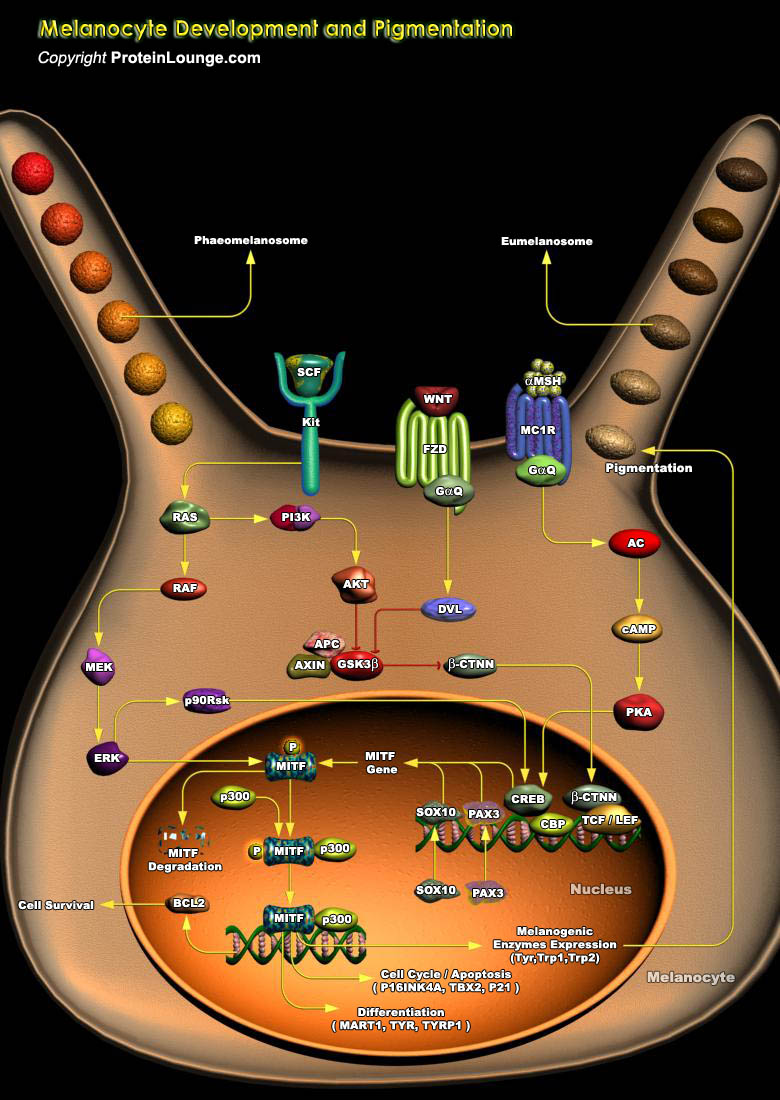
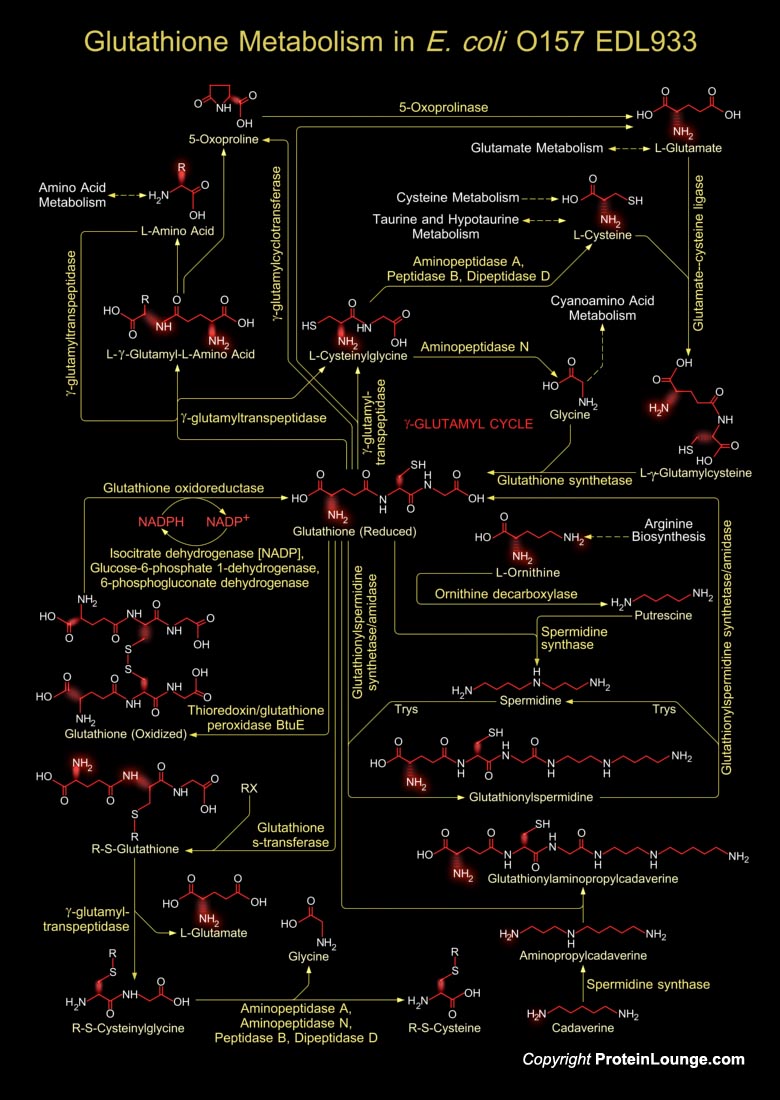
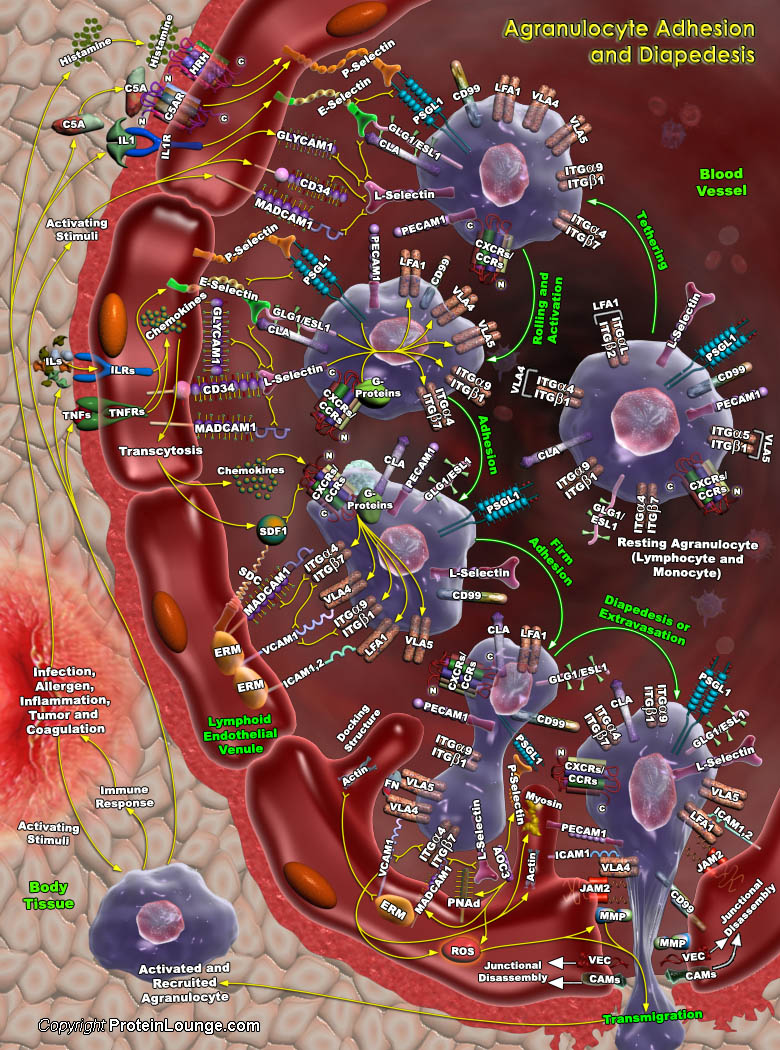
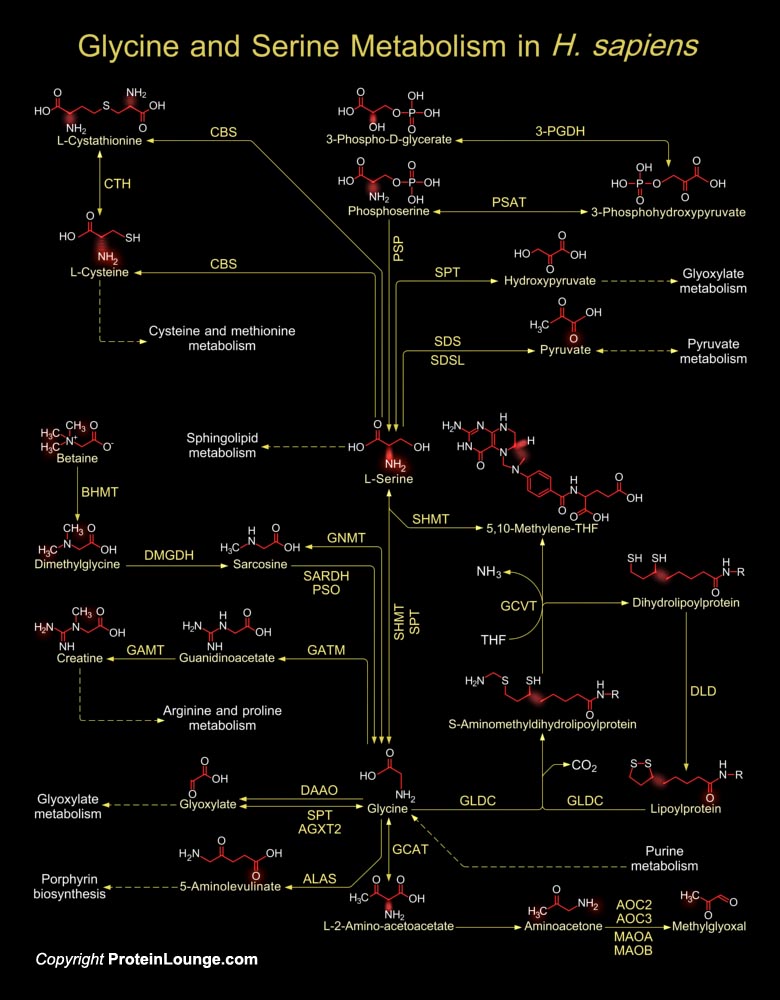
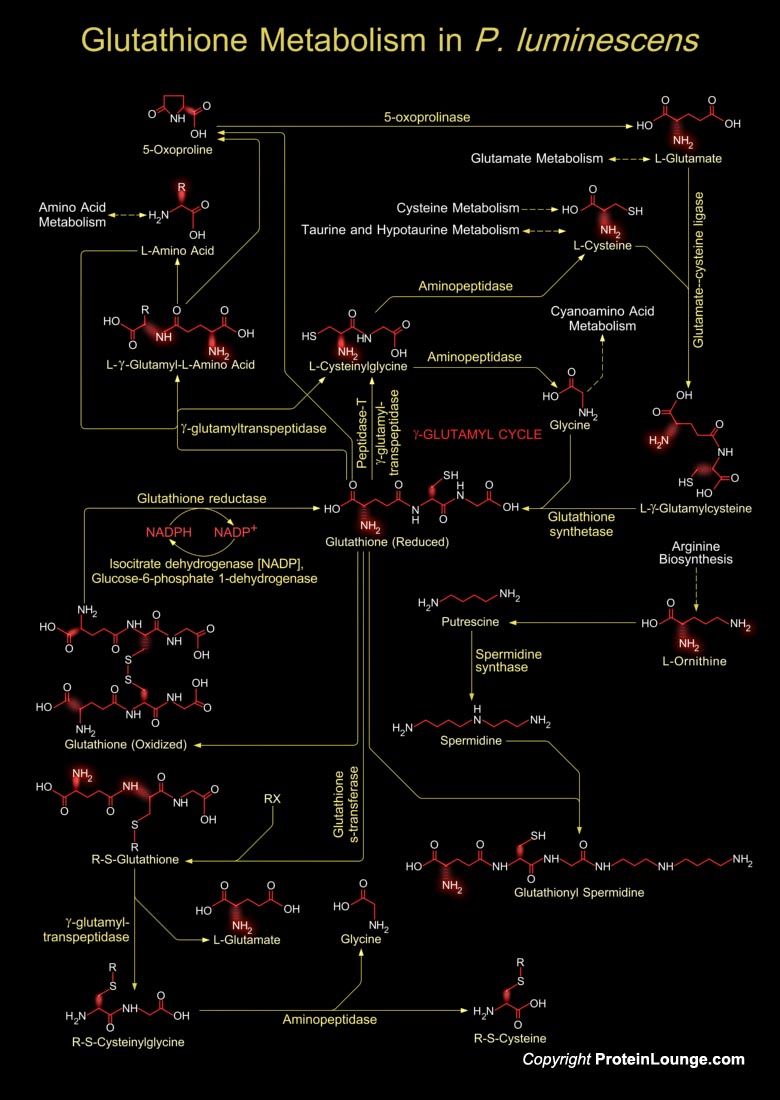
