Featured Pathways
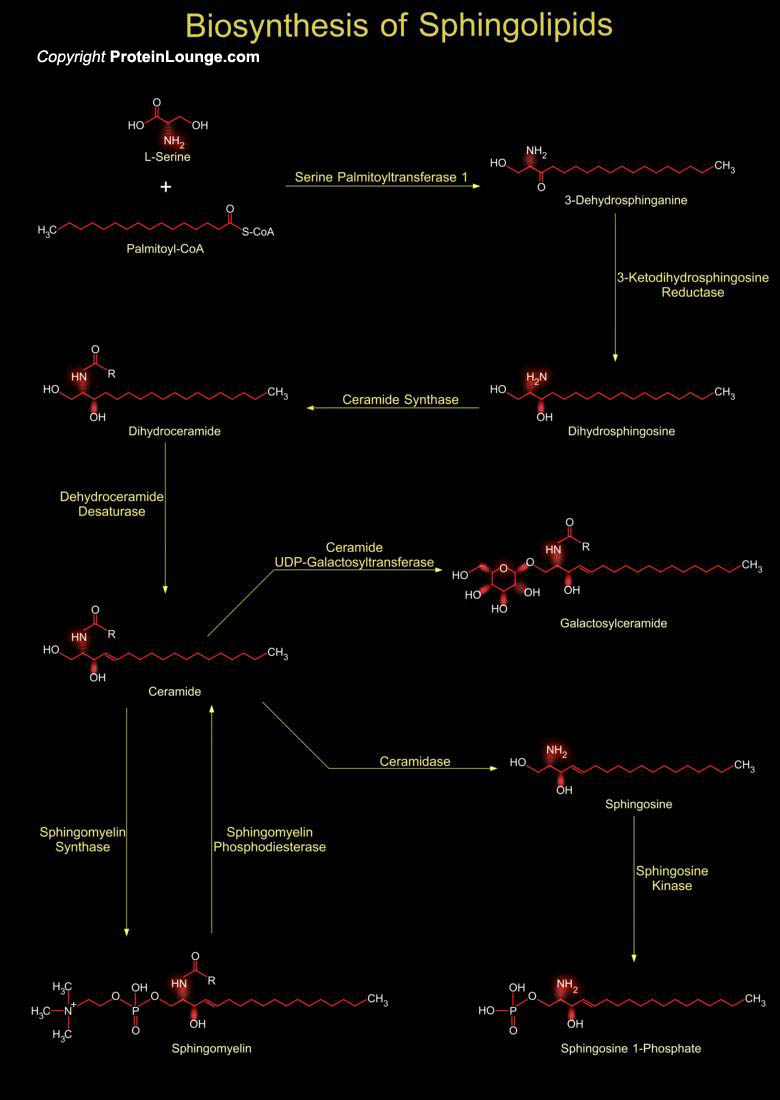
Sphingolipids structural components of the cell membrane play a key role in the regulation of several cellular processes. Cell signaling related to sphingolipids induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and cell growth. There are multiple bioactive sphingolipids metabolites which include ceramide, sphingosine-1-phosphate, sphingosine, and sphingomyelin which may act as secondary messengers in[..]
