Featured Pathways
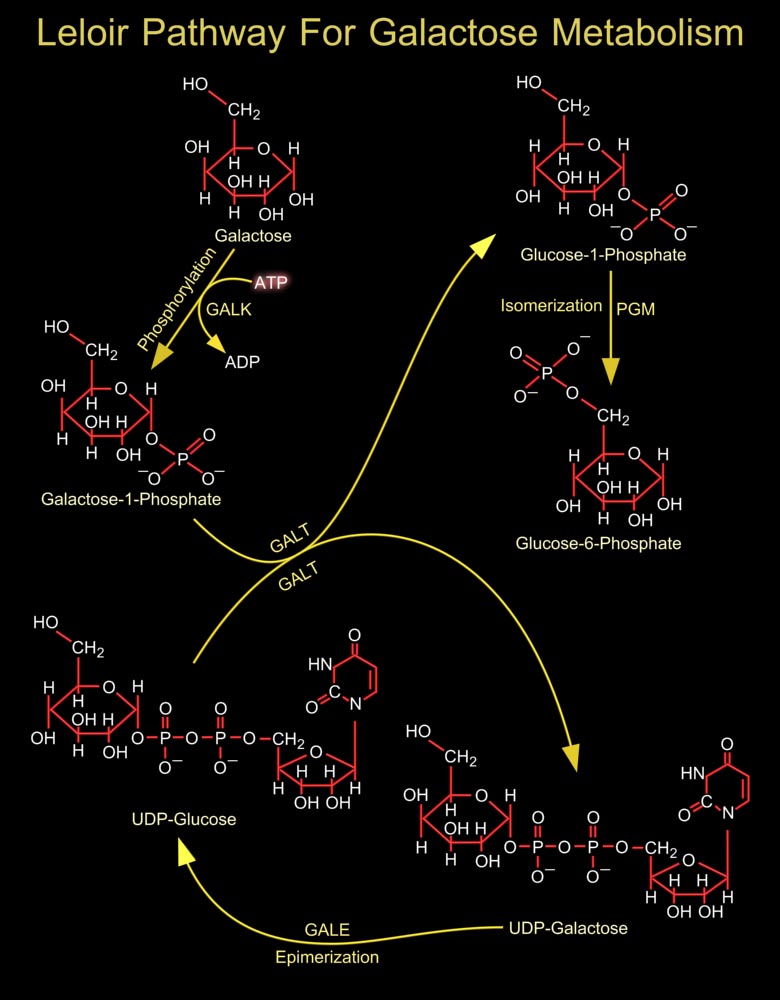
In most organisms, the conversion of Galactose to the more metabolically useful Glucose-1-Phosphate is accomplished by the action of four enzymes that constitute the Leloir pathway. In the first step of this pathway, Beta-D-Galactose is epimerized to Alpha-D-Galactose by GALM (Galactose Mutarotase/Aldose 1-Epimerase) (Ref.1). The active site of GALM is positioned in a rather open cleft with[..]