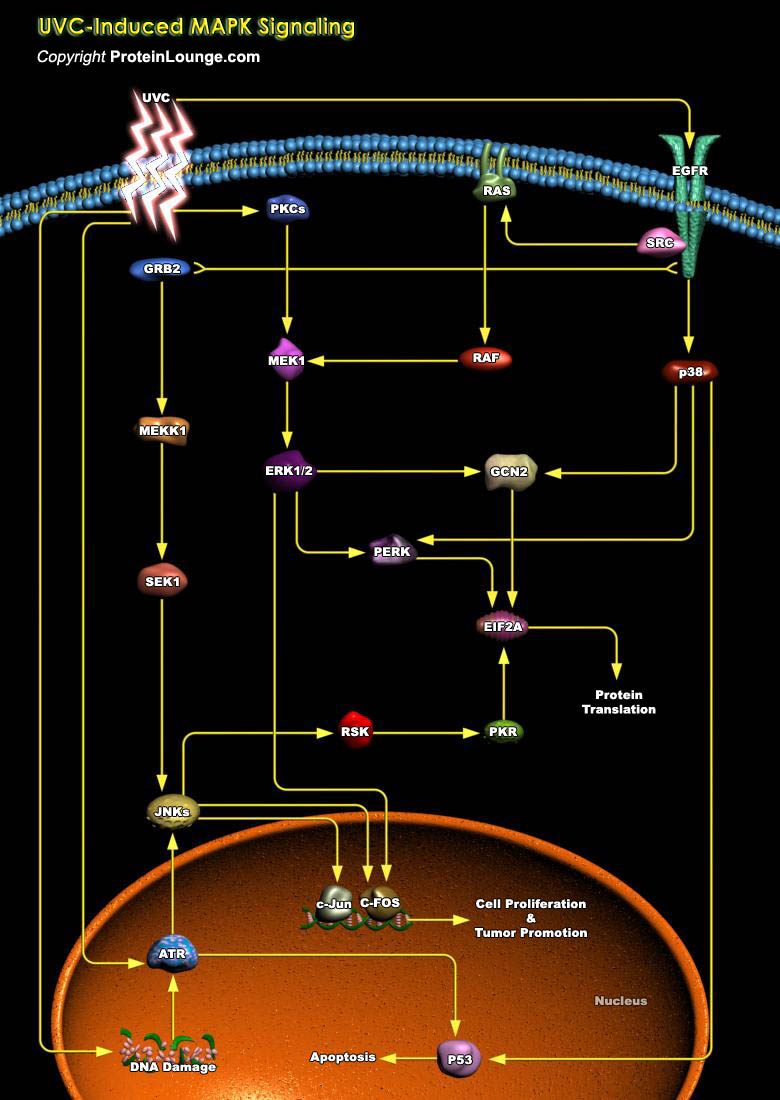
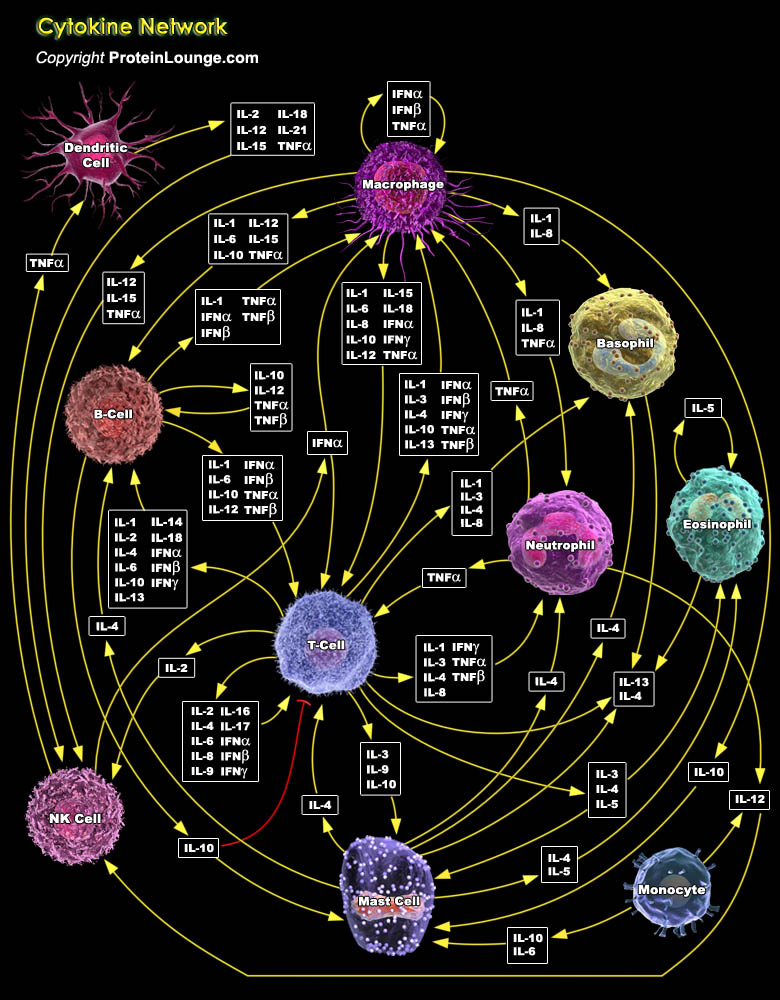
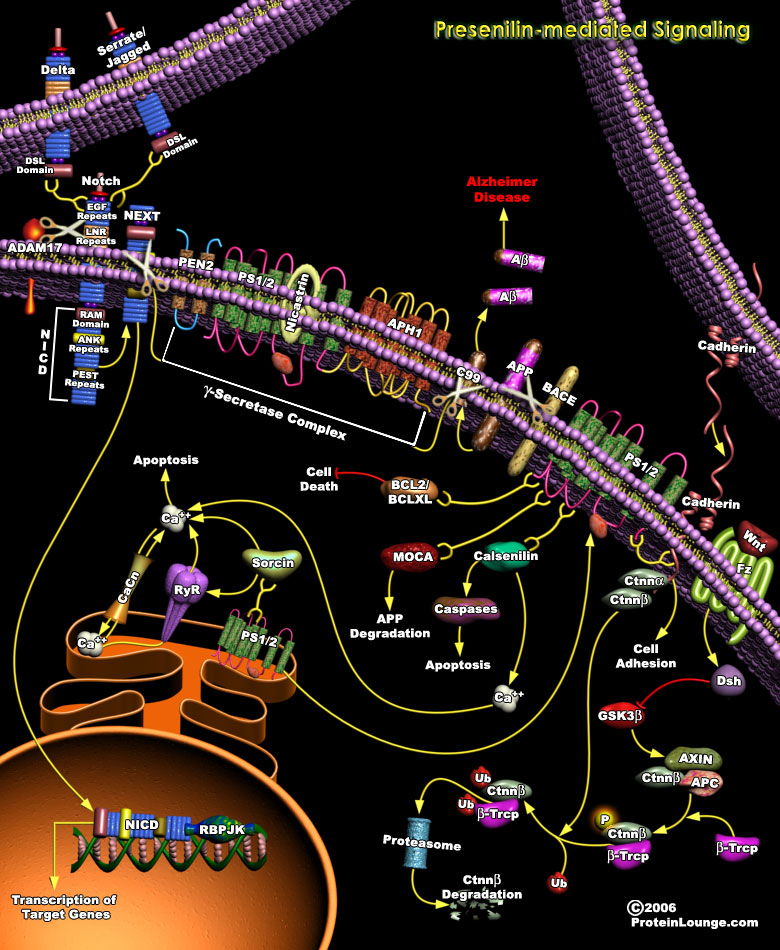
Featured Pathways
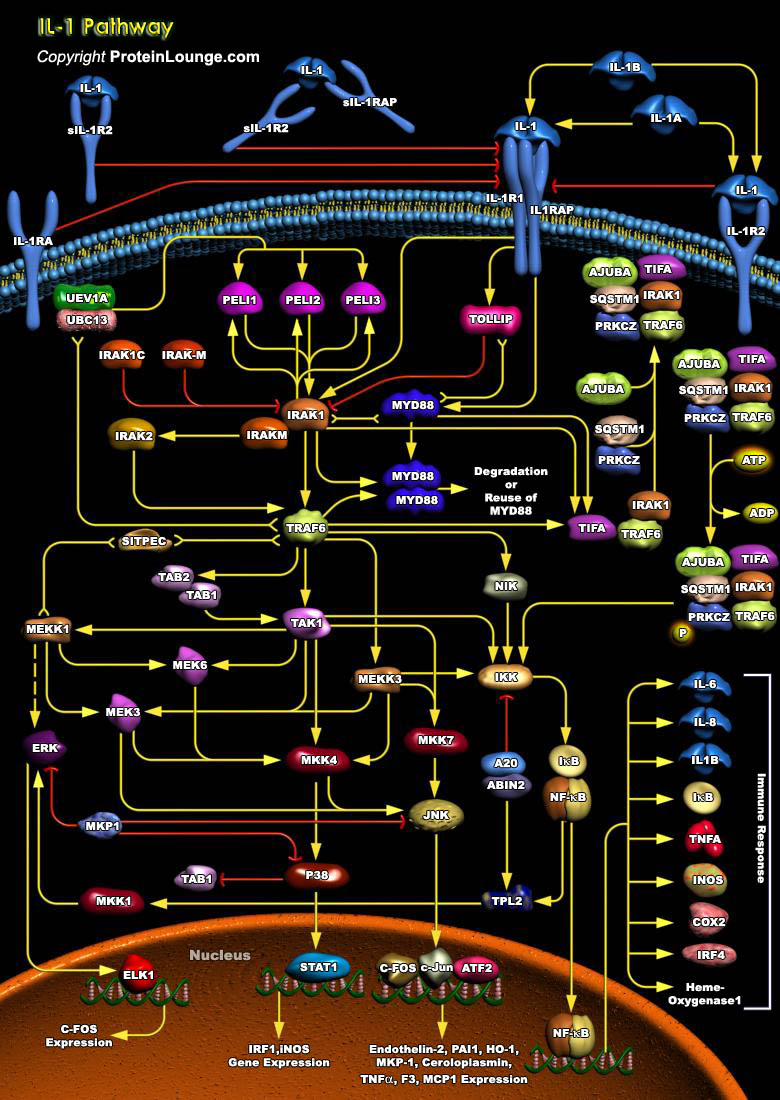
IL-1 (Interleukin-1) is a proinflammatory cytokine that stimulates a broad spectrum of immune and inflammatory responses. IL-1 is produced by activated macrophages, endothelia cells, B-Cells, and fibroblast cells. It induces inflammatory responses, edema, promotes the production of Prostaglandins, IL-2, and the growth of leukocytes (Ref.1). There are two forms of IL-1 encoded by distinct[..]