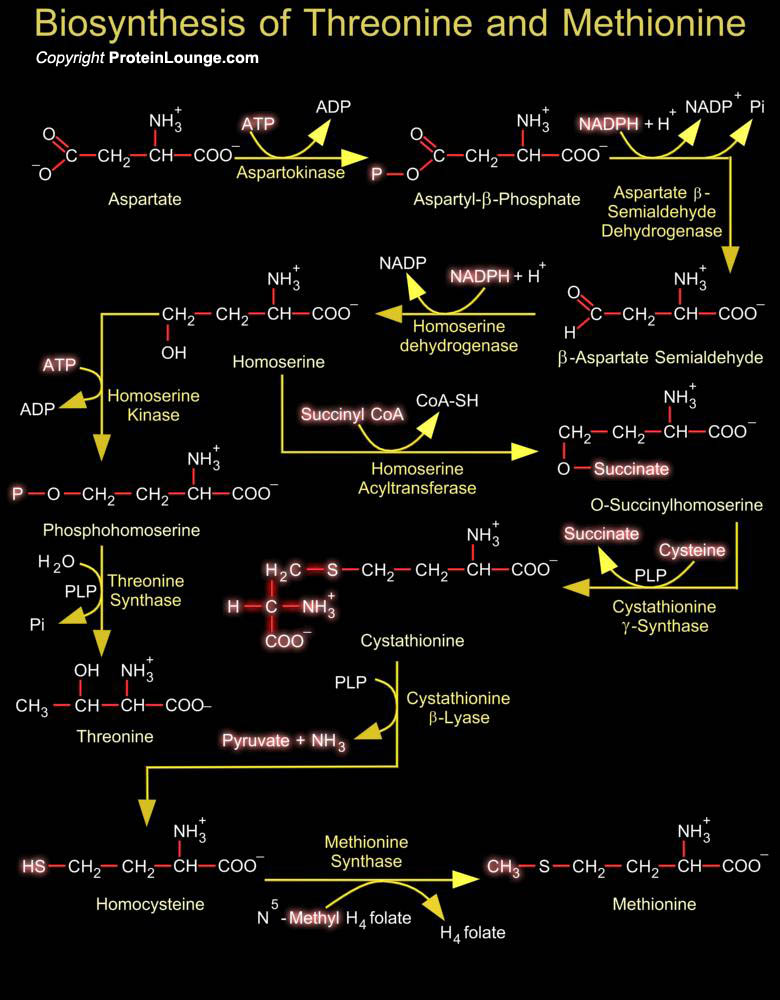
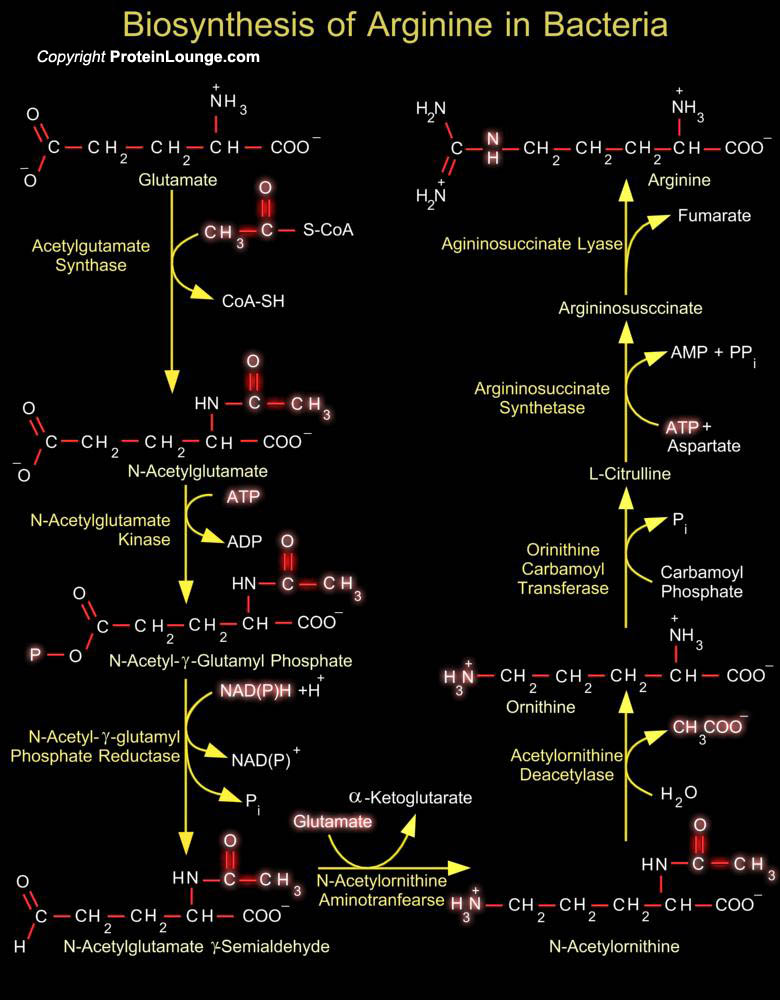
In bacteria, biosynthesis of arginine proceeds from glutamate in eight enzymatic steps initiated by the acetylation of glutamate by N-Acetyl Glutamate Synthetase. The N-Acetylated intermediates lead to ornithine. The synthesis of ornithine, like that of proline, involves the activation and reduction of the 5-carboxyl group of glutamate. In prokaryotes the pathway of arginine biosynthesis[..]
