Featured Pathways
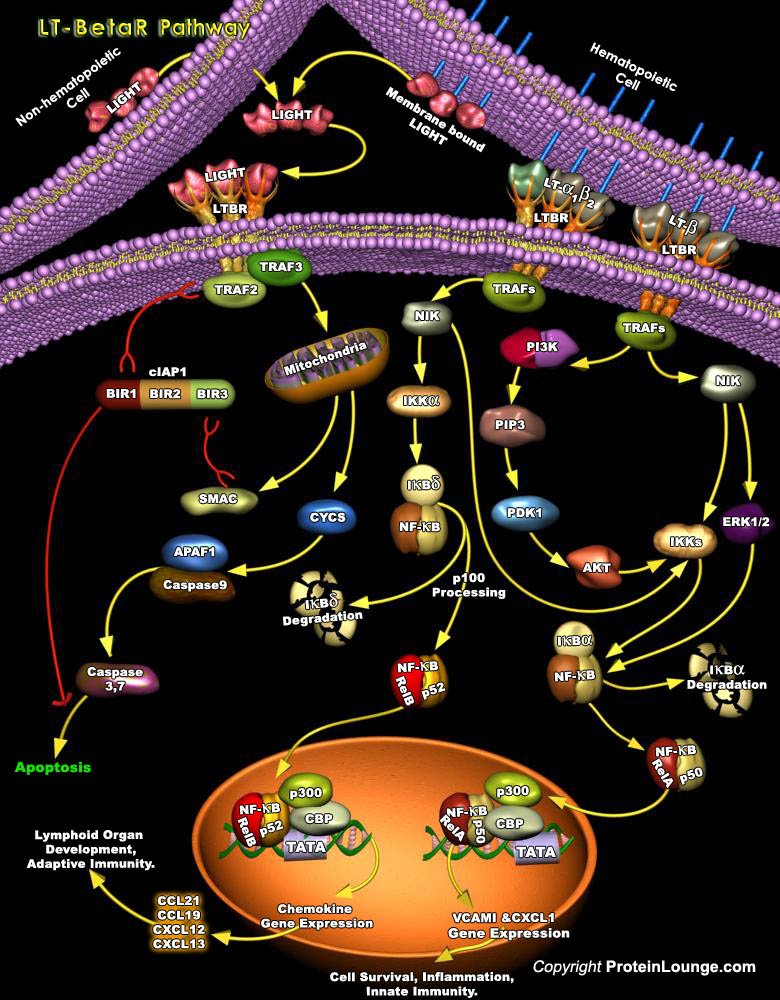
Much of the efficiency of the immune system is attributed to the high degree of spatial and temporal organization in the secondary lymphoid organs. Signaling through the LT-BetaR (Lymphotoxin-Beta Receptor) pathway is a crucial element in the maintenance of this organised microenvironment (Ref.1). LT-BetaR, a member of the TNFR (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor) superfamily, plays[..]
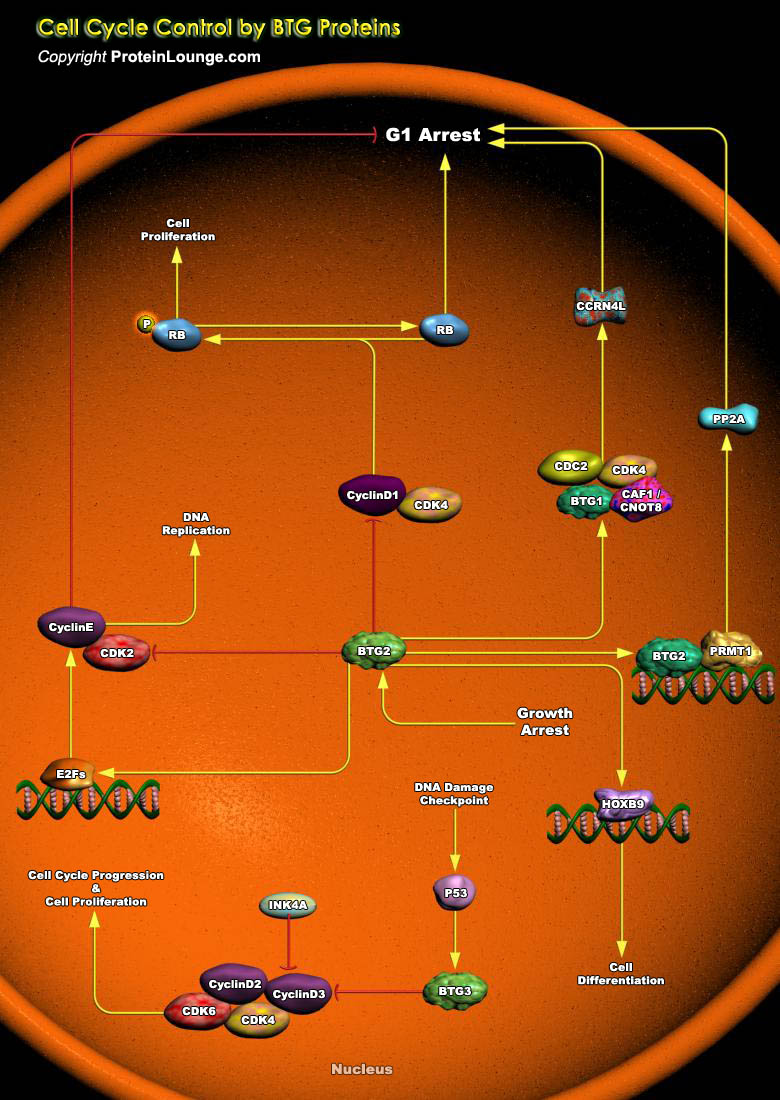
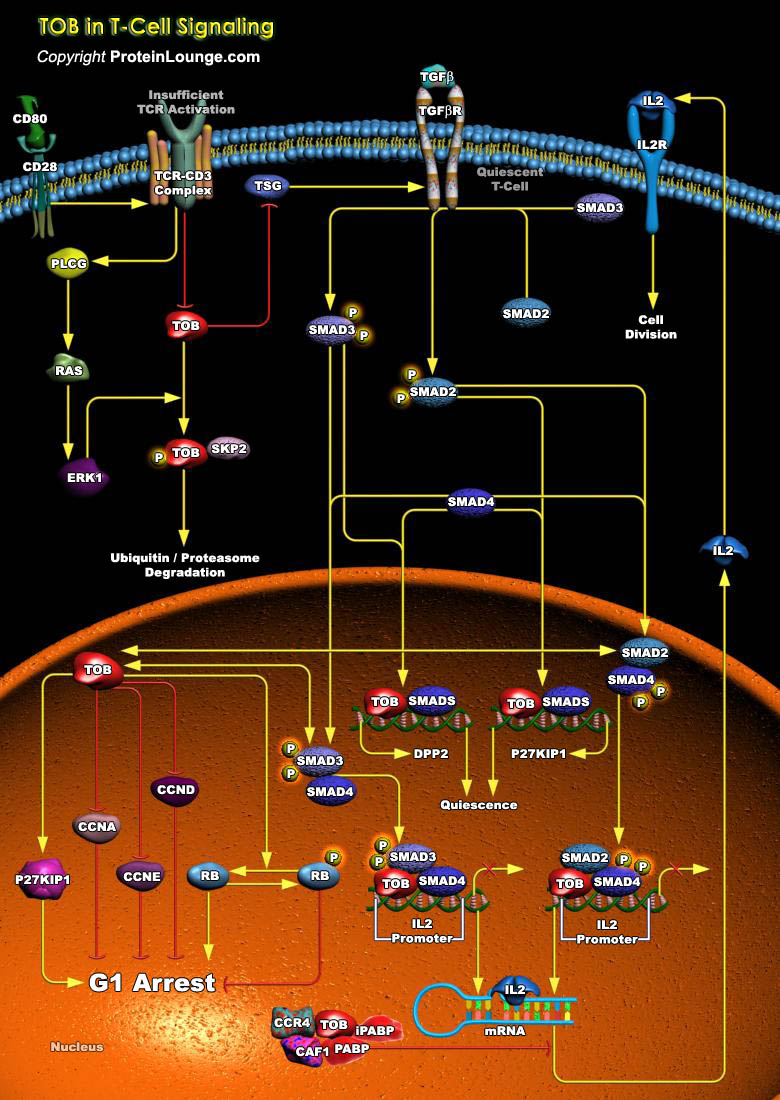
BTG2 (BTG Family Member-2) is endowed with antiproliferative activity. The expression of BTG2 in cycling cells induces accumulation of