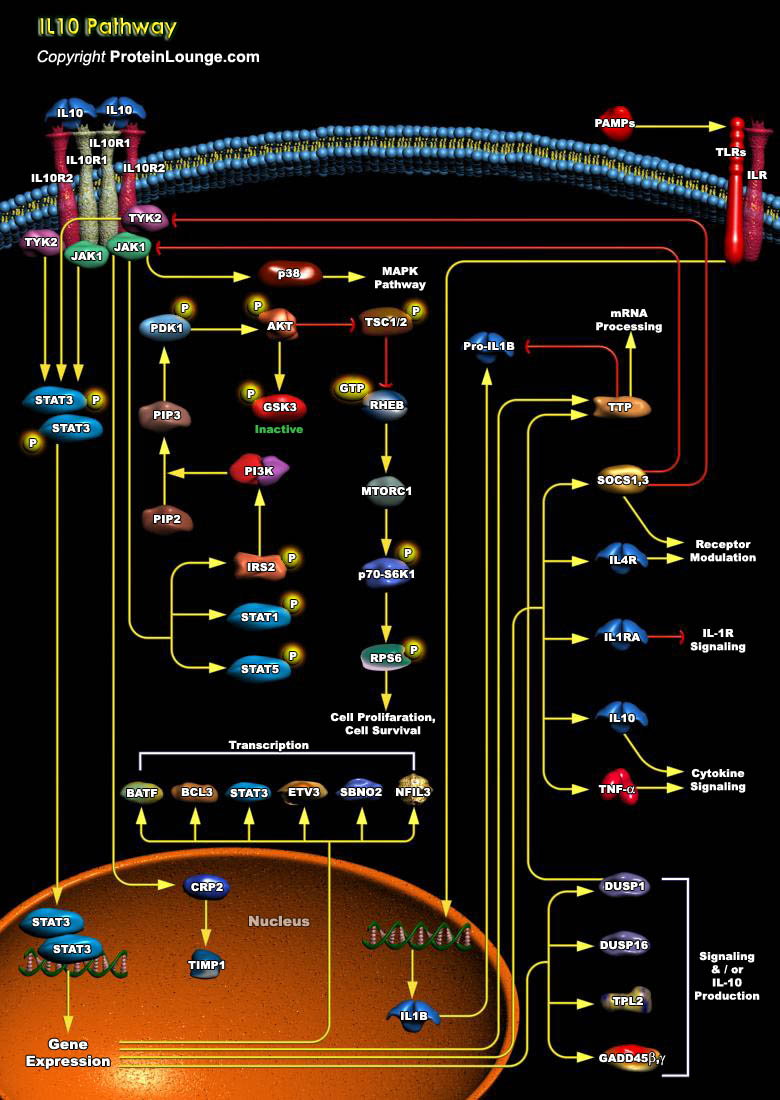
IL-10 (Interleukin-10) is a pleiotropic cytokine with important immunoregulatory functions whose actions influence activities of many of the cell-types in the immune system. It is a cytokine with potent anti-inflammatory properties, repressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-Alpha (Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha), IL-6 (Interleukin-6) and IL-1 (Interleukin-1) by activated[..]
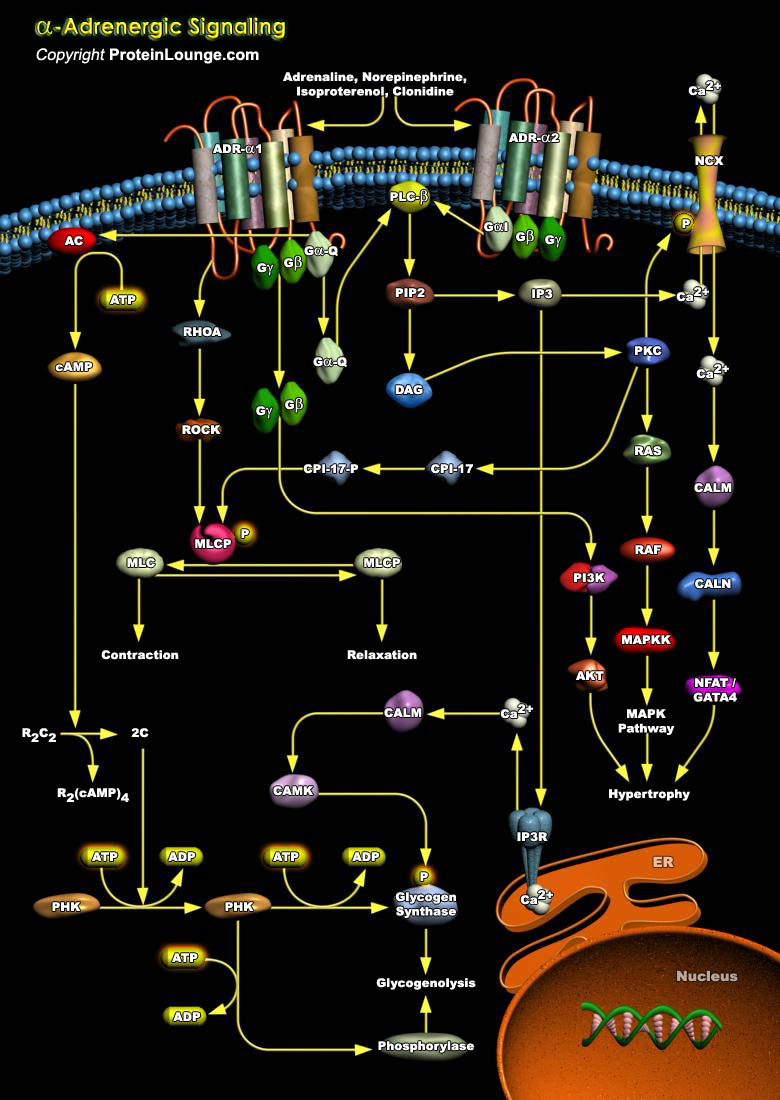
ADRs (Adrenergic Receptors) are expressed on virtually every cell type in the body and are the receptors for Adrenaline, Epinephrine and Norepinephrine within the Sympathetic Nervous System. They serve critical roles in maintaining homeostasis in normal physiologic settings as well as pathologic states. These receptors are also targets for therapeutically administered agonists and antagonists[..]