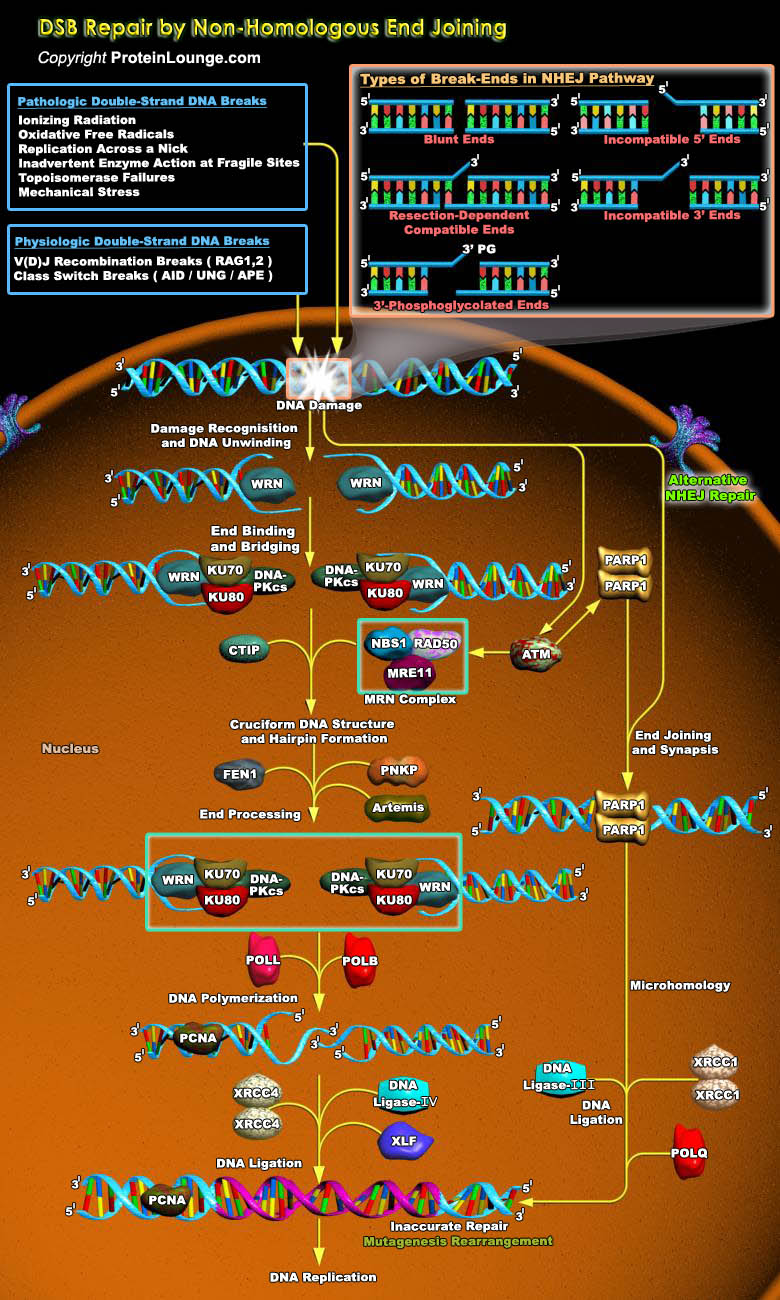
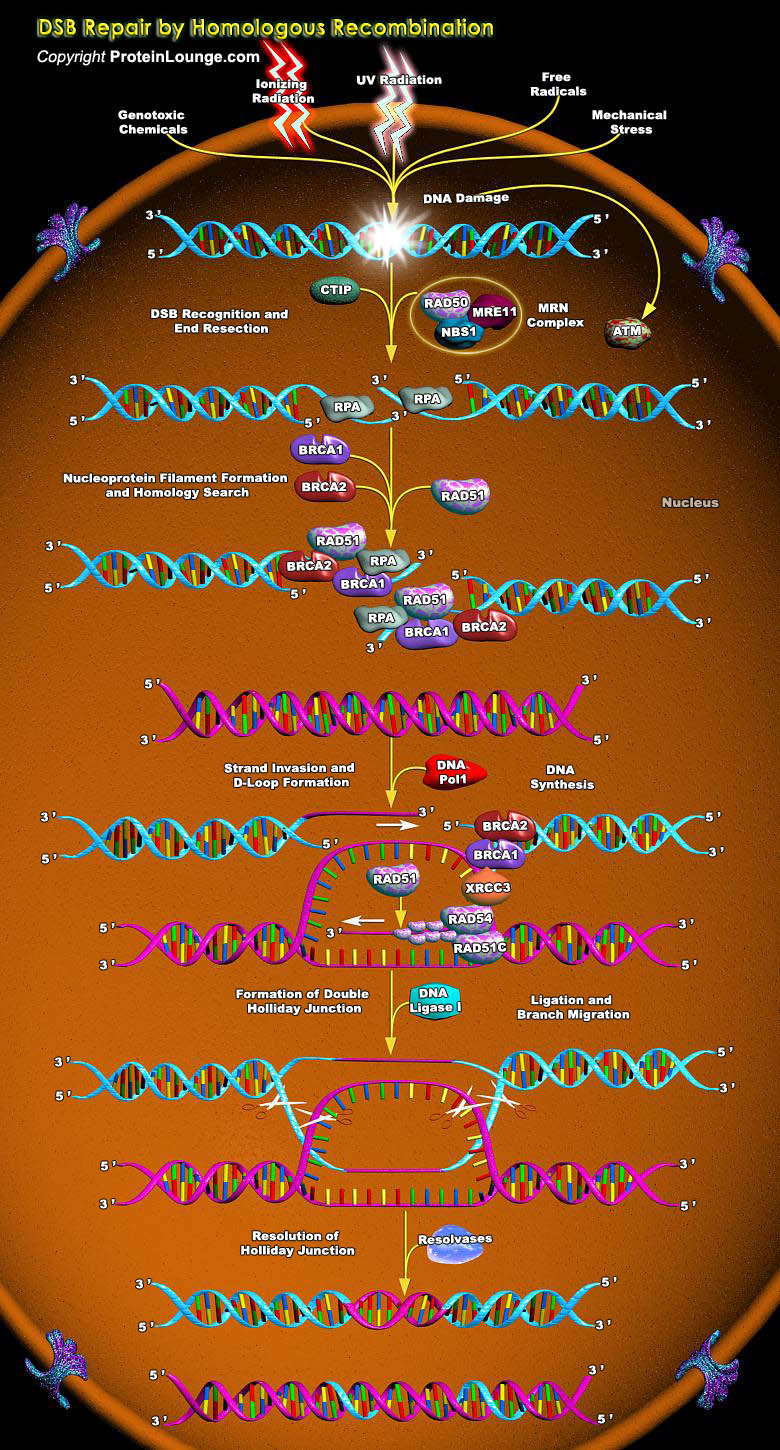
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are serious lesions that threaten a loss of chromosomal content. Repair of DSBs is particularly challenging because, unlike all other lesions, the DNA substrate is inherently bimolecular. Bringing two DNA molecules together is also dangerous because local mutations and chromosome rearrangements can arise if ends are inappropriately coupled. The cell has two[..]