hypophosphorylated, growth-inhibitory forms of Rb (Retinoblastoma) and led to G1 arrest through impairment of DNA synthesis. Overexpression of CcnD1 (Cyclin-D1) counteracts G1 arrest. Rb is a nuclear phosphoprotein whose phosphorylation state oscillates[..]
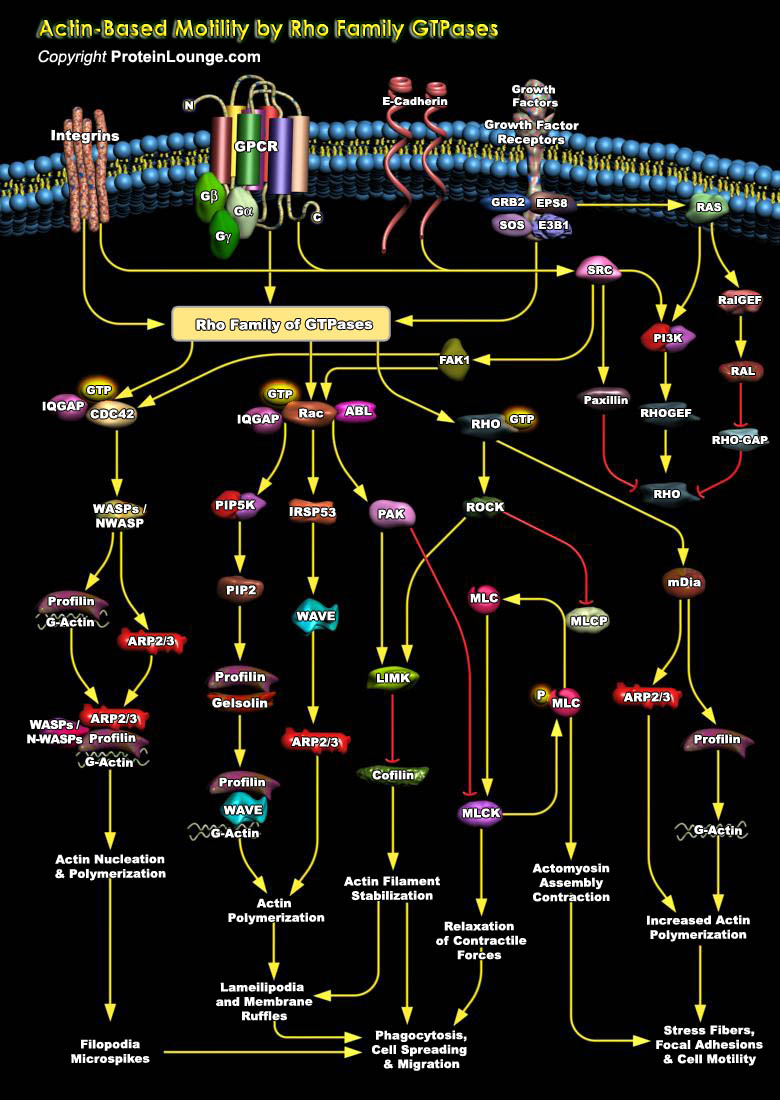
In response to a variety of extracellular stimuli, actin filament assembly at the leading edge of motile cells causes protrusion during cell crawling and chemotaxis, nerve growth and cell spreading. The actin filament network immediately under the plasma membrane in regions of rapid cellular protrusion consists of short, branched filaments while those deeper in the cortex, as well as at[..]