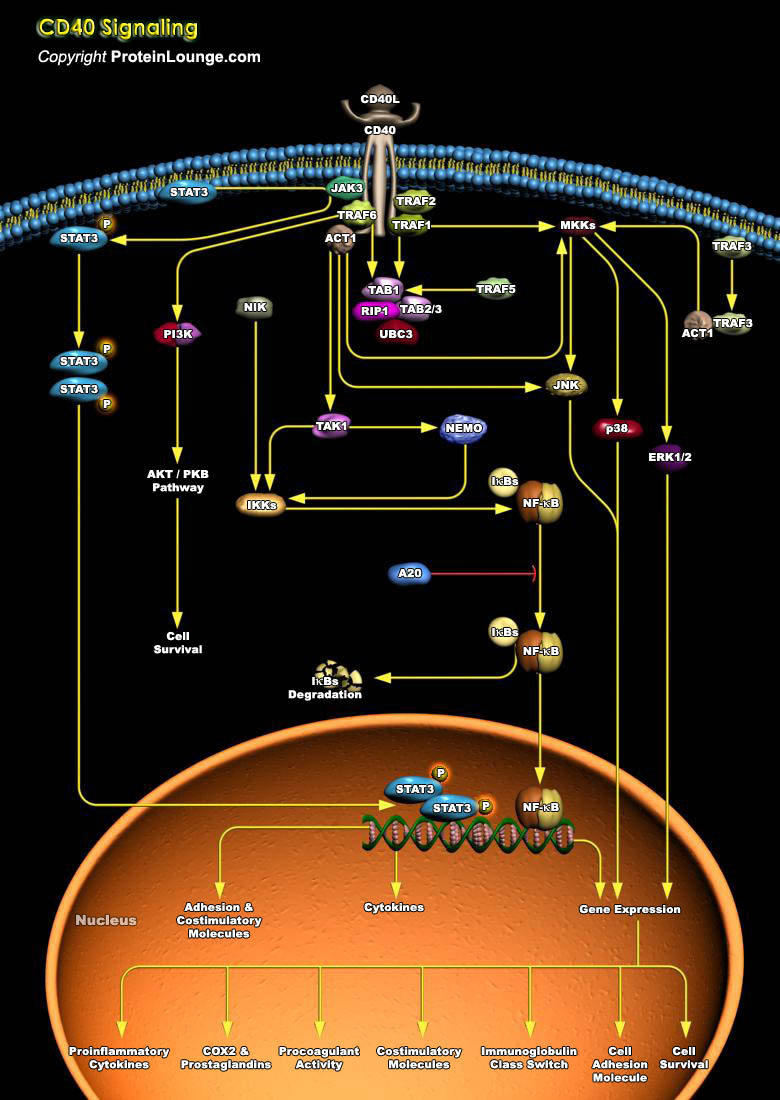
CD40, a TNFR (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor) family member, conveys signals regulating diverse cellular responses, ranging from proliferation and differentiation to growth suppression and cell death. First identified and functionally characterized on B-Cells, CD40 is expressed on a plethora of different cell types, including B-Cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, endothelial cells, and[..]
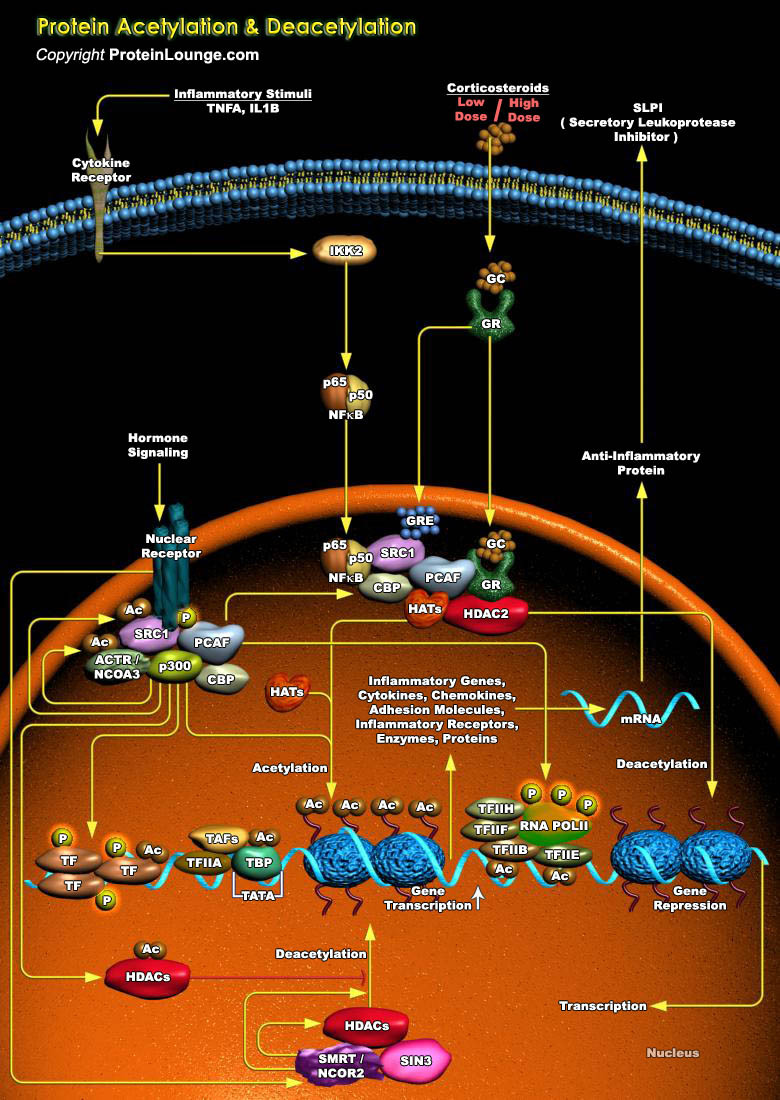
Eukaryotic transcription is a highly regulated process, and acetylation plays a major role in this regulation. Acetylation can occur on histones, DNA-binding TF (Transcription Factors), acetylases, nuclear import factors, non-nuclear proteins (Alpha-tubulin) and proteins that shuttle from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, such as the Importin-Alpha family of nuclear import factors. Acetylation can[..]

