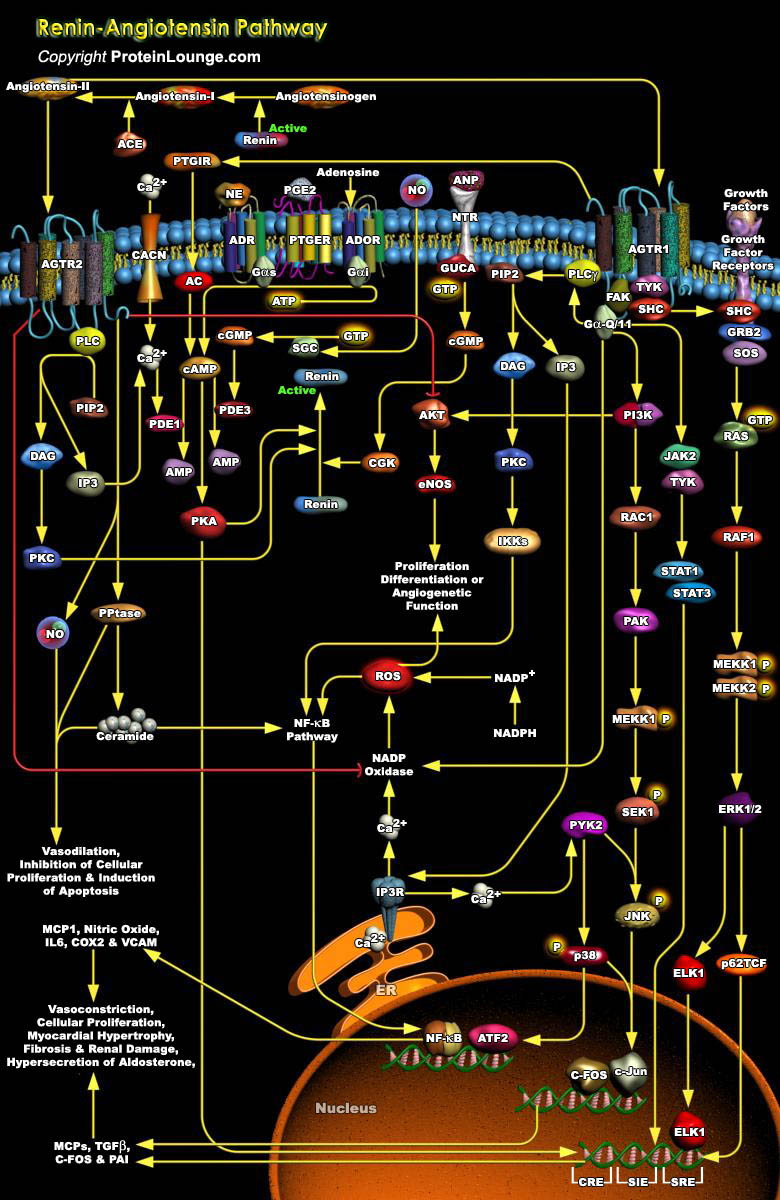
Proliferation and migration of VSMCs (Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells) in arteries plays an important role in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis, hypertension, and restenosis after angioplasty. A wide variety of growth factors, cytokines, and hormones activate these responses in blood vessels. A prominent growth factor for VSMCs is Angiotensin (Angiotensin-I and II), the main peptide of the[..]