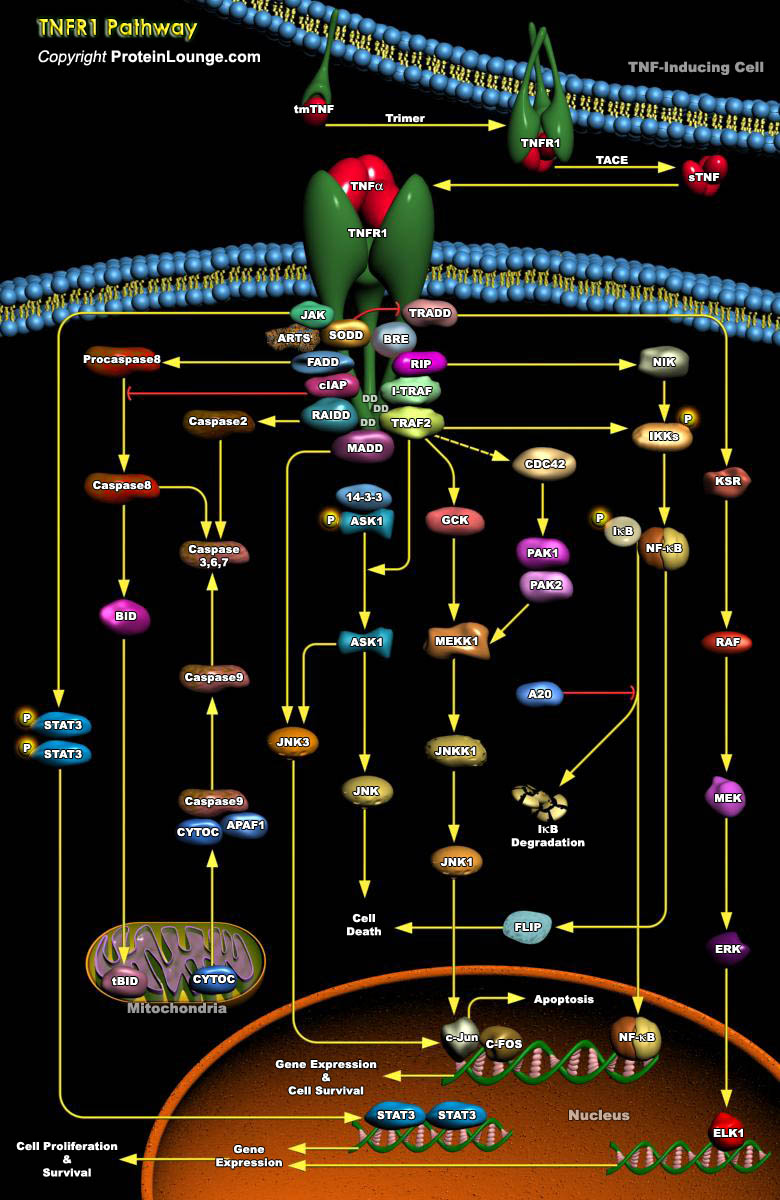
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine with the capacity to induce apoptosis. It is enriched in the tumor microenvironment, promotes tumor growth and subverts innate immune responses to cancer cells. TNF is the best studied member of the TNF superfamily. TNF-alpha can bind to two related receptors, TNF receptors 1 and 2 (TNFR1 and TNFR2), which are also used by other,[..]
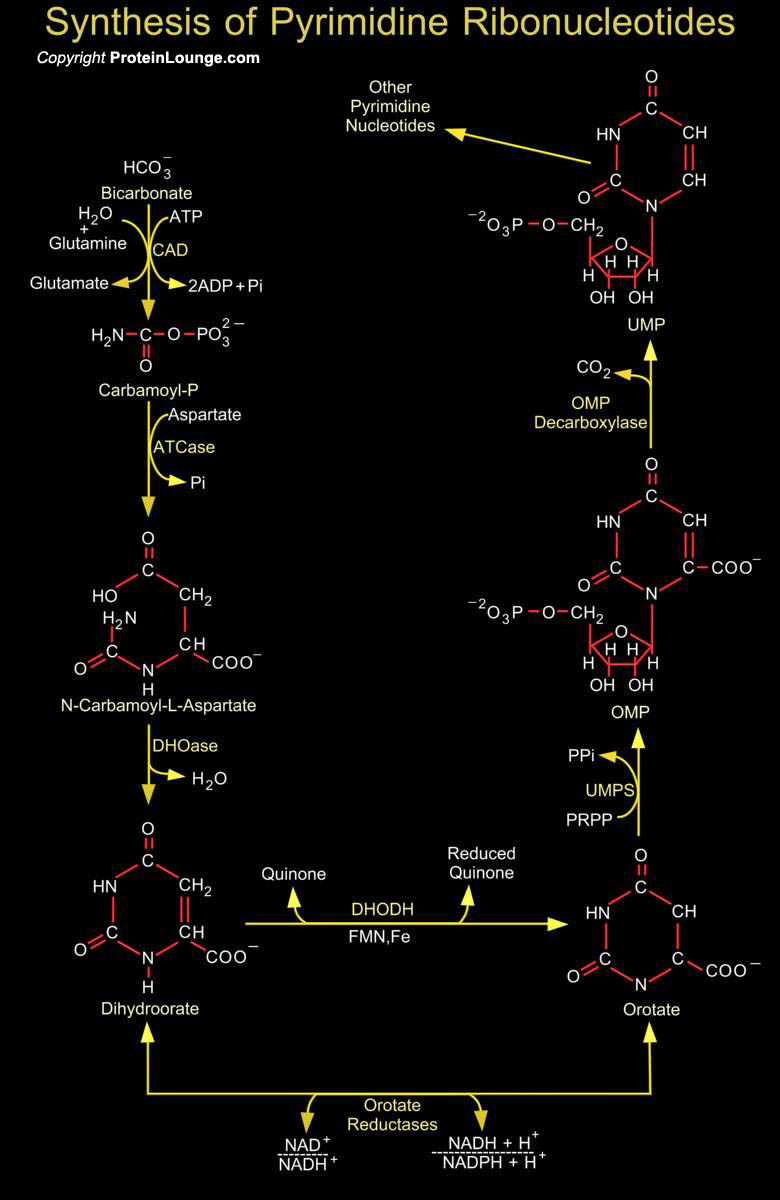
Synthesis of the Pyrimidines is less complex than that of the Purines, since the base is much simpler. Synthesis of Carbamoyl-P (Carbamoyl Phosphate) is the first reaction of Pyrimidine biosynthesis. Carbamoyl-P is formed from HCO3- (Bicarbonate) and the amide nitrogen of Glutamine by the cytosolic enzyme CPSase (Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase). This reaction consumes two molecules of ATP[..]