The DNA damage response network involves several kinases to inactivate CDK/ cyclin complexes and result in cell cycle arrest for DNA repair. In the presence of DNA damage or incomplete DNA replication, eukaryotic cells activate cell cycle checkpoints that temporarily halt the cell cycle to permit DNA repair or completion of DNA replication to take place. In the presence of extensive damage or[..]
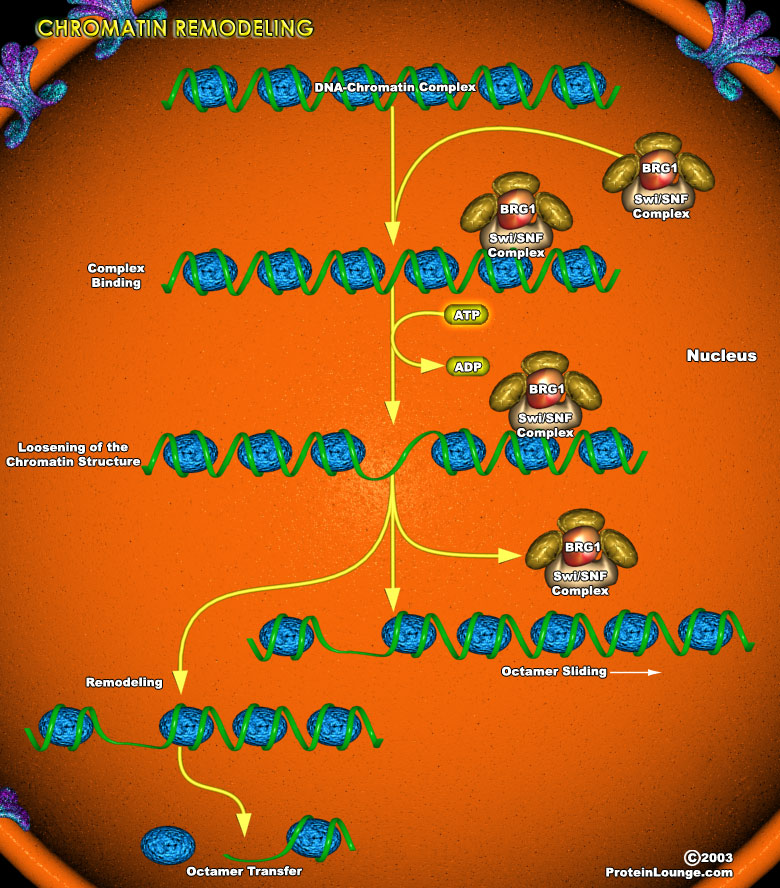
The condensation of DNA into an ordered chromatin structure allows the cell to solve the topological problems associated with storing huge molecules of chromosomal DNA within the nucleus. DNA is packaged into chromatin in orderly repeating protein-DNA complexes called nucleosomes. Each nucleosome consists of approximately 146bp of dsDNA (double-stranded DNA) wound 1.8 times around a histone[..]