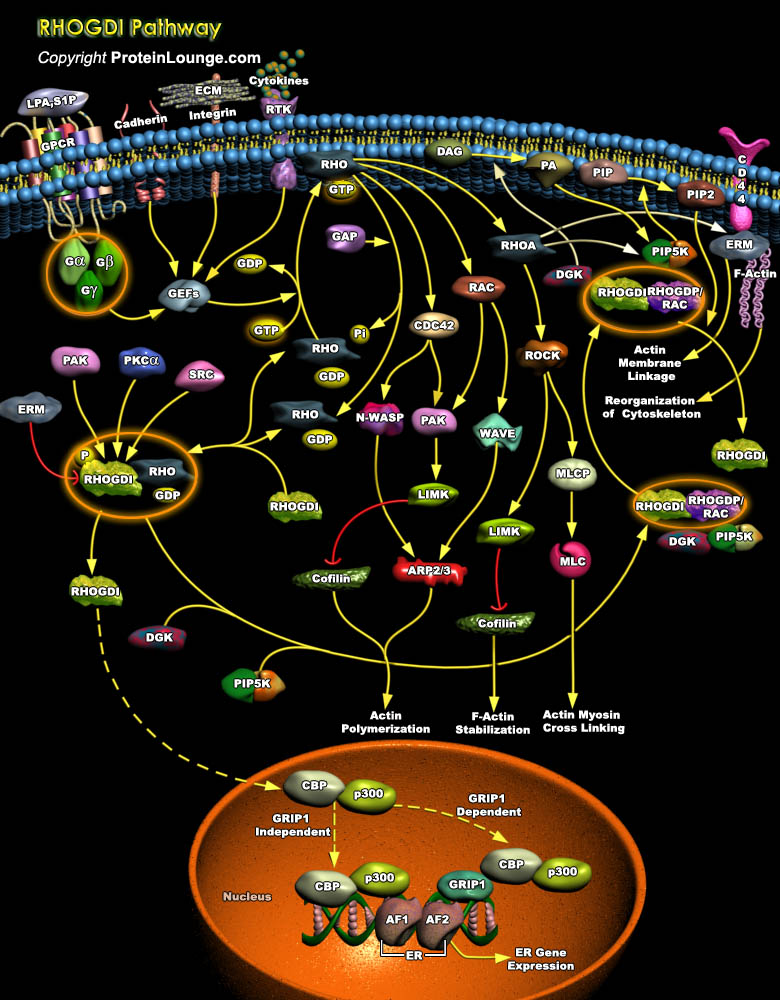
The Rho family of small GTPase proteins comprises CDC42 (Cell Division Cycle-42), Rac, and Rho. Proteins of the Rho/Rac subfamily (Rho proteins) of small GTP-binding proteins function as molecular switches that regulate a multitude of biological processes including cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, migration, cytoskeletal reorganization, and membrane trafficking. Like most of the[..]
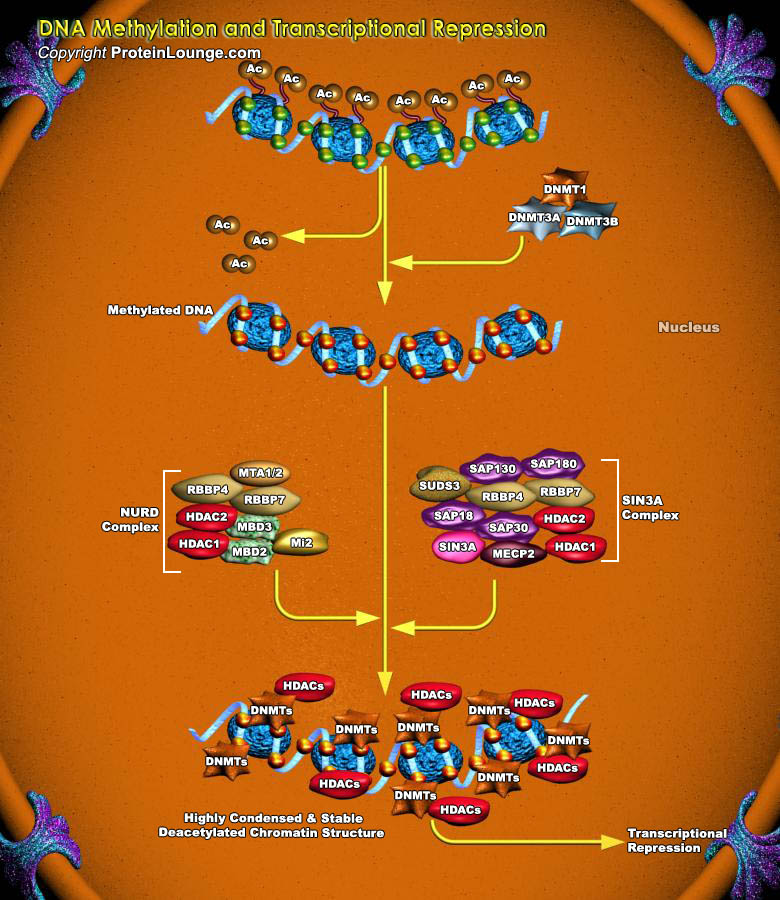