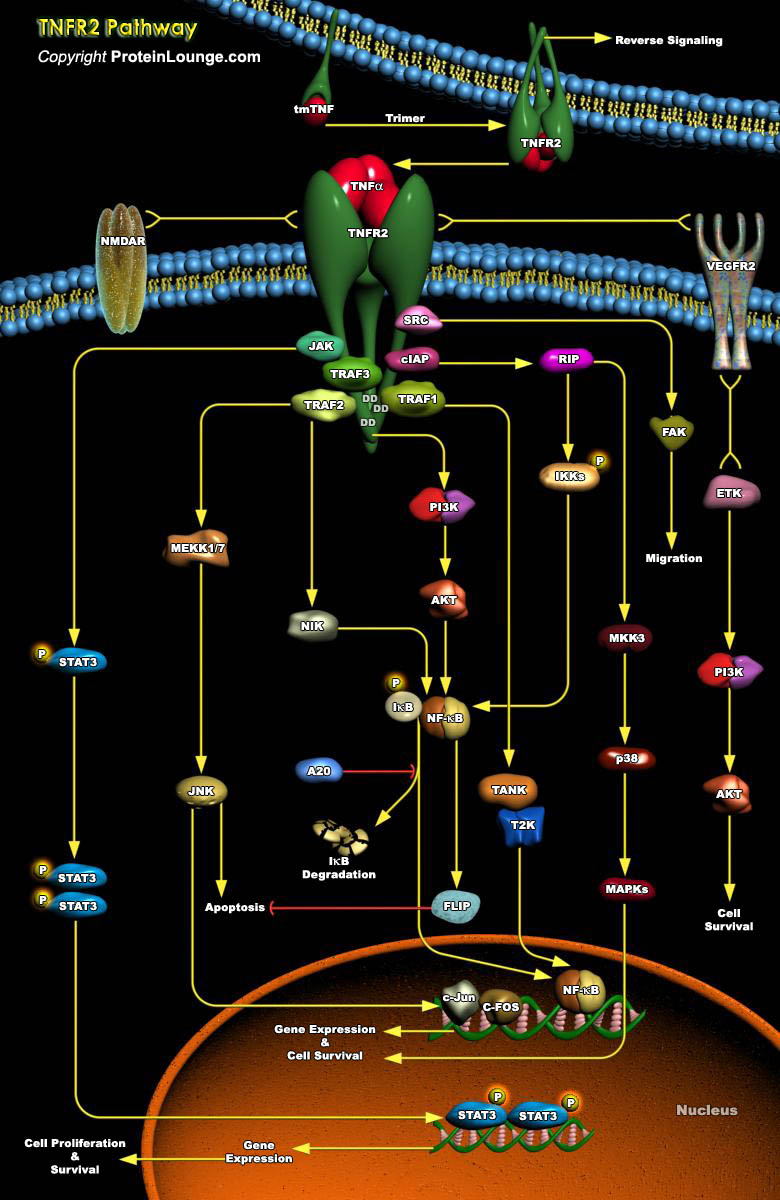
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine with the capacity to induce apoptosis. It is enriched in the tumor microenvironment, promotes tumor growth and subverts innate immune responses to cancer cells. TNF is the best studied member of the TNF superfamily. TNF-alpha can bind to two related receptors, TNF receptors 1 and 2 (TNFR1 and TNFR2), which are also used by other,[..]
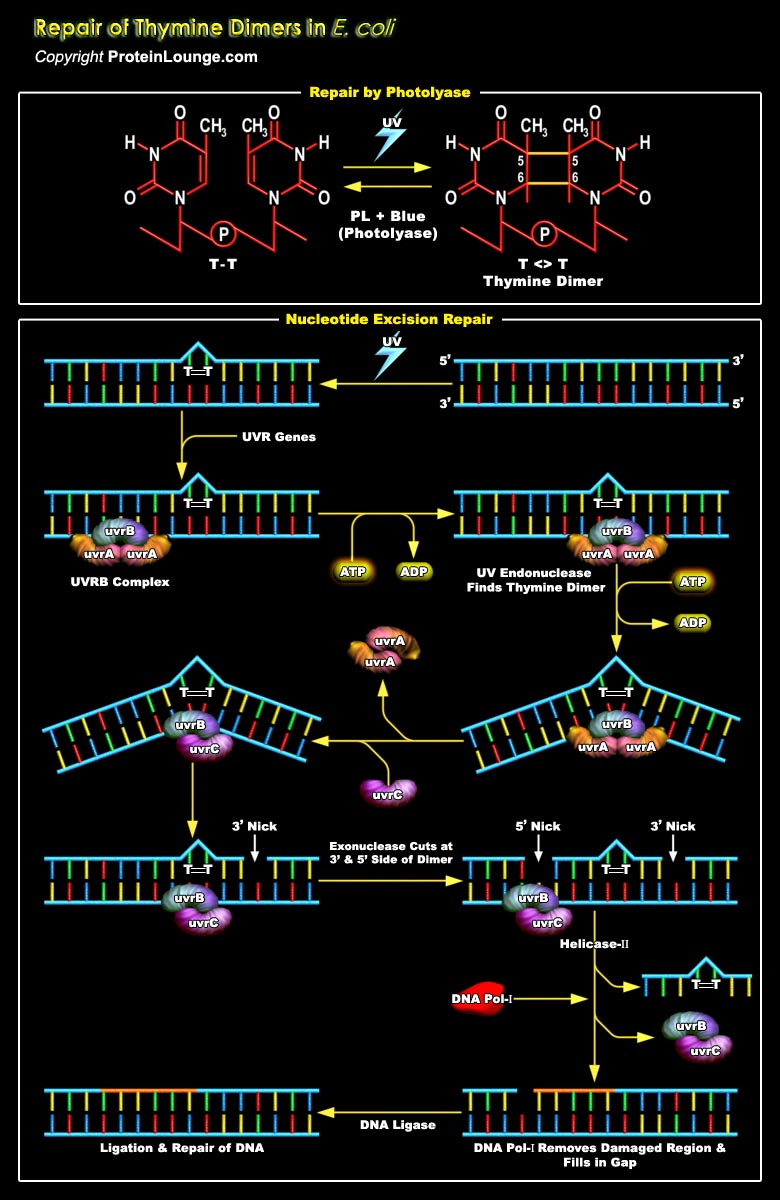
UV radiation induces two of the most abundant mutagenic and cytotoxic DNA lesions such as CPD (Cyclobutane-Pyrimidine Dimers) or 6-4PPs (6-4 Pyrimidine Pyrimidone). The most common covalently linked adjoining pyrimidines are TT(Thymine dimers), T-C (Thymine-Cytosine dimers) and C-C (Cytosine-Cytosine dimers). T-T dimers cause kinks in the DNA strand that prevent both[..]