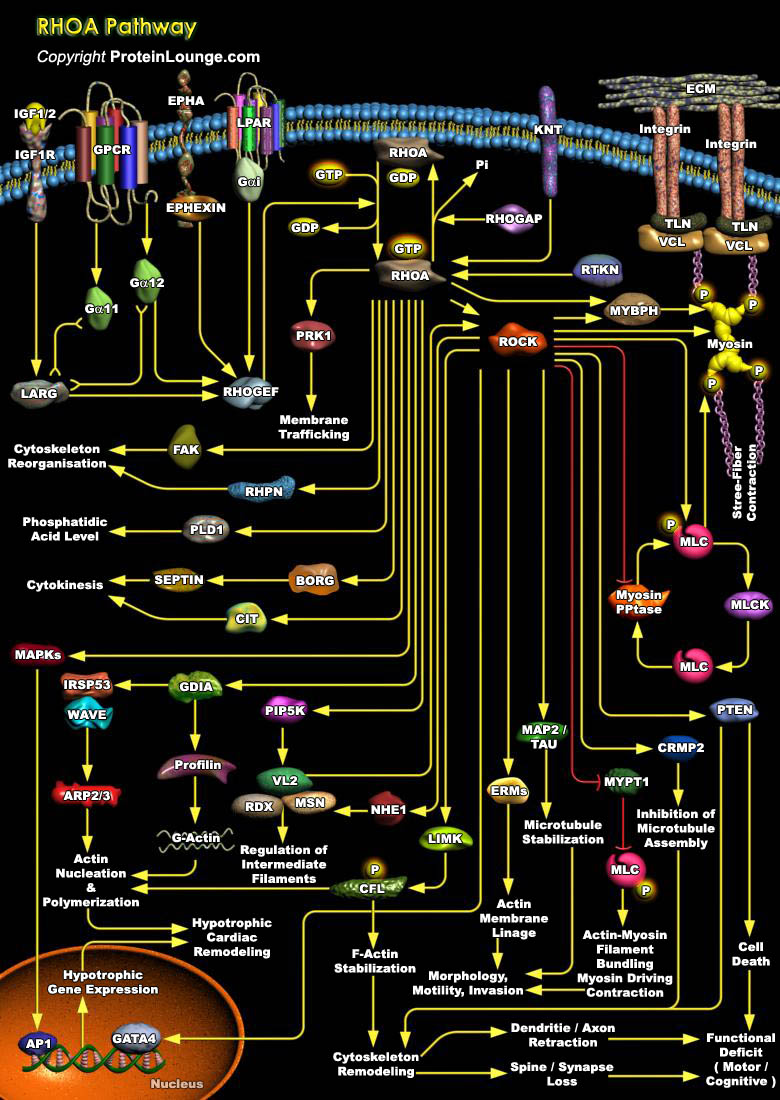
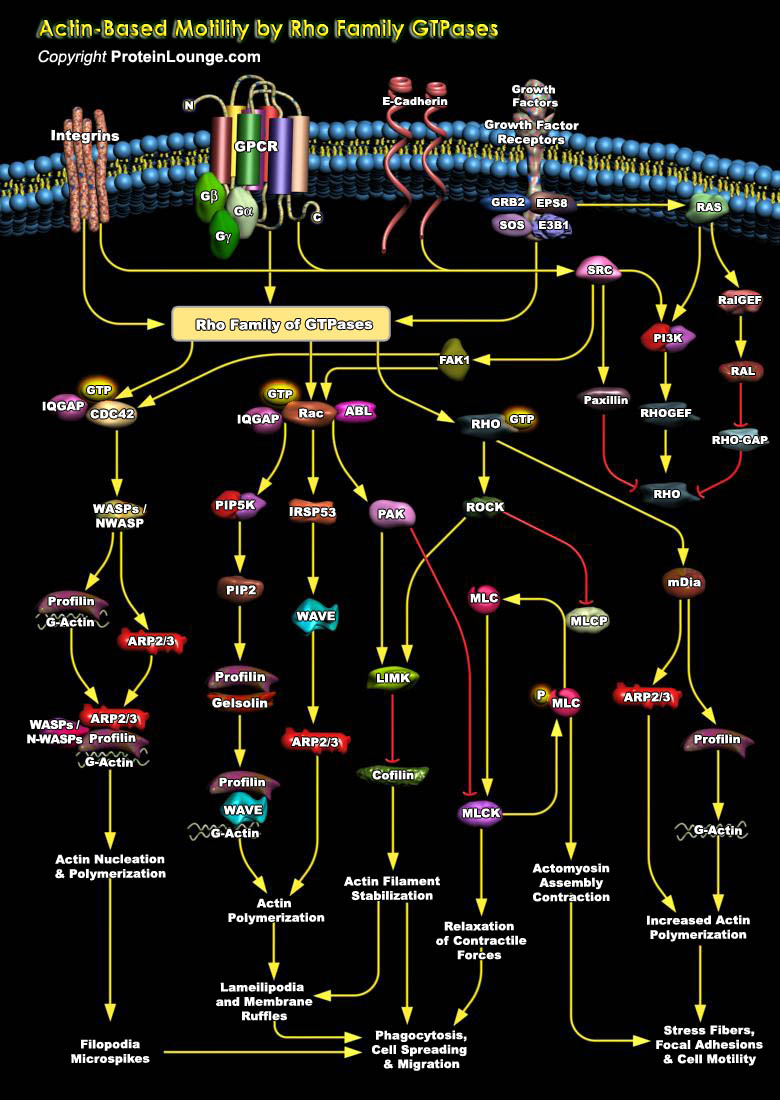
Rho is a member of the Ras superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins that play a central role in diverse biological processes such as Actin cytoskeleton organization, Microtubule dynamics, Gene transcription, Oncogenic transformation, Cell cycle progression, Adhesion and Epithelial wound repair. To date, 20 genes encoding different members of the Rho family have been identified in the human[..]