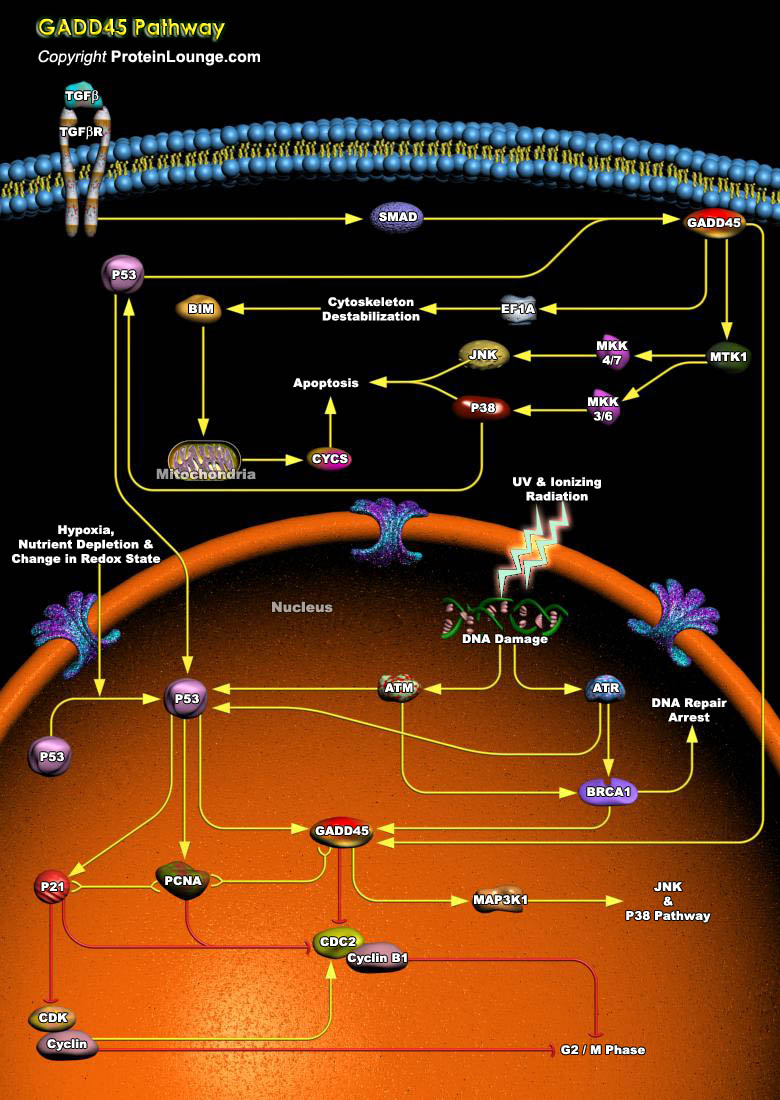
Genotoxic stress is an important and ubiquitous type of stress that cells are inevitably exposed to over the life span of an organism. Many potentially damaging agents both from the environment and from endogenous processes involving activated oxygen species and other reactive agents can damage the DNA in cells (Ref.1). GADD45 induction by BRCA1 leads to programmed cell death through the JNK[..]
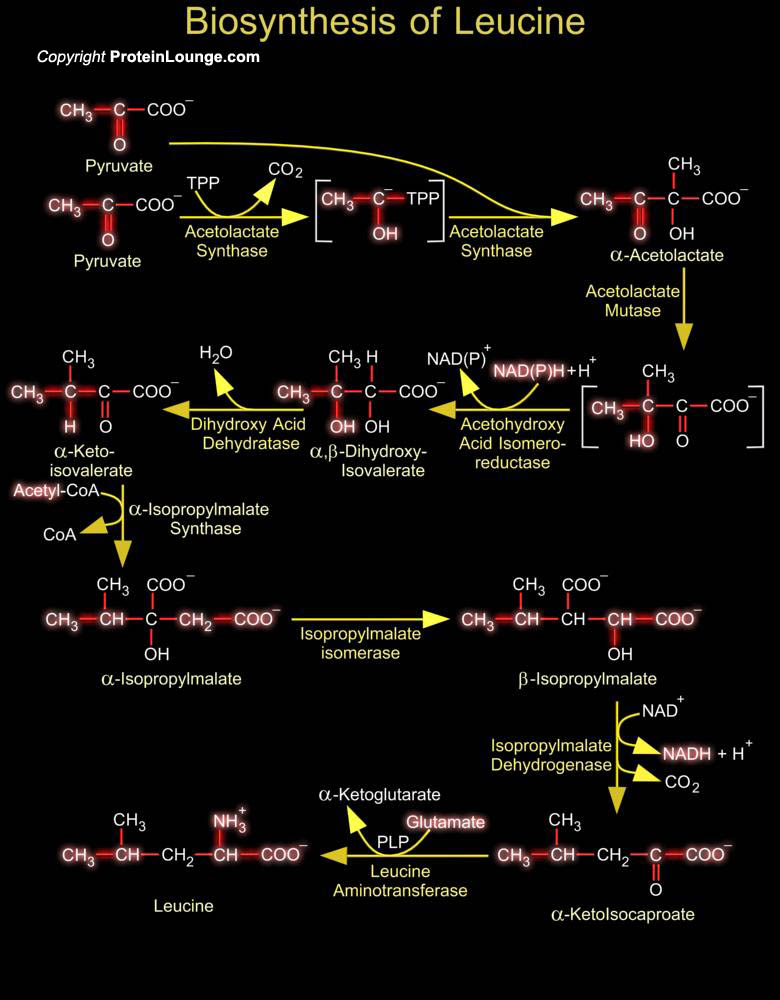