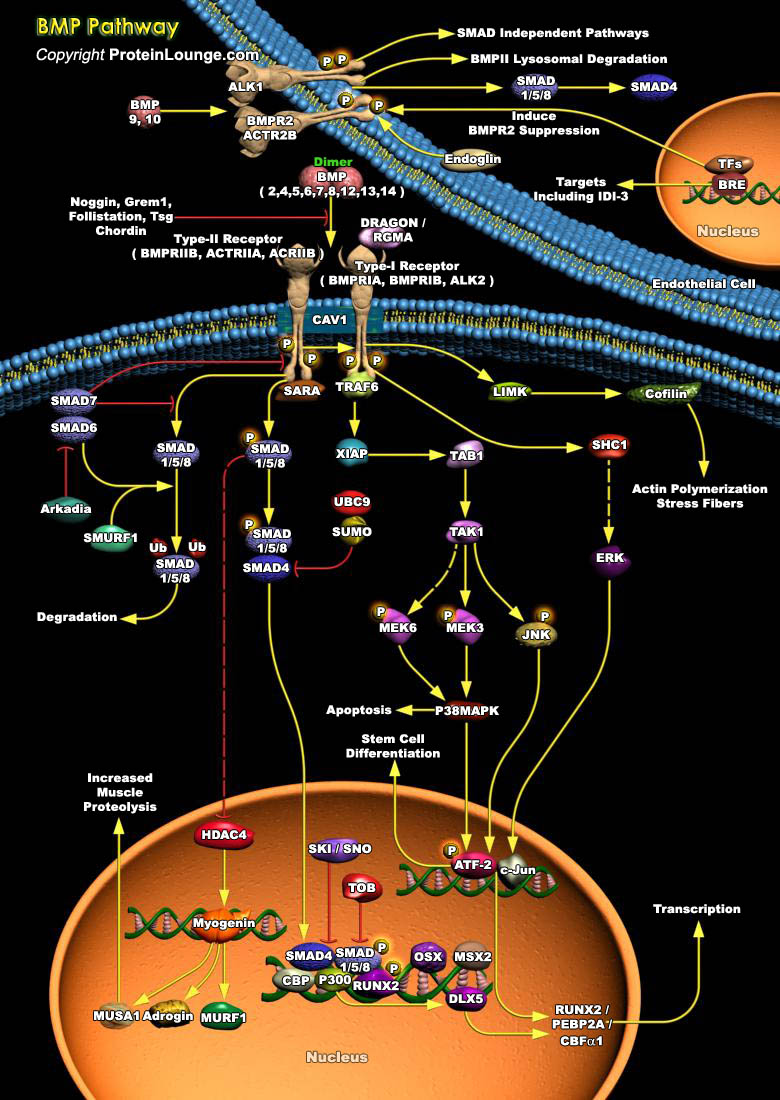
BMPs (Bone morphogenetic proteins) are the members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily of secreted signaling molecules [Ref.1]. Transduction of BMP signal involves two types of transmembrane serine/threonine kinase receptors: type I and type II [Ref.1]. BMP2, BMP4, BMP5,BMP6, BMP7, BMP8, BMP9, BMP10, BMP12, BMP13 and BMP14 (Bone morphogenetic protein 2, 4, 5, 6 ,7, 8, 9, 10, 12,[..]