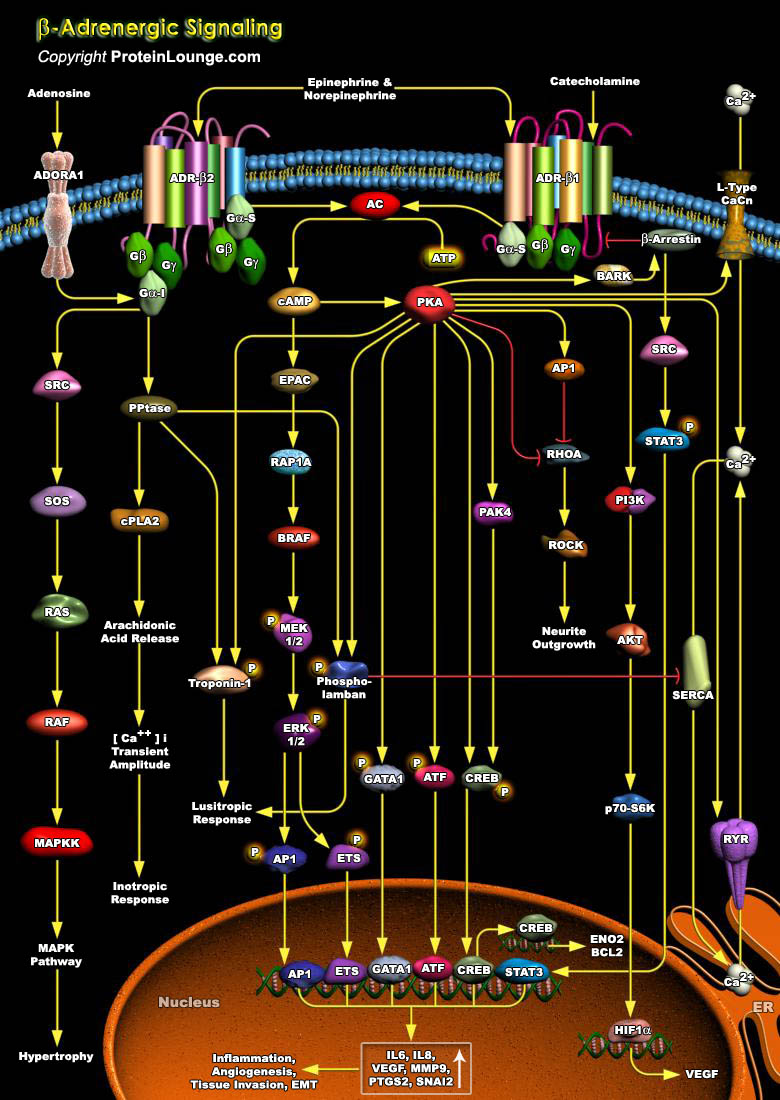
The rate and strength of beating of the heart is under the reciprocal control of the Adrenergic (sympathetic) and Cholinergic (parasympathetic) systems. Increased strength (inotropy) in cardiac beating in response to hormones like the blood-borne Epinephrine or to neurally delivered Norepinephrine is mediated by ADR-Beta (Beta-Adrenergic Receptors) , which are members of the superfamily of[..]
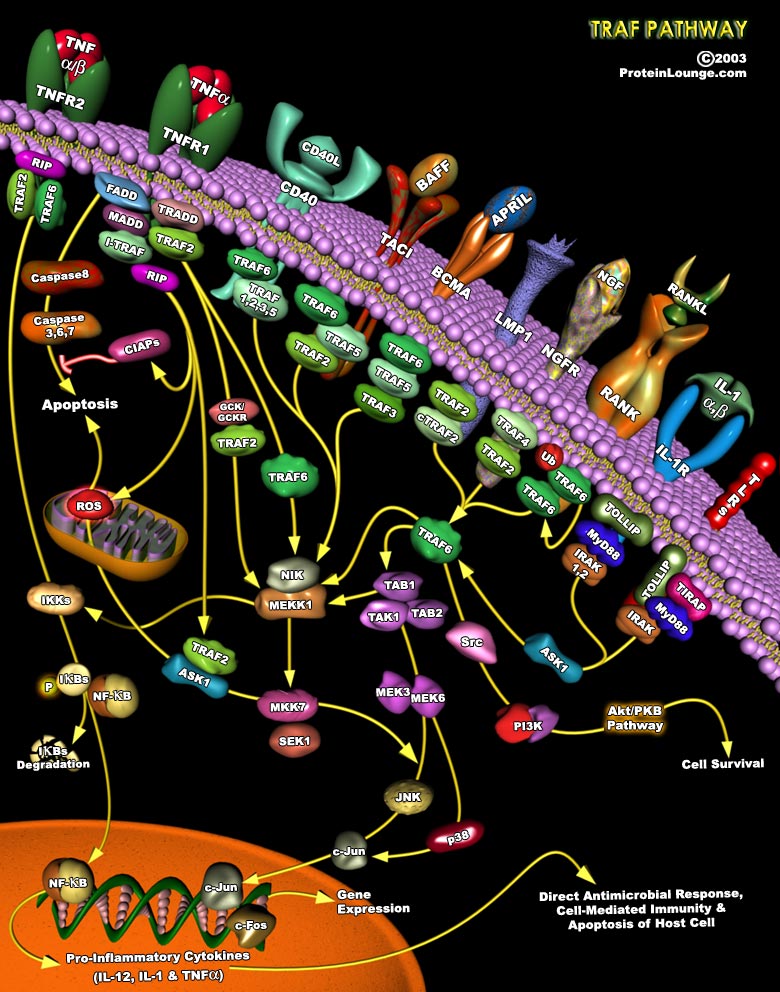
The structural and metabolic integrity of bone is maintained through the dynamic process of bone remodeling those results from the coordinate action of bone resorption and the formation of new bone by osteoblasts. Regulation of bone remodeling occurs through multiple mechanisms that ultimately converge on the interaction of osteoclasts or their precursors with osteoblasts and bone marrow stromal[..]