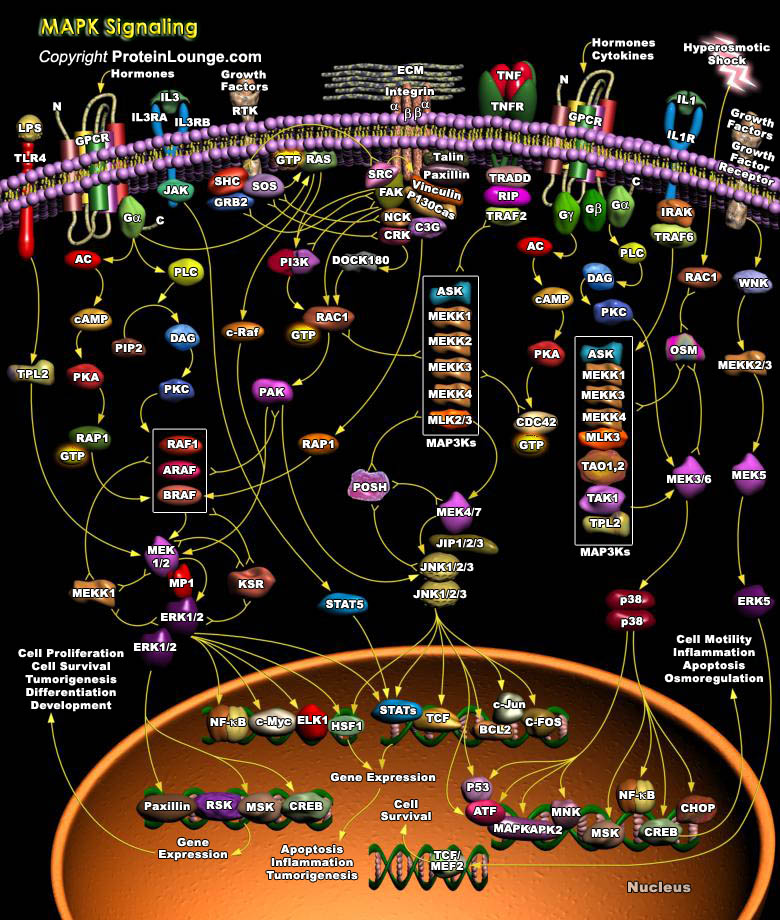
MAPKs are a group of protein Serine/threonine Kinases that are activated in response to a variety of extracellular stimuli and mediate signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus. In combination with several other signaling pathways, they can differentially alter phosphorylation status of numerous proteins, including Transcription Factors, Cytoskeletal proteins, Kinases and other[..]

mTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin) is a 289-kDa serine/threonine protein kinase and a member of the PIKK (Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-related Kinase) family. The protein consists of a Catalytic Kinase domain, an FRB (FKBP12–Rapamycin Binding) domain, a putative Auto-inhibitory domain (Repressor domain) near the C-terminus and up to 20 tandemly repeated HEAT motifs at the Amino[..]
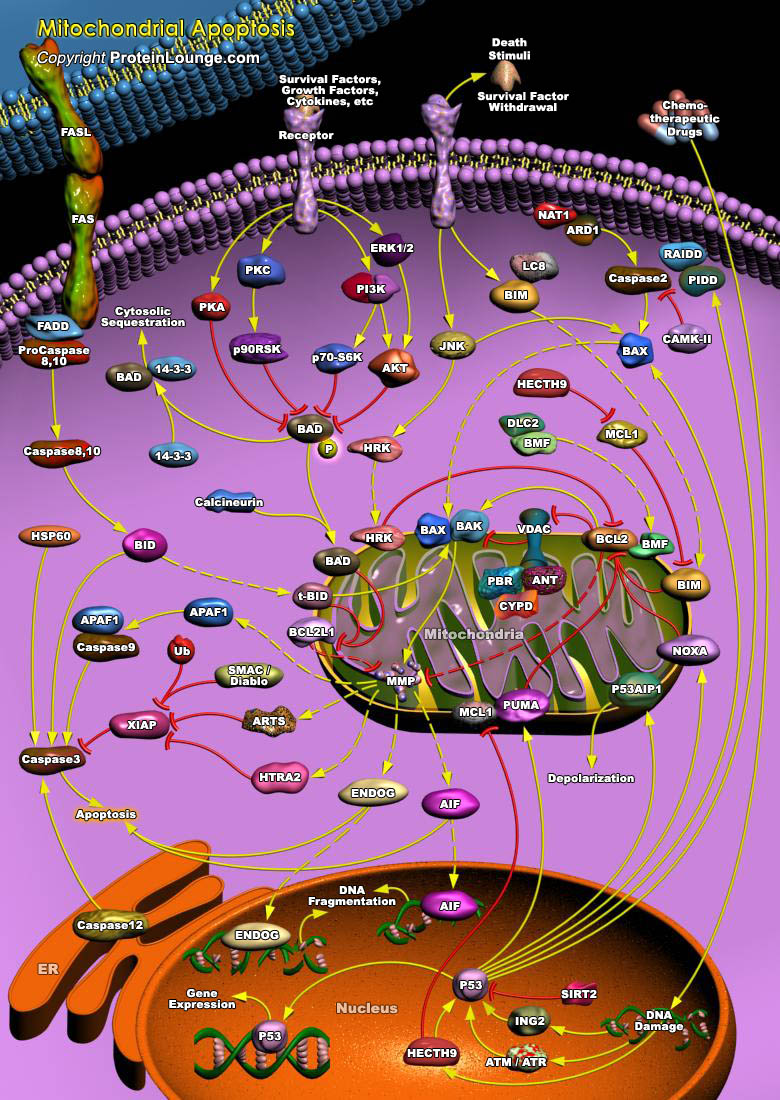
Apoptosis is a naturally occurring process by which a cell is directed to Programmed Cell Death. Apoptosis is based on a genetic program that is an indispensable part of the development and function of an organism. In this process, cells that are no longer needed or that will be detrimental to an organism or tissue are disposed of in a neat and orderly manner; this prevents the development of an[..]