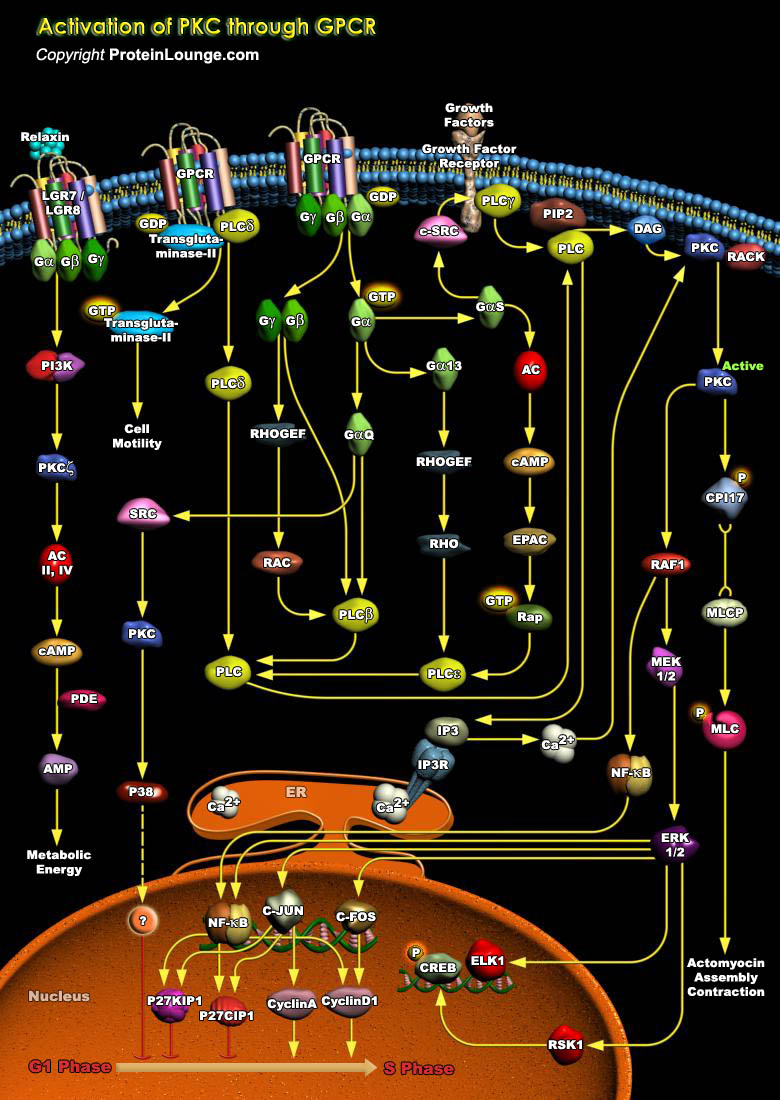
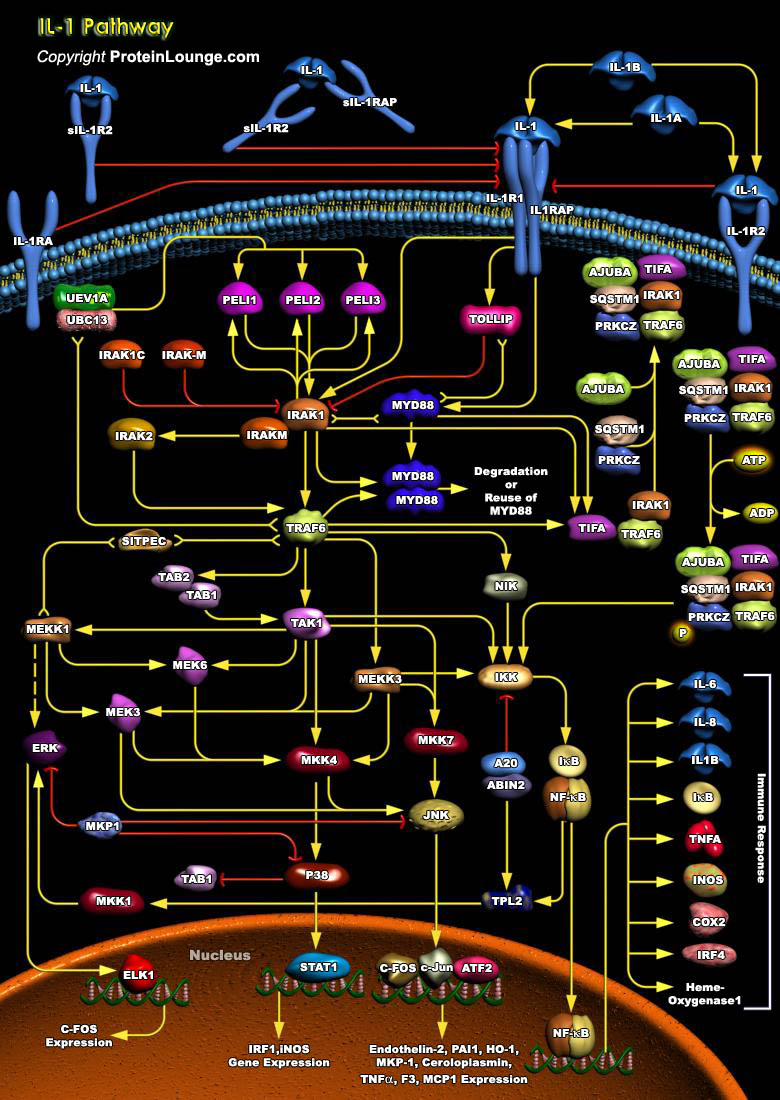
PKC (Protein Kinase-C) is a cyclic nucleotide-independent enzyme that phosphorylates serine and threonine residues in many target proteins. PKC plays a pivotal role in mediating cellular responses to extracellular stimuli involved in proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and exocytotic release in a number of non-neuronal systems such as Islet cells, Chromaffin cells and Paramecium. PKC has[..]