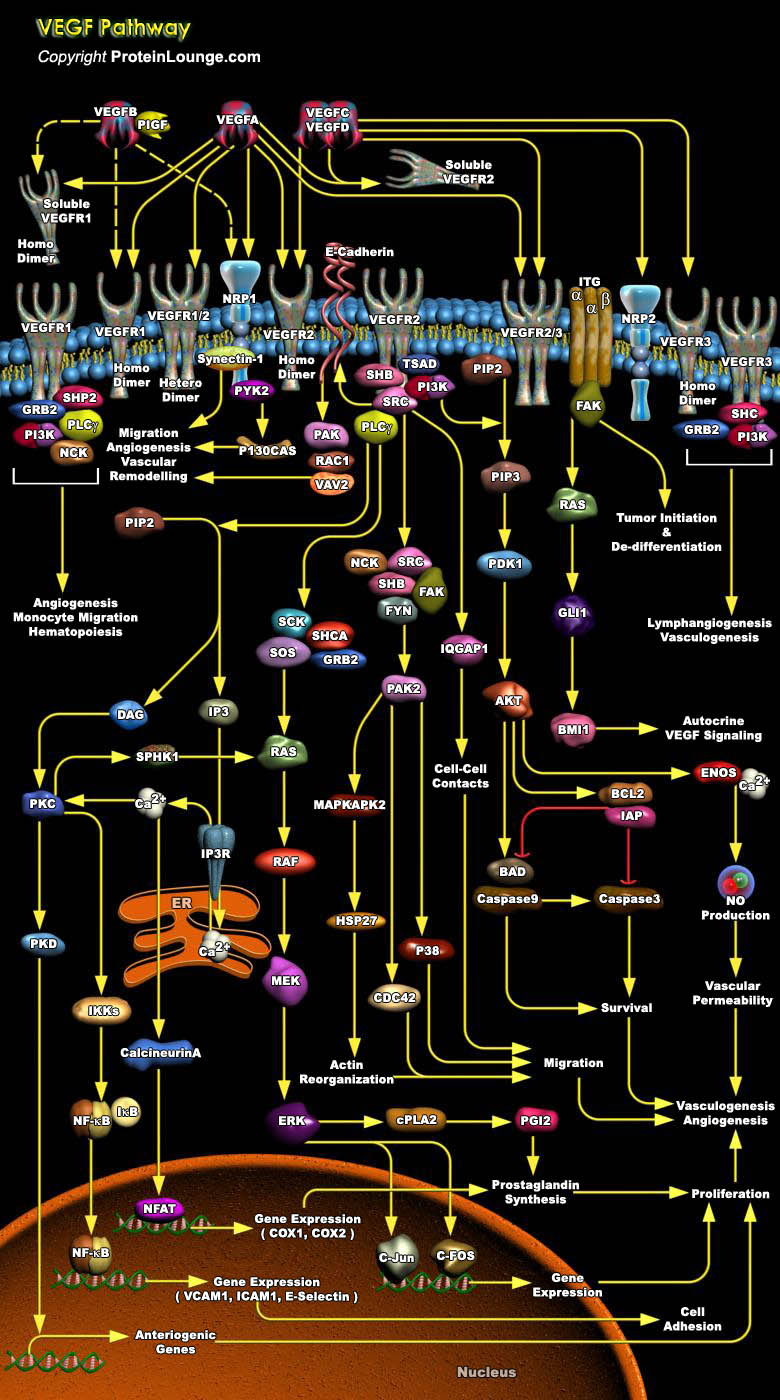
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family of soluble protein growth factors is master regulators of
IL-2 (Interleukin-2) is a T-Cell-derived cytokine important in the regulation of growth and differentiation of T-Cells, B-Cells, natural killer cells, glioma cells, and cells of the monocyte lineage after specifically interacting with its receptors. Human IL-2 is a 133-amino acid polypeptide with a molecular mass of 15-18 kDa. IL-2 signaling is mediated by a multichain receptor complex[..] 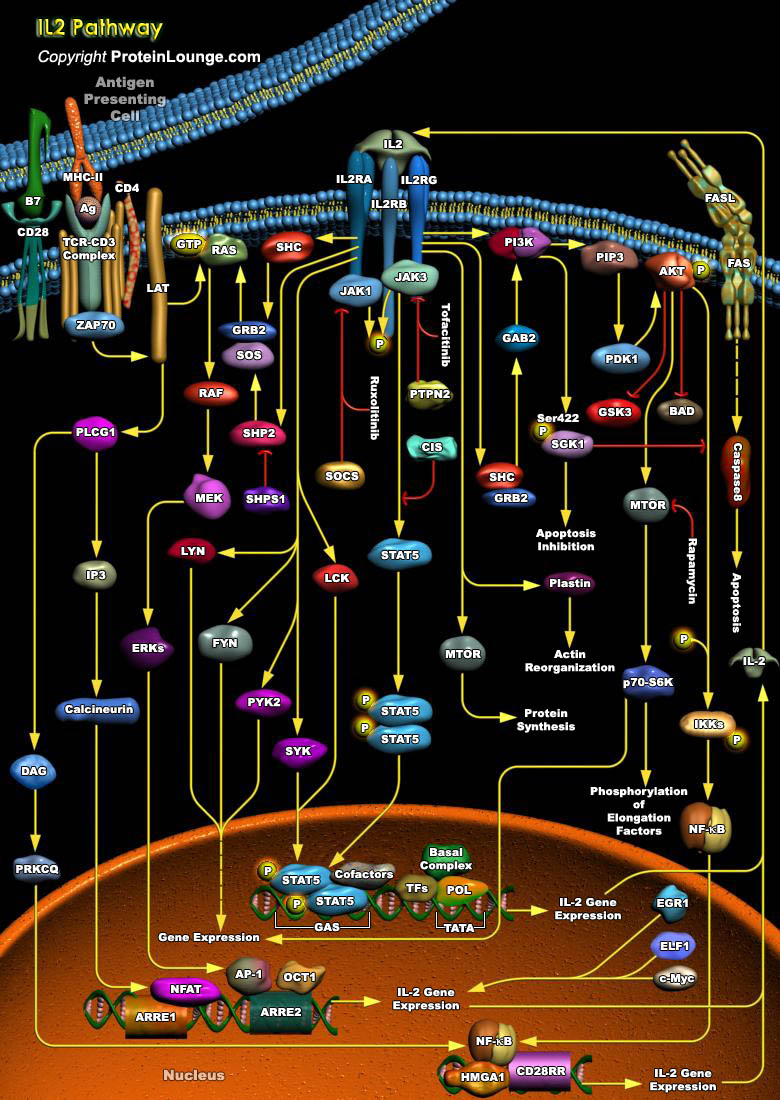
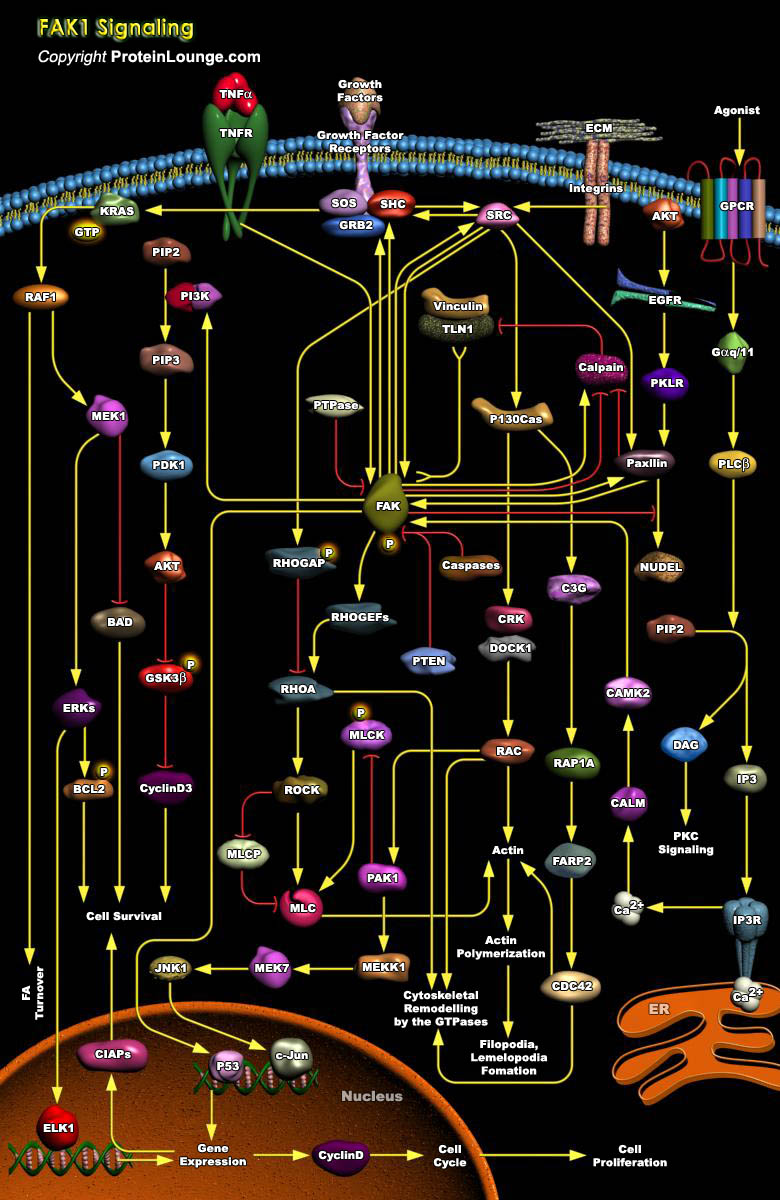