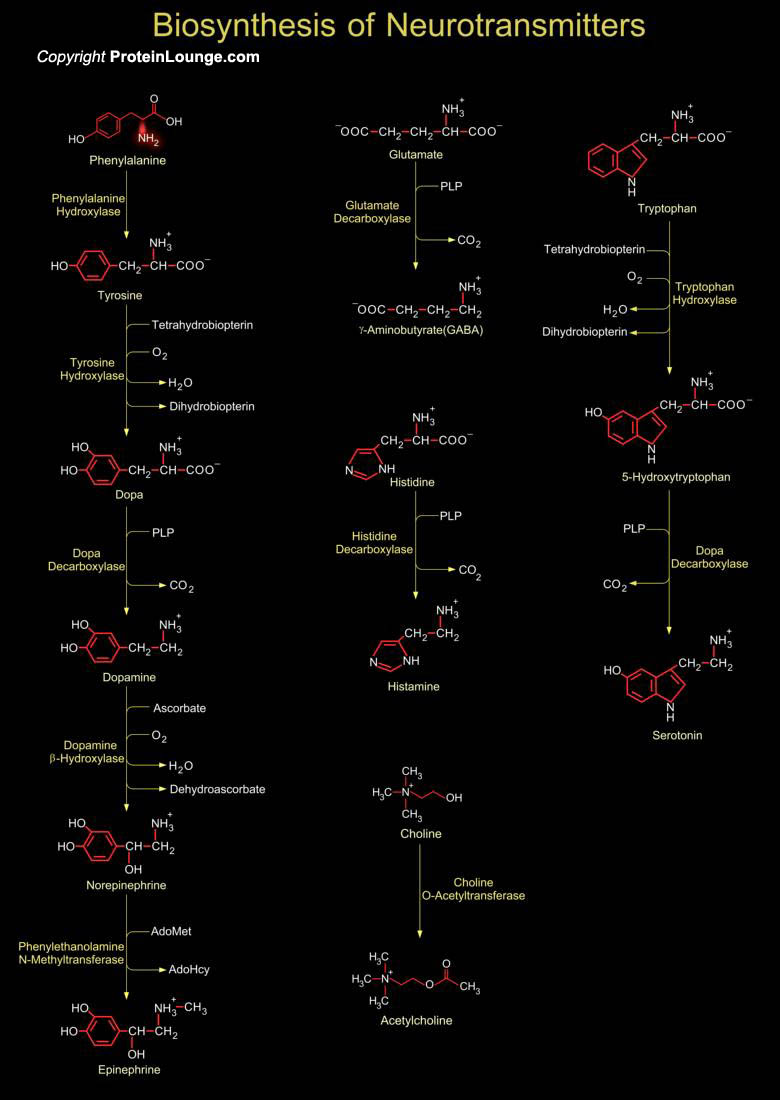
For neuronal signal transduction, the presynaptic cell synthesizes neurotransmitters that then traverse the synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitters are signaling molecules used by neurons to communicate across chemical synapses. The receptors for neurotransmitters include GPCRs (G-Protein Coupled Receptors) and ligand-gated ion channels. The biogenic amines are neurotransmitters derived from[..]