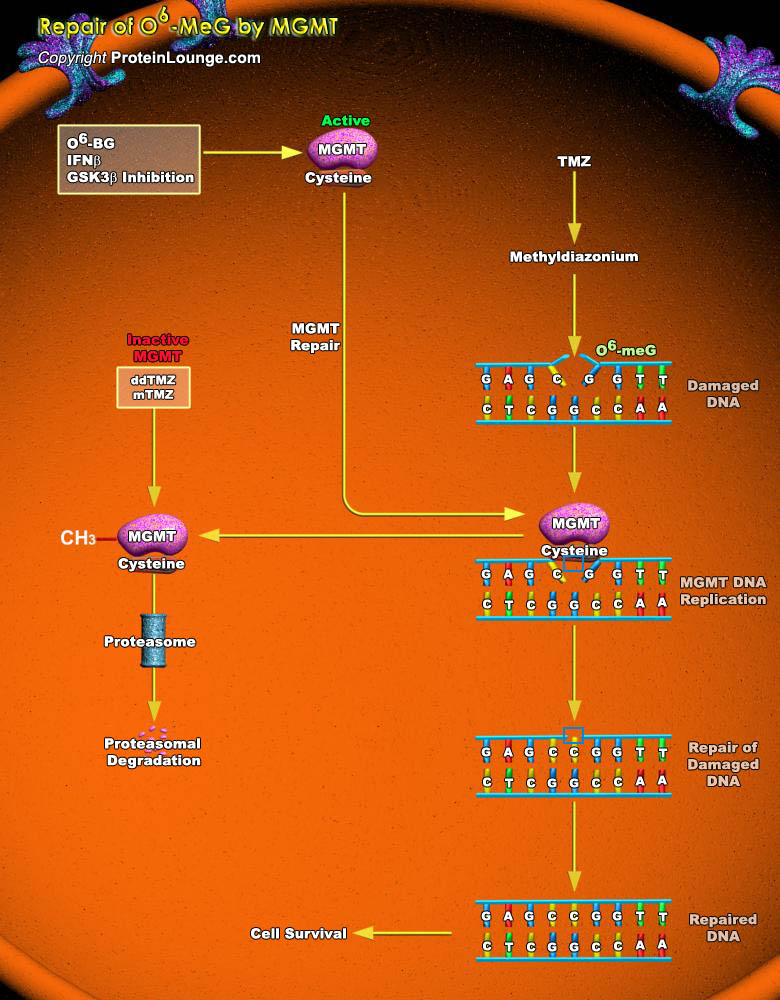
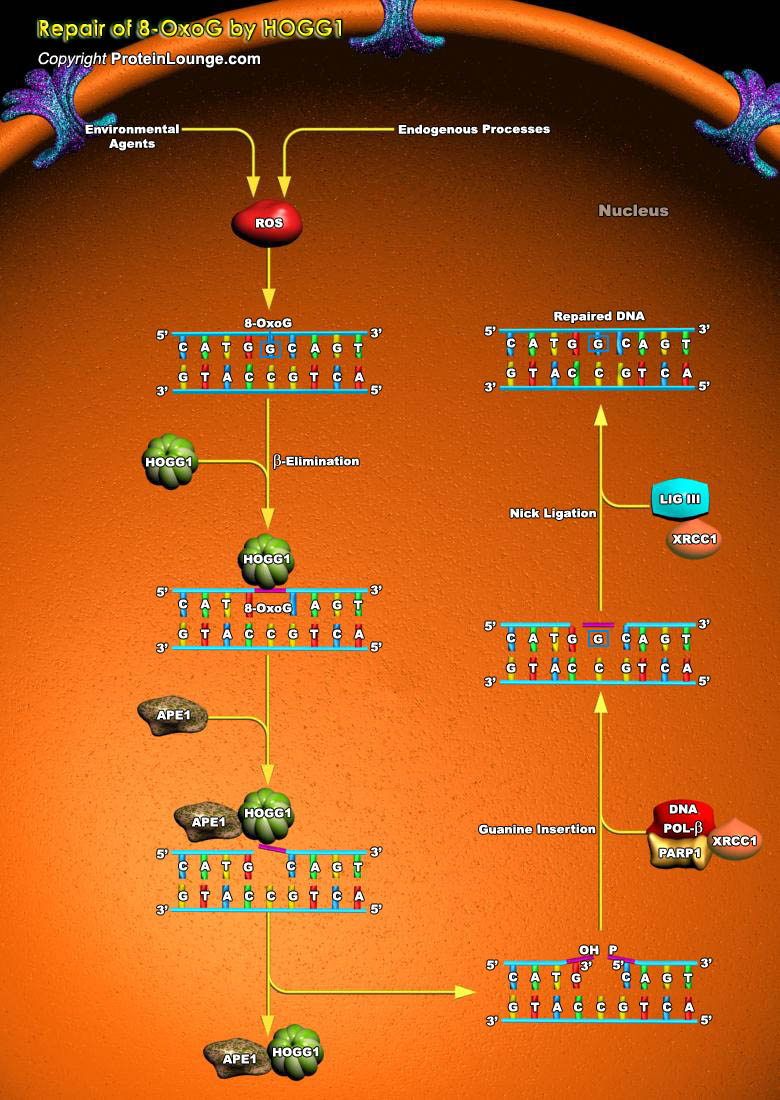
Alkylating agents are compounds that cause cytotoxic DNA damage as well as collateral mutagenic damage. They work by adding an alkyl group to the guanine base of the DNA molecule and cause breakage of DNA strands. Methylation at the guanine O6 position forms the greatest promutagenic and lethal toxic DNA lesion. O(6)-methylguanine (O6-meG) is formed in DNA by alkylation of the oxygen[..]
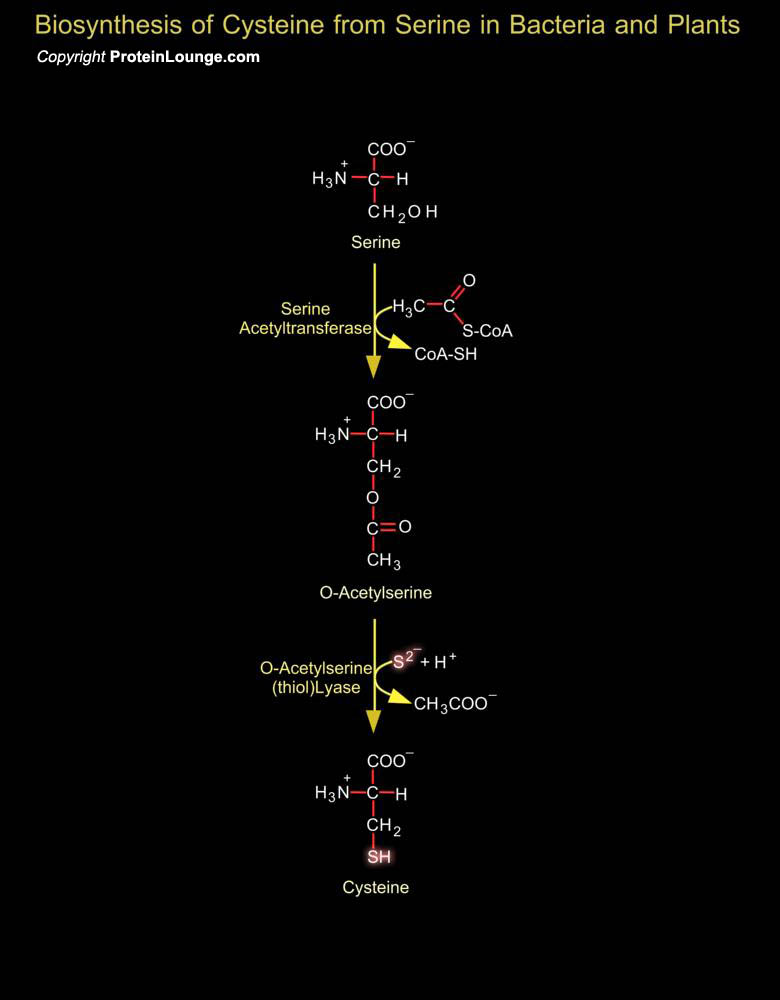
Inorganic sulfur in the environment (primarily sulfate, but also sulfur, and sulfite) must undergo fixation to be utilized by organisms. The fixation of sulfate is largely confined to plants and bacteria and biosynthesis of cysteine represents the final step of sulfate assimilation in these organisms. Fixation begins with the formation of PAPS (3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-Phosphosulfate).[..]