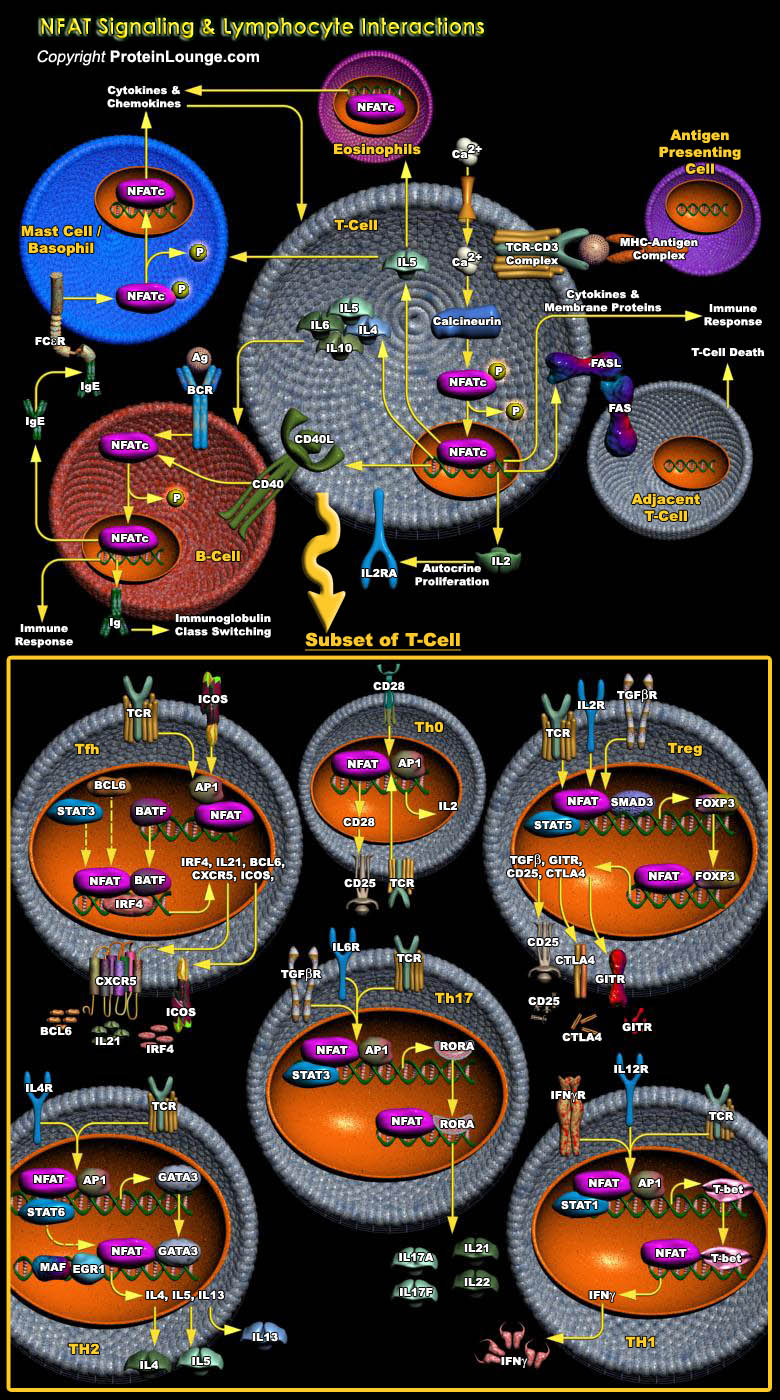
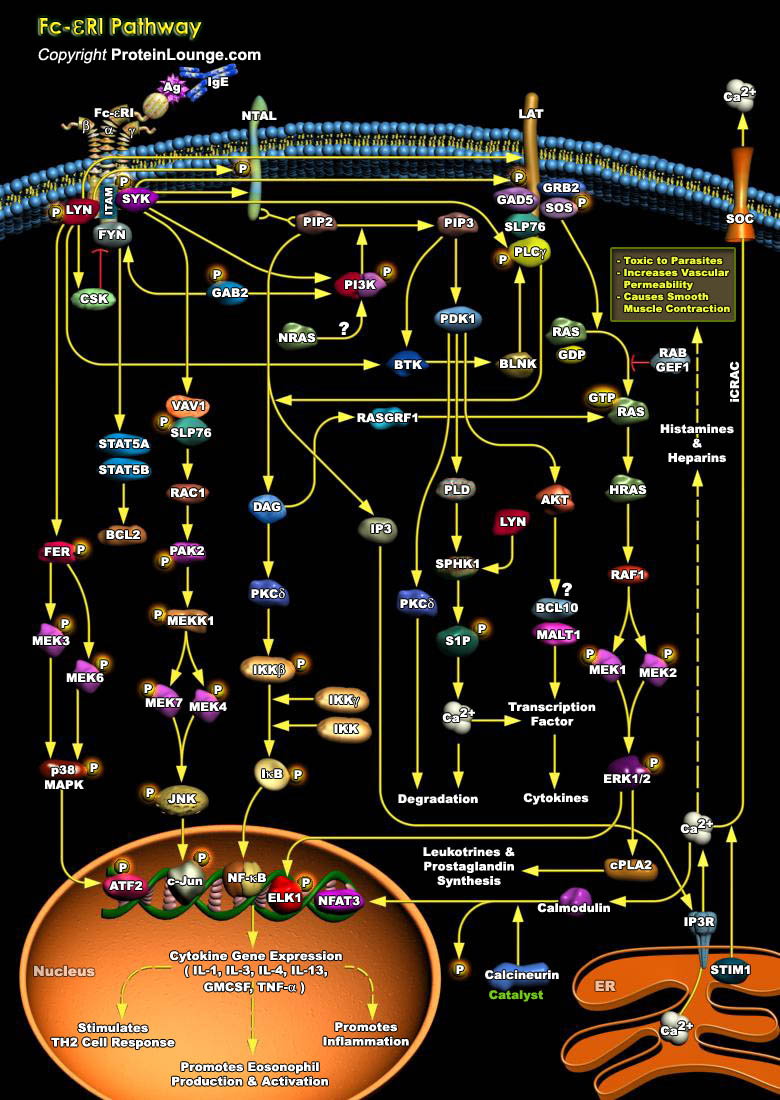
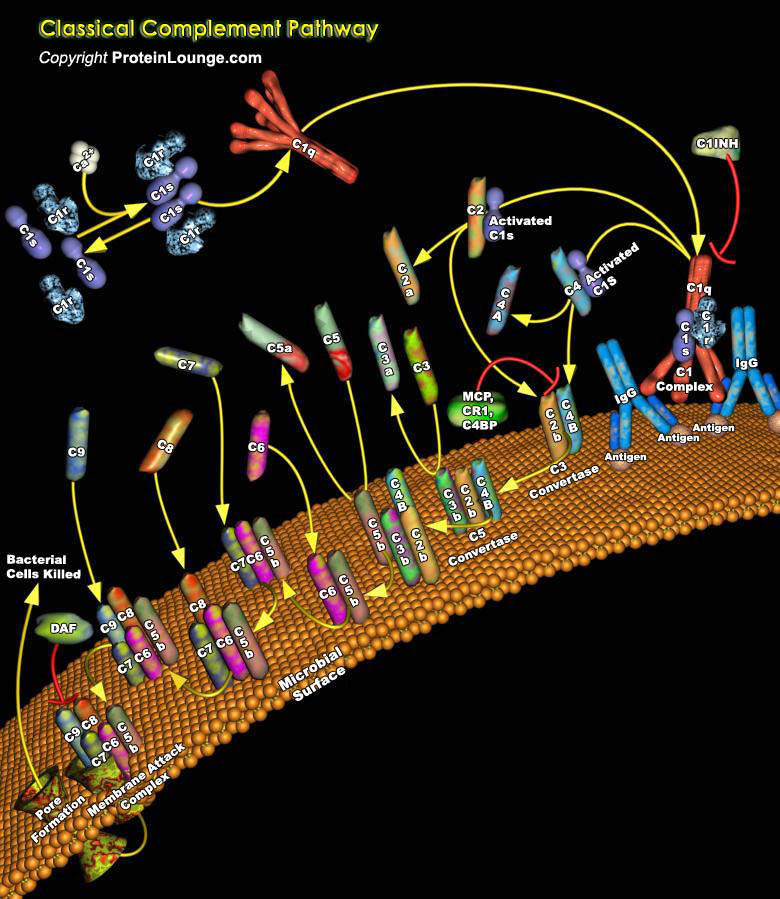
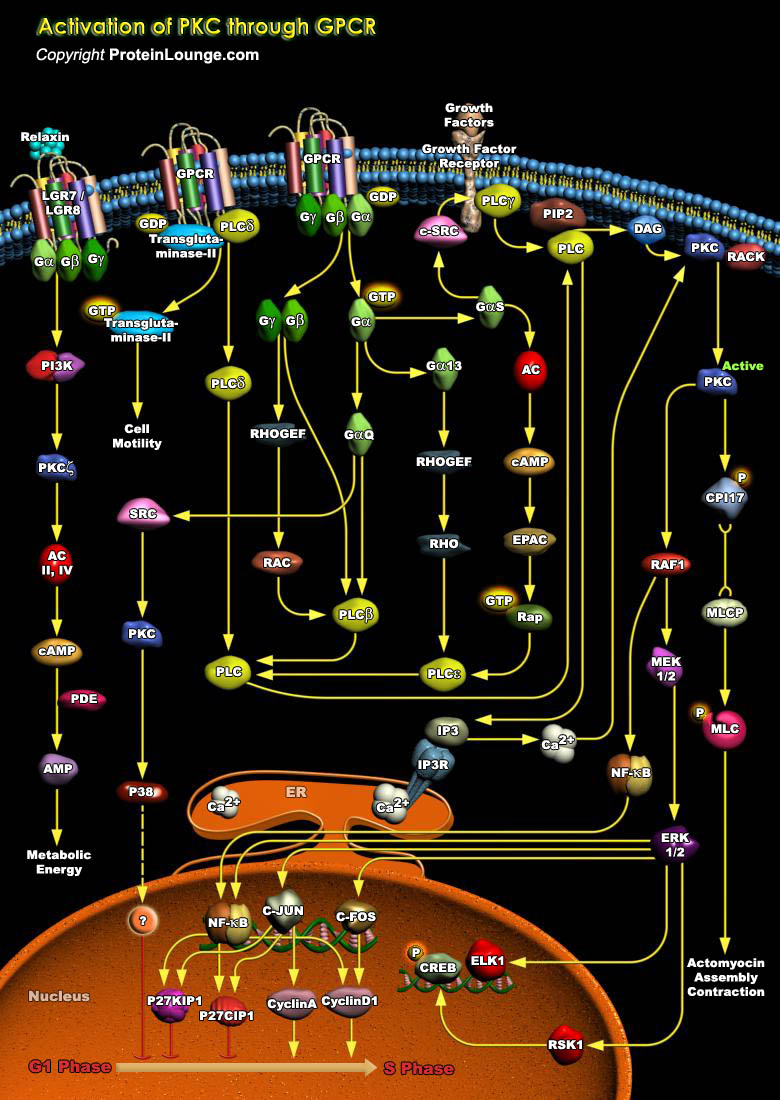
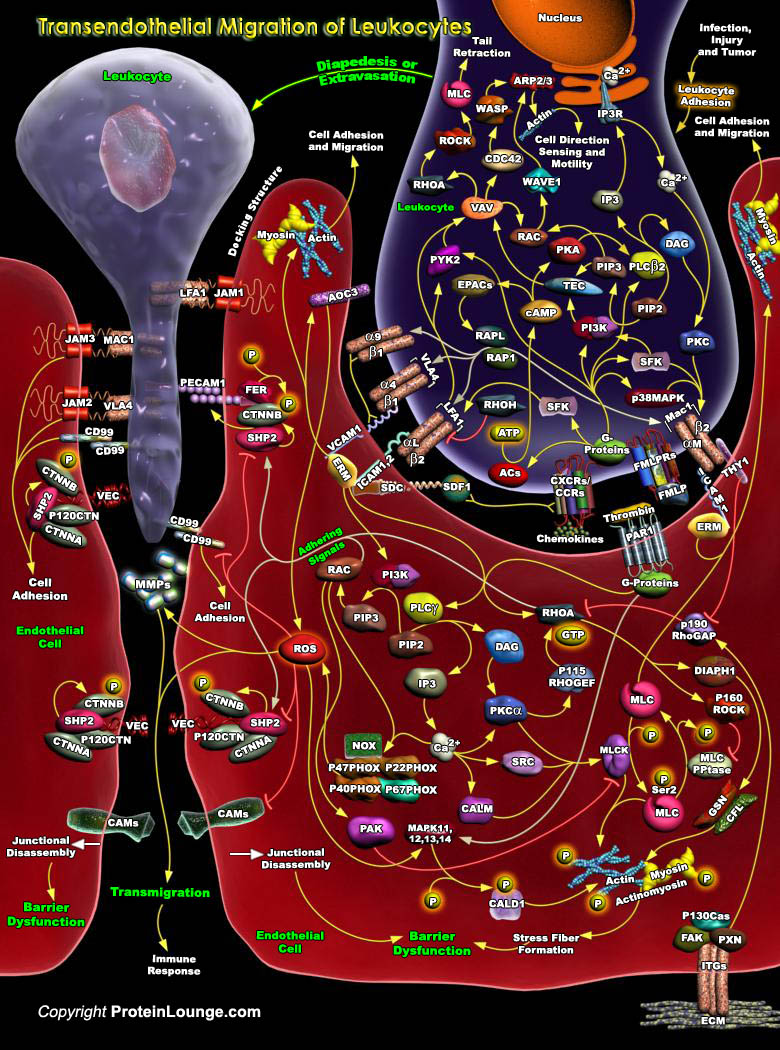