Engagement of integrin receptors with extracellular ligands gives rise to the formation of complex multi-protein structures that link the ECM (Extracellular Matrix) to the cytoplasmic actin cytoskeleton and signaling proteins including Talin, Alpha-actinin, Vinculin, Zyxin, Paxillin and FAK (Focal Adhesion Kinase). These adhesive complexes are dynamic, often heterogeneous[..]
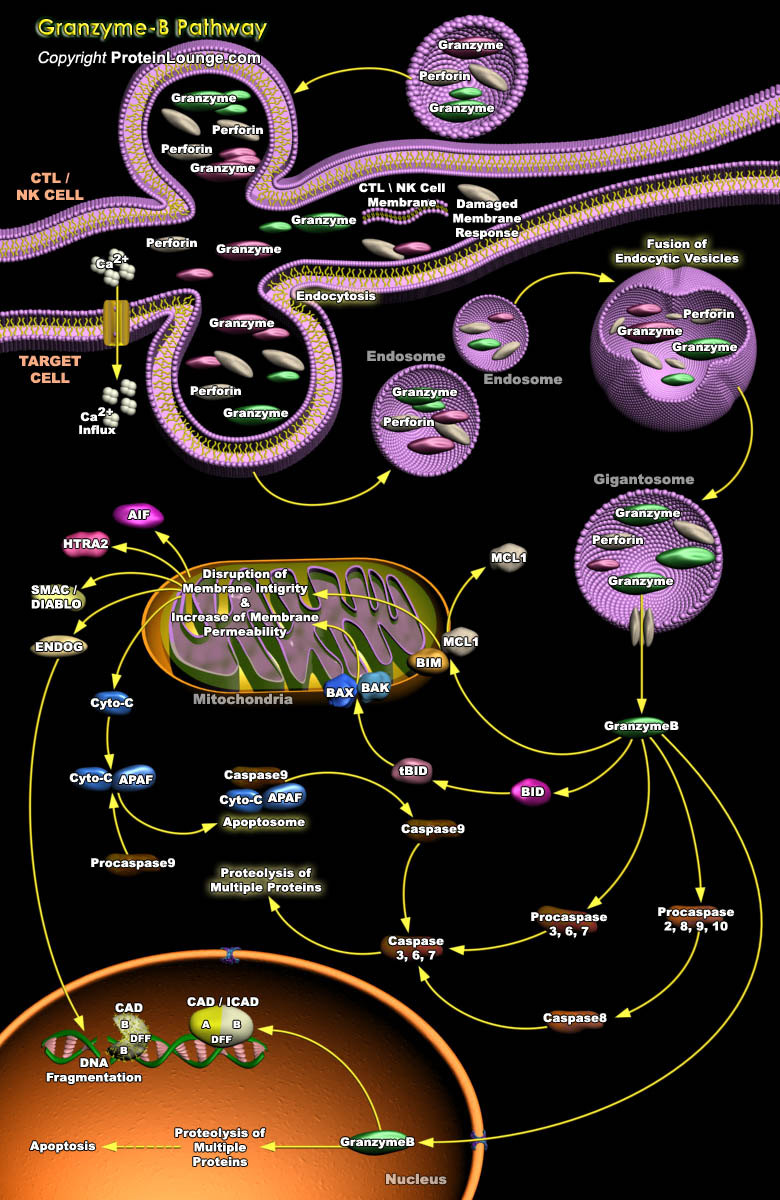
CTLs (Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes) and NK (Natural Killer) cells are the key immune effectors that eradicate infected cells or tumors. To destroy these targets, CTLs and NK cells mostly use the granule exocytosis pathway, which releases perforin and Granzymes from cytolytic granules into the immunological synapse formed with the target. Granzyme-A and Granzyme-B, the most abundant Granzymes,[..]