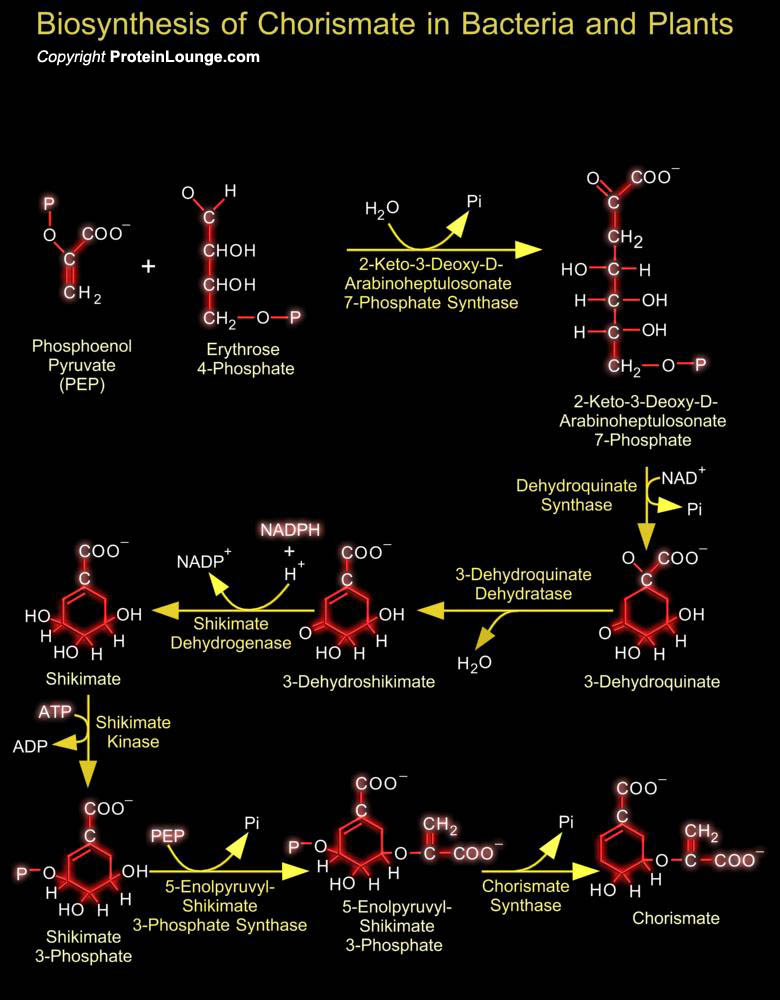
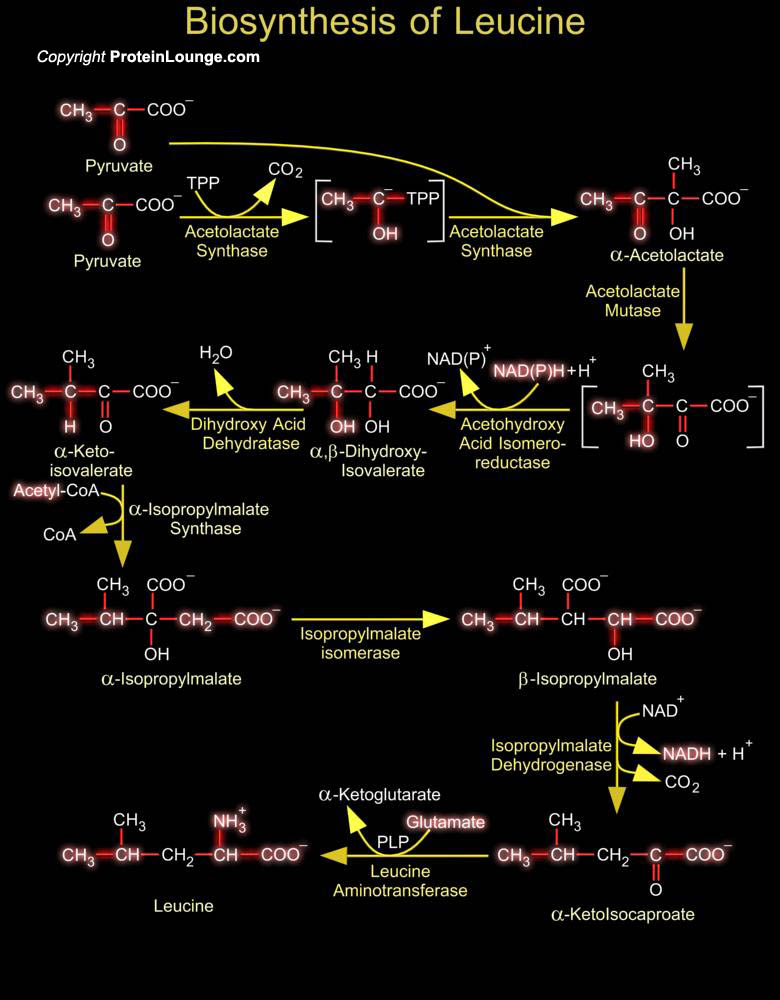
In micro-organisms and plants the biosynthesis of aromatic compounds proceeds via the common seven-step aromatic or shikimate pathway to the branch point intermediate chorismate. This intermediate is subsequently converted to the three aromatic amino acids via specific terminal pathways. Many other aromatic compounds are derived either partially or entirely from chorismate or from other[..]