The optimum functioning of the immune system is crucial for human survival. The invading pathogens are encountered by the cells of the immune system, which include T-Cells, B-Cells, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, endothelial cells, or mast cells. These cells have distinct roles in the immune system, and cell-to-cell communication among these cells is an indispensable[..]
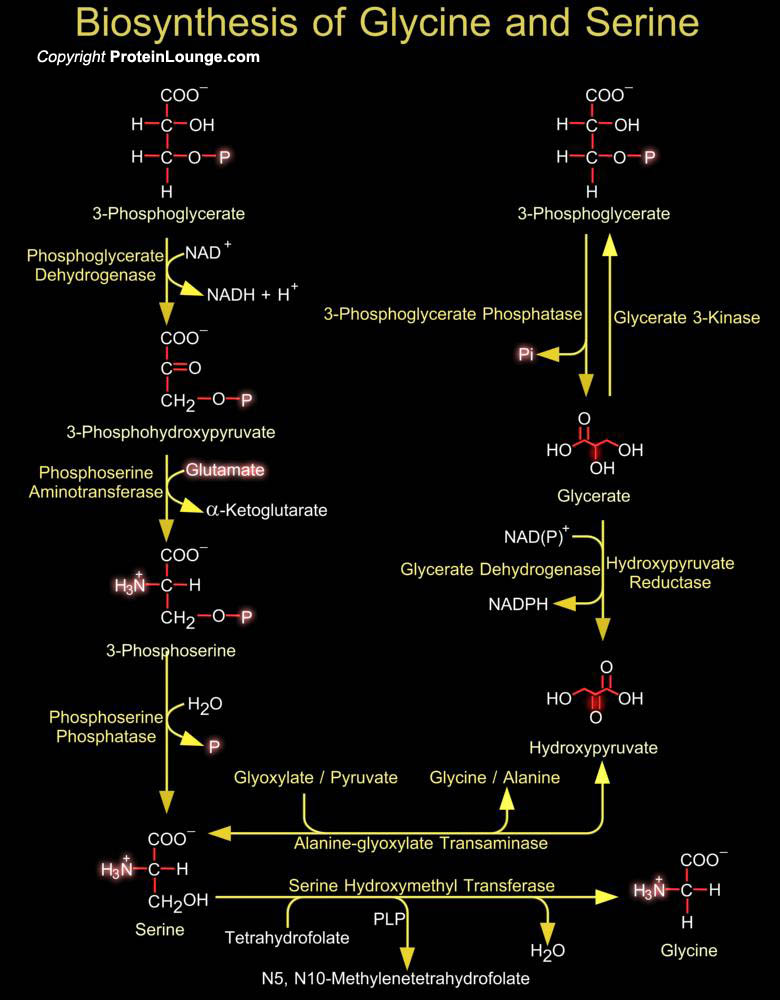
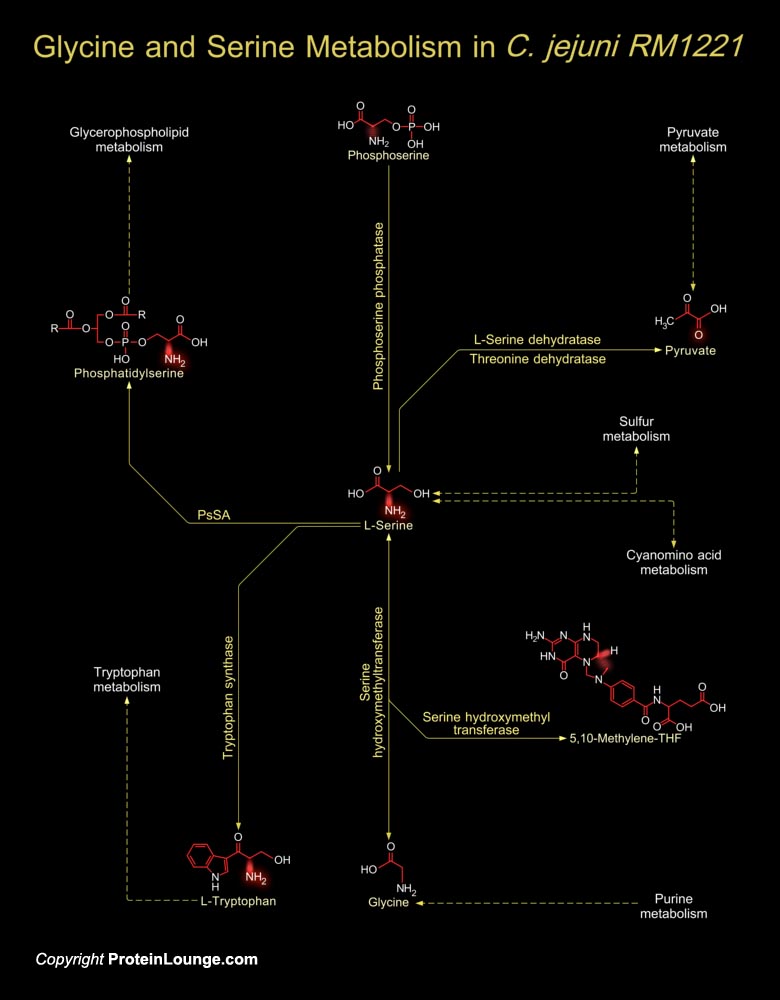
Intermediates in energy production pathways such as glycolysis and the Krebs cycle are commonly the starting point for the biosynthesis of amino acids. The biosynthesis of serine and glycine constitute a major metabolic pathway that plays a central role in the formation of other amino acids, nucleic acids and phospholipids. Serine an ɑ-amino acid used in the biosynthesis of proteins can be[..]